Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Aaaaaaaaaa
Uploaded by
Aszad RazaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Aaaaaaaaaa
Uploaded by
Aszad RazaCopyright:
Available Formats
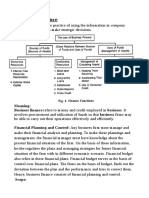
WHAT IS FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT?
financial management
is the business function that deals with investing the available
financial resources in a way that greater business success and
return-on-investment (ROI) is achieved. Financial
management professionals plan, organize and control all
transactions in a business. They focus on sourcing the capital
whether it is from the initial investment by the entrepreneur,
debt financing, venture funding, public issue, or any other
sources. Three Major Decisions in Financial Management-1.
INVESTMENT DECISIONS-The investment decision relates to
the selection of assets in which funds will be invested by a
firm. The assets as per their duration of benefits, can be
categorized into two groups: (i) long-term assets which yield a
return over a period of time in future (ii) short-term or current
assents which in the normal course of business are convertible
into cash usually with in a year. Accordingly, the asset
selection decision of a firm is of two types. The investment in
long-term assets is popularly known as capital budgeting and
in short-term assets, working capital management. 2.
FINANCE DECISIONS -The second major decision involved in
financial management is the financing decision, which is
concerned with the financing — mix or capital structure of
leverage. The term capital structure refers to the combination
of debt (fixed interest sources of financing) and equity capital
(variable — dividend securities/source of funds).3.DIVIDEND
POLICY DECISIONS-The third major decision of financial
management is relating to dividend policy. The firm has two
alternatives with regard to management of profits of a firm.
They can be either distributed to the shareholder in the form
of dividends or they can be retained in the business or even
distribute some portion and retain the remaining. The course
of action to be followed is a significant element in the
dividend decision.
FINANCE AND OTHER RELATED DISCIPLINES-Finance and
Economics-The relationship in between these two disciplines
are studied in two different headings viz Micro and Macro
economics.The major part of the financial management is to
raise the financial resource to the requirements. Finance and
Accounting-The two are embedded with different disciplines.
The finance is the discipline which is mainly based on the cash
basis of operations but the accounting is totally governed by
the accrual system.Finance and Marketing: These two are
disciplines are interrelated to plan for introduction of new
product. The major reason is that the introduction of new
product normally warrants huge sum of money for research
and development; which needs immense planning and
execution to succeed over the other competitors Finance and
Production: The changes in the production policy of the
organization will impact the capital expenditures. The fixed
assets of the organization should be effectively utilized which
neither over capitalization nor under capitalization.Finance
and Quantitative methods: These are inter related to solve
complex problems in order to take decisions.The objectives of
the financial management are classified into two categories
viz 1.Profit maximization 2.Wealth maximization
SCOPE OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT-Planning-The financial
manager projects how much money the company will need in
order to maintain positive cash flow, allocate funds to grow or
add new products or services and cope with unexpected
events, and shares that information with business
colleagues.Budgeting-The financial manager allocates the
company’s available funds to meet costs, such as mortgages
or rents, salaries, raw materials, employee T&E and other
obligations. Managing and assessing risk-Line-of-business
executives look to their financial managers to assess and
provide compensating controls for a variety of risks,
including:1.Market risk2.Credit risk3.Liquidity
risk4.Operational risk.Procedures-The financial manager sets
procedures regarding how the finance team will process and
distribute financial data, like invoices, payments and reports,
with security and accuracy.
FUNCTIONS OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT-More practically, a
financial manager’s activities in the above areas revolve
around planning and forecasting and controlling
expenditures.The FP&A function includes issuing P&L
statements, analyzing which product lines or services have the
highest profit margin or contribute the most to net
profitability, maintaining the budget and forecasting the
company’s future financial performance and scenario
planning.Managing cash flow is also key. The financial
manager must make sure there’s enough cash on hand for
day-to-day operations, like paying workers and purchasing
raw materials for production. This involves overseeing cash as
it flows both in and out of the business, a practice called cash
management. Importance of Financial Management-Solid
financial management provides the foundation for three
pillars of sound fiscal governance:Strategizing-Identifying
what needs to happen financially for the company to achieve
its short- and long-term goals. Leaders need insights into
current performance for scenario planning, for
example.Decision-making-Helping business leaders decide the
best way to execute on plans by providing up-to-date financial
reports and data on relevant KPIs.Controlling-Ensuring each
department is contributing to the vision and operating within
budget and in alignment with strategy.
