Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Table 16-2b - Opioid Analgesics (Adapted From Joffe Et Al - Sup
Uploaded by
Dragutin PetrićOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Table 16-2b - Opioid Analgesics (Adapted From Joffe Et Al - Sup
Uploaded by
Dragutin PetrićCopyright:
Available Formats
Critical Care >Analgesia, Sedation, and Neuromuscular Blockade
John M. Oropello, Stephen M. Pastores, Vladimir Kvetan+
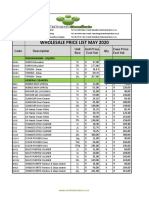
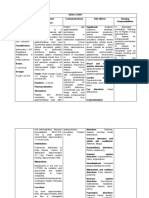
Table 16–2bOpioid analgesics (adapted from Joffe et al6).
Opioid Elimination Half-Life Metabolic Pathway Active Metabolites Notes
Histamine release may be important
Morphine 1.5-2 h Liver: glucuronidation Morphine 6- and 3-glucuronide from a cardiovascular and pulmonary
perspective. Caution in renal failure.
Accumulation with hepatic
Hydromorphone 2-3 h Liver: glucuronidation None
dysfunction.
Significant increase in context-
Fentanyl 3-4 h Liver: N-dealkylation CYP3A4/5 None sensitive half-time with infusions >12
h.
Remifentanil 10-20 min Plasma esterase hydrolysis None Abrupt discontinuation of analgesia.
Oxycodone 3-4 h Liver: CYP2D6 Noroxycodone and oxymorphone
NMDA receptor-antagonist,
unpredictable pharmacokinetics (risk
Methadone 8-59 h Liver: N-methylation CYP3A4, 2D6 none
for accumulation). Multiple drug–drug
interactions. Can prolong QTc.
NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate.
Date of download: 01/01/23 from AccessMedicine: accessmedicine.mhmedical.com, Copyright © McGraw Hill. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- Respiratory DrugsDocument2 pagesRespiratory Drugsmed testNo ratings yet
- PHARMA SupertableDocument2 pagesPHARMA SupertablelpanatalioNo ratings yet
- Etika (Benedikt de Spinoza) (Z-Library)Document238 pagesEtika (Benedikt de Spinoza) (Z-Library)Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology NotesDocument48 pagesPharmacology NotesBheru Lal100% (1)
- Spinal Cord CompressionDocument4 pagesSpinal Cord Compressionian3yeung-2No ratings yet
- Clinical Handbook of Psychotropic Drugs, 25e (May 8, 2023) - (0889376328) - (Hogrefe Publishing) (Etc.) (Z-Library)Document555 pagesClinical Handbook of Psychotropic Drugs, 25e (May 8, 2023) - (0889376328) - (Hogrefe Publishing) (Etc.) (Z-Library)Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Psychopharmacology (Fourth Edition) (Jerry Meyer) (Z-Library)Document841 pagesPsychopharmacology (Fourth Edition) (Jerry Meyer) (Z-Library)Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Clin Pharm Notes Alasdair ScottDocument91 pagesClin Pharm Notes Alasdair ScottARUSHI ARVINDNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Exams Ms - LavarraDocument15 pagesDRUG STUDY Exams Ms - LavarraCharm Abyss la MorenaNo ratings yet
- Lab Test Report of Smaple & Bulk Chemicals: International Classic Composite LTDDocument1 pageLab Test Report of Smaple & Bulk Chemicals: International Classic Composite LTDDyeing Dyeing100% (1)
- McDoman Cleaning Chemicals Wholesale May Price List - 2020Document5 pagesMcDoman Cleaning Chemicals Wholesale May Price List - 2020TinasheNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyMichelle TamorNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Antagonists "Anticholinergic Drugs" (ParasympatholyticsDocument32 pagesCholinergic Antagonists "Anticholinergic Drugs" (ParasympatholyticsmiznahNo ratings yet
- Chlorpromazine Drug StudyDocument10 pagesChlorpromazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Antiseizure DrugsDocument10 pagesAntiseizure DrugsJoyce SumagaysayNo ratings yet
- CH 28 Nausea/VomitingDocument2 pagesCH 28 Nausea/VomitingkandeeNo ratings yet
- Farmakologi Obat Obesitas Dislipidemia 2022Document57 pagesFarmakologi Obat Obesitas Dislipidemia 2022Meidy PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Anti DepressantDocument6 pagesAnti Depressantyahyaahmed152000No ratings yet
- Parasympathomimetic AgentsDocument26 pagesParasympathomimetic Agentsrushikesh ugaleNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic Present and FutureDocument34 pagesAntipsychotic Present and FuturepabitraNo ratings yet
- Metocloprramide HydrochlorideDocument2 pagesMetocloprramide HydrochlorideBeatrizz P GellaNo ratings yet
- MethyldopaDocument4 pagesMethyldopaMichael TokongNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic AntagonistsDocument3 pagesCholinergic Antagonistszkhan260No ratings yet
- Drug Study: Atracurium: RecommendedDocument5 pagesDrug Study: Atracurium: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Important Questions of Pharmacology by Medical Study CenterDocument10 pagesImportant Questions of Pharmacology by Medical Study CenterLin YunNo ratings yet
- Dopamine Antagonist: Generic Name: Chemical EffectDocument2 pagesDopamine Antagonist: Generic Name: Chemical EffectMajeed AlzahraniNo ratings yet
- Antipsychotic Drugs: Presentation By-Sumaiya SadafDocument19 pagesAntipsychotic Drugs: Presentation By-Sumaiya SadafSweta ShahNo ratings yet
- Finals Activity 1 - Drug StudyDocument5 pagesFinals Activity 1 - Drug StudyElly LazaroNo ratings yet
- Anti-Emetics: B. Dian Novita, DR., MkedDocument9 pagesAnti-Emetics: B. Dian Novita, DR., MkedwdqqqdwNo ratings yet
- Metaclopramide: 4. Drug StudyDocument8 pagesMetaclopramide: 4. Drug StudyFrauline GagaracruzNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: TramadolDocument5 pagesDrug Study: TramadolOmyl-Khayr M. SulogNo ratings yet
- MetoclopramideDocument1 pageMetoclopramideJack SolomonNo ratings yet
- Complete List of Drugs PDFDocument21 pagesComplete List of Drugs PDFAnalizaNo ratings yet
- 200912git Drugs1 PDFDocument8 pages200912git Drugs1 PDFNav ThiranNo ratings yet
- 3 Treatment of HypertensionDocument7 pages3 Treatment of HypertensiontiaraNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Concise Notes NEET-PGDocument30 pagesPharmacology Concise Notes NEET-PGMohamed TayyabNo ratings yet
- 8 BSC 2014 Sweeney B Individual Variability in Pharmacological PDFDocument46 pages8 BSC 2014 Sweeney B Individual Variability in Pharmacological PDFBogdan CarabasNo ratings yet
- Mosby PharmacologyDocument3 pagesMosby PharmacologyMillene Aurelle SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Lidocaine: Generic Name: Lidocaine Pharmacologic: Mechanism of ActionDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Lidocaine: Generic Name: Lidocaine Pharmacologic: Mechanism of ActionShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Dopamine Antagonist: Generic Name: Chemical EffectDocument2 pagesDopamine Antagonist: Generic Name: Chemical EffectMajeed AlzahraniNo ratings yet
- 4 12 ToxicologyDocument8 pages4 12 ToxicologyLionelWrightNo ratings yet
- Ace Inhibitors: Drug Name Clinical Use Pharmacokineti Cs Cautions Adverse Effect Interactions HyperkalemiaDocument1 pageAce Inhibitors: Drug Name Clinical Use Pharmacokineti Cs Cautions Adverse Effect Interactions HyperkalemiaSalomeSibashviliNo ratings yet
- PitavastatinDocument46 pagesPitavastatinSeLecToR ck LeeNo ratings yet
- Seizure and Anticonvulsant Medications GridDocument1 pageSeizure and Anticonvulsant Medications Gridpiyush RautNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy 2: Dr. Zuraini, SP.SDocument40 pagesEpilepsy 2: Dr. Zuraini, SP.SYulanda Gusti CibiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology (All Lectures)Document283 pagesPharmacology (All Lectures)Youssef ElzataryNo ratings yet
