Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Set Theory
Uploaded by
Mary Jane AguinaldoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Set Theory
Uploaded by
Mary Jane AguinaldoCopyright:
Available Formats
What is Set Theory
Set Theory is a branch of mathematics that deals with the properties of well-
defined collections of objects, which may or may not be of a mathematical
nature, such as numbers or functions. Objects in the collection are called
elements of the set.
A set is a structure, representing an unordered collection (group, plurality) of
zero or more distinct (different) objects.
Set theory deals with operations between, relations among, and statements
about sets.
Set theory, using as primitives the notions of set (as a synonym for
“collection”), atom (i.e., an object that is not subdivisible, not a collection),
and the relation belongs to (∈), has sufficient expressive power to serve as
the foundation of all mathematics. Mathematicians use notation and results
from set theory in their everyday practice. We call the sets that
mathematicians use the “real sets” of our mathematical intuition.
Set theory is the study of collections of “mathematical
objects”, such objects are either
(1) atomic – an object that is not a collection of other objects – such as a
number or a point on a Euclidean line, or
(2) collections of mathematical objects.
Atoms are very often called “urelements”, pronounced “¯ ur-´ elements” – an anglicized form of the German word
Urelemente – “primeval elements”.
Types of Sets
1. Empty Sets - A set that contains no members is called the empty set or
null set. The empty set is written as { } or ᴓ .
2. Finite Sets - A set is it finite if it consists of a definite number of different
elements. If W be the set of people living in a town, then W is finite.
3. Infinite Sets - are a set that is not a finite set. Infinite sets may be
countable or uncountable.
4. Subsets - Sets which are the part of another set are called subsets of the
original set.
5. Power Sets - The set of all set or group off all subset for any given set,
including the empty set. A set that has ‘n’ elements has 2 n subsets in all.
6. Singleton Sets - A set that have only one element.
7. Super Sets - A set of another smaller set if almost all elements of that
smaller set are elements of the set.
8. Equal Sets - Are sets which have the same members.
9. Universal Sets - A set which contains all objects, including itself.
Set Operations
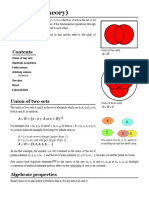
Given sets A and B we define their
Union - is the set of elements that are members of A or B, or both too.
A ∪ B={x ∨x ∈ A∨x ∈ B }
Intersection - is the set of elements that are in A and B.
A ∩ B={ x∨x ∈ A∧x ∈ B }
Complements - is the set of elements of universal set (U) that are not
elements of A.
The Laws of Set Theory
Law of Double Complement A=A
Demorgan’s Laws A ∪B= A ∩ B
A ∩ B= A ∪ B
You might also like
- Discrete Structures: TopicDocument5 pagesDiscrete Structures: TopicMuhammad Rayyan100% (1)
- DM Unit 1Document30 pagesDM Unit 1Rushikesh ShindeNo ratings yet
- SET Theory: Presented By: Richelle Catabay BSED III MathematicsDocument28 pagesSET Theory: Presented By: Richelle Catabay BSED III MathematicsLovely CarbonelNo ratings yet
- Sets and Subsets: Some Example of SetsDocument4 pagesSets and Subsets: Some Example of SetsJuvy AlcazarNo ratings yet
- Gumemba EricaDocument1 pageGumemba EricaEmia John CarloNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Discrete Structures - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument29 pagesUnit 1 - Discrete Structures - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- BE - IT - AIDS - II - Module1 - W 2 - Fuzzy Logic and Its ApplicationDocument51 pagesBE - IT - AIDS - II - Module1 - W 2 - Fuzzy Logic and Its ApplicationShivamNo ratings yet
- Aditya Kumar Foc AssignmentDocument4 pagesAditya Kumar Foc Assignmentetbfzrf8No ratings yet
- Week 1 - Set Theory and Mathematical ProofsDocument16 pagesWeek 1 - Set Theory and Mathematical ProofsGame AccountNo ratings yet
- GEC 104 Week 4 - Basic Concept of SetsDocument7 pagesGEC 104 Week 4 - Basic Concept of SetsReygie FabrigaNo ratings yet
- HO 1 3 Intro Sets RelDocument14 pagesHO 1 3 Intro Sets RelFarjad AliNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Discrete Unit 1Document46 pagesLecture Notes Discrete Unit 1Aryan pathakNo ratings yet
- Birth of Set TheoryDocument17 pagesBirth of Set TheoryMaturan, Ma. Kayesha Camille A.No ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document14 pagesLesson 1jaspertaguiam7No ratings yet
- KRR Unit 1Document73 pagesKRR Unit 1Mogili sivaNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematical Structures 15CS3 6: Set TheoryDocument34 pagesDiscrete Mathematical Structures 15CS3 6: Set TheoryShruti LadageNo ratings yet
- BTech 4th Lecture Notes SetsDocument16 pagesBTech 4th Lecture Notes SetsPrabhjot SinghNo ratings yet
- TOCmodule 1Document21 pagesTOCmodule 1msanees005No ratings yet
- 2.2 - Set - Basic Definitions and NotationDocument26 pages2.2 - Set - Basic Definitions and NotationJustin BidanNo ratings yet
- Set Mathematics ProjectDocument38 pagesSet Mathematics ProjectVijay VijayNo ratings yet
- LIET III CSE AIML II SEM A & B OU Soft Computing UNIT II LNDocument43 pagesLIET III CSE AIML II SEM A & B OU Soft Computing UNIT II LNAbdul Azeez 312No ratings yet
- Unit 3 DMSDocument14 pagesUnit 3 DMSshubhamNo ratings yet
- Well - Defined Collections and SetsDocument8 pagesWell - Defined Collections and SetsGilbert GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - SetsDocument5 pagesChapter 5 - Setshassoon221 / حسوون٢٢١No ratings yet
- Number Sets, Numerosity of Number SetsDocument3 pagesNumber Sets, Numerosity of Number SetsbcsopiNo ratings yet
- Set Theory LogarithmDocument26 pagesSet Theory Logarithmsajib HossinNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structure L#1Document3 pagesDiscrete Structure L#1Hassan BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - Aspx: Sets 1. What Is Set? Give Suitable Exaples 2. What Are Types (Kinds) of Set 3Document3 pagesMathematics - Aspx: Sets 1. What Is Set? Give Suitable Exaples 2. What Are Types (Kinds) of Set 3skdvsdjNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - SetsDocument5 pagesChapter 3 - SetsJeremy Dalangin PosadaNo ratings yet
- Math 013Document2 pagesMath 013graidamarielleveniseNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Set Theory and Point-Set TopologyDocument10 pagesLecture Notes On Set Theory and Point-Set TopologyGiven MteweleNo ratings yet
- Union (Set Theory) : Union of Two Sets Algebraic Properties Finite Unions Arbitrary UnionsDocument4 pagesUnion (Set Theory) : Union of Two Sets Algebraic Properties Finite Unions Arbitrary Unionsamrin jannatNo ratings yet
- Institute of Management Studies Discrete MathematicsDocument7 pagesInstitute of Management Studies Discrete MathematicsSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- CMT Fuzzy LogicDocument36 pagesCMT Fuzzy Logiclama209721No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Discrete Structures - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument10 pagesUnit 2 - Discrete Structures - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inPiuDevNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Language and SymbolsDocument4 pagesMathematical Language and SymbolsJohn Carlo G. NolascoNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to Matrices, Sets and Groups for Science StudentsFrom EverandAn Introduction to Matrices, Sets and Groups for Science StudentsNo ratings yet
- Discrete MathematicsDocument75 pagesDiscrete MathematicsJean Rances Amparo RanidoNo ratings yet
