Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology
Biology
Uploaded by
karadanversOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology
Biology
Uploaded by
karadanversCopyright:
Available Formats
CORE
2. The kidney filter blood, removing urea, excess water and some ions.
All the glucose also filtered out, but it is all reabsorbed , some water is also
reabsorbed, depending on the state of hydration of the body. On a hot day, more
water is absorbed, resulting in a small amount of concentrated urine. Water is
reabsorbed by the process of osmosis , and white glucose and ions are diffusion
and active uptake
3. a. surplus of amino acids are removed from the blood by the liver and broken
down into urea by the process of deamination
b. 1. Breakdown of poisons or alchohol
2. Controlling levels of glucose in the blood
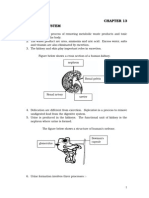
4. a. Ii. cortex contains glomeruli
Ureter transfers urine to the bladder
b. I. filters the blood, some things that are filtered are water, glucose, urea, and
salts
Ii. nephron function is reabsorbing glucose, most water, and salts.
Iii. passes urine.
CORE
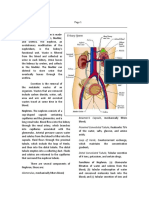
1. a. I. a: renal vein, b: left kidney, c: ureter, d: bladder, E, urethra
Ii. amino acids and glucose will be present in par A, and also more salts than part C
Iii. smaller volume, more concentrated, urea also more concentrated
b. vena cava has a thinner wall; larger lumen and contains valves.
2. a. I. a method of removing one or more components from a solution using the process of
diffusion
Ii. pump: keeps blood flowing through the machine; dialysis fluid: receives wastes/toxins
from the blood by diffusion.
b. i Visking tubing/ cellulose
Ii. provides a large surface area for efficient diffusion
Iii. to maintain a concentration gradient the concentration of removed substance builds
up; so diffusion slows down.
C. expensive to buy or maintain, and really tiring for the user. And also may require a
frequent hospital visit
You might also like
- Bio Factsheet: The Kidney: Excretion and OsmoregulationDocument4 pagesBio Factsheet: The Kidney: Excretion and OsmoregulationjesvinjesvinNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument2 pagesExcretionJessica KunderNo ratings yet
- Important Points of Excretory SystemDocument3 pagesImportant Points of Excretory SystemDhruv Nair IX ANo ratings yet
- Regulation of Body FluidsDocument5 pagesRegulation of Body FluidsAlwìn GarciaNo ratings yet
- Excretion Chapter NotesDocument7 pagesExcretion Chapter NotesMohammad Sayed AliNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument31 pagesThe Urinary SystemMuhamed Shexbzeny100% (1)
- Excretory SystemDocument6 pagesExcretory SystemDessy AnnisyahNo ratings yet
- Excretory Organ PDF Invertebrates.Document13 pagesExcretory Organ PDF Invertebrates.E RAMESHBABUNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument54 pagesExcretionSarah SabirNo ratings yet
- X Life Processes Excretion Handout 2 of 3Document3 pagesX Life Processes Excretion Handout 2 of 3Waziri MbarukuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 ExcretionDocument5 pagesChapter 13 ExcretionWezu heavenNo ratings yet
- PT3 Science Chapter 20 ExcretionDocument4 pagesPT3 Science Chapter 20 ExcretionSpike ChingyenNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 ExcretionDocument14 pagesLesson 4 ExcretionNUMAIRA UROOJNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument2 pagesExcretionSD card 32 gbNo ratings yet
- Biology 12 Urinary System Bonus PackageDocument4 pagesBiology 12 Urinary System Bonus PackageKen WuNo ratings yet
- BIOL 286 Lecture 8 EXCRETION With AnnotationsDocument14 pagesBIOL 286 Lecture 8 EXCRETION With Annotationsevahhassane2003No ratings yet
- Lecture 28: Excretion 44.1 - 44.3: Friday, April 29, 2016 5:05 AMDocument20 pagesLecture 28: Excretion 44.1 - 44.3: Friday, April 29, 2016 5:05 AMGena DaoNo ratings yet
- Excretion CIS VIIIDocument6 pagesExcretion CIS VIIIelizabethNo ratings yet
- Ch-8 Excretion in Animals & PlantsDocument4 pagesCh-8 Excretion in Animals & PlantsRonnith NandyNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument13 pagesExcretionjerome jeromeNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology Ii: School of BiochemistryDocument15 pagesHuman Physiology Ii: School of Biochemistrykeerthana t reddyNo ratings yet
- (BIO) Chapter 9 - Excretion in HumansDocument14 pages(BIO) Chapter 9 - Excretion in Humansanya desilvaNo ratings yet
- Excretion 22-23Document4 pagesExcretion 22-23hiNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument6 pagesExcretory SystemAJAYI PETERNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - ExcretionDocument4 pagesLife Processes - ExcretionRajvir tradaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Biology 11th Term II Ch. 7Document2 pagesCBSE Biology 11th Term II Ch. 7JAGGA GAMING OFFICIALNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 13 NotesDocument6 pagesTOPIC 13 NotesAlya AfifiNo ratings yet
- 3.4.6 Excretory System H 3.4.8Document9 pages3.4.6 Excretory System H 3.4.8Joy FernandezNo ratings yet
- Excretory System Chapter 9thDocument4 pagesExcretory System Chapter 9thशंकराय नमोNo ratings yet
- m6 Urinary System For WebsiteDocument29 pagesm6 Urinary System For Websiteapi-464344582No ratings yet
- Unit 2.43: Excretion: Removal of Waste Products of MetabolismDocument20 pagesUnit 2.43: Excretion: Removal of Waste Products of MetabolismxspiirONo ratings yet
- Bio Notes Excretion and HomeostasisDocument52 pagesBio Notes Excretion and HomeostasisvictoriawaguraNo ratings yet
- Urinary System Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesUrinary System Lecture NotesBettina ColobongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - ExcretionDocument51 pagesChapter 12 - ExcretionKareem DmourNo ratings yet
- Excretion - Excretion Is The Removal of The Metabolic Wastes of An Organism. Wastes That AreDocument10 pagesExcretion - Excretion Is The Removal of The Metabolic Wastes of An Organism. Wastes That ArejoelNo ratings yet
- Review in AUBFDocument37 pagesReview in AUBFMichelle T. MabasaNo ratings yet
- Biology Section 2 Lesson 6Document53 pagesBiology Section 2 Lesson 6hui sin limNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument39 pagesExcretory Systemaditya varteNo ratings yet
- Execretion in HumanDocument12 pagesExecretion in Humanayman.hazem66No ratings yet
- UNIT 10 Excretion in Humans NotesDocument27 pagesUNIT 10 Excretion in Humans NotescyumadripNo ratings yet
- PP24 Functioning of The KidneyDocument79 pagesPP24 Functioning of The Kidneyangie432meNo ratings yet
- The Kidneys and Formation of Urine 3 New 0Document22 pagesThe Kidneys and Formation of Urine 3 New 0Iph anyiNo ratings yet
- Filtering Wastes From The Bloodstream: Dihydroxycholecalciferol (Calcitriol) and ProstaglandinsDocument7 pagesFiltering Wastes From The Bloodstream: Dihydroxycholecalciferol (Calcitriol) and ProstaglandinsJerome Miguel SantosNo ratings yet
- AUBFDocument8 pagesAUBFIssha CasañasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 - ExcretionDocument3 pagesChapter 13 - ExcretionhanifNo ratings yet
- 3 - Excretion NotesDocument33 pages3 - Excretion NotesJenny YoonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - ExcretionDocument3 pagesChapter 3 - ExcretionSuntharan MuniandyNo ratings yet
- Excretory System by Macalin Axmed OmaarDocument9 pagesExcretory System by Macalin Axmed OmaarAhmed OmaarNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Urine FormationDocument15 pagesMechanism of Urine FormationDharshinimk Dr.NGP ItechNo ratings yet
- Excretory System HoDocument4 pagesExcretory System HodoraNo ratings yet
- Excretion TestDocument4 pagesExcretion TestMonique NelsonNo ratings yet
- Excretory SystemDocument61 pagesExcretory Systemalayca cabatanaNo ratings yet
- L-9 The Excretory System: A. Multiple Choice TypeDocument6 pagesL-9 The Excretory System: A. Multiple Choice TypeNeha ChandelNo ratings yet
- Urine FormationDocument76 pagesUrine FormationPrakash PanthiNo ratings yet
- S3 Biology HOMEOSTASIS Notes - pdf417539Document26 pagesS3 Biology HOMEOSTASIS Notes - pdf417539SsebuumaNo ratings yet
- Chem 3 2 NonproteinDocument7 pagesChem 3 2 NonproteinAndrew NguyenNo ratings yet
- Excretory Sys..ss2Document4 pagesExcretory Sys..ss2sunoyebimpeNo ratings yet
- ExcretionDocument9 pagesExcretionVeer RamloghunNo ratings yet
- Kidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandKidney Diseases, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Economics AQA A2 Un 4 Workbook AnswersDocument28 pagesEconomics AQA A2 Un 4 Workbook AnswerskaradanversNo ratings yet
- HW-Hak Asasi AnswerDocument2 pagesHW-Hak Asasi AnswerkaradanversNo ratings yet
- HTML For Khun KruDocument14 pagesHTML For Khun KrukaradanversNo ratings yet
- Derivative (Turunan)Document1 pageDerivative (Turunan)karadanversNo ratings yet