Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Automation in Analytical Chemistry
Uploaded by
ENTREPRENEUR 8211Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Automation in Analytical Chemistry
Uploaded by
ENTREPRENEUR 8211Copyright:
Available Formats
CHM- 608
Standard Methods and Quality Assurance
Automation in Analytical Methods
Assignment Title: Types of Automation with Examples
Submitted To: Dr. Kiran Aftab
Submitted By: Ayesha Sattar
Roll No. 15712
Program: BS Chemistry (Morning)
Types of Automation with Examples
Automation Methods:
One of the major developments in analytical chemistry during the last few decades has been
appearance of commercial automated analytical systems which provide control information
and advanced data management capacity by the use of modern controllers, sensors and other
devices without human intervention.
Types of Automation:
Today, many routine determinations and analysis as well as demanding analysis are made with
totally or partially automated systems. In various fields like pharmaceutical, environmental,
forensic, governmental, and universities research laboratories, it has been widely spread for
various purposes.
Following are the major types which revolutionized the global village.
(a) Information Technology (IT):
It is a powerful tool that accelerates the IT infrastructure and applications by
automating manual procedures that required human touch before. It allows IT staff to
do work more strategically rather than administratively. Through automation, IT has
been more responsive to business world and with minimal human errors.
Example:
Recent IT automation work includes Artificial Intelligence that creates smarter processes
for unpredictable situations. To create networking or security templates ad to configure
applications allowing IT staff to do work more quickly.
(b) Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM):
To automate the manufacturing process, the use of software and computer-controlled
machinery, CAM has been widely used. It allows to create designs and objects directly
from computer designs and software rather than human involvement.
Example:
To create a 3D model or design of a part, a designer will use CAD (Computer Aided
Design) software that will talk with CAM tools to further set up the processes and
produce number of identical copies of the physical item automatically, thus reducing the
production time and errors.
(c) Computer Numerically-Controlled Equipment (CNC):
In modern era, the machine tools execute operations sequentially on parts or products
in a programmed version. For that purpose, all individual machines have their own
computers, referred as computerized numerical controlled (CNC) machines. If they
share the same computer then called as direct numerical controlled machines.
Example:
• CNC Plasma\Laser Cutter- which cuts the material such as steel or other heavy
metal using plasma torch.
• CNC Milling Machine- can translate specific programs of numbers and letters to
move the spindle. It involves tapping, drilling and milling.
• CNC Electric Discharge Machine- which creates specific shape within certain
material using electric spark.
(d) Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS):
One of the best systems in automation is FMS, that provides a great flexibility for any
kind of changes or modification or amendment in the product design or its output level.
This can be done within seconds by giving commands through codes by human
operators. Due to proper planning and programming precision, it reduces inventory.
Example:
• Autonomous Mobile Robots.
• Container-Based Industrial Control.
• Buffer Storage.
• Autonomous Skilled Robots.
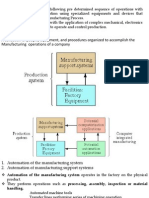
(e) Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM):
To control entire production process, the manufacturing approach of using integration
of computers exchanging information with each other. It is commonly used in factories
or plants for cost accounting, inventory control etc.
Major elements of CIM are:
• Storage and retrieval automated system.
• Central management control system.
• Proper communication system
• Continuous conveyor.
Example:
In an automated canning factory, CIM is mainly concerned with the information
processing tasks at all levels of the factory and its management, including
humans and technology, such as CAD, CAM and the business data processing
system, whereas FMS provides the essential computer-controlled manufacturing
tools and shop floor control system for CIM to execute the computer-generated
plans and schedules that take account of a total system rather than just one
machine, one cell or shop.