- Status EpilepticusDocument3 pagesStatus EpilepticusVandeosNo ratings yet
- KetamineDocument12 pagesKetaminepierhot_11No ratings yet
- Neuropharmacology 1Document15 pagesNeuropharmacology 1Pranjali WeladiNo ratings yet
- Charts and Hearts PDFDocument51 pagesCharts and Hearts PDFBen ScottNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Atropine: RecommendedDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Atropine: RecommendedShara Lailanie A. AzisNo ratings yet
- Acetaminophen Drug TabDocument2 pagesAcetaminophen Drug TabJeshamae TrinillaNo ratings yet
- Ketamine: Ketamine Is 2 - (O-Chlorophenyl) - 2 - (Methylamino) Cyclohexanone (Hydrochloride)Document15 pagesKetamine: Ketamine Is 2 - (O-Chlorophenyl) - 2 - (Methylamino) Cyclohexanone (Hydrochloride)Astrid Ghea GayatriNo ratings yet
- ColchicineDocument3 pagesColchicineTri Purma SariNo ratings yet
- Antidepressants: Elisabeth F. BildenDocument14 pagesAntidepressants: Elisabeth F. BildenSNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mode of Action Indications Side Effects Nursing Interventions Generic NameDocument6 pagesDrug Name Mode of Action Indications Side Effects Nursing Interventions Generic Namedodong skyroseNo ratings yet
- Sulfamethaxazole, Salbu + IpraDocument5 pagesSulfamethaxazole, Salbu + IpraGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Age Drug StudyDocument13 pagesAge Drug StudyLadybelle GototosNo ratings yet
- Pheo Presentation FinalDocument52 pagesPheo Presentation FinalArhanNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorders and Carbamazepine PharmacokinetiDocument5 pagesBipolar Disorders and Carbamazepine PharmacokinetiAgr YuroNo ratings yet
- Propranolol, Prophylactic Warfarin, Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH), Furosemide, AntibioticsDocument8 pagesPropranolol, Prophylactic Warfarin, Low Molecular Weight Heparin (LMWH), Furosemide, AntibioticsArlyn MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- UW Notes - 5 - PharmacologyDocument12 pagesUW Notes - 5 - PharmacologyDarshi BNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Therapy and Drugs For Renal Failure: DiureticsDocument7 pagesDiuretic Therapy and Drugs For Renal Failure: DiureticsApple MaeNo ratings yet
- Dapa HF TrialDocument36 pagesDapa HF Trialvarshith kumarNo ratings yet
- Presynaptic Receptors and Neuronal Transporters: Official Satellite Symposium to the IUPHAR 1990 Congress Held in Rouen, France, on 26–29 June 1990From EverandPresynaptic Receptors and Neuronal Transporters: Official Satellite Symposium to the IUPHAR 1990 Congress Held in Rouen, France, on 26–29 June 1990S.Z. LangerNo ratings yet
- ŠizofrenijaDocument216 pagesŠizofrenijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Emocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDocument153 pagesEmocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- PsihijatrijaDocument223 pagesPsihijatrijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Emocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDocument153 pagesEmocionalna Ucjena Susan Forward Donna FraizerDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Selected Root Causes of Moral DistressDocument1 pageSelected Root Causes of Moral DistressDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- EtikaDocument218 pagesEtikaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Agitacija Verbalna DeeskalacijaDocument2 pagesAgitacija Verbalna DeeskalacijaDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Gender PsychiatryDocument12 pagesGender PsychiatryDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- S ADHD LDocument4 pagesS ADHD LDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Upitnik o CAGE-uDocument1 pageUpitnik o