Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Screenshot 2023-12-11 at 9.52.48 PM
Uploaded by
Ahmed Mahmoud0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views3 pagesScreenshot 2023-12-11 at 9.52.48 PM
Uploaded by
Ahmed MahmoudCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
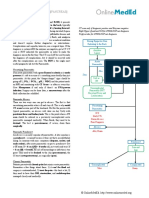
Hepatobiliary Gold Standard
Disease Gold Standard Diagnostic Tool Gold Standard Treatment
Symptomatic US: shows echogenic gall stones with acoustic Laparoscopic cholecystectomy: is the appropriate
Chronic shadows, target sign, little or no GB wall treatment for ALL patients with symptomatic with
calcular thickening or other evidence of cholecystitis gall stones, not for asymptomatic except 5
cholecystitis Lab: all normal (calcified, stone >3 cm, SS, DM
Acute Best diagnostic: HIDA scan Initial mx: hospitalization, IV fluids, antibiotics
calculous Most commonly done: US GB stones, GB wall If Mild\responsive: do either
cholecystitis thickening, peri-cholecystic fluid, sonographic 1-Early Approach: within 72 h. do LC
murphy sign 2-Delayed Approach: after 6 w. do LC
Note: CT done for acute abdomen is less If Complicated\failed medical treatment:
sensitive to detecting stones 1-Emergency cholecystectomy
Lab: leukocytosis 2-Percutaneous cholecystostomy
Acute HIDA scan
acalculous
cholecystitis
Choledoco- US GB stones, If dilated intrahepatic biliary TREAT THE CAUSE
lithiasis radicles proceed to MRCP 2ndry: cholecystectomy
Lab elevated Alk ph, bilirubin (total&direct), TREAT THE SYMPTOMS; STONES
slight increase LFT <1cm ERCP
>1cm CBD exploration, cholecystectomy
PREVENT STONE RECURRANCE IN BILIARY DILATAT
<1.5 cm: no bypass
>1.5 cm: Bypass; choledoco-jejunostomy
\duodenostomy (dilated=stasis=more stones) + I
bypassed sphincter of Oddi so, cholecystectomy
If 1ry usually large, single stone: due to stricture
CBD exploration, Bypass the stricture:
choledoco-duodenostomy, cholecystectomy
If 2ndry usually small, multiple stones:
ERCP or CBD explore على حسب, cholecystectomy
Gall stone IO diagnosis Exploratory laparotomy remove the stone by
ileus milking it back to enterotomy, search for other
stones, cholecystectomy, close the fistula
Ascending Clinical: Charcot triad, Reynaud triad Initial: NPO, fluids, analgesic, ICU, IV antibiotics
cholangitis Lab: leukocytosis (ciprofloxacin and metronidazole OR tazocin) for
Definitive diagnosis: ERCP\PTC level of gram -ve bacteria
obstruction, bile culture, stone or foreign body If no improvement: ERCP\PTC
removal, draining catheter insertion If cause is stent: stent removal and replacement
US and CT: may reveal gall stones and biliary + Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
dilatation
Biliary [MRCP] initial imaging of choice; identifies If diagnosed intra-operative: open and repair
stricture biliary anatomy and associated vascular injuries If simple injury: ERCP + stent
US initial imaging; collection\biliary dilatation If clip injury: proximal PTC decompression
CT/MRI bile collection for percutan. Drainage If delayed diagnosis: 8-week temporization, PTC
HIDA for ongoing biliary leaks nutrition and sepsis control meanwhile, repair.
