0% found this document useful (0 votes)
189 views9 pagesEngineering Evaluation Exam Review 2023
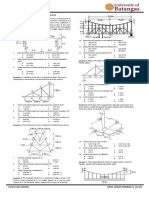
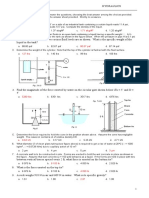
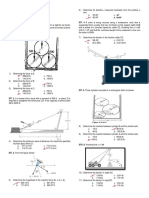
This document contains a 37 multiple choice question evaluation exam on engineering mechanics concepts. The exam covers topics such as forces, hydrostatics, cables, beams, friction, and projectile motion. Test-takers are instructed to choose one answer for each question and mark their responses on an answer sheet, with no erasures allowed.
Uploaded by
Shu RubioCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
189 views9 pagesEngineering Evaluation Exam Review 2023
This document contains a 37 multiple choice question evaluation exam on engineering mechanics concepts. The exam covers topics such as forces, hydrostatics, cables, beams, friction, and projectile motion. Test-takers are instructed to choose one answer for each question and mark their responses on an answer sheet, with no erasures allowed.
Uploaded by
Shu RubioCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd