Professional Documents
Culture Documents
OCT 5 (Ward, Lap, Abd Pain)
Uploaded by
Stephanie TrigsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
OCT 5 (Ward, Lap, Abd Pain)
Uploaded by
Stephanie TrigsCopyright:
Available Formats
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
October 5, 2020
I. Ward
Other 10 group were presented
Doc’s comments on the presented cases:
Concise
Stages of appendicitis
Appendix is part of the lymphatics
Obstruction of the appendix there will increase the
intraluminal pressure-> impingement of LE with a BS from
the basement membrane.
Contents of appendix: Fecal material and bacteria
Fecalith adults, lymphoid hyperplasia pedia
1st stage: Congestive general diffuse visceral pain which is
non localized. It also stimulates vomiting via vagus nerve
impingement.
2nd stage: Suppurative. Neutrophils go into another layer.
Inflammation goes outside it will.
All hollow organs outer layer is adventitia but in GIT it is
serosa. Therefore this is neutrophilic.
3rd stage: Gangrenous. Prolonged ischemia
4th stage: Perforated
SIRS: >90HR, >20RR(tachypnea), >38(Fever) or <
36(Hypothermia), >12 Leukocytosis or <4 Leukopenia. You
need at least 2 to conclude you have SIRS. BP not included.
Without identifiable causes of infection.
Sepsis: SIRS plus identifiable cause of infection
BS of appendix is ASIA. Aorta, Superior Mesenteric artery,
Aorta…..
It is more prone to ischemia…
Diagnostic:
Cxr
CBC
BT
Electrolytes
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 1
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
Whole abdomen ultrasound II. Cine Clinics
Topic: Laparoscopic Appendectomy
Imaging: Lecturer: Dr. Richard Velarde-FELLOW, FOCALS
Most important...: PE ad History Review the important surgical anatomy in laparoscopic
Most accurate CT with contrast chole
Share the basic
CRP is recently added to Alvarados scoring Lifted from PALES
Anatomy
CT scan and Uts if equivocal
Pregnant and children we use UTZ if inconclusive do CT
scan.
Gold standard is laparoscopy: EArly recovery and less
scaring
Antibiotics given as prophylactic , empiric are broad
spectrum. Therapeutic t=it is susceptible
To prevent SSI (Surgical Site Infection) 1hr prior OR DOC
Cefoxitin 2g IV 1 hr prior OR for prophylaxis. In WHO it is
given 30 mins prior to OR, if general surgeon …. 1 hr prior
to OR
If no Cefoxitin give …..
Therapeutic AB
Gangrenous and Ruptured Mx as Complicated AP DOC
Ertapinemen for adults, Ticarcillin/Clavulanic Acid for Pedia
it is an extended spectrum penicillin
Alternative: give CoAmoxiclav or 2nd gen cephal plus
metronidazole.
Rocky Davis. We draw an imaginary line from ASIS going to
the umbilicus and then 1/3 from ASIS is the Mcburney’s
point. This is where you put a transverse incision called the
Rocky Davis incision 1-2inches from.
In this case since we are dealing with ruptured
appendicitis. Usually we start with Low Midline incision for
better exposure. When you have a patient with ruptured
appendicitis most likely there will be generalized
peritonitis already
Emergency Appendectomy NPO 8 hrs agad this is not an
elective so NPO agad. ● The gallbladder is a hollow organ, sits in the
NGT is not needed in this case’ gallbladder fossa in the segments 4b and 5
IFC because dehydrated px. ● In adults the gallbladder measures approximately
LTM incision 10 cm in length and 4 cm in diameter when fully
distended
Psoas:.... ● Function is to store and concentrate bile
Obturator : px supine ad flex hip and knee with internal
rotation passive if pain elicited positive.
Planes: Retrocecal, pelvis, postileal , pre ileal
If negative AP after opening;
Still take out the appendix. Explain that appendix is at a
normal looking but still needs to take out it might be the
cause of pain.
Antibiotics given IV …
IV antibiotic is stopped when
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 2
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
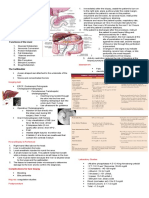
Ducts – cystic, common bile and common hepatic duct
Cystic duct is connected to the GB.
Vasculature – cystic artery
2 approaches in cholecystectomy
· Open
· Laparoscopy – gold standard Advises training
Indication for cholecystectomy institution to do 4 ports, but any number of ports will do
Trauma
Malignancy
Asymptomatic indication would be:
Needed for work
…
Suspected GB malignancy
Choledocholithiasis – is the presence of stone in the bile
duct, most common is type secondary stones.
· The secondary are the most common stones if it
came from the GB
· The primary stones are from the common bile or
common hepatic duct
· If the patient is asymptomatic, the gallbladder is not Team position:
remove The camera operator will be at the left side, the 1st assist
will be at the side of the patient
Cholelithiasis
· Except
o In patients who are diabetic, and they have an
asymptomatic gallbladder disease
o Asymptomatic patients like seafarers, because the
company will require to do the surgery since it will be
difficult to air travel the patient when he is on board
Cholangitis – as impacted stone causing stasis of the bile
in the ampula and it would promote growth of
microorganisms, schedule patients for cholecystectomy
and removal of the stone by ERCP or choledocotomy and
remove GB to prevent recureences
Trauma - Rare. Removed if vasculature affected
Malignancy
Cholecystitis – most common indication
· The presence of stone
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 3
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
cleavage of lines of skin, heal better than incisions
that cross those lines
Trocar placement
· Working port – Rt MCL
· RT AAL port – Assist port Upon entry
· Epigastric port: working port · Limited diagnostic lap
· Umbilical Port: Optical Port o Trocar related injuries
o Status of the gallbladder
o Other intra abdominal pathology
· Position the patient on reverse Trendelenburg
with right side up
· Insert other trocars under direct visualization
Difference of 4 port and 3 port
4 ports
Optical in the umbilicus
3 port
The difference is the 3rd port is placed 1cm under, but they
are still the same
The initial access
· Surgical incisions made along or parallel to the
lines of langer, in the umbilicus, which define natural
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 4
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
· Traction of the hartmann's pouch is done infero
laterally
o Opens the hepato cystic triangle
· Contains the cystic artery “triangle of calot”
