Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lec 1 - 2004010060
Lec 1 - 2004010060
Uploaded by
mai linhOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lec 1 - 2004010060
Lec 1 - 2004010060
Uploaded by
mai linhCopyright:
Available Formats
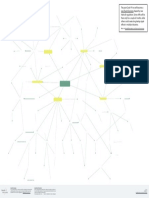
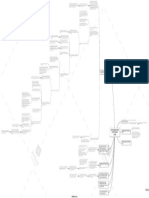
direct f inance - borrowers borrow f unds directly f orm
lenders in f inancial markets by selling them securities.
indirect f inance - borrowers borrow f unds through a third-
party, such as a f inancial intermediary.
channeling f unds f rom people surplus of f unds to people
shortage of f unds
f unction
f lows of f unds through the f inancial system
promotes economic ef f iciency by producing an ef f icient
allocation of capital, which increases production
directly improve the well-being of consumers by allowing
them to time purchases better
f ixed f inancial market income securities are bought and
sold
debt holder
Debt holders are considered as a creditor to the company
debt - a company’s borrowed capital
T he returns are comparatively less
T he market is less volatile
lower transaction costs (time and money spent in carrying T here is a guarantee of f ixed returns most of the time
our f inancial transactions)
Debt vs Equity markets
financial markets
Place where stocks of a company are bought and sold
reduce the exposure of investors to risk
f unctions shareholders
adverse selection - a situation where one party of ten does
not know enough about the other party to make accurate
decisions Shareholders are considered as owners of the company
equity - a company’s owned capital
moral hazard - a situation where the borrower might deal with asymmetric inf ormation problems T he returns are comparatively high
engage in activities that are undesirable f rom the lender’s
point of view because they make it less likely that the loan
will be paid back. T he market is more volatile
commercial banks T here is no guaranty of f ixed returns on a regular basis
saving and loan associations financial institutions primary - investment banks underwrite securities in primary
depository institutions (banks) markets
mutual savings banks
secondary - the previously issued securities will be sold in
the secondary market
credit unions
lif e insurance companies
structure
Primary vs Secondary markets
f ire and casually insurance companies contractual savings institutions
types
pension f unds, government retirement f unds
f inance companies
mutual f unds
Overview of the financial system
money market mutual f unds investment intermediaries
1 central location standardized
exchanges - NYSE, NASDAQ, HNX, HSX, ..
hedge f unds
A stock in the Exchange market has one price only.
Exchanges vs OT C markets
investment banks
network of dealers and brokers
OT C - Foreign exchange, Federal f unds
reduce adverse selection and moral hazard problems A stock has dif f erent prices in the OT C market.
to increase the inf ormation available to investors
reduce insider trading (SEC) money markets - short term debt instruments
Money vs Capital markets
restrictions on entry (chartering process) f unctions capital markets - long term debt instruments
regulations
restrictions on assets and activities (control holding of risky
assets) U.S. T reasury bills
to ensure the soundness of f inancial intermediaries
deposit insurance (avoid bank runs) negotiable bank certif icates of deposits
limits on competition money market instruments commercial papers
f ed f unds
repurchase agreements
stocks
financial instruments
mortgages and mortgage-backed securities
corporate bonds
capital market instruments U.S. government securities
U.S. government agency securities
state and local government bonds
consumer and bank commercial loans
You might also like