OPERATIVE REPAIR= debridement + roux-en-Y
hepatico-jejunostomy + tension-free mucosa
anastomosis
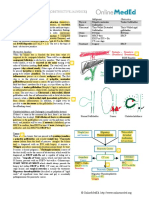
Gall bladder Incidental in cholecystectomy specimens (1\3) Adjuvant chemotherapy +
cancer Stage I,II: gall stone symptoms If suspicious before LC: open cholecystectomy
Stage III,IV: weight loss, CBD obstruction If Tis \ T1a: LC with cystic duct -ve margins
US thickening, irregularity, polypoid, porcelain If T2: radical cholecystectomy; GB, GB liver bed,
hepato-duodenal ligament, para-duodenal,
peripancreatic, hepatic artery, caeliac LN
If metastatic\T3\T4N: more radical resection
If jaundice: palliation by endosc. Or surgical stent
If duodenal obstruction: bypass
Cavernous US can tell the dx, if you want to make sure: NO TREATMENT
Hemangioma CT arterial phase: peripheral then central NO malignant potential
enhancement venous phase: complete filling or Stop contraceptive pills
enhancement If severe symptoms/complications/to exclude
MRI features as CT malignancy = surgical resection
Note: biopsy is contra-indicated
Focal nodular US+Doppler mass+ central feeding artery can NO TREATMENT
hyperplasia tell the dx, if you want to make sure: NO malignant potential
CT arterial phase: enhancement (central artery) Stop contraceptive pills
but scar is hypodense venous phase: wash-out If severe symptoms/complications/to exclude
MRI features as CT malignancy in doubtful patients = surgical
Biopsy to reassure the patient resection for frozen section biopsy
Liver cell MRI best tool: sensitive to fat & hemorrhage, Stop contraceptive pill: can causetumor regression
adenoma heterogeneity of single intensity If <3 cm: follow up, stop OCP & pregnancy
US or CT If >4 cm, doubtful, symptomatic: liver resection
HCC Triphasic CT If child A: liver resection
Early enhancement, early wash-out If Milan criteria: liver transplant
US, MRI, metastatic workup by X-RAY & PET If solitary <3 sm: local ablation
AFP: >200: suggestive >2000: diagnostic If inoperable: palliative; TACE(best), local radio,
targeted chemo(sorafenib), systemic chemo,
ethanol, arterial ligation
Liver US CT or MRI If inoperable (usually): palliat chemo; syst. or local
metastasis If Colon, GIST, Neuroenocrine: resection
Autoimmune 1-CT or MRCP or ERCP
Pancreatitis + either
2-Positive serology: IgG, IgG4 OR
3-Pancreatico-biliary/extra-pancreatic findings
Sialadenitis, nephritis, pneumonitis
Acute Two of the following 3 criteria (Atlanta 2012) If Mild to Mod: Supportive measures, nothing per
Pancreatitis 1-Abdominal pain (its characteristic features) mouth for 1-2 days, hydration and IV fluids (in
2-Lipase/Amylase ≥ 3 times (lipase is better) absence of CVS disease), pain (meperidine
(BUT don’t indicate severity, prognosis, >morphine), ERCP (in CBD stones), correct alcohol
complications) (1+2 are the mainstay of + Ca + triglycerides + drugs affecting the pancreas
diagnosis) If more severe: peripancreatic fluid, peripancreatic
3-Imaging characteristic of acute pancreatitis pseudocysts, pancreatic necrosis, renal,
if mod to severe, unclear diagnosis, no respiratory, circulatory complicatons
improvement, biliary pancreatitis Aggressive mx, ICU admission, parenteral feeding,
CT with IV: fluid collection, pseudocyst, necrosis ERCP in biliary pancreatitis
if mild, biliary pancreatitis (MRCP) OTHERS
MRI with gadolinium: fluid collection, If necrosis: parenteral not enteral feeding, surgical
pseudocyst, necrosis debridement, percutaneous pus drainage
US: Hyperechoic, enlarged, GB or CBD stones If systemic inf. response syndrome or sepsis,
MSOF, extra\pancreatic infection, increased CRP:
(EUS can be used as tx to stones + ERCP at the Antibiotics; imipenem, meropenem, fluoroquinolo
same time ) If cyst = <4w: percutaneous drain not? VARD
>4w: EUS drainage ± ERCP (look book algorhithm)
