Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Decision Making
Uploaded by
Johanna ElesterioOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Decision Making
Uploaded by
Johanna ElesterioCopyright:
Available Formats
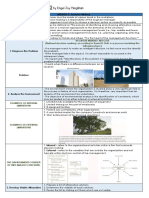
DECISION MAKING Example of external limitations
WHAT IS DECISION MAKING? 1. Patents are controlled by other organizations.
It may be defined as “the process of identifying 2. A very limited market for the company’s products and
and choosing alternative courses action in a manner services exists
appropriate to the demands of the situation”.
3. Strict enforcement of local zoning regulations
The Decision-making Process
Develop viable alternatives
1. Diagnose problem
Oftentimes, problems may be solved by any of
2. Analyze environment the solutions offered. The best among the alternative
solutions must be considered by management. This is
3. Articulate problem or opportunity made possible by using a procedure w/ the following
steps
4. Develop viable alternatives
1. Prepare a list of alternative solutions.
5. Evaluate alternatives
2. Determine the viability of each solution.
6. Make a choice
3. Revise the list by striking out those which are
7. Implement decision
not viable
8. Evaluate and adapt decision results
Develop alternatives
Diagnose Problem
After determining the viability of the alternatives
If a manager wants to make intelligent decision, and a revised list has been made, an evaluation of the
his first move must be to identify the problem. If the remaining alternatives is necessary. This is important
manager fails in this aspect, it is almost impossible to because the next step involves making a choice. Proper
succeed in the subsequent steps. An expert once said evaluation makes choosing the right solution less difficult.
“identification of the problem is tantamount to having
Make a Choice
the problem half-solved.”
Choice-making refers to the process of selecting
What is a Problem? A problem exists when there
among alternatives representing potential solutions to a
is a difference between an actual situation and a desired
problem. At this point, Webber advices that “. . .
situation.
particular effort should be made to identify all significant
Analyze the environment consequences of each choice.”
The environment where the organization is Implement decision
situated plays a very significant role in the success or
Implementation refers to carrying out the
failure of such an organization.
decision so that the objectives sought will be achieved.
The objective of environmental analysis is the To make implementation effective, a plan must be
identification of the constraints, which may be spelled out devised.
as either internal or external limitations
Evaluate and adapt decision results
Example of internal limitations
In implementing the decision, the results
1. Limited funds available for the purchase of equipment. expected may or may not happen. It is, therefore,
important for the manager to use control or feedback
2. Limited training on the part of employee. mechanisms to ensure results and to provide information
for future decisions.
3. Ill-designed facilities.
Feedback refers to the process which requires Network models
checking at each stage of the process to assure that the
alternatives generated, the criteria used in evaluation, and The two prominent network models are:
the solution selected for implementation are in keeping
1. The Program Evaluation Review Technique (PERT) – a
with the goals and objectives originally specified.
technique that enables engineer managers to schedule,
Control refers to actions made to ensure that monitor, and control large and complex projects by
activities performed match the desired activities or goals, employing three time estimates for each activity.
that have been set.
2. The Critical Path Method (CPM) – this is a network
APPROACHES IN SOLVING PROBLEMS technique using only one time factor per activity that
enables engineer managers to schedule, monitor, and
Qualitative evaluation – evaluation of alternatives control large and complex projects.
using intuition and subjective judgement.
Forecasting
Quantitative evaluation – evaluation of alternatives
using any technique in a group classified as rational and It may be defined as “the collection of past and
analytical current information to make predictions about the
future.”
Quantitative Models for Decision Making
Simulation
1. Inventory models
Simulation is a model constructed to represent
2. Queuing theory reality, on which conclusions about real-life problems can
be used
3. Network models
Linear programming
4. Forecasting
5. Regression analysis
Linear programming is a quantitative technique that is
used to produce an optimum solution within the bounds
6. Simulation imposed by constraints upon the decision.
7. Linear programming Sampling theory
8. Sampling theory Sampling theory is a quantitative technique
where samples of populations are statistically determined
9. Statistical decision theory
to be used for a number of processes, such as quality
Inventory models control and marketing research.
1. Economic order quantity model Statistical Decision-Theory
2. Production order quantity model Decision-Theory refers to the “rational way to
conceptualize, analyze, and solve problems in situations
3. Back order inventory model involving limited, or partial information about the
decision environment.