Dissection of the peritoneal covering at the infundibulo –
cystic junction using either the ESU or by peeling
1. Separate the liver from the cystic plate
2. -
To prevent biliary duct injury during lap
1. Rouviere's sulcus or right hepatic sulcus.
Dissection above Sulcus
2. 1st portion of the duodenum
CBD is located superiorly
3. Pulsating proper hepatic artery
a. The CBD is located parallel and lateral to the
artery
4. Common bile duct
a. Must be identified if possible
5. Infundibulo-cystic junction
a. Where you see the cystic duct, above the
rouviere's sulcus
b. Where dissection is done
Traction and initial dissection
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 5
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
Some use retrieval bags such as condoms to prevent SSI
Titanium clips are usually used. Hemoclip is also used
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 6
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
III. Lecture
CASE STUDY: “ABDOMINAL PAIN IN ACUTE APPENDICITIS”
WITH DOCTOR MEDINA
BLUE MEANS OCTOBER NOTES
A 30y/o female was admitted due to hypogastric pain >24
hours, LMP: last month with regular menstrual cycle. PE:
stable vital sign, T-38.4 C: abdomen: globular (+) Direct and
rebound tenderness right iliac fossa and hypogastric area
(+) involuntary muscle guarding.
Labs: WBC: 10 000/uL (N-80%, E-1%, B-1%, L-20%, M-5%)
Urinalysis: yellow, ph-5 pus cells 20-25, leukocyte (+), sp.gr Visceral:
- 1.015 ● The receptor of visceral is visceral peritoneum
and that is why when we conduct our surgery
QUESTIONS: (i.e. hernia surgery via local technique/approach,
1. Is this an acute abdomen? whenever I open the sac, I put anesthesia
a. Yes (ans) because that’s part of the visceral peritoneum,
b. No that’s very painful!
2. Does the patient need immediate surgery? ● It has a poor specificity because it has primitive
a. Yes qualities. (Clinical correlation: “If you ask the
b. No (ans) patient ‘Saan ba masakit?’, ‘Where is the most
3. What will be the appropriate management for painful site?’Due to poor localization, they will
this case? use a much bigger way to cover the area such as
a. Broad spectrum antibiotic the hand.)
b. Ultrasound (ans) ● Almost all organs are being covered by visceral
c. CECT Scan peritoneum.
d. Immediate Surgery ● It is vague and dull! Patient usually uses his hand
and touches a huge area.
Let’s suppose that this patient underwent surgery, ● Early stage of acute abdomen
SIDE QUESTION: What is acute abdomen?
- Sudden, abrupt pain, first time experience,
unbearable
- Important: You need to do immediate
evaluation! (mandated/warranted)
- After assessing, doing blood work, you will
decide if it’s surgical or non-surgical
- All surgical abdomen presents as ACUTE
abdomen but NOT ALL acute abdomen are
4. Intraoperative findings of the appendix. What surgical in nature!
will be the manner of administration of
antibiotics in this patient? Somatic:
a. Prophylactic (ans) ● If you ask the patient where the pain is mostly
b. Therapeutic (BUT IN THE CASE OF THE located, the patient can easily point to the
VIDEO THIS IS THE ANSWER) specific area that is in pain. Finger and hand
tests could help us.
● Directly above the organ being addressed (target
organ)
● Acute appendicitis is the best example of
inflammatory pain.
● When you palpate, you create pressure in the
abdomen and this will stimulate pain receptors
in the parietal peritoneum.
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 7
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
These are the sites which represent the specific organs.
Midgut derivatives such as our appendix are found in the
periumbilical area. That’s why the patient says “there is
pain in my umbilicus”.
Hindgut, the remaining transverse colon up to the distal Lungs and myocardium (extraperitoneal organs).
colon and rectal can be found infraumbilical. Those highlighted organs, CONSIDER THEM FIRST.
In order of occurrence!
Organs found in pelvic cavities (presentation is usually at
the back) are difficult to diagnose by history and PE). Somatic pain is more specific.
In our case, RUQ pain, our #1 consideration is the
APPENDIX, #2 Gynecologic problems (affects ovary and
fallopian tubes together with some retroperitoneal organs
like the ureter).
Patients >50 age, consider malignancy (LLQ)
Usually, when we have strangulated hernia, we have a
perforated bowel like in typhoid infection. The tenderness
is at the center. When it’s at the center, the primary
consideration would be a small bowel!
Pain at the back, aorta is highlighted because it is the
most common presentation of dissecting aortic aneurysm.
Shoulder, when you have a ruptured ectopic pregnancy,
the tip of the shoulder is most commonly in pain as your
patient is lying down the blood can touch the diaphragm
which is innervated by your C4 and C5 which is the same
innervation as your shoulders -> There would be
diaphragmatic irritation which would manifest as shoulder
pain.
RUQ pain: Abscess and infusion
In our case “Acute Appendicitis”, midgut would be a
favorite spot initially, this can more or less confirm that Doc’s diaries: Shoulder pain, BP is going down -> Ruptured
you are in the right track of your evaluation. ectopic pregnancy
Retroperitoneal can occupy the renal colic and hindgut.
Manifestation of pancreas is usually at the back.
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 8
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
A patient with a chief complaint of pain the first thing to
ask always includes age. Majority of Acute appendicitis
occurs at less than 30 y/o or middle age group (70 %) will
manifest. Also consider the sex it is more common in
females in some studies it is 22% in female.
Sometimes, you may open the female patients and there is
no appendicitis. They do less imaging in males compared
to females even if the patient has RUQ.
You need to be very cautious in females!
In clinical practice, there are 3 clinical patterns namely:
Colicky, Inflammatory and Ischemic or vascular type.
Colicky: PROGRESSION (CRESCENDO AND DECRESCENDO)
hollow viscus, intermittent & there is a period of normal
phase followed by abnormal, antispasmodic will give relief
since it is secondary to contraction of muscle. Obstructive
in nature, patients like to move!
Inflammatory: PROGRESSIVE! main focus: involvement of
peritoneum (initially visceral peritoneum and parietal
peritoneum) and condition known as secondary Advance age 60> or 70>: variability in the presentation of
peritonitis. Inflammatory type is usually somatic in nature. these patients.
