Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lube Oil Parameters
Uploaded by
Ganapathi SankarOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lube Oil Parameters
Uploaded by
Ganapathi SankarCopyright:
Available Formats
Sl.
No Lube oil Properties Description Duty Chemical Compone
This property permits the oil to react against corrosive wear by neutralizing acidic
1 Alkalinity (TBN) combustion products from the fuel sulphur and from the oxidation of the oil.
To avoid metal to metal contact it is essential to have a stable and sufficiently thick oil
film between piston ring and liner, and in the bearings.The Viscosity Index (VI), expresses
2 Viscosity&Viscosity index how the oil viscosity changes with temperature.
The oil circulates through the engine at very high speed (up to around 40 times per
hour).During this circulation, air and oil are mixed intensively with a significant foam risk. REDUCTION OF SURFACE TENSION OF SILICONES,
The foam can adversely affect the bearing lubrication. Air release properties need to be AIR/GAS BUBBLES TO PREVENT FOAMING POLYACRYLATES
considered as part of the overall foaming control.
3 Antifoaming
PREVENTION OF ABRASIVE AND ADHESIVE ZDTP
Anti-Wear (AW) and Extreme Pressure (EP) additives in order to help reduce abrasive WEAR, IMPROVEMENT OF LOAD (Zn, S, P, C, H,)
4 Antiwear and adhesive wear where possible. CARRYING
This property is required to protect surfaces of bearings and other sensitive engine PROTECTION OF YELLOW METALS, e.g. N-DISPERSANTS, S
5 Corrosion protection components from corrosion COPPER COMPONENTS
Ca SULPHONATE,
The oil has to clean and to keep clean cylinder liner, piston, ring pack and ring grooves CLEANLINESS,ACID Ca PHENATE,
from combustion products of fuels and lubricants. This property of the lubricating oil is NEUTRALISATION(PREVENTION OF Ca SALICYLATE,
6 Detergency called High Temperature Detergency. CORROSIVE WEAR), RUST PROTECTION (Ca, O, H, S )
POLY-ISOBUTYLENE,
The Dispersancy defines the ability of the oil to maintain in suspension all particles and SUCCINIMIDES,
unburnt components picked up by the oil in the piston and liner region, and elsewhere in CLEANLINESS STABILIZERS ESTER SUCCINIMIDES,
7 Dispersancy the engine (N, O, H, C)
The contribution of evaporation to oil consumption can be significant if excessively
8 Volatility volatile components are used to blend the lubricant.
The lubricating oil must be capable of “covering” surfaces which need protection.
Therefore, good Spreadability characteristics are required, as well as a reliable cohesion
9 Lubricity to the metallic surfaces
AROMATIC AMINES,
Oxidation Stability is required to prevent the oxidation of a lubricant due to high HINDERED PHENOLS,
temperatures and oxygen surplus in blow-by gases and air trapped in the engine interior. PREVENTION OF OXIDATION DITHIO CARBAMATES,
Otherwise this may result in oil viscosity increase and a lack of deposit control in the ZDTP
10 Oxidation Stability engine (Zn, S, P, C, H,)
The oil is exposed to long periods of high temperature during its passage through the
