Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Calvin Cycle
Uploaded by
peachyskizOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Calvin Cycle
Uploaded by
peachyskizCopyright:
Available Formats
The Calvin cycle, light-independent reactions, bio synthetic phase, dark reactions, or
photosynthetic carbon reduction cycle of photosynthesis are the chemical reactions that
convert carbon dioxide and other compounds into glucose
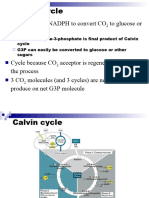
The first phase , carbon dioxide fixation, basically captures the co2 from atmosphere, so it
can be used in the reactions.
To do this, co2 is attached to rubp, a five carbon molecule.
The enzyme used in this reaction is called rubisco, and the result of the reaction is unstable 6
carbon molecule that quickly splits into 2 3 carbon molecules called 3 phosphoglycerate, or
3pg
Next the process of converting the co2 to carbohydrate begins
This phase is called carbon dioxide reduction phase, because we’re adding electrons and
energy to the co2 molecule.
During this phase, a sequence of reaction uses NADPH and some of the ATP from the light
reactions.
These molecule supply the needed electrons and energy for co2 reduction
Electrons are added from NADPH and through a series of reactions, 3pg is reduced to form
g3p, a carbohydrate
ADP and nad+ return to the thylakoids, to be converted back to atp and nadph by the light
reactions
One of the g3p molecules is set aside as a building block for glucose.
But the majority of thed g3p molecules move forward into the third phase of the calvin cycle
In this phase, atp is used to combine the rest of the g3p molecules to form rubp molecules
This rubp can then combine with additional carbon dioxide molecules continuing the carbon
reactions.
To form a glucose molecule, the cycle actually has to turn 6 times, because each turn of the
cycle adds only one atom from the incoming carbon dioxide
You might also like
- Calvin Cycle Reaction of Photosynthesis Reflection PaperDocument1 pageCalvin Cycle Reaction of Photosynthesis Reflection PaperMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- The Krebs CycleDocument4 pagesThe Krebs CycleAliaNo ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument4 pagesThe Calvin CycleVerena Raga100% (1)
- Lesson 5. (Photosynthesis 3)Document3 pagesLesson 5. (Photosynthesis 3)Cristina MaquintoNo ratings yet
- Calvi CycleDocument16 pagesCalvi CycleLenor TunacNo ratings yet
- 5.12C The Calvin CycleDocument2 pages5.12C The Calvin Cyclemadeline macalaladNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument5 pagesCalvin Cyclemingibabie2025No ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument4 pagesGeneral BiologyCIANO, Dellaney Joy A.No ratings yet
- Carbon Cycle General Biology Short SummaryDocument1 pageCarbon Cycle General Biology Short SummaryANO BYNOUUSNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument3 pagesCalvin Cyclekumarscribd5482No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)Document3 pagesPhotosynthesis (Calvin Cycle)Althea EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument8 pagesThe Calvin CycleAmabelle Anne BaduaNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument7 pagesCalvin Cyclehasan jamiNo ratings yet
- The Calvin Cycle Dark Reaction G1Document15 pagesThe Calvin Cycle Dark Reaction G1GeminiNo ratings yet
- Light IndependentDocument31 pagesLight IndependentMadame UrsulaNo ratings yet
- Significant Events of The Calvin CycleDocument15 pagesSignificant Events of The Calvin CycleClaire MNo ratings yet
- The Light Reaction Events and Calvin Cycle of PhotosynthesisDocument17 pagesThe Light Reaction Events and Calvin Cycle of PhotosynthesisAngel Mae Masa FloresNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Photosynthesis in Plants Educational Presentation in Green and Yellow Illustrative StyleDocument53 pagesThe Basics of Photosynthesis in Plants Educational Presentation in Green and Yellow Illustrative Styleefesonbantillo18No ratings yet
- The Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesThe Calvin CycleNeha SaxenaNo ratings yet
- The Calvin Cycle - Dark ReactionDocument2 pagesThe Calvin Cycle - Dark ReactionVanna Shane MadejaNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesCalvin Cycleela ravenaNo ratings yet
- L4.3 - Supplementary-PhotosynthesisDocument8 pagesL4.3 - Supplementary-Photosynthesislizzy.baongocNo ratings yet
- Bio 11 c4 and CAMDocument15 pagesBio 11 c4 and CAMBik WodeNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle UpdatedDocument31 pagesCalvin Cycle UpdatedClipNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument5 pagesCalvin CycleSaman ArshadNo ratings yet
- Reactions of The Calvin CycleDocument1 pageReactions of The Calvin CycleFred CanamaNo ratings yet
- Light Independent Reactions Calvin Cycle Lecture GuideDocument3 pagesLight Independent Reactions Calvin Cycle Lecture GuideRogianna IsidroNo ratings yet
- Function of Carbon Dioxide in PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesFunction of Carbon Dioxide in Photosynthesisapi-310095373No ratings yet
- Cyclic PhotophosphorylationDocument5 pagesCyclic Photophosphorylationmoiz23236No ratings yet
- Light Independent Reaction - BiologyDocument3 pagesLight Independent Reaction - BiologyHidayah SakinahNo ratings yet
- Presentation1 Biosynthetic PhaseDocument14 pagesPresentation1 Biosynthetic PhaseKalyani SreejithNo ratings yet
- Calvin Cycle Steps and DiagramDocument12 pagesCalvin Cycle Steps and Diagrammaria genio100% (1)
- Light IndepDocument19 pagesLight IndepiasdfasfsfasfsNo ratings yet
- Q2Week-2 PhotosynthesisDocument36 pagesQ2Week-2 Photosynthesisjustin charles jerimy raymundoNo ratings yet
- Edexcel B A Level Biology 2015 Topics 5-10 Revision Notes PDFDocument120 pagesEdexcel B A Level Biology 2015 Topics 5-10 Revision Notes PDFMaha NaserNo ratings yet
- Light DependentDocument1 pageLight DependentJESICA OXALESNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Glycolysis and Krebs CycleDocument10 pagesDifference Between Glycolysis and Krebs CycleKuresh RabidNo ratings yet
- The Calvin Cycle Uses ATP and NADPH To Convert CO To Sugar:: 3-Phosphate (G3P)Document2 pagesThe Calvin Cycle Uses ATP and NADPH To Convert CO To Sugar:: 3-Phosphate (G3P)Almighty HunyNo ratings yet
- In The Light ReactionsDocument4 pagesIn The Light ReactionsAzmie Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Notes Calvin CycleDocument2 pagesNotes Calvin Cycleneelp331No ratings yet
- Independent Reactions Because They Are Not Directly Driven by LightDocument3 pagesIndependent Reactions Because They Are Not Directly Driven by LightPauline TayabanNo ratings yet
- CALVIN CycleDocument13 pagesCALVIN CycleDaphne CuaresmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Bioenergetics (Part 2)Document19 pagesChapter 4 - Bioenergetics (Part 2)Nasir KhanNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument21 pagesCalvin CycleBelac ZepolNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis FactsDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis Factsapi-345670716No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument4 pagesCellular Respiration Notessarah parkNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument2 pagesCalvin CycleJoyce Anne Mae AdorioNo ratings yet
- 02 Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Light Independent ReactionsDocument38 pages02 Photosynthesis Calvin Cycle Light Independent ReactionsLaeliaMunawarohNo ratings yet
- GENOGRAMDocument7 pagesGENOGRAMarloaguinaldo1No ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument21 pagesCalvin Cyclejadenikomariano2132No ratings yet
- Match Structure and FunctionDocument27 pagesMatch Structure and FunctionDiyon JohnNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesisDavid PetalcurinNo ratings yet
- Q2 STEM General Biology 1 Week 2Document4 pagesQ2 STEM General Biology 1 Week 2MarkElijah ObelNo ratings yet
- 1. Chuyển hóa carbohydrate (metabolism of carbohydrates) : GlycolysisDocument20 pages1. Chuyển hóa carbohydrate (metabolism of carbohydrates) : GlycolysisAnh Tuyet NguyenNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis (2 Meeting)Document33 pagesPhotosynthesis (2 Meeting)shanta gintingNo ratings yet
- MetabolismeDocument31 pagesMetabolismeLalu Aldi PratamaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Photosynthesis Carbon MetabolismDocument46 pagesChapter 6 - Photosynthesis Carbon Metabolismsayidah nafisahNo ratings yet
- Calvin CycleDocument11 pagesCalvin CycleELVIRA L. ABULOKNo ratings yet
- Aerobic RespirationDocument12 pagesAerobic RespirationShrirang JoshiNo ratings yet
- Travel Agency Business Plan - by SlidesgoDocument85 pagesTravel Agency Business Plan - by SlidesgopeachyskizNo ratings yet
- Planning Methods (Contraceptives, Pills, Condoms)Document7 pagesPlanning Methods (Contraceptives, Pills, Condoms)peachyskizNo ratings yet
- Science, Technology, Society NotesDocument12 pagesScience, Technology, Society NotespeachyskizNo ratings yet
- History of NarvacanDocument1 pageHistory of NarvacanpeachyskizNo ratings yet
- Theories and Principle of Health Care EthicsDocument6 pagesTheories and Principle of Health Care EthicspeachyskizNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect ESSAYDocument2 pagesPractice Makes Perfect ESSAYpeachyskizNo ratings yet
- Grey's Anatomy Medical NotesDocument6 pagesGrey's Anatomy Medical Notespeachyskiz100% (2)
- Binary To Decimal ConversionDocument32 pagesBinary To Decimal ConversionpeachyskizNo ratings yet
- Two Components of Mail MergeDocument3 pagesTwo Components of Mail MergepeachyskizNo ratings yet