If biliary pancreatitis: LC to prevent recurrence
Pancreatic Lab Routine, bilirubin (total/direct), APh & GGT, CANCER HEAD PANCREAS
cancer CA19 – 9, CEA, CA 125 Whipple Operation only hope for cure
Imaging to assess lesion cancer head & tail We remove6: distal stomach, duodenum, proximal
Multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT) jejunum, head of pancreas, ampulla of Vater, CBD
pancreatic protocol = gold standard dx & stage + pancreatico/hepatico/gastro-jejunostomy
Resectability: invasion of PV, SMV, SMA, CA If Resectable no distant mets, no SMA contact, no
Staging: liver mets, LN invasion SMV or portal contact
+If cancer head, assess jaundice by =Whipple
US then can do CT, MRCP If Borderline no distant mets, SMA contact <180 ,
Note: no role for biopsy except If metastatic/ reconstructable SMV or portal contact
unresectable before chemo not percutaneous =Neoadj Chemo, reassess by MDCT then Whipple
but by: ERCP or EUS guided biopsy If Unresectable distant mets, SMA contact >180 ,
If extra-pancreatic mets are questionable= PET non-reconstructable SMV or portal contact
ﻣن اﻻﺧر =Palliate: Pain by narcotics or caeliac neurolysis
Cancer Head: US for jaundice then MRCP Biliary obstruction by ERCP, PTC
MDCT pancreatic protocol for the tumor Gastric outlet obst. by stent\gastro-jejunostomy
Cancer Tail: CANCER BODY AND TAIL PANCREAS
MDCT pancreatic protocol for the tumor Distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy
Pancreatic Surgical resection
Neuroendocri
Simple liver May be slight LFT elevation If asymptomatic: observation
cyst US or CT homogenous, uniform, thin-wall If symptomatic: laparoscopic deroofing
Polycystic More LFT elevation, RFT elevation If asymptomatic: observation
liver US or CT multiple cysts If symptomatic: laparoscopic deroofing +
fenestration OR involved segment resection
Rare: transplantation
Choledochal MRCP most diagnostic Segmentectomy or Lobectomy
liver cyst CT or US If cholangitis: antibiotics
If large cyst: US or CT guided aspiration
(temporary)
Can do liver transplantation
Hydatid cyst Eosinophilia 40% Surgery definitive treatment + peri-operative
US larger cyst, daughter cysts, scolices medical treatment (roof top incision)
CT monolocular cyst + peripheral calcifications If small, accidentally discovered: Medical by
+ attenuation , (water lily sign) albendazole, mebendazole can be curative
X-Ray, cansoni test: not used If unfit for surgery, recurrent: PAIR; controversial
PAIR contraindications: very superficial cyst,
inaccessible + medical 4d before and after surgery
(1m albendazole, 3m mebendazole)
Amoebic liver Anemia, increased WBC and bilirubin, amoeba If early: Metronidazole 800, 3 per day, 10 days
abscess in stool If pus: US guided aspiration
US, CT, sigmoidoscope (lesion specific for
ameba)
Pyogenic liver US or CT multilocular cystic lesion Broad spectrum antibiotics until the result of C&S
abscess Aspiration; pus : culture and sensetivity US guided aspiration, if failed: open drainage
وﺗﻘﺑﻠﮭﺎ ﻛﻠﮭﺎ ﺑﻘﺑول ﺣﺳن ﯾﺎرب اﻟﻌﺎﻟﻣﯾن،اﻟﻠﮭم اﺟﻌل أﻋﻣﺎﻟﻧﺎ ﻛﻠﮭﺎ ﺧﺎﻟﺻﺔ ﻟوﺟﮭك اﻟﻛرﯾم وﻻ ﺗﺟﻌل ﻷﻧﻔﺳﻧﺎ وﻻ اﻟدﻧﯾﺎ وﻻ ﻟﺷﯾطﺎن ﻣﻧﮭﺎ ﺣظ وﻻ ﻧﺻﯾب
You might also like
- Hepatobiliary Notes 2.0Document18 pagesHepatobiliary Notes 2.0Sri VathanahNo ratings yet
- CholelithiasisDocument8 pagesCholelithiasissaranya amuNo ratings yet
- Investigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceDocument38 pagesInvestigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceUjas PatelNo ratings yet
- OCT 5 (Ward, Lap, Abd Pain)Document23 pagesOCT 5 (Ward, Lap, Abd Pain)Stephanie TrigsNo ratings yet
- General Surgery: (Gallbladder Disease)Document1 pageGeneral Surgery: (Gallbladder Disease)Matt100% (1)
- 4206 CR 1Document3 pages4206 CR 1Ardianto SucintaNo ratings yet
- Pproach TO Bstructive Aundice: Yeo Quan YouDocument40 pagesPproach TO Bstructive Aundice: Yeo Quan YouThaer HafiNo ratings yet