- The Complete Guide To Comprehensive Fibonacci Analysis On Forex - Viktor Pershikov PDFDocument322 pagesThe Complete Guide To Comprehensive Fibonacci Analysis On Forex - Viktor Pershikov PDFNisha Sharma83% (24)
- Persimmon PLC: A Valuation Based Financial AnalysisDocument14 pagesPersimmon PLC: A Valuation Based Financial AnalysisUsmanNo ratings yet
- Questions 33-42 Are Based On The Following Passage.: ContinueDocument3 pagesQuestions 33-42 Are Based On The Following Passage.: ContinueOmaNo ratings yet
- Shifts in The Low Touch Economy (2020-2023)Document1 pageShifts in The Low Touch Economy (2020-2023)Ali ElattarNo ratings yet
- Outline Sales UCC - Article2-1Document26 pagesOutline Sales UCC - Article2-1Kim BoSlice100% (6)
- FINA1109 Lecture 6 2019 HandoutDocument48 pagesFINA1109 Lecture 6 2019 HandoutDylan AdrianNo ratings yet
- GSU788569420 Auth LetterDocument2 pagesGSU788569420 Auth LetterRock RoseNo ratings yet
- Gym Project AppraisalDocument15 pagesGym Project AppraisalDanish Khan100% (1)
- The History of Finance: An Eyewitness AccountDocument7 pagesThe History of Finance: An Eyewitness AccountFAIZAN HASSANNo ratings yet
- Booc ClassPartiEquity InvestmentDocument13 pagesBooc ClassPartiEquity Investmentjaocent brixNo ratings yet
- A Ransom Note Regarding Your Life: ... and UndermineDocument5 pagesA Ransom Note Regarding Your Life: ... and UnderminexdeadxNo ratings yet
- What Are The Effects of Gen Budget SupportDocument6 pagesWhat Are The Effects of Gen Budget SupportChremataNo ratings yet
- Woman Who Purchased Portion of Metrocenter Mall Arrested For Defaulting On Payments in 2013 ConvictionDocument11 pagesWoman Who Purchased Portion of Metrocenter Mall Arrested For Defaulting On Payments in 2013 ConvictionWLBT3No ratings yet
- Sanders Motion To Show CauseDocument11 pagesSanders Motion To Show Causethe kingfishNo ratings yet
- Wallstreetjournal 20191129 TheWallStreetJournalDocument44 pagesWallstreetjournal 20191129 TheWallStreetJournalNehaNo ratings yet
- Affidavit APORDocument1 pageAffidavit APORHoney Bona LanzuelaNo ratings yet
- Safari - 02-Jul-2020 at 3:51 PMKKKDocument1 pageSafari - 02-Jul-2020 at 3:51 PMKKKDEVORSHI CHATTERJEENo ratings yet
- What The Bypoll Results Point To: Let's Look Beyond Rules For ReformsDocument1 pageWhat The Bypoll Results Point To: Let's Look Beyond Rules For ReformskiranNo ratings yet
- 1845 Sea Bird LostDocument1 page1845 Sea Bird LostEduardo Keldjian ENo ratings yet
- Year 3 Economy-Term 3 GADocument2 pagesYear 3 Economy-Term 3 GASTU HE BEILENo ratings yet
- Year 3 Economy - Term 3 General Assessment On Government InterventionDocument2 pagesYear 3 Economy - Term 3 General Assessment On Government InterventionSTU HE BEILENo ratings yet
- Federalism That's Not Cooperative: Watching The WatchdogDocument1 pageFederalism That's Not Cooperative: Watching The WatchdogkiranNo ratings yet
- James BlancoDocument16 pagesJames Blancoblanco09jamesNo ratings yet
- A Visual History of The Federal Reserve SystemDocument1 pageA Visual History of The Federal Reserve Systemapi-3931606No ratings yet
- Con 1Document5 pagesCon 1Alizaman AlibhaiNo ratings yet
- A.I Video CreatorDocument1 pageA.I Video CreatorTahina ANDRIAMANGANo ratings yet
- Cultural Programming Case StudyDocument2 pagesCultural Programming Case Studydjb932661No ratings yet
- The Washington Post 2022-01-04Document48 pagesThe Washington Post 2022-01-04Kola AkindesNo ratings yet
- ISLAMIC FUNDAMENTALISM at WAR AGAINST AMERICA New Documentaries On Religionand Politics in The Islamic WorldDocument6 pagesISLAMIC FUNDAMENTALISM at WAR AGAINST AMERICA New Documentaries On Religionand Politics in The Islamic Worldarif budimanNo ratings yet
- Tourism 1Document3 pagesTourism 1nino ondrovicNo ratings yet
- CHP 8 FIDocument5 pagesCHP 8 FIHarsh Shukla [2940]No ratings yet
- The Wall Street Journal 19-12-22Document28 pagesThe Wall Street Journal 19-12-22Dario CavalieriNo ratings yet
