Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laboratory Review
Uploaded by
SHARON GABRIELOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory Review
Uploaded by
SHARON GABRIELCopyright:
Available Formats
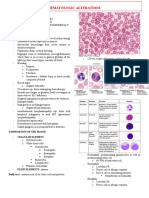
COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT
3 cell types : WBC, RBC and platelets
WBC 4.6 x10 4.6-11
RBC
-Hemoglobin
4.89 4.70-6.10
- Neutrophils -Hematocrit
- Lymphocytes
- Monocytes
- Eosinophils RBC
- Basophils -Most abundant cell in blood
Polymorphonuclear cells (PMNs) : Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Basophils -transportation in O2 and CO2 transportation
The nucleus is multilobed -cell membrane, filled with hemoglobin
-no nucleus
Neutrophils -Biconcave disc
- Part of PMNs
- Most abundant of WBCs in blood Polycythemia (increase RBC)
- major part in acute inflammation (specially bacterial infections) -Polycythemia vera :disease where our body produce too much RBC- problem in regulatin
of BM
Netrophilia (increase neutrophil) Neutropenia (decrease neutrophil) -High altitutde
-Acute bacterial infection -Folate/ b12 deficiency -congenital heart diseaes
-Acute stress -Aplastic anemia -COPD
-Burns -Chemotherapy
-Leukemia -Chloramphenicol/ Sulfonamides Anemia (decrease RBC)
-Steroid use -Aplastic anemia
-Rheumatoid Arthritis -Chronic renal failure
-Iron deficiency
-Pernicious anemia
-pregnancy
Eosinophil
-
Eosinophilia Eosinopenia HEMOGLOBIN
-Allergies -Nutritional deficiency - oxygen transport
-Parasitic infections -Glucocorticoids - >95% of the dry weight of RBCs
-Leukemia - Quaternary structure
-Polyateritis disease - 4 globular proteins : heme group & FE2+
Increase & decrease : SAME AS RBC
BASOPHIL
-very blue color HEMATOCRIT
-Participate in allergic symtomps -PACKED CELL VOLUME
-MEASURED IN PERCENTAGE
Basophilia Basopenia -Volumes % of RBCs in blood
-Allergic reactions -measured by centrifugation of blood cells
-CML
-Hodkin’s disease
- Oral contraceptive pills
MEAN CORPUSCULAR VOLUME
-average volume of the red blood cells
MONOCYTE - Hct = MCV
-Largest of the WBC RBC
-Chronic inflammation
-stored in spleen Macrocytosis (increase volume of RBC) Microcytosis (dec)
- very motile -Reticulocytosis -Iron deficiency
-What they do -Folate deficiency -Thalassemia
-Phagocytosis -B12 deficiency -Anemia of chronic disease
-helps T cells -Methotrexate -Hemolytic anemia
-cytokine production -Phenytoin -Hereditary Spherocytosis
-Lead poisoning
Monocytosis Monocytopenia
-Chronic inflammation state -Aplastic anemia
-stress -AML MEAN CORPUSCULAR HEMOGLOBIN
-cushing’s syndrome -Glucocorticoids -Average MASS of hemoglobin
-sarcoidosis -Myelotoxic drugs - Hbg = MCH
RBC
MCH increase MCH decrease
-alcoholism -Sideroblastic anemi
Three main types of lymphocytes : T,B, NK -B12 deficiency -Lead poisoning
-folate deficiency -Iron deficiency anemia
T cells - (mature in the thymus) -liver disease -Anemia of Chronic disease
1. Helper : help other cells mature and activate and function (through cytokine production) -hemochromatosis -Thalassemia
2. Cytotoxic : destroy cells infected with viruses
3. Memory : remember the antigens of past infections
B cells -(formed in the bone)
1. Plasma : produce large amounts of antibodies MEAN CORPUSULAR HEMOGLOBIN CONCENTRATION
2. Memory : remember past infections -concentration of Hgb in a given volume of RBCs
- hgb. = MCHC
NK cells - hcct
play a role similar to “Cytotoxic T cells”.. they kill virus-infected cells and tumor cells
Hyperchromic (increase) Hypochromicc (decr
-Hereditary spherocytosis -same as MCH
Lymphocytosis (increase) Lymphocytopenia (decrease) -hemolysis
-Viral infection -HIV - destroy T cells (CD4) -sickle cell disease
-Leukemia: CLL,, ALL -Glucocorticoids
-Adrenal insuficiency -Rheumatoid arthritis
-SLE
-Aplastic anemia RED CELL DISTRIBUTION WIDTH (RDW)
-The variation in RBC size or volume
INCREASE
-Anisocytosis
-Vit B12 def
-Folate def
-iron def
