0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views8 pagesMetric System-Reading Material
The metric system is the standard international system for measuring length, mass, volume, and other quantities. It uses decimal-based units like meters, liters, and grams that are related by factors of 10. The metric system originated in France in the late 18th century and was designed to be easy to use. It is now the primary system of measurement used around the world in science, manufacturing, and international trade.
Uploaded by
Hasna HussainCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views8 pagesMetric System-Reading Material
The metric system is the standard international system for measuring length, mass, volume, and other quantities. It uses decimal-based units like meters, liters, and grams that are related by factors of 10. The metric system originated in France in the late 18th century and was designed to be easy to use. It is now the primary system of measurement used around the world in science, manufacturing, and international trade.
Uploaded by
Hasna HussainCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
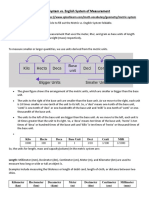
- Metric System: Introduces the metric system as a standard method for measuring distance, calculating height, and mass, emphasizing its universal application.
- Metric Units: Lists the fundamental metric units for measuring different quantities, including length, mass, and capacity.
- Origin of Metric System: Details the historical development of the metric system and its global adoption.
- What is Metric System?: Explains the basic concept of the metric system and why it is important for everyday measurements.
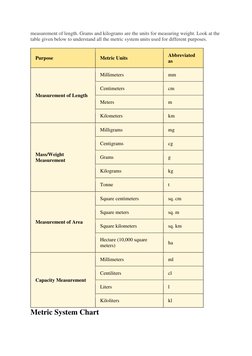
- Metric System Chart: Provides a comprehensive chart detailing metric units and their abbreviated forms for various measurements.
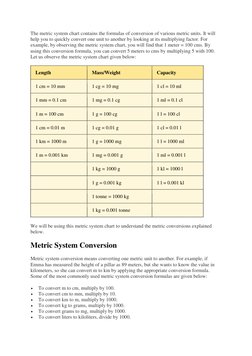
- Metric System Conversion: Illustrates the conversion methodologies for metric units and demonstrates example calculations.
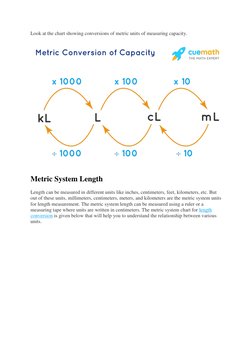
- Weight and Capacity: Introduces the concept of weight in the metric system and explains basic conversion techniques for weight and capacity.
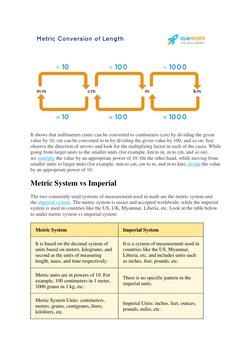
- Metric System Length: Describes the metric units used to measure length and how they relate to each other.
- Metric System vs Imperial: Compares the metric system with the imperial system, highlighting differences and advantages.
- Important Notes on Metric System: Presents important notes and standard units for metric measurements in math.
- Metric System Examples: Provides practical examples and problem-solving exercises using metric system conversions.