Somatic type of pain are specific & due to contamination We don’t consider acute appendicitis without perforation
chemical or bacterial, intestinal(perforated abscess), in this patient.
preferred not being touched, less no movement ( any Below 50 nonsurgical followed by appendicitis
movement can stimulate the parietal peritoneum and
cause severe pain to the patient). Patient is motionless! 50 and above there is markedly increasing incidence of
abdominal pain secondary to malignancy (tumor) because
Ischemic or vascular type: MOST URGENT CONDITION! of delay diagnosis, do not rely solely with on your Hx & PE
Pain is out of proportion! NEEDS IMMEDIATE AND relay also to CT Scan ( emits radiation)
URGENT ATTENTION. (deprivation of blood supply)Typical
myocardial infarction heart attack and ischemia, heart Pregnancy the gravid uterus different location of appendix
attack posture seen in the movies, grimace and pain out of depending on the AOG. It distorts clinical presentation.
proportion from being felt, vascular type of pain found in Ultrasound is more commonly used to see this. Delay
patient exhibited with obstruction such as Superior would perforation and pregnancy state would lead to fetal
Mesenteric thrombosis, difficult to diagnose, diagnosis rely loss almost 40%
only in diagnostic imaging, associated with systemic signs,
associated with delayed diagnosis, strangulated her Most common acute abdomen condition affecting
pregnancy: Acute Appendicitis (treat patient as if patient
isn’t pregnant; take out source of infection ASAP).
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 9
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
Adults food matter, parasite, adhesion
Children lymphoid hyperplasia
Obstruction increase the intraluminal pressure
CHECK LECTURIO FOR VICIOUS CYCLE OF SIRS
Further increase will initially increase the lymphatic
drainage lead to mucosal compromise; bacteria try to
invade leading to bacterial translocation
The inflammatory cell goes up reflected by CBC or WBC
count
In further progression of the disease itself then it will lead
to infarction, finally perforation with Initially localized
peritonitis and generalized peritonitis. This picture tells
you that the pathophysiology of the continuing process
causes a simple obstruction without any intervention and
eventually the natural cause would be perforation. Some
would have localized forms of peritonitis and some
patients will have generalized peritonitis. Remember that
the danger in generalized peritonitis, that in a matter of
minutes, the infection will now be absorbed in the
systemic circulation and you will enter the cycle of (zehrs,
mots and mohs)?
ASSIGNMENT FOR THURSDAY:
BREAST CARCINOMA
Visceral pain! He will use the hand to localize pain.
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 10
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
As the inflammatory process continues, it will go into likelihood of diagnosing acute appendicitis. So that, the
serosa then trigger somatic fibers. As you palpate the area combination of the series of events with the migration of
or move, it will touch the peritoneal area and the patient pain from periumbilical to the denotes only one thing that
can localize the pain in RLQ. you are dealing with that your patient is actually becoming
forced. So you now need to do something.
The most important symptom of a patient with acute
appendicitis is pain. Let’s correlate the previous formation
events to the manifestation of abdominal pain in our
patient. Because of obstruction, it will lead to distention.
distention will trigger visceral fibers and these will give you
again the visceral type of pain in the early stage of acute
appendicitis. So this will be poorly localized and usually
vague because its midgut derivative organ is felt in a
periumbilical area.
And as the inflammation causes, we already know the Always ask:
lateral cause of patients with acute appendicitis then there IS THIS THE FIRST TIME? The likelihood of diagnosing AP if
would be involvement of the serosa. And now, this will it is.
trigger the (weighing you)? when the serosa that is If the patient says, it is not! This will make a diagnosis have
remarkably touches the parietal peritoneum then the type a big difference.
of pain now would be somatic in origin, and this is being
represented by your patient as the right lower quadrant. What do we do during the preoperative? Of course we
Again, when you still remember the table right lower need to assess. But this time, before we are being thought
quadrant with the first condition that should enter your on how to do a good data gathering of a complete story
mind must be acute appendicitis. and PE. We have to know What is useful information will
lead us to correct diagnosis. So don't ask many questions
because your patient is actually in the midst of pain, he
does not want to be irritated with so many unnecessary
questions, so we must be focused. We were moderately
useful and we got to gather them. but one thing I would
like to give emphasis on would be the Measurement of
accuracy in clinical practice.
You will be encountering the word sensitivity, specificity,
Ask the patient: positive likelihood ratio, positive predictive value, negative
Is the pain more intense now or a while ago? If Yes, you are predicted value. These are the measure of accuracy. so you
already on the right track! High possibility of Acute need to know when to use them.
Abdomen which is SURGICAL in nature! In textbooks there is a table that tells the possible
likelihood ratio of all of the historical features and physical
So the change of the stimulation from the periumbilical or findings and even some laboratory tests, they are all found
the change of site, denotes the classic migration of pain in one table. There is a column under positive likelihood
and this is in progression. So this inflammatory type of ratio that tells you the probability that once they are
pain usually progresses and of course you need to present the patient is likely suffering from acute
intervene now and this is somehow giving a very high appendicitis. but there needs to be a value. a value has to
be more than 1. In clinical practice, the value has to be
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 11
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
more than 10 in considering individual patients, if you DISTENTION is important to ask because it could be
notice there, not a single parameter has been valued guess secondary to ileus (because of the presence of
the highest is 7, that is around wbc >15,000. inflammation).
In that table again, there are so many features like direct,
indirect tenderness, the value is more than 1. They can be,
but they should not be totally relied on individually. That’s
the message of that table. The combination of History and
PE is good, but should not rely totally especially when you
are dealing with a female patient.
For the PE on male, maybe, Rigidity is one of those findings
that has a high likelihood ratio (LR) or positive likelihood
ratio; therefore this can more or less guide us in deciding
whether to open the patient or to do further evaluation
using imaging modality.
RETROILEAL/POST ILEAL - RAREST LOCATION OF TIP OF Rectal examination should not be performed. Unlike
APPENDIX; can be presenting as GUT. If you examine urine before, it has been taught that you have to perform this
is normal, consider the location of the appendix in routinely, but not anymore.
retroileal and do imaging. So, the key word is Focused.
I mention the variability of symptoms; the atypical
presentation would be best because of different
anatomical variation.
Measurement of Accuracy in clinical practice:
-Sensitivity is the True Positive
-Specificity is the True Negative
The most common location is Retrocecal, followed by the
Pelvic (that’s the reason why when you are dealing with Sensitivity that is below 60% and a wide range, this tells
female patients, you have to highly consider Pelvic you that you should not consider that particular
derivative organs, so that has to be part of your evaluation examination.
of Preoperative).
Very low sensitivity 8%, very wide broad range, therefore it
should not be done. NON-RELIABLE. DON’T PERFORM
THESE ABDOMINAL MANEUVERS (accdg kay doc).
That’s the reality. You are now in the evidence based clinic
practice so you have to highly consider evidence when you
are dealing with decision making.
Abdominal signs are already out of the picture. It is very
important that you do not perform them because they can
harm your patients also. They can elicit more pain.
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 12
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
90%. If the CT scan is negative, then don’t operate on that
patient. For the Alvarado, if it’s still negative through a
negative rate of 65%, it really does not have a good
specificity. So your patient might still be having an Acute
Appendicitis even though the score is below 7. That’s the
meaning of it.
Likelihood ratio
Positive likelihood ratio -> ratio to rule in (you have) AP
Negative likelihood ratio -> ratio to rule out AP
It is part of preop evaluation. Doc doesn’t like it though. If it’s more than 1, that's good but the range is one to
infinity. So, the higher you go, the better.
Another Algorithm is the ALVARADO Scoring system
The magic number is 7. Between 2 and 9, 9 is much better.
Anything more than 7 increases the likelihood of you might
be dealing with Acute Appendicitis. In the table that i have mentioned a while ago, the highest
score would be 7 only; but here, CT scan likelihood ratio is
9. It’s really good.
Of course, the lower you go for the negative ratio, the
much better. 0.065 for CT scan, 0.224 for Alvarado score.
The summary.
P Value (P means Probability, P is a test of significance)
For you to say if all these numbers are significant, the P
Value should be less than 5%. 5 divided by 100 is 0.05.
Since the P value is less than 5%, then there results are
NOT significant, and the overall accuracy is 92.6% CT Scan
and 77.5% Alvarado score
Let us know the Sensitivity and Specificity of Alvarado
scoring compared to other diagnostic modalities that we
can use.
A study from King Hussein Hospital, Middle East
It is a prospective study, a good methodology of 320
patients. It was distributed to 196 males, 124 females, and
the average age is 26 years old. They underwent operation,
and the Gold Standard is Histopath.
In that study, the negative appendectomy rate is 14%
(which is considered as acceptable negative appendectomy
rate because the sample is 15%), same as the standard Kay doc, dapat 60% sensitivity or else di niya irerequest.
globally.
Another thing we do during pre op is CBC that's the
These are the results: (in order) Sensitivity, Specificity, favorite of all our residents, CBC and of course urinalysis,
Positive Likelihood Ratio, Negative Likelihood Ratio. It but if you will look at this slide instead of urinalysis CRP
shows there, for the CT scan, the sensitivity indicates that would even give you a much better assessment pre op, bec
there is a chance of Appendicitis (based on the CT scan the sensitivity can be as high as 85% although for
result 94.2%); therefore, you need to operate on that specificity not a good measure because of the wide range,
patient. Because 94% of the time, they are correct. the wider the range you have to reconsider that, or there
should be reservation before you say that your patient is
For those patients who underwent Alvarado scoring, it’s not having any form of inflammation inside the abdomen,
85.4%. So big a difference, almost 10%. For the specificity, so the WBC goes higher the sensitivity decreases, in clinical
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 13
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
practice 60% cut off but here it's only 62%, so I think the 3. Plain abdominal film: Abdominal obstruction
specificity is much more important than sensitivity when
you consider the usefulness of your WBC but in your table DOC:
if you have more than 15,000, I think 7 is the value for Female, abdominal pain, no scars, plain abdominal film
WBC. shows free air -> open
Urinalysis should only be requested if you are entertaining
renal problems.
Pregnancy test is mandatory for all females in their
reproductive age, it is mandatory, do not rely on verbal
response. You have to be objective!
ULTRASOUND SHOULD BE USED IN OUR PATIENT FOR
INITIAL BECAUSE SHE’S A FEMALE (no radiation).
Ultrasound is the favorite of the OB dept and also our dept
specially when we are entertaining pregnancy, so if the
patient is pregnant this is the imaging of choice, look at the
measures of accuracy 90% small range right? and then
specificity 83-95%, so what are the things that you have to
If there is doubt in initial evaluation. Resolved to imaging look for when diagnosing a patient using UZ as your
Radiography to see distention of abd primary imaging modality, the appendix should be
When uncomplicated perforation present as intestinal non-compressible and the lumen has to be more than
obstruction especial with no abd scan, with hx of abd pain. 6-7mm, the presence of appendicolith not fecalith. This is
a calcified, look white on UZ and of course when the
What is the role of imaging pre op? reader tells you there is a presence of "peri something?"
Imaging has to be selective, if there is doubt in your initial we all know that the primary limitation of your UZ is it is
evaluation using your hx and pe and even your initial blood reader dependent and coupled with retrocaecal appendix
work up then you resort to imaging, radiography has no this will more or less bring down the sensitivity of your UZ
role in diagnosing acute appendicitis, you see the range,
this is only done if the pain is more of obstructive in nature Appendicolith - hard, calcified excretion
meaning the involved organ is hollow organ like your small Fecalith - hardened stool
bowel, if you are entertaining intestinal obstruction by all
means do radiography , but let me share with you the
experience in our clinical practice, when you are dealing
with the complicated type of appendicitis like perforation
this will lead to, this will clinically present as intestinal
obstruction especially when you look at the abdomen and
no previous operative scar, so a virgin abdomen with
intestinal obstruction with the pain, with still pain before,
should make you suspect that you are dealing with
complicated type of acute appendicitis so that's the only
value of radiograph to document, if the abdomen is
distended by all means request for plain abdominal
radiograph.
3 things doc consider which leads to >50% acute
appendicitis:
1. AGE
2. HX OF OPERATION (Virgin Abdomen); distended
abdomen with no scar
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 14
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
FAT STRANDING CAN BE SEEN ON CT-SCAN ONLY.