- Discrete Math Module 1Document9 pagesDiscrete Math Module 1santillankathyrineNo ratings yet
- Math ReviewerDocument11 pagesMath ReviewerILAO, Danica S.No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Discrete Structures - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument10 pagesUnit 2 - Discrete Structures - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inAryan TamrakarNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 Set TheoryDocument4 pagesLecture1 Set Theorycsa1980No ratings yet
- Math in Our World - Module 3.1Document10 pagesMath in Our World - Module 3.1Gee Lysa Pascua Vilbar100% (1)
- Set (Mathematics) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesSet (Mathematics) : From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaBhaekenzoNo ratings yet
- File File Class 11 1634641897 1638876189Document29 pagesFile File Class 11 1634641897 1638876189Surisetti Jyothsna LathaNo ratings yet
- Set Theory MergedDocument84 pagesSet Theory Mergedkaushik kumarNo ratings yet
- Descri Te Report 1Document32 pagesDescri Te Report 1ChingChing ErmNo ratings yet
- Abstract AlgebraDocument2 pagesAbstract AlgebraAadi JainNo ratings yet
- Set TheoryDocument19 pagesSet Theory33 Ranjan ShettigarNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Lesson 1 2 REVIEWERDocument5 pagesMODULE 2 Lesson 1 2 REVIEWERAubrey Marie CabalidaNo ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS IN MODERN WORLD TermsDocument2 pagesMATHEMATICS IN MODERN WORLD TermsMa Khristina S WongNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Cse 245)Document58 pagesUnit-1 (Cse 245)Harsh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Class-Xi Set TheoryDocument2 pagesClass-Xi Set TheoryKamal Sharma100% (1)
- Sets - Its Operations (Ch2)Document52 pagesSets - Its Operations (Ch2)EMAN MURTAZA TURKNo ratings yet
- Supplement (Set Theory)Document5 pagesSupplement (Set Theory)HP ChuahNo ratings yet
- CMT Fuzzy LogicDocument35 pagesCMT Fuzzy LogicN.RAMAKUMARNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument8 pagesUntitled DocumentStem 21 - Suyat, Justine Kay N.No ratings yet
- Group Theory ReportDocument12 pagesGroup Theory ReportlunarcausticacNo ratings yet
- Supplement (Set Theory)Document5 pagesSupplement (Set Theory)mac as macNo ratings yet
- Agrarian Reform HistoryDocument6 pagesAgrarian Reform HistoryMary Jane AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- A. Definition of Child and Adolescent by UNICEF UNISCO and WHODocument6 pagesA. Definition of Child and Adolescent by UNICEF UNISCO and WHOKaylah AlipioNo ratings yet
- Meaning, Concepts ApproachesDocument2 pagesMeaning, Concepts ApproachesMary Jane AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Statistical TestsDocument3 pagesStatistical TestsMary Jane AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Math 108 Chapter 4 Amortization and Sinking FundDocument6 pagesMath 108 Chapter 4 Amortization and Sinking FundMary Jane Aguinaldo100% (2)
- 2 Chinese-LanguageDocument9 pages2 Chinese-LanguageMary Jane AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Resolving A Dispute Between Philippines and ChinaDocument10 pagesResolving A Dispute Between Philippines and ChinaMary Jane AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Greetings and Common ExpressionsDocument6 pagesGreetings and Common ExpressionsMary Jane AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4c Indirect ProofDocument2 pagesLesson 4c Indirect ProofMary Jane AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Lessons 2 4b Definitions To PMIDocument5 pagesLessons 2 4b Definitions To PMIMary Jane AguinaldoNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics,: 9e, GE (Groebner/Shannon/Fry) Chapter 3 Describing Data Using Numerical MeasuresDocument43 pagesBusiness Statistics,: 9e, GE (Groebner/Shannon/Fry) Chapter 3 Describing Data Using Numerical MeasuresCeline Clemence胡嘉欣No ratings yet
- Thc2: Risk Management As Applied To Safety, Sanitation and Security Bshm-IDocument5 pagesThc2: Risk Management As Applied To Safety, Sanitation and Security Bshm-ISheena HarrienNo ratings yet
- Sex Determination and Primary Sex Differentiation in Amphibians - Genetic and Developmental MechanismsDocument27 pagesSex Determination and Primary Sex Differentiation in Amphibians - Genetic and Developmental MechanismsAltaicaNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics. ProblemsDocument3 pagesElectrostatics. Problemsscs942609No ratings yet
- GILLIGANDocument4 pagesGILLIGANVAIDEHI AGARWALNo ratings yet
- BITSAT Preparation Tracker - MathonGo PDFDocument3 pagesBITSAT Preparation Tracker - MathonGo PDFGaurang MathurNo ratings yet
- Advantage 100 Series: Fixed-Mount OEM Vision SystemDocument2 pagesAdvantage 100 Series: Fixed-Mount OEM Vision SystemGovardhan JainNo ratings yet
- Building Information Modeling (BIM) Implementation For SustainabiDocument7 pagesBuilding Information Modeling (BIM) Implementation For SustainabiRicky KhannaNo ratings yet
- ADSS Cable Spiral Vibration DamperDocument1 pageADSS Cable Spiral Vibration DamperoknfnklfNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Test MHF4U - Fatima YahyaDocument2 pagesUnit 6 Test MHF4U - Fatima YahyafatimatumbiNo ratings yet
- Sailor Moon Vol 1 - Naoko TakeuchiDocument204 pagesSailor Moon Vol 1 - Naoko TakeuchiKate Yati100% (4)
- Scientific Design Choices in Data VisualizationDocument11 pagesScientific Design Choices in Data VisualizationAdil Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- Fed Question BankDocument5 pagesFed Question BankAnonymous eWMnRr70qNo ratings yet
- Physics FYUGPDocument57 pagesPhysics FYUGPNilotpal PuzariNo ratings yet
- CV Emil SatriaDocument1 pageCV Emil SatriaazmiazfarNo ratings yet
- Of Studies: Francis BaconDocument9 pagesOf Studies: Francis BaconAfreen FaiyazNo ratings yet
- Diversity of The Skin Microbiota of Fishes: Evidence For Host Species SpecificityDocument12 pagesDiversity of The Skin Microbiota of Fishes: Evidence For Host Species SpecificityDiana CalderaNo ratings yet
- CSR Paper ResearchDocument14 pagesCSR Paper ResearchJacqueline GalletoNo ratings yet
- S TypeDocument29 pagesS TypedenisNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Logic and LanguageDocument16 pagesChapter Three: Logic and LanguageTagayNo ratings yet
- Impact of In-Service Training On Economics Teachers' Productivity in Secondary SchoolsDocument27 pagesImpact of In-Service Training On Economics Teachers' Productivity in Secondary SchoolsOjo Oluwaseun JuliusNo ratings yet
- Cultural Diffusion and The Kingdom of Kongo Essay OutlineDocument3 pagesCultural Diffusion and The Kingdom of Kongo Essay OutlineAbenzer MamoNo ratings yet
- Ainstorming An Important EventDocument1 pageAinstorming An Important EventMaveth Varinia Pacheco YepezNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Syllabus Class 6 Maths The City SchoolDocument3 pages1st Term Syllabus Class 6 Maths The City SchoolDaGreat Umama100% (1)
- Grand Hyatt Dubai Internship ReportDocument49 pagesGrand Hyatt Dubai Internship ReportKareena Jain100% (1)
- Data Sheet: Item N°: Curve Tolerance According To ISO 9906Document3 pagesData Sheet: Item N°: Curve Tolerance According To ISO 9906Aan AndianaNo ratings yet
- Parts Catalogue For Detroit DieselDocument27 pagesParts Catalogue For Detroit DieselEduardo CabreraNo ratings yet
- Work Procedure & Check ListDocument14 pagesWork Procedure & Check ListHARSHADNo ratings yet
- Perno A325 HDG 5-8 X 1 1-2 (JN+6654225)Document1 pagePerno A325 HDG 5-8 X 1 1-2 (JN+6654225)Alexander Ortiz CarrionNo ratings yet
- XY Power 30kW Power Module For Fast EV Charging StationsDocument2 pagesXY Power 30kW Power Module For Fast EV Charging StationsSam GuoNo ratings yet