- Etm 2010 8 31 10Document1 pageEtm 2010 8 31 10Jess JoseNo ratings yet
- Module 70Document3 pagesModule 70avril genaoNo ratings yet
- Defective ContractsDocument1 pageDefective Contractsdinm6230No ratings yet
- Mothers PF FirstDocument2 pagesMothers PF FirstSidney OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Gabriel Malancioiu Traulos 43876Document28 pagesGabriel Malancioiu Traulos 43876belgarath_89No ratings yet
- Final - Bad Faith SurveyDocument134 pagesFinal - Bad Faith SurveyJohnNo ratings yet
- January 24, 2003 (Page 38 of 9Document1 pageJanuary 24, 2003 (Page 38 of 9Allegheny JOB WatchNo ratings yet
- Legislative History - withMarginNotesDocument1 pageLegislative History - withMarginNotesRhege AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Cerrone Margo ResumeDocument2 pagesCerrone Margo Resumeapi-558280939No ratings yet
- All Editorials PDFDocument18 pagesAll Editorials PDFMD NADEEM ASGARNo ratings yet
- Mint Editorial 01.10.2019Document2 pagesMint Editorial 01.10.2019kowsalya mathiNo ratings yet
- How Faith WorksDocument1 pageHow Faith Worksdaniel0% (1)
- 02-Urban Project-All Plans ApartmentsDocument1 page02-Urban Project-All Plans ApartmentsmehwishNo ratings yet
- Investment Banking U4EBIIDocument2 pagesInvestment Banking U4EBIIjoseNo ratings yet
- Missa de AngelisDocument16 pagesMissa de AngelisMICHAEL DAVIDNo ratings yet
- Multi-Family ChecklistDocument1 pageMulti-Family Checklistarturo7942No ratings yet
- Introduction To EconomicsDocument16 pagesIntroduction To EconomicsAndrei StoianNo ratings yet
- Thought Leadership - Kojo ParrisDocument2 pagesThought Leadership - Kojo Parrisspesa_1No ratings yet
- Soft-Tissue Conditions Around Dental Implants: A Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesSoft-Tissue Conditions Around Dental Implants: A Literature ReviewPaul Youn-seok HamNo ratings yet
- Understanding Title InsuranceDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Title InsuranceFrank GalatiNo ratings yet
- On The Dialectics of The Value-Form: Money Is No Sig Objectified SociaDocument1 pageOn The Dialectics of The Value-Form: Money Is No Sig Objectified SociaAbhishek Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- CNPA - General Excellence 1Document20 pagesCNPA - General Excellence 1The UnionNo ratings yet
- Ending The Federal Reserve From The Bottom Up: Re-Introducing Competitive Currency by State Adherence To Article I, Section 10Document17 pagesEnding The Federal Reserve From The Bottom Up: Re-Introducing Competitive Currency by State Adherence To Article I, Section 10Carl MullanNo ratings yet
- F3 Course NotesDocument278 pagesF3 Course NotesShayan GooneratneNo ratings yet
- Fund ComparisonsDocument1 pageFund Comparisonsarom09No ratings yet
- Tóm tắt chương 5Document1 pageTóm tắt chương 5Đức Thành NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Morning India - 10-Oct.-'20?Document11 pagesMorning India - 10-Oct.-'20?GauravNo ratings yet
- Shadow BankingDocument82 pagesShadow Bankingdbhangui6528No ratings yet
- Themes and QuotationsDocument1 pageThemes and QuotationssaraNo ratings yet
- Wallstreetjournaleurope 20170309 The Wall Street Journal EuropeDocument20 pagesWallstreetjournaleurope 20170309 The Wall Street Journal EuropestefanoNo ratings yet
- Informal Sector in SADocument6 pagesInformal Sector in SARaymond MNo ratings yet
- L4 AnovaDocument12 pagesL4 Anovamai linhNo ratings yet
- L2 - Inference About One Population VarianceDocument8 pagesL2 - Inference About One Population Variancemai linhNo ratings yet
- Tut 1Document7 pagesTut 1mai linhNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 - 2004010060Document1 pageLec 3 - 2004010060mai linhNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - 2004010060Document1 pageLec 2 - 2004010060mai linhNo ratings yet
- Lec 4 FMTDocument1 pageLec 4 FMTmai linhNo ratings yet