-Hemolytic anemia
-RBC fragmentation
-liver disease
You might also like
- Extraordinary HealingDocument386 pagesExtraordinary HealingBill Honaker98% (82)
- Hematopoiesis PDFDocument10 pagesHematopoiesis PDFJezzah Mae CañeteNo ratings yet
- Between The Erythrocytes and PlasmaDocument5 pagesBetween The Erythrocytes and Plasmajonette carataoNo ratings yet
- Blood Cell AnomaliesDocument4 pagesBlood Cell AnomaliesCiullaeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Haematology-Lecture SlidesDocument55 pagesClinical Haematology-Lecture SlidesShiv Sookun100% (1)
- RBC Morphology and InclusionsDocument3 pagesRBC Morphology and InclusionsDeomicah SolanoNo ratings yet
- Microneedling AftercareDocument2 pagesMicroneedling AftercareRuth ann Micol RiveraNo ratings yet
- Physical - Therapy - Skills ChecklistDocument2 pagesPhysical - Therapy - Skills ChecklistMohamed EssmatNo ratings yet
- RBC DISORDERS StudentsDocument84 pagesRBC DISORDERS Studentskimberly abianNo ratings yet
- Nurse Aide Practice TestDocument10 pagesNurse Aide Practice TestHerman Matias75% (4)
- BENIGN OVARIAN DISEASES - Updated January 2018Document31 pagesBENIGN OVARIAN DISEASES - Updated January 2018daniel100% (1)
- Passing StrategyDocument1 pagePassing StrategySHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- MED (App17) - Approach To AnaemiaDocument5 pagesMED (App17) - Approach To AnaemiaFlora XuNo ratings yet
- HemoglobinopathiesDocument3 pagesHemoglobinopathiesChatie PipitNo ratings yet
- Inflammation DetailedDocument12 pagesInflammation Detailedsimi yNo ratings yet
- Kuliah AnemiaDocument185 pagesKuliah AnemiaAchmad Nur AffendickNo ratings yet
- DR Bambang - Anemia OverviewDocument263 pagesDR Bambang - Anemia OverviewOkta Dwi Kusuma AyuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Rodaks HematologyDocument10 pagesChapter 13 Rodaks HematologyRALPH JAN T. RIONo ratings yet
- ASIA Impairment ScaleDocument10 pagesASIA Impairment Scaleazimahzainal211No ratings yet
- 1 PediatricsDocument21 pages1 PediatricsHannah Lei100% (1)
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer SeminarDocument34 pagesDiabetic Foot Ulcer SeminarShidevNo ratings yet
- AnemiaDocument8 pagesAnemiasibanah menor100% (1)
- EpidemiologyDocument23 pagesEpidemiologyBabita DhruwNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pathology ReviewDocument11 pagesClinical Pathology Reviewrob hNo ratings yet
- Hema - General Characteristics of Blood and Hematological TestsDocument5 pagesHema - General Characteristics of Blood and Hematological TestsBSMT Kharylle divine FuentibellaNo ratings yet
- Rate of Reticulocyte Release Rate of Removal of Spent Rbcs by Spleen & LiverDocument4 pagesRate of Reticulocyte Release Rate of Removal of Spent Rbcs by Spleen & Liverraiansuyu2495gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Anemias: RBC Morphology & Approach To Diagnosis: Physiologic AdaptationsDocument5 pagesAnemias: RBC Morphology & Approach To Diagnosis: Physiologic AdaptationsASHLEY ALEXIS GUEVARRANo ratings yet
- 1.05 - 1 - 2020 Anaemia Dr. AGDocument18 pages1.05 - 1 - 2020 Anaemia Dr. AGPalavi PalNo ratings yet
- Blood FunctionsDocument3 pagesBlood FunctionshelloaNo ratings yet
- CBC (Complete Blood Count)Document38 pagesCBC (Complete Blood Count)yeshitla amsaluNo ratings yet
- Blood Physiology: Biconcave Discs 120 DaysDocument6 pagesBlood Physiology: Biconcave Discs 120 DaysHanamiNo ratings yet
- OS 216 - Myelodysplastic SyndromesDocument5 pagesOS 216 - Myelodysplastic Syndromesx_xtattooedx_x1636100% (1)
- Physiological Blood CountDocument4 pagesPhysiological Blood CountRhea SaldanhaNo ratings yet
- Blood 2Document4 pagesBlood 2Jhes D.No ratings yet
- Colored Scab Followed by Red MarksDocument2 pagesColored Scab Followed by Red MarksRanjith LuckyNo ratings yet
- Blood - Mcon 01 (Lec) A4Document5 pagesBlood - Mcon 01 (Lec) A4Lemon AdeNo ratings yet
- Intravascular Extravascular: Fe Storage Tibc SerumDocument2 pagesIntravascular Extravascular: Fe Storage Tibc Serumazhar hussinNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Anemia: Within The Red Cell Outside The Red CellDocument27 pagesHemolytic Anemia: Within The Red Cell Outside The Red CellmuliamayangsariNo ratings yet
- OB Blood Transfusions PregnancyDocument37 pagesOB Blood Transfusions Pregnancykhadzx100% (2)
- Hematology NotesDocument3 pagesHematology NotesFarisa Jane BanggoNo ratings yet
- Hematological Disorders ErythropoiesisDocument4 pagesHematological Disorders Erythropoiesis3S - JOCSON, DENESE NICOLE LEE M.No ratings yet
- Complete Blood Count - GERENTEDocument3 pagesComplete Blood Count - GERENTEFLORENCE GERENTENo ratings yet
- 1 HEMATOLOGIC ALTERATIONS HematologyDocument2 pages1 HEMATOLOGIC ALTERATIONS HematologyRhea Andrea UyNo ratings yet
- HO Notecards3 IncompleteDocument12 pagesHO Notecards3 IncompleteMrSomnambululNo ratings yet
- Hematology CHapter 1Document3 pagesHematology CHapter 1Rheila DuyaNo ratings yet
- Mtap 2 HematologyDocument15 pagesMtap 2 HematologyNaomi NicoleNo ratings yet
- BLOODDocument3 pagesBLOODAlowee AbelloNo ratings yet
- Anemia & Sickle Cell AnemiaDocument5 pagesAnemia & Sickle Cell AnemiaDIANA CAMILLE CARITATIVONo ratings yet
- تجميع اسئله الاخصائين 1Document36 pagesتجميع اسئله الاخصائين 1Osama BakheetNo ratings yet
- Clase 6 Anemias A Lab Clin 2022-IiDocument14 pagesClase 6 Anemias A Lab Clin 2022-IiAbelardo MedianeroNo ratings yet
- RBC anomalies-ANEMIADocument19 pagesRBC anomalies-ANEMIAJeremiahNo ratings yet
- RD THDocument5 pagesRD THKLIPPNo ratings yet
- How To Read A Lab Report " Simply and Precisely "Document18 pagesHow To Read A Lab Report " Simply and Precisely "WiaZafarNo ratings yet
- Hematologic Disorders AnemiaDocument30 pagesHematologic Disorders AnemiaYjah Cheimira ASEBONo ratings yet
- Physiology Lab V2Document14 pagesPhysiology Lab V2Mohammed EljackNo ratings yet
- Ghe Lec BloodDocument2 pagesGhe Lec BloodALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANNo ratings yet
- M6 Decreased RBC ProdnDocument3 pagesM6 Decreased RBC ProdnJan TrishaNo ratings yet
- Hemoglobinopati: Dr. Charles Antoni S.,M.Kes, Sp.ADocument26 pagesHemoglobinopati: Dr. Charles Antoni S.,M.Kes, Sp.AKaren PatriciaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Pancytopenia: Moderator - DR Vishal Gupta MD Medicine Presented By-Dr Narendra Singh Resident Doctor 2Document35 pagesApproach To Pancytopenia: Moderator - DR Vishal Gupta MD Medicine Presented By-Dr Narendra Singh Resident Doctor 2ntnquynhproNo ratings yet
- Ascp StudyDocument18 pagesAscp StudyJamaica EstorninosNo ratings yet
- Hematologi Css UploadDocument40 pagesHematologi Css UploadtutuptekoNo ratings yet
- AnaemiaDocument4 pagesAnaemiaRichardNo ratings yet
- Hematopoiesis: RbcsDocument27 pagesHematopoiesis: Rbcsjamba juiceNo ratings yet
- Systematic Approach in Anemia Evaluation and Review of Peripheral SmearsDocument72 pagesSystematic Approach in Anemia Evaluation and Review of Peripheral SmearsSukma Eka PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Anemia Hemolitik Yang DidapatDocument15 pagesAnemia Hemolitik Yang DidapatAngel 冯晓君No ratings yet
- Midterm Topics Hema 1 LecDocument37 pagesMidterm Topics Hema 1 Lec4jzbxz64kqNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Hemolytic Anemia OkDocument26 pagesIntroduction To Hemolytic Anemia OkNayana M RNo ratings yet
- How To Interpret HEMATOLOGY Test ResultsDocument36 pagesHow To Interpret HEMATOLOGY Test Resultssylvia haryantoNo ratings yet
- Blood, Lymphatic, and Immune SystemDocument6 pagesBlood, Lymphatic, and Immune Systemaliexpress0230170No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 BloodDocument3 pagesChapter 10 BloodinitaygracileshayneNo ratings yet
