Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mypearth Ch4answers
Mypearth Ch4answers
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mypearth Ch4answers
Mypearth Ch4answers
Copyright:
Available Formats
4 Potential energy, kinetic energy
and gravity
Answers
Page 55 Critical thinking skills: Observing carefully in order to
recognize problems
If the electricity from the solar panel is used to power a lamp, some energy will
be lost. This might be through electrical resistance heating the wires, or the
lamp getting hot and emitting thermal energy, or from light traveling off in
different directions. The solar panel will not be able to convert all of the light
energy to electrical energy either. As a result, not enough energy will shine on
the solar panel to power the lamp.
Page 56 Data-based question: Units of energy
1. a) 90 × 4,200 = 378,000 J
b) 378,000 ÷ 1.36 = 278,000 foot-pounds
2. a) 3,000,000 × 4.184 × 109 = 1.255 × 1016 J
b) 1.255 × 1016 ÷ 1.6 × 1020 = 7.8 × 10–5 cubic miles of oil
3. a) 4 × 1.6 × 1020 = 6.4 × 1020 J
b) 6.4 × 1020 ÷ 4.184 × 109 = 1.5 × 1011 tonnes of TNT
Page 60 Activity: Identifying energy transfers
1. a) Electrical energy sound energy
b) Kinetic energy electrical energy
c) Electrical energy light energy
2. a) Microphone
b) Electric motor
c) Solar cell
Page 64 What is gravity?
1. Students’ answers will vary – will be student’s mass in kg × 9.8
2. Students’ answers will vary – will be student’s mass in kg × 3.7
Summative assessment
Criterion A: Energy, gravity and cars
1. D
2. B
3. A
4. A
5. D
© Oxford University Press 2019 1
Criterion B: Investigating stopping distances
Independent variable = mass of car
6.
Dependent variable = distance it travels
7. Any sensible, valid control variable e.g. same ramp angle, same
distance/height up the ramp, same surface, same toy car used each time.
8. Pupil will need to measure the mass of the car
9. Ruler/tape measure; balance
10. 1 mark: suitable hypothesis
2 marks: valid hypothesis with explanation
3 marks: scientific explanation for valid hypothesis
For example: Adding more toy putty to the car will increase the distance
that it travels. This is because as more mass is added to the car, the more
gravitational energy it will have at the top of the ramp. This will mean
that it will have a greater kinetic energy at the bottom of the ramp. Since
work done = force × distance, the car will travel a greater distance for the
frictional force to do enough work to stop the car.
Criteria C and D: Speed management
11. Author; year/date of publication; where was it published (e.g. which
book, journal, website address etc…)
12. A greater speed will result in greater kinetic energy
13. Independent variable = speed of car
Dependent variable = probability that crash is fatal
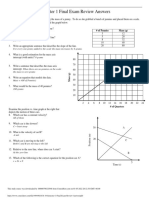
14. Experiment is dangerous/would cause death; experiment is not ethical.
15. 100
probability that crash is fatal
80
60
(%)
40
20
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
speed (km/h)
Suitable axes; axes labelled; points plotted correctly; line of best fit
16. Correct values read from graph
Speed (km/h) Probability (%)
32 13
40 36
48 81
17. Reduction in speed is small; reduction in danger is large; comparison of
importance of these two points; 1 mark for quality of written work.
