Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Carbon Cycle General Biology Short Summary
Uploaded by
ANO BYNOUUSOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Carbon Cycle General Biology Short Summary
Uploaded by
ANO BYNOUUSCopyright:
Available Formats
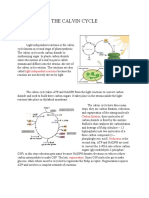
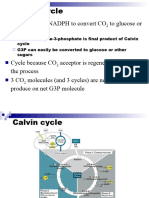
THE SIGNIFICANT EVENTS OF THE CALVIN CYCLE
Using the energy carriers formed in the first steps of photosynthesis, the light-independent
reactions, or the Calvin cycle fixes CO2, taken from the environment. An enzyme, RuBisCO,
catalyzes a reaction with CO2, and another molecule, RuBP. After three cycles, a three-carbon
molecule of G3P leaves the cycle to become part of a carbohydrate molecule. The remaining
G3P molecules stay in the cycle to be regenerated into RuBP, which is then ready to react with
more CO2.
THREE STAGES OF THE CALVIN CYCLE
CARBON FIXATION
● In stage 1, the enzyme RuBisCO incorporates carbon dioxide into an organic molecule,
3-PGA
REDUCTION
● In Stage 2, the organic molecule is reduced using electrons supplied by NADPH
REGENERATION
● In Stage 3, RuBP, the molecule that starts the cycle, is regenerated so that the cycle can
continue. Only one carbon dioxide molecule is incorporated at a time, so the cycle must
be completed three times to produce a single three-carbon G3P molecule, and six times
to produce a six-carbon glucose.
You might also like
- The Calvin CycleDocument1 pageThe Calvin CyclepeachyskizNo ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument4 pagesThe Calvin CycleVerena Raga100% (1)
- Calvi CycleDocument16 pagesCalvi CycleLenor TunacNo ratings yet
- 5.12C The Calvin CycleDocument2 pages5.12C The Calvin Cyclemadeline macalaladNo ratings yet
- The Krebs CycleDocument4 pagesThe Krebs CycleAliaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)Document3 pagesPhotosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)Althea EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5. (Photosynthesis 3)Document3 pagesLesson 5. (Photosynthesis 3)Cristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle Reaction of Photosynthesis Reflection PaperDocument1 pageCalvin Cycle Reaction of Photosynthesis Reflection PaperMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Significant Events of The Calvin CycleDocument15 pagesSignificant Events of The Calvin CycleClaire MNo ratings yet
- Light Independent Reactions Calvin Cycle Lecture GuideDocument3 pagesLight Independent Reactions Calvin Cycle Lecture GuideRogianna IsidroNo ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesThe Calvin CycleNeha SaxenaNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Photosynthesis in Plants Educational Presentation in Green and Yellow Illustrative StyleDocument53 pagesThe Basics of Photosynthesis in Plants Educational Presentation in Green and Yellow Illustrative Styleefesonbantillo18No ratings yet
- Reactions of The Calvin CycleDocument1 pageReactions of The Calvin CycleFred CanamaNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument5 pagesCalvin Cyclemingibabie2025No ratings yet
- The Calvin Cycle Dark Reaction G1Document15 pagesThe Calvin Cycle Dark Reaction G1GeminiNo ratings yet
- The Calvin Cycle Uses ATP and NADPH To Convert CO To Sugar:: 3-Phosphate (G3P)Document2 pagesThe Calvin Cycle Uses ATP and NADPH To Convert CO To Sugar:: 3-Phosphate (G3P)Almighty HunyNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle UpdatedDocument31 pagesCalvin Cycle UpdatedClipNo ratings yet
- Light IndepDocument19 pagesLight IndepiasdfasfsfasfsNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument3 pagesCalvin Cyclekumarscribd5482No ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument4 pagesGeneral BiologyCIANO, Dellaney Joy A.No ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument5 pagesCalvin CycleSaman ArshadNo ratings yet
- Notes Calvin CycleDocument2 pagesNotes Calvin Cycleneelp331No ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument21 pagesCalvin CycleBelac ZepolNo ratings yet
- The Calvin Cycle - Dark ReactionDocument2 pagesThe Calvin Cycle - Dark ReactionVanna Shane MadejaNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument7 pagesCalvin CyclertfNo ratings yet
- Function of Carbon Dioxide in PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesFunction of Carbon Dioxide in Photosynthesisapi-310095373No ratings yet
- Q2Week-2 PhotosynthesisDocument36 pagesQ2Week-2 Photosynthesisjustin charles jerimy raymundoNo ratings yet
- The Light Reaction Events and Calvin Cycle of PhotosynthesisDocument17 pagesThe Light Reaction Events and Calvin Cycle of PhotosynthesisAngel Mae Masa FloresNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument7 pagesCalvin Cyclehasan jamiNo ratings yet
- Light IndependentDocument31 pagesLight IndependentMadame UrsulaNo ratings yet
- CALVIN CycleDocument13 pagesCALVIN CycleDaphne CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument21 pagesCalvin Cyclejadenikomariano2132No ratings yet
- 8.3.1 Carbon FixationDocument12 pages8.3.1 Carbon Fixationnersyanhariri71No ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesCalvin Cycleela ravenaNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 c4 and CAMDocument15 pagesBio 11 c4 and CAMBik WodeNo ratings yet
- The Calvin Cycle: Light Independent ReactionsDocument1 pageThe Calvin Cycle: Light Independent ReactionssintapuspitaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (2 Meeting)Document33 pagesPhotosynthesis (2 Meeting)shanta gintingNo ratings yet
- 02 Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Light Independent ReactionsDocument38 pages02 Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Light Independent ReactionsLaeliaMunawarohNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle Steps and DiagramDocument12 pagesCalvin Cycle Steps and Diagrammaria genio100% (1)
- Cyclic PhotophosphorylationDocument5 pagesCyclic Photophosphorylationmoiz23236No ratings yet
- Independent Reactions Because They Are Not Directly Driven by LightDocument3 pagesIndependent Reactions Because They Are Not Directly Driven by LightPauline TayabanNo ratings yet
- Photosyn-Thesis: Calvin Cycle: Reporters: Group 4Document11 pagesPhotosyn-Thesis: Calvin Cycle: Reporters: Group 4John Allen GuisdanNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 Biosynthetic PhaseDocument14 pagesPresentation1 Biosynthetic PhaseKalyani SreejithNo ratings yet
- 02 Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Light Independent ReactionsDocument15 pages02 Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Light Independent ReactionsMA. HAZEL TEOLOGONo ratings yet
- Calvin-Cycle ReviewerDocument2 pagesCalvin-Cycle Reviewer2JoshDaveTernedaNo ratings yet
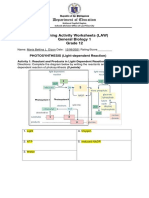
- Department of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 1 Grade 12Document5 pagesDepartment of Education: Learning Activity Worksheets (LAW) General Biology 1 Grade 12Maria Bettina DizonNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesCalvin CycleELVIRA L. ABULOKNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesisDavid PetalcurinNo ratings yet
- 02 Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Light Independent ReactionsDocument33 pages02 Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Light Independent ReactionsAlyssa Grace BayagNo ratings yet
- Light DependentDocument1 pageLight DependentJESICA OXALESNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Light Independent ReactionsDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis Calvin Cycle Light Independent Reactionselnini salaNo ratings yet
- Bio2 PhotosynthesisDocument24 pagesBio2 Photosynthesisjvvuvuuv lopezNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle On CAM PlantsDocument33 pagesCalvin Cycle On CAM PlantseraasyahirahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Photosynthesis Carbon MetabolismDocument46 pagesChapter 6 - Photosynthesis Carbon Metabolismsayidah nafisahNo ratings yet
- Labador, Wenyl B. Bs-CriminologyDocument5 pagesLabador, Wenyl B. Bs-CriminologyBon TikNo ratings yet
- Photosynthetic Carbohydrate synthesis (Calvin Cycle) : Lectured by Dr. Qin Yongmei (秦咏梅) :Nov. 28, 2007Document55 pagesPhotosynthetic Carbohydrate synthesis (Calvin Cycle) : Lectured by Dr. Qin Yongmei (秦咏梅) :Nov. 28, 2007bbaaddaarrNo ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument8 pagesThe Calvin CycleAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument20 pagesCellular RespirationLezel LaracasNo ratings yet
- Bio Worksheet (Calvin Cycle)Document2 pagesBio Worksheet (Calvin Cycle)jerellNo ratings yet