Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lec 3 - 2004010060
Lec 3 - 2004010060
Uploaded by
mai linhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lec 3 - 2004010060
Lec 3 - 2004010060
Uploaded by
mai linhCopyright:
Available Formats
the total resources owned by the individual, including all assets
wealth
T he quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to wealth
the return expected over the next period on one asset relative to alternative assets
expected return
T he quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to its expected return relative to alternative asset
the degree of uncertainty associated with the return on one asset relative to alternative assets
risk
Determinants of asset Demand T he quantity demanded of an asset is negatively related to the risk of its returns relative to alternative assets
the ease and speed with an asset can be turned into cash alternative assets
liquidity
T he quantity demanded of an asset is positively related to its liquidity relative to alternative assets
Wealth growing wealth (in expansion) -> the demand curve f or bonds shif ts to the right
expected returns expected interest rates in the f uture rise -> the expected return f or long-term bonds f all -> the demand curve shif t lef t
expected inf lation the expected rate of inf lations increase -> the expected return f or bonds reduce -> the demand curve shif t lef t
risk the riskiness of bonds increase-> the demand curve shif t lef t
liquidity the liquidity of bonds increase -> the demand curve shif t right
expected prof itability of investment opportunities in an expansion -> the supply curve shif ts right
Supply and demand in the bond market expected inf laction the expected inf lation increase -> the supply curve shif t right
Government budget budget def icits increase -> the supply curve shif t right
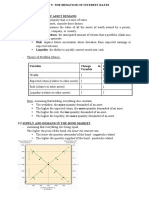
Bd= Bs -> def ines the equilibrium (or market clearing) price and interest rate
Bd > Bs -> there is excess demand, price will rise and interest rate will f all.
Bd < Bs -> there is excess supply, price will f all and interest rate will rise.
supply and demand f or bonds
THE BEHAVIOR OF INTEREST RATES
income ef f ect higher level of income -> demand f or money at each interest rate increase -> demand curve shif t right
shif t in the demand f or money
price-level ef f ect price level rise -> demand f or money at each interest rate increase -> demand curve shif t right
shif ts in the supply of money the money supply (engineered by the Federal Reserve) increase -> the supply curve f or money shif t right
Bs+ Ms= Bd+ Md
Supply and demand in the Market for money
the market money is in equilibrium (Ms = Md) -> bond market is in equilibrium (Bs = Bd)
equilibrium in the market f or money
lower interest rates (the liquidity ef f ect)
income ef f ect: national income and wealth rise -> rise in interest rates (demand curve shif ts right)
rise in the price level -> money demand increase -> rise in interest rates
liquidity pref erence f ramework: increase in money supply
price-level ef f ect
remains even af ter prices have stopped rising.
expect a higher price level in the f uture -> demand curve shif t right -> increase in interest rates
expected-inf lation ef f ect
persists only as long as the price level continues to rise.
liquidity ef f ect larger than other ef f ects
Topic branch 4
liquidity ef f ect smaller than other ef f ects and slow
adjustment of expected inf lation
liquidity ef f ect smaller than expected-inf lation
ef f ect and f ast adjustment of expected inf lation
You might also like
- (Citibank) Using Asset Swap Spreads To Identify Goverment Bond Relative-ValueDocument12 pages(Citibank) Using Asset Swap Spreads To Identify Goverment Bond Relative-ValueMert Can GencNo ratings yet
- The Behavior of Interest Rates: Cecchetti, Chapter 7Document41 pagesThe Behavior of Interest Rates: Cecchetti, Chapter 7Trúc Ly Cáp thịNo ratings yet