You might also like
- EftDocument44 pagesEftAparna SamuelNo ratings yet
- Delphi XE2 Foundations - Part 1 - Rolliston, ChrisDocument160 pagesDelphi XE2 Foundations - Part 1 - Rolliston, ChrisJoel Quezada100% (2)
- HD One X S User Guide PDFDocument19 pagesHD One X S User Guide PDFprasad100% (1)
- CNC AutomationDocument19 pagesCNC Automationsameersaurabh5No ratings yet
- S L Meena Assistant Professor Rajasthan Technical UniversityDocument27 pagesS L Meena Assistant Professor Rajasthan Technical UniversityJâîñ HïmåñßhûNo ratings yet
- Huawei HCIA-AI V3.0 Exam Questions & Answers PDFDocument93 pagesHuawei HCIA-AI V3.0 Exam Questions & Answers PDFArif Mohammad100% (2)
- CIM Communication SystemsDocument125 pagesCIM Communication Systemssarul_murugan2483100% (2)
- Benefits of CIM Integration in ManufacturingDocument18 pagesBenefits of CIM Integration in ManufacturingJackson ..No ratings yet
- Coa M2017-006Document4 pagesCoa M2017-006Arnel Pablo100% (1)
- CMMS Unleashed: Harnessing the Power of Technology for Efficient Maintenance Management: Cryotos CMMS, #1From EverandCMMS Unleashed: Harnessing the Power of Technology for Efficient Maintenance Management: Cryotos CMMS, #1No ratings yet
- Computer-Integrated ManufacturingDocument17 pagesComputer-Integrated ManufacturingnguyendaibkaNo ratings yet
- CIM: Computer Integrated Manufacturing ExplainedDocument93 pagesCIM: Computer Integrated Manufacturing ExplainedEbrahim Hakami100% (1)
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) .Document5 pagesComputer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) .BHAGYESH JHANWARNo ratings yet
- Report SummaryDocument4 pagesReport SummaryJudeline PastoresNo ratings yet
- Computer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM)Document3 pagesComputer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM)anurajNo ratings yet
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) DefinitionDocument6 pagesComputer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) DefinitionSaranya DuraisamyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CIMDocument6 pagesIntroduction To CIMzuhaib alamNo ratings yet
- Unit-Iv CNC: Direct Numerical Control (DNC)Document4 pagesUnit-Iv CNC: Direct Numerical Control (DNC)farhan fahimNo ratings yet
- Computer Integrated ManufacturingDocument3 pagesComputer Integrated ManufacturingfarhanjohariNo ratings yet
- Mechatronics Integration in ManufacturingDocument50 pagesMechatronics Integration in ManufacturingSanniNo ratings yet
- M.Tech Automation Lecture 1 IntroductionDocument28 pagesM.Tech Automation Lecture 1 IntroductionMohamed Essam MohamedNo ratings yet
- Computer Integrated ManufacturingDocument17 pagesComputer Integrated ManufacturingMvk Chaitanya100% (1)
- CIM Lecture Overview Computer Integrated ManufacturingDocument37 pagesCIM Lecture Overview Computer Integrated ManufacturingSatheesh SekarNo ratings yet
- Computer Integrated ManufacturingDocument19 pagesComputer Integrated ManufacturingMani KandanNo ratings yet
- Introduce Computer Integrated Manufacturing System Architecture (CIMOSA) and Manufacturing Process ManagementDocument26 pagesIntroduce Computer Integrated Manufacturing System Architecture (CIMOSA) and Manufacturing Process ManagementRanjit TharuNo ratings yet
- CIM Introduction and BenefitsDocument24 pagesCIM Introduction and BenefitsLitesh AmberkarNo ratings yet
- Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) blends development in manufacturing with information technologyDocument4 pagesComputer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) blends development in manufacturing with information technologyAbbas YerimaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to CAD-CAM Systems and Their EvolutionDocument30 pagesIntroduction to CAD-CAM Systems and Their EvolutionkoalaboiNo ratings yet
- Computer Aided Manufacturing - Janak ValakiDocument23 pagesComputer Aided Manufacturing - Janak ValakijanakNo ratings yet
- Computer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) Is TheDocument5 pagesComputer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) Is TheanashussainNo ratings yet