This picture shows an appendicolith, presented with the
solid big arrow, the presence of the appendicolith, you can
see the posterior shadowing 2 appendicolith with the
corresponding shadowing, it is a dilated bowel or some air,
so this confirms the diagnosis via UZ of acute appendicitis
You can see the appendicolith!
Another way is non-compressible appendix as you can see
the lumen, that is the lumen of the appendix, the criteria is
more than 6mm or more than 7 mm, here it measures 1cm
or 10mm, and another observation is the thicken
appendiceal wall with 3mm in thickness, so this can
confirm the diagnosis of acute appendicitis
Dilated Cecum
Comes with radiation!
Positive predictive value tells you the chance you are
dealing with an AP post op.
Positive predictive value like in mammography higher
specificity of microcalcification but only 10% positive
predictive value.
PPV is important in diagnosing px.
Fat stranding refer to inflammatory processes
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 15
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
The last is the use of Laparoscopy. This is very
advantageous – you do this especially in situations in
which the picture is so obscure. Resolution – to see is to
believe – there is direct visualization through laparoscopy.
High risk aerosolized generating procedure! Can contribute
for transmission of COVID-19 airborne.
When you perform open for AP, you always have to
remove the appendix but in MIS, there is a choice NOT to
remove the appendix esp. If it turns out to be ovarian cyst
(normal looking appendix), deal with pathology.
If you do open, Rocky-Davis incision, take out the
appendix.
More advanced AP Fat stranding there is marked ACTUAL PATIENT:
inflammation with abscess. You have to send px to the This is a case of a 30 year old female who presented with
operating room. abdominal pain initially. Patient was having pleuritic pain,
presenting with RUQ. She was treated differently
More advanced AP Fat stranding there is marked conservative and then the Px developed dyspnea and then
inflammation with abscess. You have to send px to the there was pain with RUQ. Hepatobiliary but also lung is
operating room. included.
We also have MRI in our institution – look at the sensitivity Chest X Ray was done with a result of massive effusion -
of the MRI compared to CT Scan, they are almost the >50% of lung is obliterated with fluid. They were referred
same. What is good about MRI is that it has no Radiation to surgery.
so you can do this on a pregnant patient if the ultrasound There was also generalized tenderness (rigidity) on the
is inconclusive – it’s not operator dependent and you can abdomen. The team decided to do a Diagnostic
see the positive predictive value of 92% and negative laparoscopy (VIDEO).
predictive value of 99.7%.
The only limiting factor of MRI is its cause. And it is not
also for claustrophobic people because a slight movement
will distort the image.
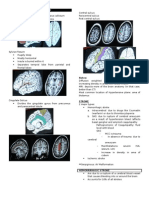
This is an example of a coronal view of MRI – you can see
here a fluid filled appendix. Anatomical location is very
clear if you do the MRI.
Axial view – Arrow pointing to the fluid filled appendix
which confirms the diagnosis.
Part of the pre operative assessment would be forming a
The 21st century entails use of imaging selectively. You
lot of differential diagnosis. The most important here is
don’t use this routinely.
gynecologic. 32% of the location of the tip of the appendix
is found in the pelvic area and this can confuse the surgeon
or the initial evaluator.
Standard of care is Appendectomy. We all know that
laparoscopic now is seen to be more advantageous than
open because as you witnessed a while ago, you make a
small incision – if you do that using the open technique the
incision would be from xiphoid down to the pubis.
One of the basic principles in surgery is – Exposure.
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 16
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
You can see a 1cm incision in the umbilicus, leading to the
exploration of the entire abdomen. That’s the Diagnostic
Laparoscopy
Appendectomy addresses the principle of bacterial
peritonitis – source control. Take off the source of
infection, that’s the principle.
The other principle is treatment – Antibiotics
MAINTENANCE: 2L PER DAY
So, we label now our diagnosis based on the Actual case!
Intraoperative findings, whether uncomplicated such as Suppurative with fibrins
(this particular appendix).
Pinkish Appendix – congestive
Fibrins and Reddish – suppurative
Complicated – which you have witnessed a while ago.
Intraoperatively, you need to label whether your patient is
having an uncomplicated or complicated case. And of
course, the giving of antibiotics is based on the .. college of
surgeons evidenced based clinical practice. Guidelines for
uncomplicated, you just give it as prophylaxis. Principles of
prophylactic administration – you have to review them
because they are very important.
And then of course, for the complicated, you have a
different shift from a more broader antibiotic and a more
potent one and (Tapenem?) is the first line for your
information and of course the duration is up to 1 week –
that’s the maximum.
Ertapenem is the first one max of one week max.
FF up:
1 week after
1 month after
To check for recurrence of SSI
Assess/monitor:
1. Monitor urine output -monitor every hour
There would be huge or tremendous loss of
fluids in the 3rd space. Tea colored means
concentrated
2. The site of the wound
3. Intra abdominally bowel moves 3-4days
4. Px released from the operating room with Ngt -
check if properly placed and know the content
that comes out.
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 17
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
5. Monitor if there would be abdominal distension -
with ngt there should be no distention
AP is life threatening because it can lead to sepsis
Appendectomy is the most commonly performed
operation secondary to trauma
Most common non-traumatic condition: Appendicitis
(second is gallbladder)
Algorithm by PSGS
- Telemedicine approach
- The patient and the doctor are separated by a
glass to avoid airborne transmission
- Both Wearing of mask
- Until now we only cater what is urgent and life
threatening
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 18
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
No aerosolized generating procedure - we use level 3 PPE
In AP we do gen anes in open or lap. Lap is now a
secondary priority. Wear the highest level of PPE level 4.
MONA
Less Hx we rely more on imaging.
Examination is subjective! You don’t want to do operation
via hx and pe only.
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 19
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
Success rate is 50% if with appendicolith
Grade 2, Obese patient, intubated, bombared antibiotics
There is resumption of GI tract. First Successful
conservative management of AP.
4-6 contrast enhanced CT. Non operative bombarded with Percutaneous drainage if toxic to remove microorganism
antibiotic present (If patient is toxic, ultrasound guided).
7-10 do Open CT scan percutaneous drainage to remove microorganism
in the abdomen
Complicated Appendicitis the risk for morbidity and
mortality increase
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 20
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
3 division of ward
1. COVID ward : (+) COVID PCR 2.PUI-ANSWER
4. Use of drain in Appendectomy should be discourage.?
The principle of drainage is to drain locally(only the area
involved)
If you have mass from pelvic to subhepatic space. Drainage
will not serve the purpose; the drainage will be foreign
body harboring more infection.
I will not use intra abdominal drainage.
Friable base I could probably place drain near the ileocecal
area creating controlled fistula.
Abdominal area has so many compartments used in
pancreatic infection(use drains) but not usually is AP
Drain use for local infection
General infections drain will not serve its purpose
Additional set- up: ULPA (ultra-low particulate air) filter,
HEPA (high frequency particulate air), Vacuum Lecture
Case discussion
QUESTIONS: A 24 year old female was admitted due to hypogastric pain
1. Mas maganda if one group of drug; if there’s > 24 hours. LMP: last month with regular menstrual cycle.
availability, then you can! Clinical improvement is PE: stale vital signs, Temp: 38.4֩ C; abdomen: globular, (+)
the main dictator on when to stop your direct and rebound tenderness right iliac fossa and
antibiotics. Govt institution - do less ideal but hypogastric area, (+) involuntary muscle guarding.
still safe and acceptable. If the patient is hungry, Laboratories: WBC- 10,000/ uL (N-80%, E- 1%, B-1%,
then there is GI resumption. L-20%, M-5%),
2. urinalysis: yellow, ph-5, pus cells- 20-25, leukocyte (+), sp.
Gr.- 1.015
MGA INISKIP NI DOC: If VS becomes unstable and with abd consider aneurysm
Globular not meaningful but distended is meaningful
Drainage if toxic to remove microorganism present
1.Arcofeola (meandering artery) will have ischemic AP Not
all but possible in can more or less delay.
The value of focus history resolve to other imaging
modalities
High index of suspicion is needed. Answer:
Treat patients more rather than laboratories CECT is more specific provided stable and not pregnant Px
Management for Female Non-pregnant patient
Should we treat it cumulative?
The message of the table is you can’t solely rely on one 1. CECT scan
diagnostic 2. Broad spectrum antibiotics
Manner of antibiotic administration depends on the result
2. Table in Schwartz how would we treat as cumulative or of CT scan
dependent
Summary of the table cannot solely rely,does not totally 2. What will be the matter of administration of antibiotics
relay and resort to other approach for diagnosis in this patient?
a.) Prophylactic
Individually di pwede. If cumulative, better. b.) Therapeutic
Imaging will help
3. Patients will undergo emergency appendectomy with a Answer:
pending COVID19 result, where should we put them Prophylactic
post-operatively in the COVID ward or regular ward? ● Broad-spectrum antibiotics can be part of the
management.
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 21
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
● I would suggest first CECT before giving this if the o Abdominal signs are of no use
patient is not pregnant. ● Alvarado score: >7 increases likelihood
● If in case, you are going to give antibiotics, o Due to the pandemic, there is a new
always start with Prophylaxis. approach: Alvarado Score with CT scan.
● The answer to this will depend on CT scan if with ● Clinical assessment
abscess give immediately antibiotic as ● HIGH RISK GROUP: Ultrasound, CT scan, MRI,
Therapeutic rather than Prophylactic and carry Diagnostic laparoscopy
this on. o During pre-operative assessment Identify
● If there is really abscess or perforation detected high risk groups such as females, advanced
by CT scan then you have to continue this age, pregnant. In this group you can’t
further. totally rely only on focus history and PE.
● It is very important to consider these things in You have to make things clearer by the
making a decision from general data upto selective use of ultrasound, CT scan,
utilization. sometimes MRI and when indicated
Key Points invasive procedures. Now in the days of
● Obstruction= progression of pain. pandemic they prefer Open but because of
o Initiating event would be obstruction. good et up like negative pressure room,
o Since the obstruction is kinda permanent smoke evacuator during lap then it is
would result in the progression of pain already feasible to perform laparoscopic
such as migration of pain very important. examination. You got to protect yourself
● Historical features: RLQ pain, migration of pain, and other health care worker by using
pain precedes vomiting, no history of prior appropriate PPE level 4.
similar pain. ● Surgery mainstay: Open vs laparoscopy
● Physical features: RLQ tenderness, rigidity, pain ● Antibiotics prophylactic vs therapeutic
at McBurney’s Point ● Conservative treatment selected cases.
o If male not request CT scan I would do o If grade 2 then you can try
diagnostic lap or proceed with lap o If a patient is covid positive and is exposed to
appendectomy surgery the mortality rate goes up. Save life
● Psoas, Obturator, Rovsing sign???
not only take out the Appendix. o tachycardia >90 beats/minute
o tachypnea >20 breaths/minute
o leukocytosis >12*10^9/l or leukopenia
<4*10^9/l.
● Age and sex
● Female
● Hypogastric pain possible location in pelvic area.
● Pain with tenderness
● VS is stable if unstable aneurysm and ruptured
ectopic pregnancy
● Fever score of 1 meaning there is inflammatory Kartagener Syndrome if the appendix is on the left side
reaction ongoing rather than right.
● SIRS was defined as fulfilling at least two of the Left side atypical resort to imaging. The CT scan will help
following four criteria: you in these findings.
o fever >38.0°C or hypothermia <36.0°C
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 22
PUSTAHAN GROUPMATES (SURGERY ROTATION 2: OCT 2020)
Dictum Transcribed by the future PGIs of January 2021
When in doubt Open but now when in doubt assess SRT INT JRT LAV JST MDT JT MLT MAT
further using imaging. ·
The atypical presentation would prompt you more on
imaging modalities or diagnostic laparoscopic.
Pleural effusion on right but with tenderness on the left
Transcribed by the future PGIs of January 2021
SRT INT JRT JT
PGI BY JANUARY 2021, GOD’S WILL! 23
You might also like
- Contraception - Medrevision NotesDocument22 pagesContraception - Medrevision NotesswamysamsonNo ratings yet
- EMERGENCY CASE REPORTSDocument15 pagesEMERGENCY CASE REPORTSashyNo ratings yet
- High Yield General Surgery Topics PDFDocument85 pagesHigh Yield General Surgery Topics PDF1031 Muhammad zaryabNo ratings yet
- Benazir Bhutto Hospital, Surgical Unit-Ii Final Year Ward TESTDocument6 pagesBenazir Bhutto Hospital, Surgical Unit-Ii Final Year Ward TESTHassan Ahmad100% (1)
- CHOLANGITISDocument7 pagesCHOLANGITISWill GutierrezNo ratings yet
- 4206 CR 1Document3 pages4206 CR 1Ardianto SucintaNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-12-11 at 9.52.48 PMDocument3 pagesScreenshot 2023-12-11 at 9.52.48 PMAhmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Abdominopelvic Ectopic Spleen With A Comprehensive Imaging Examination: A Case ReportDocument6 pagesAbdominopelvic Ectopic Spleen With A Comprehensive Imaging Examination: A Case ReportceciliaNo ratings yet
- DAILY-ENDORSEMENT-Oct 21, 2020Document25 pagesDAILY-ENDORSEMENT-Oct 21, 2020Apmc SchwartzNo ratings yet
- Primary Congenital Choledochal Cyst With Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case ReportDocument6 pagesPrimary Congenital Choledochal Cyst With Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Case ReportRais KhairuddinNo ratings yet
- Incidentally Exploration of The Fusiform Cystic Duct 2024 International JourDocument4 pagesIncidentally Exploration of The Fusiform Cystic Duct 2024 International JourRonald QuezadaNo ratings yet
- Blunt Abdominal Trauma Case ReviewDocument3 pagesBlunt Abdominal Trauma Case ReviewGio Tamaño BalisiNo ratings yet
- Doctors in the Making: Introduction to General SurgeryDocument2 pagesDoctors in the Making: Introduction to General SurgerysammyNo ratings yet
- Use Only: Investigating A Rare Cause of Intestinal OcclusionDocument2 pagesUse Only: Investigating A Rare Cause of Intestinal OcclusionDannyMichelleNo ratings yet
- End of 4 Year OSCE - SurgeryDocument53 pagesEnd of 4 Year OSCE - SurgerySyed Irfan ArifNo ratings yet
- Case: Exploratory Laparotomy, Appendectomy: Presented By: Panelo, Joe Francis, RNDocument16 pagesCase: Exploratory Laparotomy, Appendectomy: Presented By: Panelo, Joe Francis, RNKvothe EdemaRuhNo ratings yet
- Basic Ercp InterpretationDocument19 pagesBasic Ercp Interpretationhoneyworks100% (2)
- Duodenal Injury PCNLDocument3 pagesDuodenal Injury PCNLAkhmad MustafaNo ratings yet
- ParacentesisDocument18 pagesParacentesistsnim saadNo ratings yet
- Surgery NotesDocument200 pagesSurgery NotesJasneet SinghNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain MARS 2.0 - Dr. Siswidiyati, SP - RadDocument34 pagesAbdominal Pain MARS 2.0 - Dr. Siswidiyati, SP - RadarifdeathsciethNo ratings yet
- Notes in RLE FebruaryDocument2 pagesNotes in RLE FebruaryShainnie IsmaelNo ratings yet
- Diseases of Rectum and Anal CanalDocument68 pagesDiseases of Rectum and Anal CanalKoridor Falua Sakti Halawa 21000063No ratings yet
- 0 Yazan Mini-OSCE Others and ToolsDocument68 pages0 Yazan Mini-OSCE Others and Toolsmoyasserayoub78No ratings yet
- WWW Mcqsurgery ComDocument4 pagesWWW Mcqsurgery ComSajag GuptaNo ratings yet
- Todani IVDocument3 pagesTodani IVJoshua Patrick MuljadiNo ratings yet
- Oral SURGERY REVALIDA1Document27 pagesOral SURGERY REVALIDA1Bea Y. Bas-ongNo ratings yet
- Lecture-25 Cesarean SectionDocument21 pagesLecture-25 Cesarean SectionMadhu Sudhan PandeyaNo ratings yet
- SGD AppendicitisDocument11 pagesSGD Appendicitisนีล ไบรอันNo ratings yet
- LESSON 6 Physiological Variables That Influence LaboratoryDocument5 pagesLESSON 6 Physiological Variables That Influence LaboratoryAlthea EspirituNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology - DiverticulaDocument1 pageGastroenterology - DiverticulaEugen MNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology - DiverticulaDocument1 pageGastroenterology - DiverticularaNo ratings yet
- Surgery Extra NotesDocument2 pagesSurgery Extra NotesrohalawiNo ratings yet
- Sept 2019 RecallsDocument18 pagesSept 2019 RecallsAbdullah Mohammad Ibne HaiderNo ratings yet
- Hepatic Subcapsular BIloma A Rare Complication of Laparoscopic CholecystectomyDocument4 pagesHepatic Subcapsular BIloma A Rare Complication of Laparoscopic CholecystectomyIndra PrimaNo ratings yet
- Functions and anatomy of the small intestineDocument8 pagesFunctions and anatomy of the small intestineErald PaderangaNo ratings yet
- Penetrating Abdominal Trauma Emergency ManagementDocument29 pagesPenetrating Abdominal Trauma Emergency Managementanjali singhNo ratings yet
- Successful Surgical Management of An Extrahepatic Biliary CystadenocarcinomaDocument4 pagesSuccessful Surgical Management of An Extrahepatic Biliary CystadenocarcinomaVlad IchimNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Truama (Handout)Document6 pagesAbdominal Truama (Handout)Ayuub AbdirizakNo ratings yet
- Surgery Class Biliary System SurgeryDocument69 pagesSurgery Class Biliary System SurgeryKashif BurkiNo ratings yet
- Surgery Notes Yr 4Document31 pagesSurgery Notes Yr 4Razeen RiyasatNo ratings yet
- Management of Abdominal Trauma: By: Chong Lih YinDocument71 pagesManagement of Abdominal Trauma: By: Chong Lih YinRakaNo ratings yet
- Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in A Young Male PatientDocument4 pagesRuptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm in A Young Male PatientKristanto Ayomi Ayomi AriNo ratings yet
- Obturator Hernia6Document3 pagesObturator Hernia6Ioana DumitraşcuNo ratings yet