11 Thermal stability engine. An adequate Thermal Stability, therefore, is vital.
The lubricant must be water tolerant and still able to lubricate the engine components NEUTRAL
Water Resistance/rust
when contaminated with some water. Additives must be as water resistant as possible to Ca_x0002_SULPHONATES,
inhibitor
avoid additive losses and the formation of hard crystals during the removal of water in PREVENTION OF WATER/ACID ATTACK ON N – DISPERSANTS
12 the treatment system. They should not emulsify with the water seal of the purifier. IRON
You might also like
- Process TrainingDocument49 pagesProcess TrainingMuddassar Mahmood0% (2)
- Grease BasicsDocument6 pagesGrease BasicsnagbabuiNo ratings yet
- API 610 HighlightsDocument26 pagesAPI 610 Highlightsmmihai_popa2006No ratings yet
- EvaporadortoyotaDocument108 pagesEvaporadortoyotaPaco LozadaNo ratings yet
- Resume Jean-Marie Luijkx - Subsurface Manager - Petroleum Reservoir EngineerDocument7 pagesResume Jean-Marie Luijkx - Subsurface Manager - Petroleum Reservoir EngineerjeanmarieluijkxNo ratings yet
- Gear Lubrication 3Document9 pagesGear Lubrication 3rashm006ranjan100% (1)
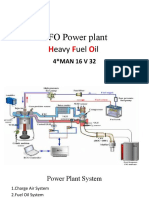
- HFO Power PlantDocument22 pagesHFO Power PlantGanapathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual For The CITIZEN Promaster Eco-Drive AQUALAND Titanium Divers Watch JV0055-51EDocument50 pagesInstruction Manual For The CITIZEN Promaster Eco-Drive AQUALAND Titanium Divers Watch JV0055-51EMeor Amri100% (2)
- P&ID Check ListDocument6 pagesP&ID Check ListSrihari Kodimela0% (1)
- WilliamsFire-Storage Tank Fire ProtectionDocument29 pagesWilliamsFire-Storage Tank Fire ProtectionSherif Abdel Hamid Fakhry100% (4)
- Properties of Lubricating OilDocument4 pagesProperties of Lubricating OilAbdallah MansourNo ratings yet
- ROTAIR Lubricants Leaflet PDFDocument16 pagesROTAIR Lubricants Leaflet PDFPhuc DcNo ratings yet
- Transformer Oil 1-24Document24 pagesTransformer Oil 1-24NikosNo ratings yet
- Shell Marine Pocketbook For International MarineDocument60 pagesShell Marine Pocketbook For International MarineGage Cendk HNo ratings yet
- Machinery Oil Analysis & Condition Monitoring : A Practical Guide to Sampling and Analyzing Oil to Improve Equipment ReliabilityFrom EverandMachinery Oil Analysis & Condition Monitoring : A Practical Guide to Sampling and Analyzing Oil to Improve Equipment ReliabilityRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (4)
- Roto Inject Fluid NDURANCE enDocument2 pagesRoto Inject Fluid NDURANCE enMartín BaezaNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco Roto Inject Fluid JECDocument2 pagesAtlas Copco Roto Inject Fluid JECアラファト イスラム教No ratings yet
- Melina S 30Document2 pagesMelina S 30HydbbNo ratings yet
- Gpcdoc Sa Tds MelinaDocument2 pagesGpcdoc Sa Tds Melinamohammad andiantoNo ratings yet
- Applications For Slideway Oils - DFLTSDocument9 pagesApplications For Slideway Oils - DFLTSandi massarappiNo ratings yet
- Chemical InspectionDocument75 pagesChemical InspectionUsamaNo ratings yet
- SINOPEC船用润滑油产品手册 PDFDocument30 pagesSINOPEC船用润滑油产品手册 PDFWilman OngNo ratings yet
- Shell Gas Compressor Oil S1 P: Corena KDocument2 pagesShell Gas Compressor Oil S1 P: Corena Kwill billNo ratings yet
- Petronas Disrol 50: Premium Quality 6 TBN Marine Diesel Engine OilsDocument1 pagePetronas Disrol 50: Premium Quality 6 TBN Marine Diesel Engine OilsHazrulnizam HassanNo ratings yet
- Mobil Rarus 800 Series FactsheetDocument2 pagesMobil Rarus 800 Series FactsheetSiswantoro Adi WibowoNo ratings yet
- PP Mobilgard M50 Series A4 LRDocument2 pagesPP Mobilgard M50 Series A4 LRA.S.M Jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- PP Mobilgard M50 Series A4 LRDocument2 pagesPP Mobilgard M50 Series A4 LRA.S.M Jahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- Mobilgard M50 SeriesDocument2 pagesMobilgard M50 Seriesdhavit wijayantoNo ratings yet
- MANUAL LUBGICACION NORD b1100 - Us - 1010Document10 pagesMANUAL LUBGICACION NORD b1100 - Us - 1010Walter JimenezNo ratings yet
- Grease Selection GuideDocument3 pagesGrease Selection GuideDon - BIN95.comNo ratings yet