OBJECTIVES OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT-PROFIT
MAXIMISATION/WEALTH MAXIMATION-Profit
maximisation-it is a process business firms undergo to ensure
the best output and price levels are achieved in order to
maximise its returns.Influential factors such as sale price,
production cost and output levels are adjusted by the firm as a
way of realising its profit goals. ADVANTAGES OF PROFIT
MAXIMISATION- Economic survival: Profit is vital for the
survival of any businessMeasurement standard: Profits are
the right measurement of the viability of a business model. In
the absence of profits, the business loses its key goal and
incurs a direct risk to its survival.Social and economic welfare:
In a business, profits demonstrate proficient use and
allotment of resources. Resource allocation and payments for
land, labour, capital and the organisation lends itself to social
and economic welfare. DISADVANTAGES OF PROFIT
MAXIMISATION‘Profit’ definition is unclear: Different
perceptions of the term exist among organisations and
individuals. For example, profit can be the gross profit, net
profit, before tax profit or the profit rate.Time value of money
is ignored: The formula is based on the idea that the higher
the profit, the better the proposal, but what about its timing?
In finance, when considering present value, we know that
cash now won’t have the same value in the future.Attention
not paid to risk: In the pursuit of profit, risks involved are
ignored, which may prove unaffordable at times, simply
because higher risk directly questions the survival of a
business.WEALTH MAXIMIZATION-Wealth maximization is
the concept of increasing a firm's worth to increase the value
of stockholders' shares.Wealth maximization is also known as
net worth maximization. A stockholder's wealth increases
when a company's net worth maximizes. Advantages-It is
more related to cash flows than profits. 1.Cash flows are more
certain and regular, and there is a lack of uncertainty that
otherwise is associated with profit.2.Profits are more
manipulative, but cash flows are not. Thus, wealth
maximization is less prone to manipulation than profit
maximization, which relies on profit. Disadvantages-1.It is
more based on an idea that is prospective and not
descriptive.2.The objectives laid in such a technique are not
clear.
###MAIN MODERN FUNCTION APPROACH OF FINANCIAL
MANAGEMENT DECISION/ SCOPE/ELEMENT--Investment
Decision-One of the most important finance functions is to
intelligently allocate capital to long term assets. This activity is
also known as capital budgeting. It is important to allocate
capital in those long term assets so as to get maximum yield in
future. Financial decision is yet another important function
which a financial manger must perform. It is important to
make wise decisions about when, where and how should a
business acquire funds. Funds can be acquired through many
ways and channels. Dividend Decision-Earning profit or a
positive return is a common aim of all the businesses. But the
key function a financial manger performs in case of
profitability is to decide whether to distribute all the profits to
the shareholder or retain all the profits Liquidity Decision-It is
very important to maintain a liquidity position of a firm to
avoid insolvency. Firm’s profitability, liquidity and risk all are
associated with the investment in current assets.
OBJECTIVES OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT--The financial
management is generally concerned with procurement,
allocation and control of financial resources of a concern. The
objectives can be-1.To ensure regular and adequate supply of
funds to the concern.2.To ensure adequate returns to the
shareholders which will depend upon the earning capacity,
market price of the share, expectations of the
shareholders.3.To ensure optimum funds utilization. Once the
funds are procured, they should be utilized in maximum
possible way at least cost.4.To ensure safety on investment,
i.e, funds should be invested in safe ventures so that adequate
rate of return can be achieved.5.To plan a sound capital
structure-There should be sound and fair composition of
capital so that a balance is maintained between debt and
equity capital.