- Gastric Perforation by A Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in An AdultDocument5 pagesGastric Perforation by A Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in An AdultStereo PodNo ratings yet
- Gastric Perforation by A Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in An AdultDocument5 pagesGastric Perforation by A Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt in An AdultStereo PodNo ratings yet
- Gastric PerforationDocument5 pagesGastric PerforationReyhan AristoNo ratings yet
- Penetrating Abdominal Trauma ManagementDocument27 pagesPenetrating Abdominal Trauma ManagementhoangducnamNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Guidelines for MIS-CDocument8 pagesPediatric Guidelines for MIS-CSaima UmairNo ratings yet
- Jurding 1Document7 pagesJurding 1Yuda DanangNo ratings yet
- Sign up to receive weekly anaesthesia tutorialsDocument8 pagesSign up to receive weekly anaesthesia tutorialsDwiyanti OktaviaNo ratings yet
- Usmleworld NotesDocument181 pagesUsmleworld NotesAaiza AamerNo ratings yet
- Observations on Types and Treatment of GoiterDocument7 pagesObservations on Types and Treatment of GoiterIGNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Infectious Diseases: Anshuman Pandey, Shakeel Masood, Namrata P. AwasthiDocument3 pagesInternational Journal of Infectious Diseases: Anshuman Pandey, Shakeel Masood, Namrata P. Awasthijohanna monsalveNo ratings yet
- Review of Ortho QuestionsDocument33 pagesReview of Ortho QuestionsMohammadSaebNo ratings yet
- Data Interpretation: Additional Resources: Section1: Interpreting Abdominal Radiographs Systematic ApproachDocument17 pagesData Interpretation: Additional Resources: Section1: Interpreting Abdominal Radiographs Systematic ApproachRaju NiraulaNo ratings yet
- PancreatitisDocument59 pagesPancreatitisAarif RanaNo ratings yet
- Liver DiseasesDocument66 pagesLiver DiseasesDONALD UNASHENo ratings yet
- LESSON 6 Physiological Variables That Influence LaboratoryDocument5 pagesLESSON 6 Physiological Variables That Influence LaboratoryAlthea EspirituNo ratings yet
- Accessory OrgansDocument6 pagesAccessory OrgansNadia AbdurasidNo ratings yet
- Vartes Io-A2 Final VersionDocument94 pagesVartes Io-A2 Final VersionAlex CastelNo ratings yet
- Histology of the Urinary SystemDocument48 pagesHistology of the Urinary SystemNel TinduganiNo ratings yet
- Episode ListDocument33 pagesEpisode ListAbdulMoiz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Neuroelectronic Interface Drug DeliveryDocument3 pagesNeuroelectronic Interface Drug DeliveryAbilash muraliNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Exercise Prescription in Stroke RehabilitationDocument27 pagesAerobic Exercise Prescription in Stroke RehabilitationDaniel Alberto Murillo ArcilaNo ratings yet
- Acute and Chronic Response To Exercise in Athletes The "Supernormal Heart No Ovlidar 2017Document21 pagesAcute and Chronic Response To Exercise in Athletes The "Supernormal Heart No Ovlidar 2017Cristian YanezNo ratings yet
- Arab Board 2017 Internal MedicineDocument37 pagesArab Board 2017 Internal MedicineAFAQ MAMMEDZADENo ratings yet
- 2018 Regional Schools Press Conference Cliniquing Participant InfoDocument1 page2018 Regional Schools Press Conference Cliniquing Participant InfoRebecca MaderalNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs - WsDocument45 pagesCardiovascular Drugs - WsCowox Post PartumNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Test - QuestionsDocument5 pagesAnatomy Test - QuestionsNom NomNo ratings yet
- NeuroradiologyDocument11 pagesNeuroradiologysarguss14100% (2)
- Why 360j Clinical OverviewDocument8 pagesWhy 360j Clinical OverviewPepperNo ratings yet
- Hemodynamic Monitoring Pocket CardDocument5 pagesHemodynamic Monitoring Pocket CardFitz JaminitNo ratings yet
- 5-HT Modulating Drugs, Drugs For Migraine (PH 1.16)Document13 pages5-HT Modulating Drugs, Drugs For Migraine (PH 1.16)shruti sangwanNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument2 pagesPulmonary Function TestsSafuan Sudin100% (1)
- SVT PresentationDocument39 pagesSVT PresentationReinsy NoviNo ratings yet
- Therapy: Dr. Ravinder Narwal MPT Cardiopulmonary MPT-OrthoDocument27 pagesTherapy: Dr. Ravinder Narwal MPT Cardiopulmonary MPT-OrthoRavin NarwalNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Biomarker PresentationDocument29 pagesCardiac Biomarker PresentationMohana PreeshaNo ratings yet
- Perioperative Fluid and Electrolyte ManagementDocument45 pagesPerioperative Fluid and Electrolyte ManagementRobby_CassanovaNo ratings yet
- Life of A Cerebral Palsy PatientDocument5 pagesLife of A Cerebral Palsy PatientRathimalar MogarajaNo ratings yet
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument196 pagesDeep Vein ThrombosisCismaru Mirela Veronica0% (1)
- JCI Library Measurable (STROKE)Document204 pagesJCI Library Measurable (STROKE)dewi ratna sariNo ratings yet
- Systemic Medicines Taken by Adult Special CareDocument10 pagesSystemic Medicines Taken by Adult Special CareAlistair KohNo ratings yet
- Cor Pulmonale - Introduction To Cor Pulmonale, Etiology and Pathophysiology of Cor Pulmonale, Epidemiology of Cor PulmonaleDocument18 pagesCor Pulmonale - Introduction To Cor Pulmonale, Etiology and Pathophysiology of Cor Pulmonale, Epidemiology of Cor PulmonaleRicky SpideyNo ratings yet
- 3.thorax Gross SpottersDocument55 pages3.thorax Gross SpottersDharam Pal100% (1)
- Fluid and Electrolytes Report!!Document20 pagesFluid and Electrolytes Report!!Marivic DianoNo ratings yet
- Radcliffe EducationDocument4 pagesRadcliffe EducationSherwin Buenavente SulitNo ratings yet
- نوت های مهمDocument159 pagesنوت های مهمnegarNo ratings yet
- Medical Colleges Anatomy Course OutlineDocument4 pagesMedical Colleges Anatomy Course OutlineEthel May GranilNo ratings yet