Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Day-23 Notes (EEE)
Uploaded by
Aayush KartikCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Day-23 Notes (EEE)
Uploaded by
Aayush KartikCopyright:
Available Formats
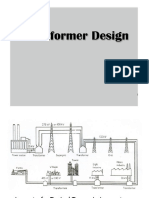
TRANSFORMER CONSTRUCTION:
Basically a transformer consists of two inductive windings and a laminated steel core. The coils
are insulated from each other as well as from the steel core. A transformer may also consist of a
container for winding and core assembly (called as tank), suitable bushings to take out the
terminals, oil conservator to provide oil in the transformer tank for cooling purposes etc.
Breather consists of silica gel used for absorption of moisture from transformer oil available in
tank. The figure illustrates the basic construction of a transformer.
In all types of transformers, core is constructed by assembling (stacking) laminated sheets of
steel, with minimum air-gap between them (to achieve continuous magnetic path). The steel used
is having high silicon content and sometimes heat treated, to provide high permeability and low
hysteresis loss. Laminated sheets of steel are used to reduce eddy current loss. The sheets are cut
in the shape as E,I and L. To avoid high reluctance at joints, laminations are stacked by
alternating the sides of joint. That is, if joints of first sheet assembly are at front face, the joints
of following assemble are kept at back face.
Transformers can be classified on basis of construction such as (i) Core type transformer and (ii)
Shell type transformer, which are described below.
(i) Core type transformer
In core type transformer, windings are cylindrical former wound, mounted on the core limbs as
shown in the figure above. The cylindrical coils have different layers and each layer is insulated
from each other. Materials like paper, cloth or mica can be used for insulation. Low voltage
windings are placed nearer to the core, as they are easier to insulate.
(ii) Shell type transformer
The coils are former wound and mounted in layers stacked with insulation between them. A shell
type transformer may have simple rectangular form (as shown in above fig), or it may have a
distributed form.
You might also like
- Solutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceFrom EverandSolutions Manual to accompany Engineering Materials ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Transformer BasicsPDFDocument64 pagesTransformer BasicsPDFShrikant KajaleNo ratings yet
- Transformer Basics (Excellent For Practical Purpose)Document40 pagesTransformer Basics (Excellent For Practical Purpose)Sandeep Kumar100% (3)
- Dimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyFrom EverandDimensions, Weights and Properties of Special and Standard Structural Steel Shapes Manufactured by Bethlehem Steel CompanyNo ratings yet
- Berrys TransrformerDocument3 pagesBerrys Transrformerjamil670No ratings yet
- Principles and Construction of TransformerDocument5 pagesPrinciples and Construction of TransformerJohn Kenneth ArellonNo ratings yet
- Power TransformerDocument14 pagesPower TransformerKashif IftikharNo ratings yet
- Core AssemblyDocument3 pagesCore AssemblyAreeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two IDocument29 pagesChapter Two IYeamlak SisayNo ratings yet
- What Is A TransformerDocument9 pagesWhat Is A TransformerAjitNo ratings yet
- What Is A TransformerDocument9 pagesWhat Is A TransformerAjitNo ratings yet
- Contents:: 1 5 2 Working Principle 6 3 Construction 7 4 Types of Transformers 8Document12 pagesContents:: 1 5 2 Working Principle 6 3 Construction 7 4 Types of Transformers 8Abhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.7 Transformers: Engr. Conrado QuinalayoDocument9 pagesExperiment No.7 Transformers: Engr. Conrado QuinalayoJaloyd MacalalagNo ratings yet