- Mega Micro para Table 1Document1 pageMega Micro para Table 1SHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Eaq123 03Document8 pagesEaq123 03SHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- IELTS Speaking Vocabulary Talking About University and Student LifeDocument1 pageIELTS Speaking Vocabulary Talking About University and Student LifeSHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Archive courseprintPDF-PointofCare Testing POCT The Applic-394442Document28 pagesArchive courseprintPDF-PointofCare Testing POCT The Applic-394442SHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Loses: Jesus Wins-SatanDocument8 pagesLoses: Jesus Wins-SatanSHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Yours TrulyDocument10 pagesYours TrulySHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Eaq223 02Document8 pagesEaq223 02SHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Flashcard Hal Leonard Piano Book C QuizletDocument1 pageFlashcard Hal Leonard Piano Book C QuizletSHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- MF Love Dings FontDocument1 pageMF Love Dings FontSHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Letter ToDocument1 pageLetter ToSHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- 200712primer Level Faber Flashcards Set A PDFDocument6 pages200712primer Level Faber Flashcards Set A PDFSHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- Get CredentialedDocument1 pageGet CredentialedSHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledSHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- File 2022-05-15 21-36-53Document1 pageFile 2022-05-15 21-36-53SHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledSHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- S SPVTJ W1 F RBDR12 YBTFxcq KLZ 6 Ak 8 AQ0 WDKLJ DJUDocument1 pageS SPVTJ W1 F RBDR12 YBTFxcq KLZ 6 Ak 8 AQ0 WDKLJ DJUSHARON GABRIELNo ratings yet
- ADHDDocument17 pagesADHDapi-3822433No ratings yet
- ALBUTEROLDocument1 pageALBUTEROLAnna LaritaNo ratings yet
- Self-Referral Form For MSK PhysiotherapyDocument4 pagesSelf-Referral Form For MSK PhysiotherapyTomiNo ratings yet
- Exercise Is Essential For Osteoarthritis: The Many Benefits of Physical ActivityDocument1 pageExercise Is Essential For Osteoarthritis: The Many Benefits of Physical ActivityFrancisco Javier Luza RamosNo ratings yet
- Bloem (2021) - Parkinson's DiseaseDocument20 pagesBloem (2021) - Parkinson's DiseaseDiane MxNo ratings yet
- Airway Management and Common ConditionsDocument34 pagesAirway Management and Common Conditionsrigo montejoNo ratings yet
- Interpretation: S01 - S01-Dr. Madhu Loomba Kanpur, KanpurDocument5 pagesInterpretation: S01 - S01-Dr. Madhu Loomba Kanpur, KanpurAshok ShivNo ratings yet
- Abscess CausesDocument2 pagesAbscess CausesMudatsir N. MileNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka SahDocument2 pagesDaftar Pustaka SahRafikaNo ratings yet
- Case 11 AsthmaDocument131 pagesCase 11 Asthmaspajda69No ratings yet
- Propedeutik 2 3 Dental FacultyDocument214 pagesPropedeutik 2 3 Dental FacultyVimal SuseeNo ratings yet
- Atopy - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf PDFDocument10 pagesAtopy - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf PDFAikawa MitaNo ratings yet
- 31.chronic Diarrhea and MalabsorbtionDocument14 pages31.chronic Diarrhea and MalabsorbtionSajjal AliNo ratings yet
- NEURO Myasthenia GravisDocument25 pagesNEURO Myasthenia GravisNasrah N. MusaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal DR Patrick 3Document9 pagesJurnal DR Patrick 3Rizkyrafiqoh afdinNo ratings yet
- Elsharnoby Pediatric PDFDocument160 pagesElsharnoby Pediatric PDFMohammed Al-hammadiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Nazim Mughal: Ms Ortho, DNB Ortho FNB Spine SurgeryDocument90 pagesDr. Nazim Mughal: Ms Ortho, DNB Ortho FNB Spine Surgerynazim mughalNo ratings yet
- ADHD - ResumeDocument4 pagesADHD - ResumeloyeaNo ratings yet
- PWD ProfilerDocument18 pagesPWD ProfilerajenNo ratings yet
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocument3 pagesNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNo ratings yet