- Tut 6Document4 pagesTut 6mai linhNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note F3 - Part 1Document45 pagesLecture Note F3 - Part 1mai linhNo ratings yet
- Tut 5 - Group 2 - VINAMILKDocument33 pagesTut 5 - Group 2 - VINAMILKmai linhNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note F3 - Part 3 2022Document41 pagesLecture Note F3 - Part 3 2022mai linhNo ratings yet
- Tut 3 - Group 21 - BLW AssignmentDocument9 pagesTut 3 - Group 21 - BLW Assignmentmai linhNo ratings yet
- F3 Kit Part 1 - 2022Document20 pagesF3 Kit Part 1 - 2022mai linhNo ratings yet
- Tut 1 Group 5 Group Presentation Auditing 2023Document21 pagesTut 1 Group 5 Group Presentation Auditing 2023mai linhNo ratings yet
- Keyboard Shortcuts in ExcelDocument33 pagesKeyboard Shortcuts in Excelmai linhNo ratings yet
- Solution Tutorial 5 TVM Application - SV 21Document6 pagesSolution Tutorial 5 TVM Application - SV 21mai linhNo ratings yet
- 10 CommandmentsDocument43 pages10 Commandmentscapitalfin100% (1)
- MOA of Actuarial Societ of BangladeshDocument22 pagesMOA of Actuarial Societ of BangladeshActuarial Society of BangladeshNo ratings yet
- American Legion TestimonyDocument8 pagesAmerican Legion TestimonyDaily Caller News FoundationNo ratings yet
- Tamfi Directory 2011 2012 PDFDocument61 pagesTamfi Directory 2011 2012 PDFsimmy68100% (1)
- Fidic Letters by ConsultanttDocument48 pagesFidic Letters by ConsultanttMohamed Elarabi50% (2)
- Philippine Civil Code Law On Sales - Case Digest (Powerpoint Presentation)Document31 pagesPhilippine Civil Code Law On Sales - Case Digest (Powerpoint Presentation)Abhor TyrannyNo ratings yet
- Ar 20115-16Document146 pagesAr 20115-16vishald4100% (1)
- Fee ScheduleDocument3 pagesFee ScheduleAnonymous HH3c17osNo ratings yet
- Inveators Perception About Various Investment Avenues Available at Financial MarketDocument84 pagesInveators Perception About Various Investment Avenues Available at Financial MarketGill Kiran75% (4)
- Ngo Financial ManagementDocument120 pagesNgo Financial Managementrafimane100% (1)
- Rehab Mob Company LimitedDocument5 pagesRehab Mob Company LimitedKehkashanNo ratings yet
- Coir Spinning Unit AutomaticDocument3 pagesCoir Spinning Unit AutomaticSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Midterm RevisionDocument2 pagesMidterm RevisionKean Christopher GandalalNo ratings yet
- Responsibility of Fiscal Policy UPDATEDDocument24 pagesResponsibility of Fiscal Policy UPDATEDFiona RamiNo ratings yet
- The Indian Trust Act 1882Document25 pagesThe Indian Trust Act 1882navinkapilNo ratings yet
- Quiz PledgeDocument2 pagesQuiz PledgeEmilie DeanNo ratings yet
- Sample TestDocument11 pagesSample Testgloworm44No ratings yet
- 2009 - Banca Mondiala - Analize Si Recomandari StrategiceDocument92 pages2009 - Banca Mondiala - Analize Si Recomandari StrategiceBalaniscu BogdanNo ratings yet
- San Isidro Labrador Consumer Cooperative: I. General InformationDocument2 pagesSan Isidro Labrador Consumer Cooperative: I. General InformationAngela May UdtohanNo ratings yet
- 10000022229Document302 pages10000022229Chapter 11 DocketsNo ratings yet
- Macro Economics-1 PDFDocument81 pagesMacro Economics-1 PDFNischal Singh AttriNo ratings yet
- Semi-Analytic Valuation of Credit Linked Swaps in A Black-Karasinski FrameworkDocument20 pagesSemi-Analytic Valuation of Credit Linked Swaps in A Black-Karasinski Frameworkstehbar9570No ratings yet
- Financial Management CH1Document17 pagesFinancial Management CH1Mahesh HadapadNo ratings yet
- LSCC Final Bill CC Form - Payments - ChequeDocument5 pagesLSCC Final Bill CC Form - Payments - ChequethareshkumarNo ratings yet
- Big Corruption Scandal in The Indonesian Bank Restructuring Agency (IBRA)Document1 pageBig Corruption Scandal in The Indonesian Bank Restructuring Agency (IBRA)Zulmy Ikhsan WNo ratings yet