- The Origins of Modern Banking: GoldsmithsDocument38 pagesThe Origins of Modern Banking: GoldsmithsVaibhav DixitNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Commercial Real Estate (Cre) Cdos: Nomura Fixed Income ResearchDocument20 pagesThe Evolution of Commercial Real Estate (Cre) Cdos: Nomura Fixed Income ResearchJay KabNo ratings yet
- Barclays BankDocument4 pagesBarclays BanktsundereadamsNo ratings yet
- People's Republic of China Credit RatingDocument5 pagesPeople's Republic of China Credit RatingasiafinancenewsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Determinants of Interest RatesDocument36 pagesChapter 2 - Determinants of Interest RatesMai Lan AnhNo ratings yet
- University MCQs SAMPLE For Project ManagementDocument11 pagesUniversity MCQs SAMPLE For Project Managementasit kandpalNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in CaddevDocument5 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in CaddevRodelia Opada67% (3)
- Chapter 5 - SummaryDocument7 pagesChapter 5 - SummaryLinh KhánhNo ratings yet
- 1gD9bOgblWhqP pCynE6pjN9cyctX Zd3Document18 pages1gD9bOgblWhqP pCynE6pjN9cyctX Zd3Asifur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: The Behaviour of Interest Rates: WealthDocument10 pagesLecture 4: The Behaviour of Interest Rates: WealthLeung Shing HeiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Interest RatesDocument34 pagesChapter 2 Interest RatesHồ Võ Cát TiênNo ratings yet
- Mishkin and Serletis 8ce Chapter 5Document32 pagesMishkin and Serletis 8ce Chapter 5김승현No ratings yet
- Presented by Amir KhanDocument47 pagesPresented by Amir KhanSyed Arham MurtazaNo ratings yet
- The Behavior Of Interest Rates: Group 9: 1/ Huỳnh Nguyễn Hạ Vy 2/ Đoàn Duy Khánh 3/ Nguyễn Đường Phương NgọcDocument40 pagesThe Behavior Of Interest Rates: Group 9: 1/ Huỳnh Nguyễn Hạ Vy 2/ Đoàn Duy Khánh 3/ Nguyễn Đường Phương NgọcNguyễn Đường Phương NgọcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Student Lecture Notes - Nominal Interest Rates 2022fDocument42 pagesChapter 5 - Student Lecture Notes - Nominal Interest Rates 2022fLuqmaan KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - DETERMINATION OF INTEREST RATESDocument36 pagesChapter 2 - DETERMINATION OF INTEREST RATES乙คckคrψ YTNo ratings yet
- ch15 Krugman 10eDocument34 pagesch15 Krugman 10etamar.mdzeluriNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Money Demand and the Equilibrium Interest RateDocument12 pagesChapter 11 Money Demand and the Equilibrium Interest RateWard AlajlouniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Summary - Group 6Document10 pagesChapter 5 Summary - Group 6Phương Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2 Determination of Interest Rates Chapter Outline: NPV Inv + CFDocument48 pagesWEEK 2 Determination of Interest Rates Chapter Outline: NPV Inv + CFSaniyaNo ratings yet
- Mishkin Econ13e PPT 05Document37 pagesMishkin Econ13e PPT 05Omar 11No ratings yet
- Chapter Preview: Why Do Interest Rates Change?Document6 pagesChapter Preview: Why Do Interest Rates Change?shahid faridNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Interest RateDocument30 pagesBehavior of Interest RateTho ThoNo ratings yet
- Wa0003.Document2 pagesWa0003.shubhamsg1222No ratings yet
- Mishkin - Chapter 5Document35 pagesMishkin - Chapter 5Jeet JainNo ratings yet
- 6 The Behavior of InterestrateDocument35 pages6 The Behavior of Interestrateyashasvipandey24682No ratings yet
- Financial Markets and InstitutionsDocument72 pagesFinancial Markets and InstitutionsMarioNo ratings yet
- The Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets: Twelfth Edition, Global EditionDocument38 pagesThe Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets: Twelfth Edition, Global EditionHiền NguyễnNo ratings yet
- MIM03 How FM Work - 8 OctoberDocument27 pagesMIM03 How FM Work - 8 OctoberkuloskiNo ratings yet
- Money & Banking: Week 3: The Behavior of Interest RatesDocument33 pagesMoney & Banking: Week 3: The Behavior of Interest RatesAhmad RahhalNo ratings yet
- ETP Econ Lecture Note 34 Winter 2012Document31 pagesETP Econ Lecture Note 34 Winter 2012Shubhika PantNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Determinants of Interest RatesDocument41 pagesChapter Two: Determinants of Interest Ratesmonica ongNo ratings yet