4. Quantity discount model
Queuing theory
The queuing theory is one that describes how to
determine the number of service units that will minimize
both customer waiting time and cost of service
You might also like
- Calculus BookDocument99 pagesCalculus BookbruhhhhNo ratings yet
- UGRD RSCH6352 2213T Prelim Quiz1 95Document7 pagesUGRD RSCH6352 2213T Prelim Quiz1 95Dr.DokieNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving and Decision MakingDocument4 pagesProblem Solving and Decision MakingJohn Francis Idanan0% (1)
- Decision MakingDocument59 pagesDecision MakingVkaeyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Economics Chapter 1Document9 pagesEngineering Economics Chapter 1Allen Glen Gil100% (1)
- Analytical Method ValidationDocument12 pagesAnalytical Method ValidationRamling Patrakar100% (3)
- Decision MakingDocument29 pagesDecision MakingShamaeNoga100% (1)
- Engineering Management (CH 2: Decision Making)Document2 pagesEngineering Management (CH 2: Decision Making)oddonekun100% (4)
- D T Stage 5 1Document37 pagesD T Stage 5 1api-354436144No ratings yet
- 3 - Decision MakingDocument33 pages3 - Decision Makingcecille corderoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Overview of Management ScienceDocument10 pagesModule 1 Overview of Management ScienceRaphael GalitNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument8 pagesDecision MakingDishuNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Decision MakingDocument39 pagesGroup 1 Decision Makinglyka.fermaaa100% (1)
- Decision MakingDocument16 pagesDecision MakingSakshi RelanNo ratings yet
- Decision Making: By: Lloyd, Klynt, Arjun, and LemDocument32 pagesDecision Making: By: Lloyd, Klynt, Arjun, and LemgeorgeNo ratings yet
- Process of Decision Making PDFDocument36 pagesProcess of Decision Making PDFJames Harvy TalensNo ratings yet
- Types of Literature ReviewDocument25 pagesTypes of Literature ReviewClaudineNo ratings yet
- Decision Making - BlablaDocument46 pagesDecision Making - BlablaNortom SilencerNo ratings yet
- Multivariable Calculus ShimamotoDocument326 pagesMultivariable Calculus ShimamotoHelloNo ratings yet
- Euler Lagrange Equations PDFDocument2 pagesEuler Lagrange Equations PDFCoryNo ratings yet
- ODCMDocument4 pagesODCMsanthiswaroopa100% (1)
- User Interface Inspection Methods: A User-Centered Design MethodFrom EverandUser Interface Inspection Methods: A User-Centered Design MethodRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- What Is Decision-Making?Document2 pagesWhat Is Decision-Making?Eelha Adad AleemanNo ratings yet
- Es15 ReviwerDocument37 pagesEs15 ReviwerfjanemichelleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Decision Making 2Document10 pagesChapter 5 Decision Making 2xxnq2wkyyxNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2Document5 pagesLesson 2JOHN IRVIN TAERNo ratings yet
- Decision Making: Engineering Management Chapter IDocument16 pagesDecision Making: Engineering Management Chapter I-Annette Dizon-No ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument2 pagesDecision MakingJohn Alester De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making: Paolo E. Mamaspas Kimberly C. Vallesterol Junuel T. Malbas Jackson S. Joanino Christian L. LeddaDocument12 pagesDecision-Making: Paolo E. Mamaspas Kimberly C. Vallesterol Junuel T. Malbas Jackson S. Joanino Christian L. LeddaEdfandy CatusalemNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 3 (Decision Making)Document2 pagesAssignment No. 3 (Decision Making)April Lyn SantosNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument8 pagesDecision MakingAron AngelesNo ratings yet
- Mngt. 8Document2 pagesMngt. 8Eleah AragonNo ratings yet
- EMAN Chapter 2 - Decision MakingDocument30 pagesEMAN Chapter 2 - Decision MakingMallari Jan DanielNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document4 pagesLecture 02deadlyoverclockNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making Eric B BernardoDocument35 pagesDecision-Making Eric B BernardoangeloNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management: Chapter 2: Decision-MakingDocument5 pagesEngineering Management: Chapter 2: Decision-MakingVincent CorpuzNo ratings yet
- M2 Assgn2 Q A 2 ABAJENZADocument3 pagesM2 Assgn2 Q A 2 ABAJENZAปุลื้ม ปุริมNo ratings yet
- ES EM Group 3 ReportingDocument72 pagesES EM Group 3 ReportingMary Ann Toni N. RasonabeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management Decision MakingDocument15 pagesEngineering Management Decision MakingCassiel Cruz100% (1)
- Chapter 2 - Engineering ManagementDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Engineering ManagementJohn Philip Molina NuñezNo ratings yet
- CH - 3Document38 pagesCH - 3TamiratNo ratings yet
- Organization and Management 1 Quarter Lesson 6: Planning and Decision Making (Continuation of Lesson 5)Document4 pagesOrganization and Management 1 Quarter Lesson 6: Planning and Decision Making (Continuation of Lesson 5)Sayno, Samantha Jade C.No ratings yet
- Management Science Prof. Irah Dianne NicolasDocument21 pagesManagement Science Prof. Irah Dianne NicolasNichole ArcletaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Management-2Document23 pagesEngineering Management-2LiaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: (Decision Support System & Expert System)Document10 pagesAssignment 1: (Decision Support System & Expert System)Ishan KakkarNo ratings yet
- 2 DT Introduction Unit 1 Lect 2Document12 pages2 DT Introduction Unit 1 Lect 2Anurag SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Decision Making in MaintaiananceDocument17 pagesChapter3 Decision Making in Maintaianancemolla biyadgieNo ratings yet
- 01 CE40 Introduction To Engineering Economy PDFDocument2 pages01 CE40 Introduction To Engineering Economy PDFAnnerose Galera100% (1)
- Written ReportDocument5 pagesWritten ReportElmaeen Bitang BagiohanonNo ratings yet
- 001 - Lab ManagementDocument8 pages001 - Lab ManagementHarold PeregrinoNo ratings yet
- EngMan Finals ReviewerDocument7 pagesEngMan Finals ReviewerJoshua Valencia SanchezNo ratings yet
- Decision-Making May Be Defined As The Process of Defining The Problem and Identifying and ChoosingDocument5 pagesDecision-Making May Be Defined As The Process of Defining The Problem and Identifying and ChoosingThe PsychoNo ratings yet
- POM (Planning and Decision Making) M - I - BCADocument13 pagesPOM (Planning and Decision Making) M - I - BCAgranth12gargNo ratings yet
- Final HboDocument2 pagesFinal HboJoana Marie Mendones RodriguezNo ratings yet
- MAN - SCI 1stsem Finals - ReviewerDocument85 pagesMAN - SCI 1stsem Finals - ReviewertygurNo ratings yet
- QM Week 10 TOOLS FOR IMPROVING QDocument8 pagesQM Week 10 TOOLS FOR IMPROVING QEdrizz RizNo ratings yet
- Decision Making and Operations Management: Unit 2Document27 pagesDecision Making and Operations Management: Unit 2Mina TarekNo ratings yet
- Decision Making: By: Bhavya Verma Sandhya Upadhyaya Shagun Dhir Swati Verma Sukriti JhambDocument18 pagesDecision Making: By: Bhavya Verma Sandhya Upadhyaya Shagun Dhir Swati Verma Sukriti JhambBhavya VermaNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving Lecture No. 1Document8 pagesProblem Solving Lecture No. 1nychopogiNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Module 2-DECISION MAKINGDocument7 pagesWeek 2 - Module 2-DECISION MAKINGJitlee PapaNo ratings yet
- De TABLAN, Dan Alfonso (Decision-Making)Document3 pagesDe TABLAN, Dan Alfonso (Decision-Making)Dan Alfonso de TablanNo ratings yet
- YOUTH International University: Assignment 1: Design and Deliver Training ProgrammeDocument14 pagesYOUTH International University: Assignment 1: Design and Deliver Training ProgrammeZwe Htet NaingNo ratings yet
- EM - Report Group 1Document7 pagesEM - Report Group 1Dylan AngelesNo ratings yet
- Decision Making in Engineering ManagementDocument9 pagesDecision Making in Engineering ManagementArthur Lhuis AquinoNo ratings yet
- Notes Eng EconomicsDocument9 pagesNotes Eng EconomicsDark XXIVNo ratings yet
- Decision Making: Powerpoint by Asst. Prof. Ibmrd, Vilad Ghat, A'NagarDocument63 pagesDecision Making: Powerpoint by Asst. Prof. Ibmrd, Vilad Ghat, A'NagarGanesh AntreNo ratings yet
- Analysis within the Systems Development Life-Cycle: Book 4 Activity Analysis—The MethodsFrom EverandAnalysis within the Systems Development Life-Cycle: Book 4 Activity Analysis—The MethodsNo ratings yet
- CPM and PERT-14Document38 pagesCPM and PERT-14Refisa JiruNo ratings yet
- NLPQLG: A Fortran Implementation of A Sequential Quadratic Programming Algorithm For Heuristic Global Optimization - User's GuideDocument24 pagesNLPQLG: A Fortran Implementation of A Sequential Quadratic Programming Algorithm For Heuristic Global Optimization - User's GuiderudsbrNo ratings yet
- Linear Independence and The Wronskian: F and G Are Multiples of Each OtherDocument27 pagesLinear Independence and The Wronskian: F and G Are Multiples of Each OtherDimuthu DharshanaNo ratings yet
- 18.445 Introduction To Stochastic Processes: Lecture 5: Stationary TimesDocument13 pages18.445 Introduction To Stochastic Processes: Lecture 5: Stationary TimesAdityaPandhareNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Text Documentabdul majeed0% (1)
- OPN-501 Individual Assignment-18264019Document5 pagesOPN-501 Individual Assignment-18264019Samiul AlamNo ratings yet
- Eml 5060 - Syllabus Fall 2016Document2 pagesEml 5060 - Syllabus Fall 2016Apratim DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 Interpolation Functions For General Element FormulationDocument25 pagesChapter - 6 Interpolation Functions For General Element FormulationWaleed TayyabNo ratings yet
- Gaussian Elimination Method PDFDocument14 pagesGaussian Elimination Method PDFUmer farooq100% (1)
- Some Identities Related To Riemann Zeta-Function: Research Open AccessDocument6 pagesSome Identities Related To Riemann Zeta-Function: Research Open AccessAnonymous BP91CXjkzNo ratings yet
- Question Bank II Sem by Hema & SandhyaDocument9 pagesQuestion Bank II Sem by Hema & SandhyaNavin KumarNo ratings yet
- HPLC - FingerprintDocument8 pagesHPLC - FingerprintMukul SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Sol. Second 271 Fall 2016Document7 pagesSol. Second 271 Fall 2016tech Nblik2No ratings yet
- RM - Risk Models Handout - Sanjay SarafDocument30 pagesRM - Risk Models Handout - Sanjay Sarafharshitha tadikamallaNo ratings yet
- Development of Accounting Information System in Micro Business Based On The FAST Method (Study On Ezyuwiz Micro Business)Document10 pagesDevelopment of Accounting Information System in Micro Business Based On The FAST Method (Study On Ezyuwiz Micro Business)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- MSCE Thesis Final Draft (Baylon As of 02 04 2016) PDFDocument124 pagesMSCE Thesis Final Draft (Baylon As of 02 04 2016) PDFMichael Bautista BaylonNo ratings yet
- What Is Logistic Regression - Statistics Solutions PDFDocument2 pagesWhat Is Logistic Regression - Statistics Solutions PDFKristel Jane LasacaNo ratings yet
- A Formula For PI (X) Applied To A Result of Koninck-IvicDocument2 pagesA Formula For PI (X) Applied To A Result of Koninck-IvicdamilovobregiaNo ratings yet
- M53 Lec2.3 Higher Order Derivatives Implicit Differentiation Linear ApproximationDocument251 pagesM53 Lec2.3 Higher Order Derivatives Implicit Differentiation Linear ApproximationKhen Mehko OjedaNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance and Its Contribution To Risk and Crisis Management in Small CompaniesDocument476 pagesCorporate Governance and Its Contribution To Risk and Crisis Management in Small CompaniesAniNo ratings yet
- KMPK - Sm015 Soalan Pka Set 1Document4 pagesKMPK - Sm015 Soalan Pka Set 1Patricia JaneNo ratings yet
- Convex It y 2015Document437 pagesConvex It y 2015sdssd sds0% (1)
- 05 - One-Sample T TestDocument26 pages05 - One-Sample T TestMady100% (1)