FUNCTIONS OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT-Estimation of
capital requirements: A finance manager has to make
estimation with regards to capital requirements of the
company. This will depend upon expected costs and profits
and future programmes and policies of a concern. Estimations
have to be made in an adequate manner which increases
earning capacity of enterprise.Determination of capital
composition: Once the estimation have been made, the
capital structure have to be decided. This involves short- term
and long- term debt equity analysis. Investment of funds: The
finance manager has to decide to allocate funds into
profitable ventures so that there is safety on investment and
regular returns is possible.Management of cash: Finance
manager has to make decisions with regards to cash
management. Cash is required for many purposes like
payment of wages and salaries, payment of electricity and
water bills, payment to creditors, meeting current liabilities,
maintainance of enough stock, purchase of raw materials,
etc.Financial controls: The finance manager has not only to
plan, procure and utilize the funds but he also has to exercise
control over finances.
ORGANIZATION OF THE FINANCE FUNCTIONS-Today, finance
function has obtained the status of a science and an art. As
finance function has far reaching significance in overall
management process, structural organization for further
function becomes an outcome of an important organization
problem. The ultimate responsibility of carrying out the
finance function lies with the top management. However,
organization of finance function differs from company to
company depending on their respective requirements. In
many organizations one can note different layers among the
finance executives such as Assistant Manager (Finance),
Deputy Manager (Finance) and General Manager (Finance).
The designations given to the executives are different. They
are 1.Chief Finance Officer (CFO)2.Vice-President
(Finance)3.Financial Controller4.General Manager (Finance)
5.Finance Officers
RISK AND RETURN IN FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT&&
RELATION- Risk and return in investing are perhaps the most
crucial parameters considered by investors while choosing
an investment option. Individuals who invest on a large scale
analyze the risks involved in a particular investment and the
returns it can yield. Let’s take a step-by-step approach to
understand the concept.First, let’s begin with risk. A risk can
be defined as the uncertainty related to the investment,
market, or company. Investors want profits, and the risks
can potentially reduce the profits, sometimes even making a
loss for them.Many types of risk are involved in investments
– market-specific, speculative, industrial, volatility, inflation,
etc. However, studying the market thoroughly can help
investors make the right decisions. They can analyze the
trends and forecast the situation. RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN
RISK AND RETURN -The correlation between financial risk
and return is fairly simple to comprehend. The risk in
choosing a certain investment is directly proportional to the
returns. Therefore, selecting a high-risk investment can give
higher profits, while a low-risk investment will minimize the
returns.
WHAT IS CAPITAL BUDGETING?- Capital budgeting is the
process a business undertakes to evaluate potential major
projects or investments. Construction of a new plant or a big
investment in an outside venture are examples of projects
that would require capital budgeting before they are
approved or rejected.As part of capital budgeting, a
company might assess a prospective project's lifetime cash
inflows and outflows to determine whether the potential
returns that would be generated meet a sufficient target
benchmark. The capital budgeting process is also known as
investment. IMPORTANCE OF CAPITAL BUDGETING (1) Large
Investments:Capital budgeting decisions, generally, involve
large investment of funds. But the funds available with the
firm are always limited and the demand for funds far
exceeds the resources. Hence, it is very important for a firm
to plan and control its capital expenditure.(2) Long-term
Commitment of Funds:Capital expenditure involves not only
large amount of funds but also funds for long-term or more
or less on permanent basis. The long-term commitment of
funds increases the financial risk involved in the investment
decision. Greater the risk involved, greater is the need for
careful planning of capital expenditure, i.e. Capital
budgeting.(3) Irreversible Nature:The capital expenditure
decisions are of irreversible nature. Once the decision for
acquiring a permanent asset is taken, it becomes very
difficult to dispose of these assets without incurring heavy
losses.(4) Long-Term Effect on Profitability:Capital
budgeting decisions have a long-term and significant effect
on the profitability of a concern. Not only the present
earnings of the firm are affected by the investments in
capital assets but also the future growth and profitability of
the firm depends upon the investment decision taken today.
(5) Difficulties of Investment Decisions:The long term
investment decisions are difficult to be taken because:(i)
Decision extends to a series of years beyond the current
accounting period,(ii) Uncertainties of future and(iii) Higher
degree of risk.(6) National Importance:Investment decision
though taken by individual concern is of national importance
because it determines employment, economic activities and
economic growth. Thus, we may say that without using
capital budgeting techniques a firm may involve itself in a
losing project.
CASH FLOW ESTIMATION&TERMINAL VALUE -A definition
often used for relevant cash flows states that they must be
cash flows that occur in the future and are incremental.In
simple terms, cash flow estimation (or cash flow forecasting)
is a prediction of how much inflow and outflow of cash a
business will have at any given time.It’s a bit more
complicated than that, of course, especially when non-cash
factors, like depreciation and compound interest, come into
play.TERMINAL VALUE There are several terminal value
formulas. Like discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis, most
terminal value formulas project future cash flows to return
the present value of a future asset. The liquidation value
model (or exit method) requires figuring the asset's earning
power with an appropriate discount rate, then adjusting for
the estimated value of outstanding debt.
You might also like
- Financial Management: For EntrepreneursDocument26 pagesFinancial Management: For EntrepreneursWadson Ushemakota100% (1)
- Bba FM Notes Unit IDocument15 pagesBba FM Notes Unit Iyashasvigupta.thesironaNo ratings yet
- FM 1Document7 pagesFM 1Rohini rs nairNo ratings yet
- According To Phillipatus, "Financial Management Is Concerned With The Managerial Decisions ThatDocument26 pagesAccording To Phillipatus, "Financial Management Is Concerned With The Managerial Decisions Thataneesh arvindhanNo ratings yet
- FM MaterialDocument32 pagesFM MaterialSree Harsha VardhanNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1: Introduction of Financial Management: New Law College, BBA LLB 3 Yr Notes For Limited CirculationDocument15 pagesUNIT 1: Introduction of Financial Management: New Law College, BBA LLB 3 Yr Notes For Limited CirculationSneha SenNo ratings yet
- Introduction of FMDocument11 pagesIntroduction of FMsonika7No ratings yet
- CORPORATE FINANCE Mba 2nd NotesDocument100 pagesCORPORATE FINANCE Mba 2nd Noteskunal roxNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Notes SummaryDocument6 pagesFinancial Management Notes SummaryAeris StrongNo ratings yet
- Sample Compre Questions Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesSample Compre Questions Financial ManagementMark KevinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction - Chapter 2 Industrial ProfileDocument74 pagesChapter 1 Introduction - Chapter 2 Industrial Profilebalki123No ratings yet
- Mba Ii Sem Finacial ManagementDocument11 pagesMba Ii Sem Finacial ManagementningegowdaNo ratings yet
- Finacial Management Full NotesDocument114 pagesFinacial Management Full NotesBhaskaran BalamuraliNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Notes PDFDocument68 pagesFinancial Management Notes PDFtirumala ReddyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Finance - Week 1Document20 pagesIntroduction To Finance - Week 1Jason DurdenNo ratings yet
- FM Notes Unit 1&2Document32 pagesFM Notes Unit 1&2prem nathNo ratings yet
- CH 1financial ManagementDocument7 pagesCH 1financial ManagementᎮᏒᏗᏉᏋᏋᏁ ᏦᏬᎷᏗᏒNo ratings yet
- 1 Financial Management Semester 4Document5 pages1 Financial Management Semester 4Satyam KumarNo ratings yet
- ACCN09B Strategic Cost Management 1: For Use As Instructional Materials OnlyDocument3 pagesACCN09B Strategic Cost Management 1: For Use As Instructional Materials OnlyAdrienne Nicole MercadoNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Chapter 1Document4 pagesBusiness Finance Chapter 1sn nNo ratings yet
- Meaning, Scope & Objectives of Financial ManagementDocument3 pagesMeaning, Scope & Objectives of Financial ManagementAmanDeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Financial Management and ControlDocument31 pagesFinancial Management and Controljeof basalof100% (1)