- M05 Mishkin599853 09 C05Document30 pagesM05 Mishkin599853 09 C05K59 Ngo Yen NhiNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Interest RatesDocument33 pagesBehavior of Interest RatesABIZEYIMANA AimableNo ratings yet
- C2 - Interest RatesDocument32 pagesC2 - Interest RatesMinh Lưu NhậtNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 cont (1)Document3 pagesChap 5 cont (1)Na PhưnNo ratings yet
- Blank 6Document4 pagesBlank 6Silva, Phoebe Chates Bridget B.No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Why Do Interest Rates ChangeDocument13 pagesChapter 4 Why Do Interest Rates ChangeJay Ann DomeNo ratings yet
- Determination of Interest RatesDocument18 pagesDetermination of Interest RatesTanvir SazzadNo ratings yet
- M05 Mishkin599853 09 C05Document30 pagesM05 Mishkin599853 09 C05Hikmət RüstəmovNo ratings yet
- Chap 34Document76 pagesChap 34Jia Wei MiaoNo ratings yet
- Session 4 - Behavior of Interest RateDocument32 pagesSession 4 - Behavior of Interest RatechuphamnamphuongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document33 pagesChapter 5KarimBekdashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Eng VersionDocument15 pagesChapter 5 Eng VersionNgọc Ninh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Behavior of Interest RatesDocument24 pagesThe Behavior of Interest RatesHikmət RüstəmovNo ratings yet
- lec 5 mbDocument42 pageslec 5 mbjaags057No ratings yet
- The Time Value of MoneyDocument2 pagesThe Time Value of Moneypier AcostaNo ratings yet
- The Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy On Aggregate DemandDocument41 pagesThe Influence of Monetary and Fiscal Policy On Aggregate DemandPutri Aprilia ManembuNo ratings yet
- Fin Cheat Sheet 3Document4 pagesFin Cheat Sheet 3ritobroto chandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document19 pagesChapter 2ebaaNo ratings yet
- 整理笔记2Document5 pages整理笔记2JoyceeNo ratings yet
- Fin 616Document7 pagesFin 616Boby PodderNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Money Supply PDFDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting Money Supply PDFhahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Exchange Rate DeterminationDocument22 pagesChapter 6. Exchange Rate DeterminationTuấn LêNo ratings yet
- Finance 5Document11 pagesFinance 5namien koneNo ratings yet
- Money Interest Rates and Exchange RatesDocument44 pagesMoney Interest Rates and Exchange RatesSaim GöküşNo ratings yet
- Content: The Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets Money, Banking, and Financial MarketsDocument12 pagesContent: The Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets Money, Banking, and Financial MarketsDung ThùyNo ratings yet
- 高考經濟筆記 (中英對照版) 微觀經濟第二冊Document68 pages高考經濟筆記 (中英對照版) 微觀經濟第二冊Edward LamNo ratings yet
- The Behavior of Interest RateDocument30 pagesThe Behavior of Interest RateSari Adinda PasaribuNo ratings yet
- C4-Factors Affecting IRDocument24 pagesC4-Factors Affecting IRDuong Ha ThuyNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Micro 2Document4 pagesReviewer in Micro 2Daisyrei CatapangNo ratings yet
- Lecture 16 - RBI, Tools and Monetary PolicyDocument19 pagesLecture 16 - RBI, Tools and Monetary PolicyParth BhatiaNo ratings yet
- L4 AnovaDocument12 pagesL4 Anovamai linhNo ratings yet
- L2 - Inference About One Population VarianceDocument8 pagesL2 - Inference About One Population Variancemai linhNo ratings yet
- Tut 6Document4 pagesTut 6mai linhNo ratings yet
- Tut 1Document7 pagesTut 1mai linhNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - 2004010060Document1 pageLec 2 - 2004010060mai linhNo ratings yet
- Tut 5 - Group 2 - VINAMILKDocument33 pagesTut 5 - Group 2 - VINAMILKmai linhNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 FMTDocument1 pageLec 4 FMTmai linhNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 - 2004010060Document1 pageLec 1 - 2004010060mai linhNo ratings yet
- Tut 3 - Group 21 - BLW AssignmentDocument9 pagesTut 3 - Group 21 - BLW Assignmentmai linhNo ratings yet