2 © Oxford University Press 2019
You might also like
- Nissan Pathfider 2005 ManualDocument84 pagesNissan Pathfider 2005 ManualDragos StefanNo ratings yet
- Cost Analysis and Comparison of HVAC, LFAC and HVDC For Offshore Wind Power ConnectionDocument6 pagesCost Analysis and Comparison of HVAC, LFAC and HVDC For Offshore Wind Power ConnectionNathaliaNo ratings yet
- Physics: Edexcel International Gcse (9 - 1)Document20 pagesPhysics: Edexcel International Gcse (9 - 1)Heet100% (3)
- Mechanics Practice Problem Set PDFDocument41 pagesMechanics Practice Problem Set PDFErwin CabangalNo ratings yet
- Fast Bus Transfer Systems For Critical Process ContinuityDocument11 pagesFast Bus Transfer Systems For Critical Process ContinuityamdatiNo ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument12 pagesSurface Roughnessnajieyuya100% (10)
- 1 Physics FormulaeDocument99 pages1 Physics FormulaeAbrar FaqeehNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology Understanding Small Systems 3rd Rogers Solution ManualDocument12 pagesNanotechnology Understanding Small Systems 3rd Rogers Solution ManualBrian Prater100% (36)
- 2019 Physicsbowl Answers and Solutions: "For Groundbreaking Inventions in The Field of Laser Physics"Document5 pages2019 Physicsbowl Answers and Solutions: "For Groundbreaking Inventions in The Field of Laser Physics"Ajay NegiNo ratings yet
- Stretch and ChallengeDocument5 pagesStretch and ChallengeUmar SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Qcm1 February 2015 424 CorrigeDocument10 pagesQcm1 February 2015 424 CorrigeFlorian DupuyNo ratings yet
- Aiims Specialist Physics 26 Years Chapterwise Solved Papers 2Nd Edition Arihant Editorial Board Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFDocument79 pagesAiims Specialist Physics 26 Years Chapterwise Solved Papers 2Nd Edition Arihant Editorial Board Online Ebook Texxtbook Full Chapter PDFnellie.daly869100% (11)
- BBA 213 Final Exam Jan20Document4 pagesBBA 213 Final Exam Jan20Divine DanielNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Test Revision HomeworkDocument7 pagesMid Term Test Revision HomeworkAbrorNo ratings yet
- Session 5 Dealing With Risk and UncertaintiesDocument14 pagesSession 5 Dealing With Risk and UncertaintiesShabahul ArafiNo ratings yet
- Foundation Olympiad: Com - Bmatalent Sample)Document37 pagesFoundation Olympiad: Com - Bmatalent Sample)Rajesh mishraNo ratings yet
- Ain - Shams - Universit - Dynamics - Spring - 2020 (2) - 1Document24 pagesAin - Shams - Universit - Dynamics - Spring - 2020 (2) - 1Abdelrhman S. MohamedNo ratings yet
- 076BAS030 Assignment2 CFDDocument19 pages076BAS030 Assignment2 CFDPritam SahNo ratings yet
- Annotated Physics Data Booklet 2016Document17 pagesAnnotated Physics Data Booklet 2016okiknkjkbiNo ratings yet
- 18 19 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answers PDFDocument8 pages18 19 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Answers PDFTonet CompetenteNo ratings yet
- Activity 2Document5 pagesActivity 2Denielle ClementeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Measurements and Unceratinities (Answers)Document4 pagesAssignment 1 Measurements and Unceratinities (Answers)panghua tanNo ratings yet
- October November 23 Paper 12Document16 pagesOctober November 23 Paper 12avanishh914No ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced LevelSzeYee OonNo ratings yet
- ENGR 313 - Engineering Analysis and Computations - HW1 - Mohamad Yassine PDFDocument2 pagesENGR 313 - Engineering Analysis and Computations - HW1 - Mohamad Yassine PDFabdulrahman mohamedNo ratings yet
- Day 3 PICHEDocument13 pagesDay 3 PICHEKuo Garol SarongNo ratings yet
- MIT16 07F09 hw02Document7 pagesMIT16 07F09 hw02buddlightbeerlogNo ratings yet
- CAP High School Prize Exam: April 9th, 2013 9:00 - 12:00 Competitor's Information SheetDocument7 pagesCAP High School Prize Exam: April 9th, 2013 9:00 - 12:00 Competitor's Information Sheetelty TanNo ratings yet
- MathDocument43 pagesMathLaurentiuNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note 7 - Part 1Document3 pagesLecture Note 7 - Part 1charukaNo ratings yet
- Scatter GraphsDocument14 pagesScatter GraphsHilda Sarfo FrimpongNo ratings yet
- Design of Articulated Robotic Arm UsingDocument6 pagesDesign of Articulated Robotic Arm UsingEric AinslieNo ratings yet
- 0625 m18 QP 22 PDFDocument16 pages0625 m18 QP 22 PDFamalNo ratings yet
- Physical Science ComputationDocument3 pagesPhysical Science ComputationJeff LacasandileNo ratings yet
- QP Nsep p160Document16 pagesQP Nsep p160Virat KohliNo ratings yet
- PAPER 3 2015-2018pdfDocument126 pagesPAPER 3 2015-2018pdfAntony MwangiNo ratings yet
- PTG Chapter 13 Asal PhysicsDocument10 pagesPTG Chapter 13 Asal Physicszzrnwdzpsmhs951003No ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2Document3 pagesAssignment No. 2Ravi KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Fundamental (Base) Quantities and Their Units: 13/03/2019, 22?42 Page 1 of 6Document6 pages1.1 Fundamental (Base) Quantities and Their Units: 13/03/2019, 22?42 Page 1 of 6sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- 9702 Questions May June 2014Document16 pages9702 Questions May June 2014Jason RayNo ratings yet
- BPhO - Intermediate - PHC 2020 - RevDocument18 pagesBPhO - Intermediate - PHC 2020 - Rev148mloftaeNo ratings yet
- Physics: Formula Hand BookDocument39 pagesPhysics: Formula Hand BookDeepanshu FularaNo ratings yet
- SPH 4u0Document13 pagesSPH 4u0Shehab MohamedNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam 2018Document5 pagesPhysics Exam 2018naeiyuNo ratings yet
- Review - Physics Semester Exam - 1Document28 pagesReview - Physics Semester Exam - 1techzealNo ratings yet
- Sample 03 Rev 1Document5 pagesSample 03 Rev 1Dhenil ManubatNo ratings yet
- ATP Workshop 2022Document150 pagesATP Workshop 2022d3220794No ratings yet
- E06 Magnetic Force v01Document4 pagesE06 Magnetic Force v01Abdulla ZaabiNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Model 2014 G12Document11 pagesPHYSICS Model 2014 G12Kedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Scatter GraphsDocument7 pages3.5 Scatter GraphsJohn Mark HermedillaNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 Intro MLDocument60 pagesLecture1 Intro MLnathangame465No ratings yet
- OioiDocument5 pagesOioiSharaGailFuscabloNo ratings yet
- Assignment #1: Date Material Covered Reading From OhanianDocument2 pagesAssignment #1: Date Material Covered Reading From OhanianwonchaiNo ratings yet
- GIS Methods and Applications in Petroleum IndustryDocument11 pagesGIS Methods and Applications in Petroleum IndustryKaywan MuthafarNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Ultimate Vertical Capacity of Pile From Full Scale Pile Load TestDocument9 pagesEvaluation of Ultimate Vertical Capacity of Pile From Full Scale Pile Load TestBassam ElsayedNo ratings yet
- Bachelor Thesis Erste SeiteDocument6 pagesBachelor Thesis Erste Seiteafcmausme100% (2)
- 2016 Physics Questionbank - BookDocument454 pages2016 Physics Questionbank - Bookdencos2006No ratings yet
- Answers Should Be Written in QCAB Format Only.: InstructionsDocument81 pagesAnswers Should Be Written in QCAB Format Only.: InstructionsSandeep PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- IDA Paper Gondek Hafner SampsonDocument6 pagesIDA Paper Gondek Hafner Sampsonreplicant66No ratings yet
- Physics: T T T TDocument10 pagesPhysics: T T T TPraphul MalolNo ratings yet
- Exam 2Document7 pagesExam 2hasagiNo ratings yet
- A Novel Approach For The Solution of Multi Objective Interval Transportation ProblemDocument10 pagesA Novel Approach For The Solution of Multi Objective Interval Transportation ProblemNader FaroukNo ratings yet
- Mypearth Ch2answersDocument4 pagesMypearth Ch2answersVARGAS GUTIERREZ OMAR DANILO DOCENTE DE FISICANo ratings yet