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing: Presented byDocument30 pagesComputer Integrated Manufacturing: Presented bykarthiyuvenNo ratings yet
- CimDocument151 pagesCimRamesh KarnavarNo ratings yet
- Unit - Vi:: Applications in MechatronicsDocument14 pagesUnit - Vi:: Applications in MechatronicsViswanathanBalajiNo ratings yet
- Computer-Integrated Manufacturing: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 pagesComputer-Integrated Manufacturing: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAlex JordonNo ratings yet
- Smu 2 Sam Assinment 2012Document146 pagesSmu 2 Sam Assinment 2012manish_rajoria2010No ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Computer Integrated Manufacturing SystemsDocument29 pagesUnit - 1 Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systemsbest4reverNo ratings yet
- Computer-Integrated Manufacturing: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 pagesComputer-Integrated Manufacturing: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDurga SankarNo ratings yet
- Computer Integrated ManufacturingDocument16 pagesComputer Integrated ManufacturingAyesha RehmanNo ratings yet
- CIM-Computer Integrated Manufacturing ExplainedDocument16 pagesCIM-Computer Integrated Manufacturing ExplainedHarshad KondalkarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document21 pagesUnit 1John Aubrey MatiasNo ratings yet
- VTU NOTES, QUESTION PAPERS, NEWS, RESULTS & FORUMS ON CIMDocument29 pagesVTU NOTES, QUESTION PAPERS, NEWS, RESULTS & FORUMS ON CIMAbid YusufNo ratings yet
- CAD CAM CIM SystemsDocument15 pagesCAD CAM CIM SystemsdeepakmitrNo ratings yet
- 2017 IM 40 (Lab Session 1)Document3 pages2017 IM 40 (Lab Session 1)Muhammad Irfan AkramNo ratings yet
- Computer-Integrated ManufacturingDocument17 pagesComputer-Integrated Manufacturingshahnawaz875No ratings yet
- Application Fields of Computer Systems: Chapter ObjectivesDocument17 pagesApplication Fields of Computer Systems: Chapter ObjectivesEnkhbayar Enkh-AmgalanNo ratings yet
- CIM Basics: What is Computer Integrated ManufacturingDocument17 pagesCIM Basics: What is Computer Integrated ManufacturingAthikesavanNo ratings yet
- Computer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) : Hasan Oben Pullu Dokuz Eylul University Industrial Engineering DepartmentDocument17 pagesComputer Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) : Hasan Oben Pullu Dokuz Eylul University Industrial Engineering Departmentnnitinsharma87No ratings yet
- Computer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM)Document4 pagesComputer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM)Jyoti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Computer Integrated ManufacturingDocument17 pagesComputer Integrated ManufacturingPrakash GadideshNo ratings yet
- 5.5 CimDocument18 pages5.5 CimcjksdbvjkcsbNo ratings yet
- CIM COMPUTER-INTEGRATED MANUFACTURING GUIDEDocument17 pagesCIM COMPUTER-INTEGRATED MANUFACTURING GUIDEShubham KadamNo ratings yet
- CIM FundamentalsDocument36 pagesCIM Fundamentalsmohsinkhan_146No ratings yet
- 3 Technology and Operations ManagementDocument8 pages3 Technology and Operations ManagementJohn Julius MarquezNo ratings yet
- Learning Material: Department of Mechanical and Automation EngineeringDocument73 pagesLearning Material: Department of Mechanical and Automation EngineeringVipin SureshNo ratings yet
- Computer Integrated ManufacturingDocument4 pagesComputer Integrated Manufacturinguzakkhan100% (2)
- Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM)Document3 pagesComputer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM)Hadi Ahamed LipuNo ratings yet
- Industrial Automation - Lecture 1Document56 pagesIndustrial Automation - Lecture 1Elly TongsNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Computer-Integrated-manufacturing-systems Introduction NotesDocument29 pagesMechanical Engineering Computer-Integrated-manufacturing-systems Introduction NotesPranav SinghNo ratings yet
- Cim Technology DefinationsDocument3 pagesCim Technology DefinationsengmsaudanNo ratings yet