- Transformer ConstructionDocument10 pagesTransformer ConstructionJhun Rey AceboNo ratings yet
- Unit IIDocument117 pagesUnit IIThangam MaheshNo ratings yet
- Construction of TransformerDocument33 pagesConstruction of TransformervurumuuNo ratings yet
- Transformer Construction and Transformer Core DesignDocument14 pagesTransformer Construction and Transformer Core DesignKlucifer XinNo ratings yet
- TransformerDocument17 pagesTransformerAbragam Siyon SIngNo ratings yet
- A Report On Transfomer DesignDocument26 pagesA Report On Transfomer Designeng.tushar598No ratings yet
- Kel It ReportDocument23 pagesKel It ReportshaluNo ratings yet
- Transformer Installation, Commissioning, Operation and MaintenanceDocument40 pagesTransformer Installation, Commissioning, Operation and MaintenancejunclarcNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing and Assembling of Stator and Rotor Inturbo GeneratorsDocument4 pagesManufacturing and Assembling of Stator and Rotor Inturbo GeneratorsAshfiya YazdaniNo ratings yet
- Laminated Core TransformerDocument2 pagesLaminated Core TransformerVishnu PillaiNo ratings yet
- Training Module Manufacture TransformerDocument91 pagesTraining Module Manufacture TransformerSanjeev Kadian100% (2)
- EU1Pre ReportDocument4 pagesEU1Pre ReportSERVILLA, LESTER JOHN B.No ratings yet
- Shell or Core TransformerDocument6 pagesShell or Core TransformerJorgeNo ratings yet
- 1 TransformerDocument226 pages1 TransformerSurabhi MattaNo ratings yet
- Electronic Transformers & Inductor Core Types: Toroids (Rings)Document6 pagesElectronic Transformers & Inductor Core Types: Toroids (Rings)sunny_nsecNo ratings yet
- Transformer Design-01Document21 pagesTransformer Design-01Anoop BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- BaluDocument2 pagesBalutikkalNo ratings yet
- Generator Testing Project ReportDocument95 pagesGenerator Testing Project ReportSindhu ManchukondaNo ratings yet
- Transformer: A. Transformer Basic TheoryDocument14 pagesTransformer: A. Transformer Basic TheoryBe Sar WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- Transformer Core Types - Core Type, H-Type, Shell - TypeDocument4 pagesTransformer Core Types - Core Type, H-Type, Shell - TypeEum MavNo ratings yet
- Transformer: Pritish Sharma EL-395-2K17Document22 pagesTransformer: Pritish Sharma EL-395-2K17Pritish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Generator Construction 210 MWDocument33 pagesGenerator Construction 210 MWPradeep_Vashist100% (1)
- Construction of DC MachineDocument7 pagesConstruction of DC MachineAnonymous MAit3mlYm0% (1)
- Unit 4 Single-Phase Isolation Transformers: I.l7r.ifttDocument1 pageUnit 4 Single-Phase Isolation Transformers: I.l7r.ifttRoni DominguezNo ratings yet
- Power Transformer Construction CoreDocument4 pagesPower Transformer Construction CoreJayadevDamodaran0% (1)
- Transformer 1Document29 pagesTransformer 1utharun3No ratings yet
- Generator CoreDocument12 pagesGenerator Corechilamkurti_sivasankararaoNo ratings yet
- SteelDocument22 pagesSteels63et79jgeesdgNo ratings yet
- Machine NotesDocument8 pagesMachine Notesrakesh chaturvediNo ratings yet
- 1.list Out Trouble Shooting Techniques For Transformer TransformerDocument30 pages1.list Out Trouble Shooting Techniques For Transformer Transformerrohith mukkamalaNo ratings yet
- Power Transformer: I .N I .NDocument43 pagesPower Transformer: I .N I .Nsrindira100% (1)
- Materaial ScienceDocument11 pagesMateraial ScienceNazif AzaharNo ratings yet
- Esternila D. Gadugdug Bsee 3 Assignment: Elctrical Machines-2 5/19/2022Document2 pagesEsternila D. Gadugdug Bsee 3 Assignment: Elctrical Machines-2 5/19/2022Kyle Christian CeprezNo ratings yet
- A Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesFrom EverandA Practical Workshop Companion for Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers: Containing Rules for Describing Various Kinds of Patterns used by Tin, Sheet Iron, and Copper Plate Workers, Practical Geometry, Mensuration of Surfaces and Solids, Tables of the Weights of Metals, Lead Pipe, Tables of Areas and CircumferencesNo ratings yet
- Small Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsFrom EverandSmall Dynamos and How to Make Them - Practical Instruction on Building a Variety of Machines Including Electric MotorsNo ratings yet
- Triangulation - Applied to Sheet Metal Pattern Cutting - A Comprehensive Treatise for Cutters, Draftsmen, Foremen and Students: Progressing from the Simplest Phases of the Subject to the Most Complex Problems Employed in the Development of Sheet Metal Patterns with Practical Solutions of Numerous Problems of Frequent Occurrence in Sheet Metal ShopsFrom EverandTriangulation - Applied to Sheet Metal Pattern Cutting - A Comprehensive Treatise for Cutters, Draftsmen, Foremen and Students: Progressing from the Simplest Phases of the Subject to the Most Complex Problems Employed in the Development of Sheet Metal Patterns with Practical Solutions of Numerous Problems of Frequent Occurrence in Sheet Metal ShopsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkFrom EverandSheet Metalwork on the Farm - Containing Information on Materials, Soldering, Tools and Methods of Sheet MetalworkNo ratings yet
- A Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsFrom EverandA Short Guide to the Types and Details of Constructing a Suspension Bridge - Including Various Arrangements of Suspension Spans, Methods of Vertical Stiffening and Wire Cables Versus Eyebar ChainsNo ratings yet
- Heat-Treatment of Steel: A Comprehensive Treatise on the Hardening, Tempering, Annealing and Casehardening of Various Kinds of Steel: Including High-speed, High-Carbon, Alloy and Low Carbon Steels, Together with Chapters on Heat-Treating Furnaces and on Hardness TestingFrom EverandHeat-Treatment of Steel: A Comprehensive Treatise on the Hardening, Tempering, Annealing and Casehardening of Various Kinds of Steel: Including High-speed, High-Carbon, Alloy and Low Carbon Steels, Together with Chapters on Heat-Treating Furnaces and on Hardness TestingRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- XXth Century Sheet Metal Worker - A Modern Treatise on Modern Sheet Metal WorkFrom EverandXXth Century Sheet Metal Worker - A Modern Treatise on Modern Sheet Metal WorkNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components, Tubes and Transistors: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionFrom EverandElectronic Components, Tubes and Transistors: The Commonwealth and International Library: Electrical Engineering DivisionNo ratings yet
- Standard Blacksmithing, Horseshoeing and Wagon Making: Containing: Twelve Lessons in Elementary Blacksmithing Adapted to the Demand of Schools and Colleges of Mechanic Arts: Tables, Rules and Receipts Useful to Manufactures, Machinists, Engineers and BlacksmithsFrom EverandStandard Blacksmithing, Horseshoeing and Wagon Making: Containing: Twelve Lessons in Elementary Blacksmithing Adapted to the Demand of Schools and Colleges of Mechanic Arts: Tables, Rules and Receipts Useful to Manufactures, Machinists, Engineers and BlacksmithsNo ratings yet
- Day-41 Notes (EEE)Document5 pagesDay-41 Notes (EEE)Aayush KartikNo ratings yet
- Day-37 Notes (EEE)Document4 pagesDay-37 Notes (EEE)Aayush KartikNo ratings yet
- Day-28 Notes (EEE)Document2 pagesDay-28 Notes (EEE)Aayush KartikNo ratings yet
- Day-7 Notes (EEE)Document1 pageDay-7 Notes (EEE)Aayush KartikNo ratings yet
- Day-30 Notes (EEE)Document1 pageDay-30 Notes (EEE)Aayush KartikNo ratings yet
- Day-6 Notes (EEE)Document4 pagesDay-6 Notes (EEE)Aayush KartikNo ratings yet
- Day-5 Notes (EEE)Document2 pagesDay-5 Notes (EEE)Aayush KartikNo ratings yet
- Day-2 Notes (EEE)Document2 pagesDay-2 Notes (EEE)Aayush KartikNo ratings yet
- Day-3 Notes (EEE)Document3 pagesDay-3 Notes (EEE)Aayush KartikNo ratings yet