- Petronas Disrol 120: Premium Quality 12 TBN Medium Speed Diesel Engine OilsDocument1 pagePetronas Disrol 120: Premium Quality 12 TBN Medium Speed Diesel Engine OilsHazrulnizam HassanNo ratings yet
- Everything You Always Wanted To Know About Oil: But Were Afraid To AskDocument12 pagesEverything You Always Wanted To Know About Oil: But Were Afraid To AskLogist ChinaNo ratings yet
- Info Type HuileDocument28 pagesInfo Type HuileApexiNo ratings yet
- TDS - Shell Alexia 50Document2 pagesTDS - Shell Alexia 50Ohood AlameerNo ratings yet
- Roto Inject Fluid NDURANCE: Atlas Copco LubricantsDocument2 pagesRoto Inject Fluid NDURANCE: Atlas Copco LubricantsJoao BotasNo ratings yet
- Shell Alvania GreasesDocument2 pagesShell Alvania GreasesjovenlouNo ratings yet
- Different Techniques For Life EstimationDocument29 pagesDifferent Techniques For Life Estimationhemantshah1No ratings yet
- Lubricating Oil-EscribaDocument17 pagesLubricating Oil-EscribaAbigail EscribaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic 6105Document8 pagesHydraulic 6105Deltalube TangerangNo ratings yet
- TelusDocument3 pagesTelusGembonz Crew Gon'z SpeedNo ratings yet
- Shell Marine Pocketbook V Dec 2017Document60 pagesShell Marine Pocketbook V Dec 2017Rizal NasutionNo ratings yet
- Product Information Sheet: Description: ApplicationDocument2 pagesProduct Information Sheet: Description: ApplicationgalaxiprinceNo ratings yet
- PDS Eneos Sustina 5W-30Document2 pagesPDS Eneos Sustina 5W-30Tony WijayaNo ratings yet
- TribiologyDocument36 pagesTribiologySavindra SilvaNo ratings yet
- Submarine Main Propulsion Diesels - Chapter 7Document32 pagesSubmarine Main Propulsion Diesels - Chapter 7Michael ChungNo ratings yet
- Grease and ApplicationsDocument21 pagesGrease and ApplicationsDinesh babuNo ratings yet
- Surface Lubrication 2Document42 pagesSurface Lubrication 2chawboc huabNo ratings yet
- Sydney Tramway Museum: Lubrication ManualDocument23 pagesSydney Tramway Museum: Lubrication ManualÜçler KuyumculukNo ratings yet
- Automatic and Manual GreasingDocument10 pagesAutomatic and Manual GreasingAhmed SalahNo ratings yet
- PT Agronusa Investama Sambas - Industrial Lubricants PresentationDocument20 pagesPT Agronusa Investama Sambas - Industrial Lubricants PresentationRizal Abdul AzizNo ratings yet
- Shell Melina S 30 PDFDocument2 pagesShell Melina S 30 PDFbeu catalinNo ratings yet
- Eneos Sustina Product Data Sheet 2016Document2 pagesEneos Sustina Product Data Sheet 2016dan0410No ratings yet
- PSC Specialty Lubricant 2021Document43 pagesPSC Specialty Lubricant 2021Project Sales CorpNo ratings yet
- A11.05.c - Mobilgard M50Document1 pageA11.05.c - Mobilgard M50JAHIDUL ISLAMNo ratings yet
- Mobilgard M30Document2 pagesMobilgard M30dhavit wijayantoNo ratings yet
- Lubrication SystemDocument24 pagesLubrication SystemAparna RNo ratings yet
- RS Clare Oil Gas Brochure 2022Document12 pagesRS Clare Oil Gas Brochure 2022Edmo VirgensNo ratings yet
- Shell Gadus S4 OGH 160: Superior Performance Open GearDocument3 pagesShell Gadus S4 OGH 160: Superior Performance Open GearJako MishyNo ratings yet
- Henan Dongsen Lubrication Technology Co., LTD: Multipurpose Calcium GreaseDocument1 pageHenan Dongsen Lubrication Technology Co., LTD: Multipurpose Calcium Greasesunhell1611No ratings yet
- TelusDocument3 pagesTelusMohamed SalemNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic and Lubricating Oil For Rust Protection inDocument3 pagesHydraulic and Lubricating Oil For Rust Protection inSalem IereebiNo ratings yet
- 6722 TDB Flyer PDFDocument1 page6722 TDB Flyer PDFDeltalube TangerangNo ratings yet
- Atlascopco Oil DatasheetDocument2 pagesAtlascopco Oil DatasheetAmirmasoudNo ratings yet
- GL XX Mobil SHC Grease 460 WTDocument3 pagesGL XX Mobil SHC Grease 460 WTMallikarjunareddy PNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica Shell Oil 9156 PDFDocument1 pageFicha Tecnica Shell Oil 9156 PDFcarlos arturo piedrahitaNo ratings yet
- GL XX Mobil SHC Grease 460 WTDocument3 pagesGL XX Mobil SHC Grease 460 WTRakka HardiyantaNo ratings yet
- Plastics in Building Structures: Proceedings of a Conference Held in London, 14-16 June 1965From EverandPlastics in Building Structures: Proceedings of a Conference Held in London, 14-16 June 1965No ratings yet
- DGR - 08 08 2023Document1 pageDGR - 08 08 2023Ganapathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Lube Oil System (Autosaved)Document5 pagesLube Oil System (Autosaved)Ganapathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Wartsila 31sg Product GuideDocument132 pagesWartsila 31sg Product GuideGanapathi SankarNo ratings yet
- DGR - 03 08 2023Document1 pageDGR - 03 08 2023Ganapathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Fuel Parameters ComparisonDocument6 pagesFuel Parameters ComparisonGanapathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Fuel Oil SystemDocument52 pagesFuel Oil SystemGanapathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Why HT Water Temp Should Be Between 75 - 90 Deg. C (Or) Why Preheating of Engine Required?Document14 pagesWhy HT Water Temp Should Be Between 75 - 90 Deg. C (Or) Why Preheating of Engine Required?Ganapathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Trouble Shooting SWDocument94 pagesTrouble Shooting SWGanapathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Group 1Document6 pagesGroup 1Ganapathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Group 4Document8 pagesGroup 4Ganapathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Group 3Document11 pagesGroup 3Ganapathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Group 2Document10 pagesGroup 2Ganapathi SankarNo ratings yet
- Steady State Analysis of PMSG PDFDocument16 pagesSteady State Analysis of PMSG PDF1balamanianNo ratings yet
- The Routledge Handbook of Energy Security: Edited by Benjamin K. SovacoolDocument3 pagesThe Routledge Handbook of Energy Security: Edited by Benjamin K. SovacoolNagesh K OjhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document5 pagesChapter 5Peaky HackerNo ratings yet
- 英文汉立通用版说明书(2022 4 7)Document6 pages英文汉立通用版说明书(2022 4 7)Amin ZegraniNo ratings yet
- Product Data: 39T Central Station Air-Handling UnitsDocument100 pagesProduct Data: 39T Central Station Air-Handling UnitsJesus CantuNo ratings yet
- 1996-2004 - Ford4.6Mustang Mustang Mustang Mustang GTDocument40 pages1996-2004 - Ford4.6Mustang Mustang Mustang Mustang GTPa RaNo ratings yet
- Air Cooled Packaged Air Conditioner R410A RefrigerantDocument12 pagesAir Cooled Packaged Air Conditioner R410A RefrigerantArmanNo ratings yet
- 7.4.6 SMC-209-C - enDocument22 pages7.4.6 SMC-209-C - enShahbazZahidNo ratings yet
- TG Lube Oil FlushingDocument2 pagesTG Lube Oil FlushingPipin Azrin ScreonietichNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Sustainable Building Technology and Urban DevelopmentDocument8 pagesInternational Journal of Sustainable Building Technology and Urban DevelopmentsimoneweilNo ratings yet
- Boiler Inspector TRAINING - 2021Document8 pagesBoiler Inspector TRAINING - 2021SUNIL BABURAO GAVADENo ratings yet
- 9702 w11 QP 43Document24 pages9702 w11 QP 43Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Pi2657 PDFDocument3 pagesPi2657 PDFDimitry TIRANo ratings yet
- Steam TrapDocument3 pagesSteam TrapchanchalkalraNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom PDFDocument0 pagesStructure of Atom PDFabhishekaks97No ratings yet
- Tiger N-Type 60TR: 355-375 WattDocument2 pagesTiger N-Type 60TR: 355-375 WattmoonridergNo ratings yet
- Generator Third-Harmonic Protection Explained: Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, IncDocument10 pagesGenerator Third-Harmonic Protection Explained: Schweitzer Engineering Laboratories, IncPrateek Singh TomarNo ratings yet
- Science Notes For Class9th CbseDocument3 pagesScience Notes For Class9th CbseMithilesh Kr PremNo ratings yet
- Aipu Booklet PDFDocument22 pagesAipu Booklet PDFMEHDINo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips - Programmable Logic Controllers 2009 600 Pages James A Logic ControllersDocument20 pagesDokumen - Tips - Programmable Logic Controllers 2009 600 Pages James A Logic Controllerssalim ucarNo ratings yet
- Modern Trends in Internal Combustion EnginesDocument15 pagesModern Trends in Internal Combustion EnginesMahmOud S. El-MashadNo ratings yet
- Lna03179eng-C 1912Document342 pagesLna03179eng-C 1912Michael PopeNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Linear DC Power SupplyDocument56 pagesTopic 1 Linear DC Power SupplyKu AliyaNo ratings yet