- Computer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) - 305801Document4 pagesComputer-Integrated Manufacturing (CIM) - 305801Tran Minh TriNo ratings yet
- Benefits of CIM SystemsDocument12 pagesBenefits of CIM Systemsanon_913155223No ratings yet
- CIM Definition Benefits ChallengesDocument15 pagesCIM Definition Benefits ChallengesMuzammil MuhammedNo ratings yet
- Design Automation of Cyber-Physical SystemsFrom EverandDesign Automation of Cyber-Physical SystemsMohammad Abdullah Al FaruqueNo ratings yet
- First AssignmentDocument1 pageFirst AssignmentENTREPRENEUR 8211No ratings yet
- Backbone PainDocument4 pagesBackbone PainENTREPRENEUR 8211No ratings yet
- Skin CancerDocument1 pageSkin CancerENTREPRENEUR 8211No ratings yet
- Quality standards and quality assurance in developing quality productsDocument42 pagesQuality standards and quality assurance in developing quality productsENTREPRENEUR 8211No ratings yet
- How to Stop Nose Bleeds - Causes and PreventionDocument1 pageHow to Stop Nose Bleeds - Causes and PreventionENTREPRENEUR 8211No ratings yet
- 10th Bio CH 16 MCQ'S, Short QDocument13 pages10th Bio CH 16 MCQ'S, Short QENTREPRENEUR 8211No ratings yet
- Method Development and Validation - Skills and TricksDocument9 pagesMethod Development and Validation - Skills and TricksENTREPRENEUR 8211No ratings yet
- Quality Control Circle (QCC) Story 7 StepsDocument2 pagesQuality Control Circle (QCC) Story 7 StepspsureshpNo ratings yet
- 3FE77120AAAAFMZZA V1 ISAM R6.4 Customer Release NoteDocument55 pages3FE77120AAAAFMZZA V1 ISAM R6.4 Customer Release Notehadh2311.srovtcNo ratings yet
- Infomaker 7 Quick StartDocument33 pagesInfomaker 7 Quick StartAndreea FilipNo ratings yet
- Gauri de fixare in soclu de betonDocument3 pagesGauri de fixare in soclu de betonSorin VoicuNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged AllDocument47 pagesIlovepdf Merged AllAkash VakkayilNo ratings yet
- Customer Thank You - Flows - KlaviyoDocument1 pageCustomer Thank You - Flows - KlaviyoAdeps SmithsNo ratings yet
- Handout #1: Course Information: CS 229 Machine LearningDocument3 pagesHandout #1: Course Information: CS 229 Machine LearningGurkanwal SinghNo ratings yet
- Manual Quite Imposing 3.0 PlusDocument138 pagesManual Quite Imposing 3.0 PlusFernando Torres100% (1)
- Lab # 07 Implementation of SQL Statements (DDL)Document14 pagesLab # 07 Implementation of SQL Statements (DDL)Mehak FatimaNo ratings yet
- 490 Naa 271Document2 pages490 Naa 271marcosrz2011No ratings yet
- 10kVA Online UPS Technical SpecsDocument2 pages10kVA Online UPS Technical SpecsSujith kumarNo ratings yet
- Pankaj Borthakur CVDocument4 pagesPankaj Borthakur CVMichael HolmesNo ratings yet
- Finder Relays Series 40 PDFDocument8 pagesFinder Relays Series 40 PDFCosmin ConstantinescuNo ratings yet
- Signal and System Book by Nagoor Kani - Google SearchDocument2 pagesSignal and System Book by Nagoor Kani - Google SearchHimanshu Kumar SagarNo ratings yet
- Class 10 All MCQs Complete Book SmartDocument26 pagesClass 10 All MCQs Complete Book SmartHammad Ahmed KhanNo ratings yet
- 2sc3055 PDFDocument3 pages2sc3055 PDFLuis CansinoNo ratings yet
- i3TOUCH User ManualDocument25 pagesi3TOUCH User ManualVANERUM Group - Vision InspiresNo ratings yet
- Support Job Data AnalyticsDocument1 pageSupport Job Data AnalyticsRajesh kNo ratings yet
- Pom 10Document2 pagesPom 10camilleNo ratings yet
- Simplicity: Simplicity Is The Ultimate Sophistication. - Leonardo Da VinciDocument2 pagesSimplicity: Simplicity Is The Ultimate Sophistication. - Leonardo Da VinciconyosunaNo ratings yet
- Menvier sd3 DiallerDocument2 pagesMenvier sd3 DiallerpalmerwolfNo ratings yet
- Retail Book Chap10Document23 pagesRetail Book Chap10Harman Gill100% (2)
- HCM - Form - Reporting Line Change FormDocument63 pagesHCM - Form - Reporting Line Change FormlalithkNo ratings yet
- K.S. School of Engineering and Management, Bangalore - 560109Document2 pagesK.S. School of Engineering and Management, Bangalore - 560109Pradeep BiradarNo ratings yet
- Useful Celerra CommandsDocument5 pagesUseful Celerra CommandsKumar PallavNo ratings yet