- AssignmentDocument15 pagesAssignmentagrawal.sshivaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 13th Batch Lecture OneDocument13 pagesChapter One 13th Batch Lecture Oneriajul islam jamiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - I 1.1 Introduction To The StudyDocument91 pagesChapter - I 1.1 Introduction To The StudyNaresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Module I: Financial Management - An OverviewDocument19 pagesModule I: Financial Management - An Overviewanusmayavbs1No ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument33 pagesFinancial ManagementAkash k.cNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Study PaperDocument102 pagesFINANCIAL MANAGEMENT Study PaperPriyank TripathyNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument9 pagesTopic 1 Introduction To Financial ManagementkiokocurtisNo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope of Financial ManagementDocument11 pagesNature and Scope of Financial ManagementkorlaguntaNo ratings yet
- Assignment:-1: Core PapersDocument32 pagesAssignment:-1: Core PapersAnamikaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1: Scope and Role of Financial ManagementDocument4 pagesTopic 1: Scope and Role of Financial ManagementLary Lou VenturaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument12 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To Financial ManagementPRIYA KUMARINo ratings yet
- Financial Management 2Document7 pagesFinancial Management 2Rashmi RanjanaNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Keuangan/ Financial Management: Endang Etty MerawatiDocument41 pagesManajemen Keuangan/ Financial Management: Endang Etty MerawatiilaNo ratings yet
- FM - NotesDocument40 pagesFM - NotesdeepeshmahajanNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument14 pagesFinancial ManagementTaher KagalwalaNo ratings yet
- Agency TheoryDocument7 pagesAgency TheoryDoreen AwuorNo ratings yet
- FM Module 1Document9 pagesFM Module 1ZekiNo ratings yet
- Chap 1. Financial Management 1.1 Finance and Related DisciplineDocument13 pagesChap 1. Financial Management 1.1 Finance and Related DisciplineBarkkha MakhijaNo ratings yet
- Financial MGMT BasicsDocument61 pagesFinancial MGMT BasicsLokesh GowdaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial ManagementDocument24 pagesIntroduction To Financial ManagementKabile MwitaNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument8 pagesFinancial ManagementAfifaNo ratings yet
- FM Question Bank Answers by PKGDocument14 pagesFM Question Bank Answers by PKGhimanshu shekharNo ratings yet
- Functions of Financial ManagementDocument5 pagesFunctions of Financial ManagementAthar KhanNo ratings yet
- Functions of Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesFunctions of Financial Managementarchana_anuragi100% (1)
- Goals of Financial ManagementDocument3 pagesGoals of Financial ManagementAndrea Fernandes100% (9)
- Financial Management: Financial Management Entails Planning For The Future of A Person orDocument5 pagesFinancial Management: Financial Management Entails Planning For The Future of A Person orPriya PalNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument9 pagesFinancial ManagementGogineni sai spandanaNo ratings yet
- The Challenging Role of A Finance Manager in A Dynamic Business EnvironmentDocument6 pagesThe Challenging Role of A Finance Manager in A Dynamic Business EnvironmentMuhammad ArifNo ratings yet
- Business Finance AssingmentDocument29 pagesBusiness Finance AssingmentShivaniNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument22 pagesFinancial ManagementRk BainsNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument4 pagesFinancial ManagementAkshay Pratap Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument14 pagesFinancial ManagementMru SurveNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument18 pagesFinancial ManagementJohnykutty JosephNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument48 pagesFinancial ManagementAishu SathyaNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment of FMDocument9 pagesIndividual Assignment of FMRobi MatiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledZeyNo ratings yet
- Financial Literacy for Entrepreneurs: Understanding the Numbers Behind Your BusinessFrom EverandFinancial Literacy for Entrepreneurs: Understanding the Numbers Behind Your BusinessNo ratings yet
