Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Z Score
Uploaded by
Fani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageIts a model to check risk for a certain percebtage
Original Title
Z-Score
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIts a model to check risk for a certain percebtage
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageZ Score
Uploaded by
FaniIts a model to check risk for a certain percebtage
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
FUNO_Z01.
qxd 9/19/08 17:13 Page 688
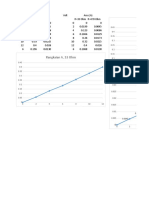
Table V NUMBER OF NUMBER OF
STANDARD AREA TO THE STANDARD AREA TO THE
Area of normal DEVIATIONS LEFT OR RIGHT DEVIATIONS LEFT OR RIGHT
distribution that is Z FROM MEAN (Z) (one tail) FROM MEAN (Z) (one tail)
standard deviations
to the left or right of 0.00 0.5000 1.55 0.0606
the mean 0.05 0.4801 1.60 0.0548
0.10 0.4602 1.65 0.0495
0.15 0.4404 1.70 0.0446
0.20 0.4207 1.75 0.0401
0.25 0.4013 1.80 0.0359
0.30 0.3821 1.85 0.0322
0.35 0.3632 1.90 0.0287
0.40 0.3446 1.95 0.0256
0.45 0.3264 2.00 0.0228
0.50 0.3085 2.05 0.0202
0.55 0.2912 2.10 0.0179
0.60 0.2743 2.15 0.0158
0.65 0.2578 2.20 0.0139
0.70 0.2420 2.25 0.0122
0.75 0.2264 2.30 0.0107
0.80 0.2119 2.35 0.0094
0.85 0.1977 2.40 0.0082
0.90 0.1841 2.45 0.0071
0.95 0.1711 2.50 0.0062
1.00 0.1577 2.55 0.0054
1.05 0.1469 2.60 0.0047
1.10 0.1357 2.65 0.0040
1.15 0.1251 2.70 0.0035
1.20 0.1151 2.75 0.0030
1.25 0.1056 2.80 0.0026
1.30 0.0968 2.85 0.0022
1.35 0.0885 2.90 0.0019
1.40 0.0808 2.95 0.0016
1.45 0.0735 3.00 0.0013
1.50 0.0668
Table V shows the area of the normal
distribution that is Z standard deviations
to the left or to the right of the mean.
The test is “one tailed” in the sense that
we are concerned with one side of the
distribution or the other. If we wished to
know the area of the curve, or probabil-
ity, that was 1.5 standard deviations or
more from the arithmetic mean on the
right, it would be depicted by the colored
area in the figure to the left. In Table V we see that this corresponds to 6.68 percent of the total area of
the normal distribution. Thus we could say that there was a 6.68 percent probability that the actual out-
come would exceed the mean by 1.5 standard deviations.
688
••
You might also like
- Chapter 10 (Tables) - 1Document8 pagesChapter 10 (Tables) - 1Joefer CuetaraNo ratings yet
- Appendix 6: Ventilation Rates and Calculations: Arbor AcresDocument1 pageAppendix 6: Ventilation Rates and Calculations: Arbor Acresr1nforrestNo ratings yet
- Mesh Size PDFDocument1 pageMesh Size PDFuntoroNo ratings yet
- Mesh Size PDFDocument1 pageMesh Size PDFuntoroNo ratings yet
- Compressed Air Pressure LossDocument1 pageCompressed Air Pressure Losswael hassanNo ratings yet
- Excel No Ssale WeDocument3 pagesExcel No Ssale WeYardy Guzman OsccoNo ratings yet
- Excel No Ssale WeDocument3 pagesExcel No Ssale WeYardy Guzman OsccoNo ratings yet
- Pitch Conversions Threads Per Inch TPI Pitch in Inches and Pitch in MM For Taps and DiesDocument3 pagesPitch Conversions Threads Per Inch TPI Pitch in Inches and Pitch in MM For Taps and DiesChetan HinganeNo ratings yet
- Detailed Measurements Pallippuraya Puthiyedath Parambu Road PremeasurementDocument3 pagesDetailed Measurements Pallippuraya Puthiyedath Parambu Road PremeasurementinsafaNo ratings yet
- Wave Scatter Data Input Table with Frequency of Occurrence and Peak PeriodDocument13 pagesWave Scatter Data Input Table with Frequency of Occurrence and Peak PeriodSeymur AkbarovNo ratings yet
- US Standard Sieve Openings: Sieve Number Opening, MM Wire Diameter, MMDocument2 pagesUS Standard Sieve Openings: Sieve Number Opening, MM Wire Diameter, MMHosein EltimimiNo ratings yet
- Tables C10Document5 pagesTables C10markreyfajuralabradorNo ratings yet
- Harsha AssignmentDocument4 pagesHarsha Assignmentsaibhargav2209No ratings yet
- Analysis of soil permeability curves and fractional flow curvesDocument4 pagesAnalysis of soil permeability curves and fractional flow curvesRaul Suxo CondoriNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Working HoursDocument1 pageConversion of Working HoursJean Valerie BrandonNo ratings yet
- DIODADocument2 pagesDIODAMuhammad RodanNo ratings yet
- Dow Engineering InformationDocument29 pagesDow Engineering InformationbenakiaNo ratings yet
- Expt 6Document11 pagesExpt 6nooneNo ratings yet
- Homework #03: U.S. Standard Sieve SizesDocument11 pagesHomework #03: U.S. Standard Sieve SizesVikaas SagerNo ratings yet
- Practico 4, Del 9 Creo Al 13Document7 pagesPractico 4, Del 9 Creo Al 13Cristian Rosas SotoNo ratings yet
- Mesh To Micron Conversion Chart Ecologix SystemsDocument1 pageMesh To Micron Conversion Chart Ecologix SystemsSantosh JayasavalNo ratings yet
- AviagenBrief VentilationRates 2018 ENDocument2 pagesAviagenBrief VentilationRates 2018 ENPOULTRY CHANNELNo ratings yet
- Materiale Cadru PortalDocument16 pagesMateriale Cadru PortalOvidiu SmadiciNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Working HoursDocument1 pageConversion of Working HoursLizjasmine DimayaNo ratings yet
- Valve lift area curve vs normalized liftDocument3 pagesValve lift area curve vs normalized liftHernan MarianiNo ratings yet
- Graph of Moisture Content Vs TimeDocument4 pagesGraph of Moisture Content Vs TimeAnonymous oFBiEqkyNo ratings yet
- M Furqon Habibie - F44180092Document5 pagesM Furqon Habibie - F44180092Furqon HabibieNo ratings yet
- Measurement MorayurDocument9 pagesMeasurement MorayurAssistant Engineer PWD Bridges Section, MannarkkadNo ratings yet
- R-P Relationship Data TableDocument2 pagesR-P Relationship Data TableAya MokatrenNo ratings yet
- Chart Title Chart TitleDocument11 pagesChart Title Chart TitleAneesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Measurement Sheet Log No 357Document5 pagesMeasurement Sheet Log No 357ejazNo ratings yet
- Standard deviations and probability areas for normal distributionDocument3 pagesStandard deviations and probability areas for normal distributionBelmin Adelisa SalkićNo ratings yet
- SWG - Standard Wire GaugeDocument1 pageSWG - Standard Wire GaugeSachin PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Cumulative distribution function chartDocument12 pagesCumulative distribution function chartKIKA CONTENTONo ratings yet
- Melth L12Document2 pagesMelth L12George TomaNo ratings yet
- Analisis Acumulativo Analisis Deiferencial: Dpi, MM Dpi, MMDocument2 pagesAnalisis Acumulativo Analisis Deiferencial: Dpi, MM Dpi, MMVALENTINA VANEGAS ARBOLEDANo ratings yet
- GrafikDocument3 pagesGrafikGede SthandilaNo ratings yet
- Water Purity Conversion ChartDocument1 pageWater Purity Conversion ChartKhizerAliRaoNo ratings yet
- Yogesh Khandelwal Es105 Lab1Document21 pagesYogesh Khandelwal Es105 Lab1Yogesh khandelwalNo ratings yet
- Aggregate ClaimsDocument3 pagesAggregate ClaimsEdgar Alexander Hernández RebolledoNo ratings yet
- Concentration of NH4Cl (MM)Document3 pagesConcentration of NH4Cl (MM)Ali TarekNo ratings yet
- P8 10 GRPHHDocument2 pagesP8 10 GRPHHMae AstovezaNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Line and Operating Line Chart AnalysisDocument10 pagesEquilibrium Line and Operating Line Chart Analysisaldino wijayaNo ratings yet
- Measurement Edavannapara Elamaram 2020Document4 pagesMeasurement Edavannapara Elamaram 2020insafaNo ratings yet
- Tasa de Fallas R (T) Y F (T)Document7 pagesTasa de Fallas R (T) Y F (T)Carlos PretellNo ratings yet
- Practicum BewegingDocument3 pagesPracticum BewegingElena PopovaNo ratings yet
- Sieve Size (MM) Mass Retained (G) Mass Passing (G) Cumulative Percentage Passing (%)Document2 pagesSieve Size (MM) Mass Retained (G) Mass Passing (G) Cumulative Percentage Passing (%)Adelbert LeeNo ratings yet
- Solution - Fractional Flow Equation Application Class WorkDocument13 pagesSolution - Fractional Flow Equation Application Class WorkgebrilleNo ratings yet
- LogaritmeDocument1 pageLogaritmeAndrew WigginNo ratings yet
- Data Praktikum LM1Document3 pagesData Praktikum LM1Fakhrusy RizqyNo ratings yet
- Triaxial C 2Document84 pagesTriaxial C 2Linbert rcNo ratings yet
- ANUL Capital Fix Rata Amortizarii (A) Capital Fix Casat (C)Document9 pagesANUL Capital Fix Rata Amortizarii (A) Capital Fix Casat (C)Robert GhitaNo ratings yet
- Waterflooding 3 y 4Document8 pagesWaterflooding 3 y 4Jorge Blanco ChoqueNo ratings yet
- Eds Revision de V Basal v1Document6 pagesEds Revision de V Basal v1Angel HernandezNo ratings yet
- Fraksi Massa Etanol (XA, YA)Document8 pagesFraksi Massa Etanol (XA, YA)Putry RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Curva NormalDocument14 pagesCurva Normalkenyi calleNo ratings yet
- Exel Unit4Document4 pagesExel Unit4anon_758938244No ratings yet
- Tarea 1.2 Ambos ProblemasDocument12 pagesTarea 1.2 Ambos ProblemasOlman VargasNo ratings yet
- Pg068 - T11 Conductor ResistanceDocument1 pagePg068 - T11 Conductor ResistanceDolyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1aDocument23 pagesLecture 1aSaritaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Screening Constants From SCF Functions. II. Atoms With 37 To 86 ElectronsDocument9 pagesAtomic Screening Constants From SCF Functions. II. Atoms With 37 To 86 ElectronsGopi TalluriNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Surface Wave Propagation in A Metallic Wire and The Lambert W FunctionDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Surface Wave Propagation in A Metallic Wire and The Lambert W Functionbenjamin omniNo ratings yet
- Bhaskara II: Casey GregoryDocument16 pagesBhaskara II: Casey GregoryVinayakaNo ratings yet
- TOSCA Structure 81 Short SeminarDocument37 pagesTOSCA Structure 81 Short SeminarmhsafeNo ratings yet
- Regression with Life Data GuideDocument32 pagesRegression with Life Data GuideKarunesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Spectrumlab 752sDocument22 pagesSpectrumlab 752sSarah Marie ArquizaNo ratings yet
- G. ACI 360R-06 Brings Slabs On Ground Into The 21st Century - Art McKinney PDFDocument2 pagesG. ACI 360R-06 Brings Slabs On Ground Into The 21st Century - Art McKinney PDFinitbashNo ratings yet
- Stress and Strain Transformation ModuleDocument14 pagesStress and Strain Transformation ModuleJennifer AquinoNo ratings yet
- Lapp Pro210738enDocument3 pagesLapp Pro210738enRatchakorn SartsermNo ratings yet
- CE 602 - Geotechnical EngineeringDocument2 pagesCE 602 - Geotechnical EngineeringJohn Michael SalasNo ratings yet
- LimitsDocument6 pagesLimitsDan GrayNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint Presentationon 28th AprilDocument14 pagesPowerPoint Presentationon 28th AprilBalakrushna SahuNo ratings yet
- F.Sc. Part-1 Physics-PTBDocument1 pageF.Sc. Part-1 Physics-PTBgarrisonian96No ratings yet
- CIE A Level Chemistry: Relative Isotopic MassDocument28 pagesCIE A Level Chemistry: Relative Isotopic MassSabina SabaNo ratings yet
- Novel Technology To Influence Hardness of Flexible Pu FoamsDocument16 pagesNovel Technology To Influence Hardness of Flexible Pu FoamsirwanchemNo ratings yet
- REVISED-3rd Quarter - MODULE 6 Week 6Document14 pagesREVISED-3rd Quarter - MODULE 6 Week 6EBAMAE OFQUERIANo ratings yet
- PVT Analysis: Compiled By: SACHIN NAMBIAR Contact No: 9067111274Document14 pagesPVT Analysis: Compiled By: SACHIN NAMBIAR Contact No: 9067111274ronak pandyaNo ratings yet
- Shriver, The Manipulation of Air-Sensitive Compounds BOOKDocument335 pagesShriver, The Manipulation of Air-Sensitive Compounds BOOKMoreno MarcatiNo ratings yet
- Locomotor Non LocomotorDocument27 pagesLocomotor Non Locomotorsadsadmae9No ratings yet
- E545-99 Neutron Image QualityDocument4 pagesE545-99 Neutron Image QualityaboutdestinyNo ratings yet
- 1 Electrostatics Coulombs LawDocument28 pages1 Electrostatics Coulombs LawJerenz Pellina100% (1)
- Acsr Astm B Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced PDFDocument10 pagesAcsr Astm B Aluminium Conductor Steel Reinforced PDFyetignrNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Series - Telescoping and Type of Series StuDocument36 pagesLecture 2 - Series - Telescoping and Type of Series StuMUHAMMAD AMIRUL THAQIF BIN NORMANNo ratings yet
- Corrosion in Flexible Burner HosesDocument88 pagesCorrosion in Flexible Burner Hosesmviteazu100% (1)
- Parscan Intrack - Systematic DiversityDocument10 pagesParscan Intrack - Systematic DiversitylqbzNo ratings yet
- Filtro SecadorDocument10 pagesFiltro SecadorGuilherme GomesNo ratings yet
- Bom Grundfox Pump HSDocument80 pagesBom Grundfox Pump HSHai DoNo ratings yet
- (the Collected Works of Eugene Paul Wigner a _ 1) Jagdish Mehra (Auth.), Arthur S. Wightman (Eds.) - The Collected Works of Eugene Paul Wigner_ Part A_ the Scientific Papers-Springer-Verlag Berlin HeiDocument725 pages(the Collected Works of Eugene Paul Wigner a _ 1) Jagdish Mehra (Auth.), Arthur S. Wightman (Eds.) - The Collected Works of Eugene Paul Wigner_ Part A_ the Scientific Papers-Springer-Verlag Berlin HeiANDRES DAVID GOMEZ VILLEGASNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 362 (1995) 487-498Document12 pagesNuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 362 (1995) 487-498AresshioNo ratings yet
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormFrom EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.From EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Calculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandCalculus Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeFrom EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceFrom EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingFrom EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorFrom EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Assessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6From EverandAssessment Prep for Common Core Mathematics, Grade 6Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)