- Mypearth Ch5answersDocument3 pagesMypearth Ch5answersVARGAS GUTIERREZ OMAR DANILO DOCENTE DE FISICANo ratings yet
- Mypearth Ch3answersDocument4 pagesMypearth Ch3answersVARGAS GUTIERREZ OMAR DANILO DOCENTE DE FISICANo ratings yet
- Mypearth Ch1answersDocument5 pagesMypearth Ch1answersVARGAS GUTIERREZ OMAR DANILO DOCENTE DE FISICANo ratings yet
- Cutler-Hammer: Type POW-R-M-S Low-Voltage Distribution SwitchboardsDocument8 pagesCutler-Hammer: Type POW-R-M-S Low-Voltage Distribution SwitchboardstecnicoopNo ratings yet
- Multiple Switch Detection Interface With Suppressed Wake-Up: Technical DataDocument32 pagesMultiple Switch Detection Interface With Suppressed Wake-Up: Technical Datakatty cumbeNo ratings yet
- Eaas0593 XaDocument24 pagesEaas0593 XaAchmad AnugrahNo ratings yet
- Meter Bridge Experiment Using Wheatstone Bridge Principle PDFDocument12 pagesMeter Bridge Experiment Using Wheatstone Bridge Principle PDFOm Kumar100% (1)
- Inverter TecoDocument12 pagesInverter TecoBotjah TjilikNo ratings yet
- Abb Pstx30 Pstx370 GuideDocument153 pagesAbb Pstx30 Pstx370 GuideHugoCabanillasNo ratings yet
- 4 Way Traffic Signal SystemDocument26 pages4 Way Traffic Signal SystemNareshKhatri100% (5)
- Explanatory Notes On CE Marking: Low Voltage Directive (NSR), EMC LegislationDocument2 pagesExplanatory Notes On CE Marking: Low Voltage Directive (NSR), EMC LegislationrocketvtNo ratings yet
- Manual Flexicompact v1.3Document37 pagesManual Flexicompact v1.3alexphan633No ratings yet
- 2116 and 2132 Multi Language User GuideDocument156 pages2116 and 2132 Multi Language User GuideGerman Vasquez SepulvedaNo ratings yet
- OsiSense XS & XT - XSAV11373 PDFDocument6 pagesOsiSense XS & XT - XSAV11373 PDFVIJAVARHOTMAILCOMNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 07 Energy Band Gap: Prepared By: Department of Physics Medi-Caps University, IndoreDocument16 pagesExperiment No. 07 Energy Band Gap: Prepared By: Department of Physics Medi-Caps University, IndorePrabal Pratap Singh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Systemair K 150 EC SileoDocument2 pagesSystemair K 150 EC SileoХажид СүрэнNo ratings yet
- Step Recovery DiodesDocument3 pagesStep Recovery DiodesfahkingmoronNo ratings yet
- Primus DescriptionDocument92 pagesPrimus Descriptionwizardgrt1No ratings yet
- Hotwire Anemometer: Product Datasheet Stock No: 193-8699Document3 pagesHotwire Anemometer: Product Datasheet Stock No: 193-8699Nordalilah Mohd SobriNo ratings yet
- Federal Republic of Nigeria Official Gazette: ExtraordinaryDocument15 pagesFederal Republic of Nigeria Official Gazette: Extraordinaryidoko191No ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Introduction To DC Motor DrivesDocument22 pagesLecture 1 Introduction To DC Motor DrivesNovic JohnsNo ratings yet
- Artikel Electric ChargeDocument3 pagesArtikel Electric ChargeYeni SurantiNo ratings yet
- Hvac VCDSDocument26 pagesHvac VCDSYuri OrlovNo ratings yet
- 2018 CatalogDocument32 pages2018 CatalogShahid SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Capacitance of Metal Spheres and of A Spherical Capacitor: (Item No.: P2420300)Document5 pagesCapacitance of Metal Spheres and of A Spherical Capacitor: (Item No.: P2420300)Nashitah AlwazNo ratings yet
- TL062CPDocument12 pagesTL062CPCleison FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Electric Vehicles in India: A Literature Review: March 2021Document4 pagesElectric Vehicles in India: A Literature Review: March 2021thumula.rameshNo ratings yet
- Sheath Over-Voltages Minh NGUYEN TUAN RTE EDFDocument17 pagesSheath Over-Voltages Minh NGUYEN TUAN RTE EDFMarko IstenicNo ratings yet
- Tablero de Control Deep Sea 6110.Document2 pagesTablero de Control Deep Sea 6110.luisNo ratings yet
- PROEL Xenia Loudspeaker - ManualDocument16 pagesPROEL Xenia Loudspeaker - ManualFranzzNo ratings yet