- Tut 1 Group 5 Group Presentation Auditing 2023Document21 pagesTut 1 Group 5 Group Presentation Auditing 2023mai linhNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note F3 - Part 3 2022Document41 pagesLecture Note F3 - Part 3 2022mai linhNo ratings yet
- Keyboard Shortcuts in ExcelDocument33 pagesKeyboard Shortcuts in Excelmai linhNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note F3 - Part 1Document45 pagesLecture Note F3 - Part 1mai linhNo ratings yet
- Solution Tutorial 5 TVM Application - SV 21Document6 pagesSolution Tutorial 5 TVM Application - SV 21mai linhNo ratings yet
- F3 Kit Part 1 - 2022Document20 pagesF3 Kit Part 1 - 2022mai linhNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh University of Professionals Faculty of Business StudiesDocument9 pagesBangladesh University of Professionals Faculty of Business StudiesTashkin MahmudNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFDocument7 pagesIlovepdf Merged PDFVijay UNo ratings yet
- QUIZtpmikhsan 11312288Document10 pagesQUIZtpmikhsan 11312288Hanindya PrajakusumaNo ratings yet
- A Practical Guide To Capitalisation of Borrowing Costs: November 2008Document23 pagesA Practical Guide To Capitalisation of Borrowing Costs: November 2008adi darmawanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Background: " A Study On SME Banking Practices in Janata Bank Limited"Document56 pages1.1 Background: " A Study On SME Banking Practices in Janata Bank Limited"Tareq AlamNo ratings yet
- Answers To The Overall Questions of Chapter SevenDocument3 pagesAnswers To The Overall Questions of Chapter SevenHamza MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Omnibus Counter Guarantee Aarti PhosphatesDocument3 pagesOmnibus Counter Guarantee Aarti PhosphatesChetan PatilNo ratings yet
- Problems With Solution Capital GainsDocument12 pagesProblems With Solution Capital Gainsnaqi ali100% (1)
- Khalid Siraj Textile Mills Limited Company InformationDocument6 pagesKhalid Siraj Textile Mills Limited Company InformationDani zNo ratings yet
- Project Report On "Cash Flow Statement at Thinknext Technologies Pvt. LTD"Document54 pagesProject Report On "Cash Flow Statement at Thinknext Technologies Pvt. LTD"Sat NamNo ratings yet
- Myanmar Tax Booklet - 2021 2022 2022 2023Document61 pagesMyanmar Tax Booklet - 2021 2022 2022 2023Ya Min KyawNo ratings yet
- Final Term 14 Papers MGT101 SOLVED by Chanda Rehman, Kamran Haider, Abr N Anjum-1Document146 pagesFinal Term 14 Papers MGT101 SOLVED by Chanda Rehman, Kamran Haider, Abr N Anjum-1Muhammad HassanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5: Cost of CapitalDocument27 pagesCHAPTER 5: Cost of Capitalgirma guddeNo ratings yet
- Pomoc Bilans Stanja 2015 ENGDocument2 pagesPomoc Bilans Stanja 2015 ENGMitarXNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 4 Handout PurposeDocument47 pagesUNIT - 4 Handout PurposemelaNo ratings yet
- Mediclinic Group 2023 ResultsDocument17 pagesMediclinic Group 2023 ResultsBack To NatureNo ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting Part 1: Seatwork - Franchise Accounting Franchise RevenueDocument4 pagesAdvanced Accounting Part 1: Seatwork - Franchise Accounting Franchise RevenueAdam SmithNo ratings yet
- Repo Rate & Reverse Repo Rate InfoDocument2 pagesRepo Rate & Reverse Repo Rate InfoGauravNo ratings yet
- B. National "Love Your Zoo Week!"Document11 pagesB. National "Love Your Zoo Week!"prima gunadiNo ratings yet
- Group Project ACC117 ReferencesDocument17 pagesGroup Project ACC117 Referencesafiqah aina100% (1)
- INTERNATIONAL FINANCE-Factors Affecting International InvestmentsDocument3 pagesINTERNATIONAL FINANCE-Factors Affecting International InvestmentsRahul R Naik100% (1)
- Outline - AC2101 Seminar 4-5 FA Outline - Revised - StudentsDocument35 pagesOutline - AC2101 Seminar 4-5 FA Outline - Revised - StudentsC.TangibleNo ratings yet
- Currency WarDocument10 pagesCurrency WarBaarsa Deb BarmaNo ratings yet
- ICAI MOCK TEST CA FOUNDATION DECEMBER 2022 Paper 1 Principles andDocument6 pagesICAI MOCK TEST CA FOUNDATION DECEMBER 2022 Paper 1 Principles andArpit GuptaNo ratings yet