0% found this document useful (0 votes)
901 views8 pagesSafety Leadership Training
This document provides an overview of safety leadership training for supervisors and managers. It discusses
the importance of supervisors and managers in influencing safe behaviors and maintaining productivity. The training covers
key responsibilities of supervisors under the WHS Act including their duty of care for employees. It also describes different
types of supervisory styles and how the "tough but caring" proactive style is best for achieving safety, morale and productivity
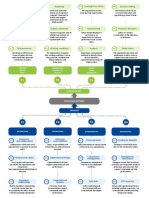
goals. The document outlines symptoms that can indicate weaknesses in individuals, systems, organizational structure and leadership
styles to help supervisors reflect on areas for improvement.
Uploaded by
MohamedSaidCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
901 views8 pagesSafety Leadership Training
This document provides an overview of safety leadership training for supervisors and managers. It discusses
the importance of supervisors and managers in influencing safe behaviors and maintaining productivity. The training covers
key responsibilities of supervisors under the WHS Act including their duty of care for employees. It also describes different
types of supervisory styles and how the "tough but caring" proactive style is best for achieving safety, morale and productivity
goals. The document outlines symptoms that can indicate weaknesses in individuals, systems, organizational structure and leadership
styles to help supervisors reflect on areas for improvement.
Uploaded by
MohamedSaidCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd