Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6.1 Bond Character and Practice Ws Key
Uploaded by
Anna RamdyalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
6.1 Bond Character and Practice Ws Key
Uploaded by
Anna RamdyalCopyright:
Available Formats
Name____________________________________________Date______________________Period__________
Section 6.1: Bond Character
A chemical bond between atoms of different elements is never completely ionic or covalent. The character of
the bond depends on how strongly each of the bonded atoms attracts electrons.
Electronegativity and Bond Character
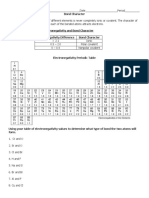
Electronegativity Difference Bond Character
> 1.7 Ionic
0.3 - 1.7 Polar covalent
0 – 0.29 Nonpolar covalent
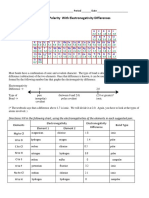
Electronegativity Periodic Table
Using your table of electronegativity values to determine what type of bond the two atoms will
form.
1. Cr and O 3.5 – 1.6 = 1.9 ionic
2. Sr and O 3.5 – 1.0 = 2.5 ionic
3. Cl and Br 3.0 – 2.8 = 0.2 nonpolar covalent
4. H and F 4.0 – 2.1 = 1.9 ionic
5. Na and S 2.5 – 0.9 = 1.6 polar covalent
6. Br and Br 2.8 – 2.8 = 0 nonpolar covalent
7. Al and F 4.0 – 1.5 = 2.5 ionic
8. Cu and Cl 3.0 – 1.9 = 1.1 polar covalent
Name____________________________________________Date______________________Period__________
6.1 Polarity & Electronegativity Worksheet
1. What does it mean to for a bond to be polar?
The molecule has a slight charge due to an unequal sharing of electrons.
2. How are ionic bonds and covalent bonds different?
Ionic bonds transfer the electrons while a covalent bond shares the electrons.
3. How does a polar covalent bond differ from a nonpolar covalent bond?
A polar covalent bond is a covalent bond which the bonded atoms have an unequal
attraction for the shared electrons.
A nonpolar covalent bond is a covalent bond which the bonding electrons are shared equally
by the bonded atoms, resulting in a balanced distribution of electrical charge.
4. How does electronegativity values help determine the type of bond created?
By calculating the difference in the electronegativities you determine the ability of the atom
to attract electrons.
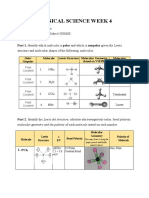
5. For each of the following molecules, determine if it is covalent, polar, or ionic. Show your work by listing the
electronegativities of each element in the bond.
Molecule Electronegativity Difference in Bond Type
Values Electronegativity
H – Cl H: 2.1 3.0 – 2.1 = 0.9 Polar covalent
Cl: 3.0
H–H H: 2.1 2.1 – 2.1 = 0 Nonpolar covalent
H: 2.1
H-I H: 2.1 2.5 – 2.1 = 0.4 Polar covalent
I: 2.5
Cl - Cl Cl: 3.0 3.0 – 3.0 = 0 Nonpolar covalent
Cl: 3.0
C–O C: 2.5 3.5 – 2.5 = 1.0 Polar covalent
O: 3.5
Ca – O Ca: 1.0 3.5 – 1.0 = 2.5 Ionic
O: 3.5
H– O H: 2.1 3.5 – 2.1 = 1.4 Polar covalent
O: 3.5
Al – Fe Al: 1.5 1.8 – 1.5 = 0.3 Polar covalent
Fe: 1.8
6. For each of the following sets of elements, identify the element expected to be most electronegative (EN) and
which is expected to be least electronegative (EN).
a. K, Sc, Ca most EN= Sc least EN= K
b. Br, F, At most EN= F least EN= At
c. C, O, N most EN= O least EN= C
You might also like
- Chapter 4 Chemical BondingDocument45 pagesChapter 4 Chemical BondingRavinder singhNo ratings yet
- Bond Polarity and ElectronegativityDocument2 pagesBond Polarity and ElectronegativityJewel Mae MercadoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Polarity of Molecules and Its PropertiesDocument38 pagesWeek 2 Polarity of Molecules and Its Propertieslily smithNo ratings yet
- Polar Non PolarDocument54 pagesPolar Non PolarJhon Gabriele CuramengNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Physical Science PDFDocument11 pagesModule 2 - Physical Science PDFDarry Blancia100% (2)
- Intermolecular Forces Worksheet With KeyDocument4 pagesIntermolecular Forces Worksheet With KeyNoreen ClarkNo ratings yet
- Physci Q1 M3Document74 pagesPhysci Q1 M3Julie Anne Portal - OdascoNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 1 CHM2210C CH 1-3 PDFDocument13 pagesPractice Test 1 CHM2210C CH 1-3 PDFkara lane100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry 3rd Edition Klein Test BankDocument86 pagesOrganic Chemistry 3rd Edition Klein Test Bankoliviabutlerogdjmztrka94% (16)
- Polarity & Electronegativity Worksheet SOLVEDDocument1 pagePolarity & Electronegativity Worksheet SOLVEDLili0% (1)
- (Krishna's Text Book) Alok Bariyar, R.P Singh, Babita Agrawal, Babita Agrawal, Prashant Singh - Organic Chemistry-I-Krishna Prakashan Media (2015)Document402 pages(Krishna's Text Book) Alok Bariyar, R.P Singh, Babita Agrawal, Babita Agrawal, Prashant Singh - Organic Chemistry-I-Krishna Prakashan Media (2015)asksankar7857100% (1)
- Covalent BondingDocument74 pagesCovalent BondingRyan Dave Macariay100% (1)
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDocument18 pagesPolar Bonds and Polar MoleculesChe PeñalesNo ratings yet
- 2 CH241 Polar Covalent BondsDocument94 pages2 CH241 Polar Covalent Bondsalyssa_marie_keNo ratings yet
- Polarity of MoleculesDocument45 pagesPolarity of MoleculesAliza Liban100% (1)
- Chemical Bonding ModuleDocument35 pagesChemical Bonding ModuleMark Paul Lipata Benitez100% (2)
- Physical Science Week 3Document7 pagesPhysical Science Week 3ruel rinconadaNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Bond Character and Practice Ws KeyDocument2 pages6.1 Bond Character and Practice Ws KeyKip Aiza FernandezNo ratings yet
- Q3 Module 2 MOLECULAR POLARITYDocument14 pagesQ3 Module 2 MOLECULAR POLARITYraelle tsuNo ratings yet
- Polarity of MoleculesDocument25 pagesPolarity of MoleculesAnalynAsuncionAtaydeNo ratings yet
- Predict Polarity With Electronegativity DiffDocument2 pagesPredict Polarity With Electronegativity DiffRaymond LiuNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity and Bond TypeDocument24 pagesElectronegativity and Bond TypeKate BarilNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument218 pagesChemical BondingveronicamniemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - CHM 261 Organic ChemistryDocument67 pagesChapter 1 - CHM 261 Organic ChemistryShuyi NeohNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 4: Name: Rico R. Candelario Grade & Section: 12 St. Gabriel HUMSSDocument4 pagesPhysical Science Week 4: Name: Rico R. Candelario Grade & Section: 12 St. Gabriel HUMSSRico R. CandelarioNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDocument27 pagesPolar Bonds and Polar MoleculesJezzebelle VenderNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDocument20 pagesPolar Bonds and Polar MoleculesLYNFORD LAGONDINo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Genchem PolarityDocument29 pagesGrade 12 Genchem PolarityJohn Milen Garvida FabiNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds&Molecules V2Document9 pagesPolar Bonds&Molecules V2vlattaetaeNo ratings yet
- 2.04-2.05 Intermediate Bonding and Intermolecular Forces PDFDocument16 pages2.04-2.05 Intermediate Bonding and Intermolecular Forces PDFBryan YeohNo ratings yet
- Polarity in Covalent BondsDocument15 pagesPolarity in Covalent BondsMarcoNo ratings yet
- Ch1 Chem BondingDocument197 pagesCh1 Chem BondingNizarNo ratings yet
- Chem 115 Po Gil Worksheet 11Document13 pagesChem 115 Po Gil Worksheet 11jag1231No ratings yet
- 04 Chemical Bonding Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument7 pages04 Chemical Bonding Formula Sheets QuizrrSwapnil SharmaNo ratings yet
- Struktur Senyawa Organik - Hibridisasi - FarmasiDocument75 pagesStruktur Senyawa Organik - Hibridisasi - FarmasiGhery ArrahmanNo ratings yet
- Bond PolarityDocument9 pagesBond PolarityIvy LunaNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Activity 8.1 - Electronegativity - Polarity of Covalent BondsDocument2 pagesQuiz - Activity 8.1 - Electronegativity - Polarity of Covalent Bondskristzia mae pitosNo ratings yet
- 2 The Chemistry of The ElementsDocument28 pages2 The Chemistry of The ElementsNazmi LatifNo ratings yet
- Q3 Module 3 Polar or Nonpolar: Prepared By: Engr. Erwin D. Rubio JRDocument25 pagesQ3 Module 3 Polar or Nonpolar: Prepared By: Engr. Erwin D. Rubio JRGumban Aaron Frances M.No ratings yet
- Electronegativitiy Worksheet - WELCHDocument5 pagesElectronegativitiy Worksheet - WELCHkamrynwelch1No ratings yet
- CHE101 ChemicalBondingII FZDDocument203 pagesCHE101 ChemicalBondingII FZDsouadalkabirNo ratings yet
- Britton High School: Chemistry Chapter 12: BondingDocument85 pagesBritton High School: Chemistry Chapter 12: BondingMatthew GraceNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2 Study Guide AnswersDocument6 pagesChemistry Unit 2 Study Guide AnswersH.sNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Physical ScienceDocument10 pagesGroup 2 Physical ScienceJay Em Kristel MengulloNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDocument21 pagesPolar Bonds and Polar MoleculesShhhhhhhhyeahNo ratings yet
- The Polarity of A Molecule Based On Its StructureDocument35 pagesThe Polarity of A Molecule Based On Its StructureCherry-Ann BernardezNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledrona grace ulzoronNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding: PHD Tamriko SupatashviliDocument112 pagesChemical Bonding: PHD Tamriko SupatashviliCypher Soth ViNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IDocument57 pagesOrganic Chemistry IMss FaixaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document32 pagesChapter 8Danilo Fronda Jr.No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Chemical Bonding and StructureDocument11 pagesChapter 3 Chemical Bonding and StructureTilak K CNo ratings yet
- 1.3! Polar Covalent Bonds - ElectronegativityDocument6 pages1.3! Polar Covalent Bonds - ElectronegativitySadeeq ArtxzNo ratings yet
- Covalent BondsDocument32 pagesCovalent BondsPualeilehuaNo ratings yet
- Covalent Bonds: The Joy of Sharing!Document33 pagesCovalent Bonds: The Joy of Sharing!premkumarNo ratings yet
- JEE Chemical Bonding Formula SheetsDocument9 pagesJEE Chemical Bonding Formula Sheetsbsarkar100% (1)
- Polar BondsDocument8 pagesPolar BondsAnthony JohanNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Smile 2Document12 pagesPhysical Science Smile 2DYLANNo ratings yet
- Reaksi Asam Basa: Reaksi Anorganik Dalam Medium AirDocument68 pagesReaksi Asam Basa: Reaksi Anorganik Dalam Medium AirHafid Nur HimawanNo ratings yet
- SGCH 09Document24 pagesSGCH 09belleblackNo ratings yet
- Chemıcal BondsDocument10 pagesChemıcal BondsDesirie MarceloNo ratings yet
- ° Polar and Non-Polar Covalent Bonds 3Document23 pages° Polar and Non-Polar Covalent Bonds 3Zayyan AliNo ratings yet
- PS Chemical BondingDocument31 pagesPS Chemical BondingSHEILA MARIE CORTADO - UNDANNo ratings yet
- Polar Bonds and Polar MoleculesDocument18 pagesPolar Bonds and Polar MoleculesGlenn ClementeNo ratings yet
- CHM131 - Chapter 3 - Chemical BondsDocument87 pagesCHM131 - Chapter 3 - Chemical BondsLeo PietroNo ratings yet
- Sub WorkDocument1 pageSub WorkAnna RamdyalNo ratings yet
- Applications of IsotopesDocument11 pagesApplications of IsotopesAnna RamdyalNo ratings yet
- Extra Periodic Table Worksheet 2 KeyDocument5 pagesExtra Periodic Table Worksheet 2 KeyAnna RamdyalNo ratings yet
- Worksheet #1 - Atomic Spectra Answer The Following Questions Using Your Class Notes. 1. How Did Bohr Expand On Rutherford S Model of The AtomDocument6 pagesWorksheet #1 - Atomic Spectra Answer The Following Questions Using Your Class Notes. 1. How Did Bohr Expand On Rutherford S Model of The AtomAnna RamdyalNo ratings yet
- 8.4 - EdlineDocument20 pages8.4 - EdlineHakim Abbas Ali PhalasiyaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - ChemistryDocument48 pagesModule 1 - ChemistryShapnil FinneyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: Polar Bears & Penguins - Electronegativity: NAMEDocument3 pagesWorksheet: Polar Bears & Penguins - Electronegativity: NAMERaymond LiuNo ratings yet
- 2 TM Class PPT - BB Aug-Nov 2019Document28 pages2 TM Class PPT - BB Aug-Nov 2019StephenNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table: Periodicity: Prepared By: Ling Pick YiengDocument15 pagesPeriodic Table: Periodicity: Prepared By: Ling Pick YiengJun Hong TeeNo ratings yet
- Ri h2 Chem p2 AnswersDocument7 pagesRi h2 Chem p2 Answersdragon slayerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Assignment 2022Document3 pagesChemistry Assignment 2022sylvia anneNo ratings yet
- Las Shs Gen - Chem Melc 7 q2 Week-4Document12 pagesLas Shs Gen - Chem Melc 7 q2 Week-4Kim Francis Beluso Dollete IINo ratings yet
- Electronegativity and Bond TypeDocument24 pagesElectronegativity and Bond TypeKate BarilNo ratings yet
- Naming Compounds FlowchartDocument1 pageNaming Compounds Flowchartapi-310503032No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Valence Bond TheoryDocument32 pagesChapter 4 - Valence Bond TheorykhadijahhannahNo ratings yet
- Average Single Bond StrengthDocument5 pagesAverage Single Bond StrengthAhmed MohsenNo ratings yet
- 13.3 Shapes of Organic Molecules Sigma and Pi BondsDocument11 pages13.3 Shapes of Organic Molecules Sigma and Pi Bondssafiya_91No ratings yet
- 139 Chap10Document32 pages139 Chap10Umer Iftikhar AhmedNo ratings yet
- MOT Inorganic: Dr. Sajjad Hussain Sumrra (CHEM-305) Chemistry-IIDocument52 pagesMOT Inorganic: Dr. Sajjad Hussain Sumrra (CHEM-305) Chemistry-IITanya Dilshad100% (3)
- Edexcel IAS Bonding 1Document14 pagesEdexcel IAS Bonding 1mostafa barakatNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Second Quarter - DraftDocument64 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Second Quarter - DraftJay-mee Claire V. DioNo ratings yet
- Lewis StructureDocument38 pagesLewis StructureNicole Joyce Catabay FloresNo ratings yet
- Task 3 QDocument1 pageTask 3 Qharishthestudent2No ratings yet
- Tutorial (Structure and Bonding) AnswersDocument3 pagesTutorial (Structure and Bonding) Answersoh khang chiangNo ratings yet
- Consumer Chemistry 9 Module 2 Organic CompoundsDocument28 pagesConsumer Chemistry 9 Module 2 Organic CompoundsSean Gabriel LacambraNo ratings yet
- Electronegativity and Bond TriangleDocument9 pagesElectronegativity and Bond TrianglePedro BarónNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Chemical Bonding IDocument80 pagesChapter 9 Chemical Bonding IFABIO DE LIMANo ratings yet
- Benzene and Aromatic CompoundsDocument15 pagesBenzene and Aromatic CompoundsMae CanlasNo ratings yet