- 12Document2 pages12Aszad RazaNo ratings yet
- What Is Financial Management?Document1 pageWhat Is Financial Management?Aszad RazaNo ratings yet
- EstimateeDocument3 pagesEstimateeAszad RazaNo ratings yet
- Skill and Semi Skill VoucherDocument1 pageSkill and Semi Skill VoucherAszad RazaNo ratings yet
- Dug Well of Masi Samad1Document21 pagesDug Well of Masi Samad1Aszad RazaNo ratings yet
- Worksite Facility & Miscellaneous - ContigenciesDocument1 pageWorksite Facility & Miscellaneous - ContigenciesAszad RazaNo ratings yet
- Fyyjguih 5Document4 pagesFyyjguih 5Aszad RazaNo ratings yet
- Hihkkj 2Document1 pageHihkkj 2Aszad RazaNo ratings yet
- GGGGGGDocument5 pagesGGGGGGAszad RazaNo ratings yet
- TPDocument4 pagesTPAszad RazaNo ratings yet
- Syllabus CCCDocument2 pagesSyllabus CCCAszad RazaNo ratings yet
- Revolut - Double Spends, Withheld Funds, Failed Top-Ups/paymentsDocument17 pagesRevolut - Double Spends, Withheld Funds, Failed Top-Ups/paymentsfoobarNo ratings yet
- Investing in The Philippine Stock MarketDocument13 pagesInvesting in The Philippine Stock MarketJohn Carlo AquinoNo ratings yet
- RizalDocument19 pagesRizalEdgar L. BajamundiNo ratings yet
- School AllotDocument1 pageSchool Allotamishameena294No ratings yet
- Seven Signs That Allaah Loves YouDocument6 pagesSeven Signs That Allaah Loves Youimti13No ratings yet
- Ee-1151-Circuit TheoryDocument20 pagesEe-1151-Circuit Theoryapi-19951707No ratings yet
- A Bureaucrat Stole $47.4M From Ontario. Why Did It Take So Long For Anyone To NoticeDocument3 pagesA Bureaucrat Stole $47.4M From Ontario. Why Did It Take So Long For Anyone To Noticerally123No ratings yet
- Banking SystemDocument5 pagesBanking SystemAdewole calebNo ratings yet
- Corsaf™ 16D: Corrosion InhibitorDocument1 pageCorsaf™ 16D: Corrosion Inhibitorsmithyry2014No ratings yet
- Muhannad Evidence 1 Contemporary PresentationDocument24 pagesMuhannad Evidence 1 Contemporary PresentationMuhannad LallmahamoodNo ratings yet
- (U) Daily Activity Report: Marshall DistrictDocument5 pages(U) Daily Activity Report: Marshall DistrictFauquier NowNo ratings yet
- The Astonishing Rise of Angela Merkel - The New YorkerDocument87 pagesThe Astonishing Rise of Angela Merkel - The New YorkerveroNo ratings yet
- Panitia Quran Borang Hafazan 1-5Document11 pagesPanitia Quran Borang Hafazan 1-5Khairiah IsmailNo ratings yet
- 1 Contract CondoDocument7 pages1 Contract CondoABNo ratings yet
- StalinDocument25 pagesStalinsairahNo ratings yet
- University of Delhi: Semester Examination Nov-Dec 2018 TranscriptDocument1 pageUniversity of Delhi: Semester Examination Nov-Dec 2018 TranscriptVarun SinghNo ratings yet
- 13 Stat 351-550Document201 pages13 Stat 351-550ncwazzyNo ratings yet
- L5M4 New PaperDocument9 pagesL5M4 New PaperibraokelloNo ratings yet
- List of 1995Document6 pagesList of 1995trinz_katNo ratings yet
- National Human Rights Commission IndiaDocument27 pagesNational Human Rights Commission IndiaPARAS IQBAL BRARNo ratings yet
- A Case Study On Academic and Vocational Training For Chil - 2021 - Children andDocument14 pagesA Case Study On Academic and Vocational Training For Chil - 2021 - Children andTeacher SafuraNo ratings yet
- 6 Master Plans - ReviewerDocument2 pages6 Master Plans - ReviewerJue Lei0% (1)
- DDocument13 pagesDGretchen Alunday SuarezNo ratings yet
- INCOME TAX Ready Reckoner - by CA HARSHIL SHETHDocument38 pagesINCOME TAX Ready Reckoner - by CA HARSHIL SHETHCA Harshil ShethNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTION TO ENVIRONMENTAL and NATURA PDFDocument31 pagesINTRODUCTION TO ENVIRONMENTAL and NATURA PDFsuruchi agrawalNo ratings yet
- Outbound Inbound Calls From External ToDocument3 pagesOutbound Inbound Calls From External TorajueeguNo ratings yet
- Aurbach VS Sanitary Wares CorpDocument3 pagesAurbach VS Sanitary Wares CorpDoll AlontoNo ratings yet
- Annex CDocument2 pagesAnnex CCruz LheoNo ratings yet
- TC1848 OmniPCX Enterprise Installation Procedure For Version J1.410.60 en Ed02Document44 pagesTC1848 OmniPCX Enterprise Installation Procedure For Version J1.410.60 en Ed02Asnake TegenawNo ratings yet