CAGE-uDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Upitnik TDocument1 pageUpitnik TDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy For Patients With Bipolar DisordersDocument1 pageDrug Therapy For Patients With Bipolar DisordersDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Upitnik o TWEAKDocument1 pageUpitnik o TWEAKDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Medications For Acute AgitationDocument1 pageMedications For Acute AgitationDragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Okvir S-2Document1 pageOkvir S-2Dragutin PetrićNo ratings yet
- Daftar Obat High Alert Dan LasaDocument11 pagesDaftar Obat High Alert Dan LasarismaimaNo ratings yet
- Inventory Checklist - GenericDocument16 pagesInventory Checklist - GenericNeil PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Aisha 1Document70 pagesAisha 1M Arif KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Lap. Per 31 DesemberDocument258 pagesLap. Per 31 DesemberSabri MondolNo ratings yet
- Pesanan Obat Klinik Bumdes Sehat Trangkil AGUSTUS 2021: NO. Tanggal Nama Obat JumlahDocument7 pagesPesanan Obat Klinik Bumdes Sehat Trangkil AGUSTUS 2021: NO. Tanggal Nama Obat Jumlahapotek bendanNo ratings yet
- List Harga Obat Plazamedis Desember 2021Document78 pagesList Harga Obat Plazamedis Desember 2021Rusma YanaNo ratings yet
- Solvent Miscibility ChartDocument1 pageSolvent Miscibility ChartmahsimaNo ratings yet
- 24 13v3i2 5Document9 pages24 13v3i2 5gopalNo ratings yet
- 17.alekhya Research ArticleDocument8 pages17.alekhya Research ArticleBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- S/N Hand Sanitizer Name & Address of ManufacturerDocument3 pagesS/N Hand Sanitizer Name & Address of ManufacturerKaceNo ratings yet
- Farmakokinetika Tugas Soal PPT EkstravaskulerDocument17 pagesFarmakokinetika Tugas Soal PPT Ekstravaskulertaka oneokrock18No ratings yet
- 6 13 4 5 Appendx1Document11 pages6 13 4 5 Appendx1yugoNo ratings yet
- K335 - Yvt019 2Document33 pagesK335 - Yvt019 2ryan permadiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act 1985 andDocument4 pagesChapter Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act 1985 andSyrax ImNo ratings yet
- 2022 Drug Computation Problem SamplesDocument2 pages2022 Drug Computation Problem SamplesXeyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction PharmacologyDocument36 pagesChapter 1 Introduction PharmacologyAbdulsalaam Mohamed OmerNo ratings yet
- Decl Indicators Germany PRODQNT: k15187074.xlsx 1Document13 pagesDecl Indicators Germany PRODQNT: k15187074.xlsx 1totpityiNo ratings yet
- 2nd LectureDocument22 pages2nd Lecturenwekar groupNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Pdis211 Lab E1Document22 pagesGroup 5 Pdis211 Lab E1Mikaela Kean JoseNo ratings yet
- PT. Mersifarma TM - Pricelist & Link Produk E-Katalog 2023 - 2024Document6 pagesPT. Mersifarma TM - Pricelist & Link Produk E-Katalog 2023 - 2024pujiNo ratings yet
- Otc SalesDocument8 pagesOtc SalesboyapallymeghanaNo ratings yet
- MBS Price List April 2021Document85 pagesMBS Price List April 2021Anonymous aaAQ6dgNo ratings yet
- RB Case StudyDocument12 pagesRB Case StudyRAHUL DUTTANo ratings yet
- d1 QuestionsDocument6 pagesd1 QuestionsaruNo ratings yet
- Medicine Inventory ListDocument3 pagesMedicine Inventory ListCT MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Products List: Sr. No. Composition Strength Dosage FormDocument3 pagesProducts List: Sr. No. Composition Strength Dosage FormDr RonakNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document2 pagesTutorial 1Liew Wen XuanNo ratings yet
- No Tahun Nama Obat / Perbelkes Satuan Expired UnitDocument5 pagesNo Tahun Nama Obat / Perbelkes Satuan Expired UnitBayu Firmansyah AlitNo ratings yet