- Surgery NotesDocument200 pagesSurgery NotesJasneet SinghNo ratings yet
- Oncologic EmergenciesDocument3 pagesOncologic EmergenciesMiguel Cuevas DolotNo ratings yet
- Corrected Final 2019Document13 pagesCorrected Final 2019Sara AlHarbiNo ratings yet
- Oral SURGERY REVALIDA1Document27 pagesOral SURGERY REVALIDA1Bea Y. Bas-ongNo ratings yet
- Gallstone, Choledocholithiasis, Ascending CholangistisDocument12 pagesGallstone, Choledocholithiasis, Ascending CholangistisNurulasyikin MAA100% (1)
- Urology SummaryDocument33 pagesUrology Summarylalo5eerNo ratings yet
- Renal Cell CarcinomaDocument10 pagesRenal Cell Carcinoma'asyura Mohd RezaNo ratings yet
- Surgery Class Biliary System SurgeryDocument69 pagesSurgery Class Biliary System SurgeryKashif BurkiNo ratings yet
- Biliary Surgery: Presenter: DR Muhuga JR Facilitator: DR MwashambwaDocument54 pagesBiliary Surgery: Presenter: DR Muhuga JR Facilitator: DR MwashambwaSamar AhmadNo ratings yet
- L1 Radiology 2Document55 pagesL1 Radiology 2Princess FNo ratings yet
- Cholelithiasis and Liver CirrhosisDocument39 pagesCholelithiasis and Liver CirrhosisKate ValdesNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Pain MARS 2.0 - Dr. Siswidiyati, SP - RadDocument34 pagesAbdominal Pain MARS 2.0 - Dr. Siswidiyati, SP - RadarifdeathsciethNo ratings yet
- Choledocholithiasis ManagementDocument20 pagesCholedocholithiasis ManagementNikoFebriRyandoNo ratings yet
- Imaging Methods for Identifying Causes of Extrahepatic CholestasisDocument7 pagesImaging Methods for Identifying Causes of Extrahepatic CholestasisJOSE ERNESTO AGUIRRE ALVAREZNo ratings yet
- Investigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceDocument38 pagesInvestigation and Treatment of Surgical JaundiceUjas PatelNo ratings yet
- Docc NotesDocument4 pagesDocc Noteslovegoodluna812No ratings yet
- High Yield General Surgery Topics PDFDocument85 pagesHigh Yield General Surgery Topics PDF1031 Muhammad zaryabNo ratings yet
- CHOLANGITISDocument7 pagesCHOLANGITISWill GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Jaundice management strategiesDocument40 pagesJaundice management strategiesAdebisiNo ratings yet
- Benign Hepatobiliary DisordersDocument29 pagesBenign Hepatobiliary DisordershafizahhoshniNo ratings yet
- General Data: Chief Complain:: Case Protocol: Colon CaDocument8 pagesGeneral Data: Chief Complain:: Case Protocol: Colon CaIC BNo ratings yet
- Surg 2 JaundicedDocument94 pagesSurg 2 Jaundicedapi-3728522No ratings yet
- Causes and Diagnosis of Lower Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument23 pagesCauses and Diagnosis of Lower Gastrointestinal BleedingSarachanda SallyNo ratings yet
- The Liver: Methods of ExaminationDocument49 pagesThe Liver: Methods of Examinationj.doe.hex_87No ratings yet
- All About The IVP: April 1 2004 Andrea WilsonDocument30 pagesAll About The IVP: April 1 2004 Andrea WilsonCory Monica MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Amoebic Liver Abscess PDF - 230409 - 165859Document16 pagesAmoebic Liver Abscess PDF - 230409 - 165859hagarfayed44No ratings yet
- Small Intestine and ColonDocument9 pagesSmall Intestine and Colonlentini@maltanet.netNo ratings yet
- Acr Incidental Findings Guidelines (598 - 0)Document20 pagesAcr Incidental Findings Guidelines (598 - 0)Yeang ChngNo ratings yet
- Oncologic Emergencies Management GuideDocument5 pagesOncologic Emergencies Management GuideAra DiocosNo ratings yet
- 10 StomachDocument10 pages10 StomachApabrita KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Kholesistis & Kholelitiasis 30-11-14Document67 pagesKholesistis & Kholelitiasis 30-11-14Dian AzhariaNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract TumourDocument40 pagesUrinary Tract TumourNu JoeNo ratings yet
- Litiasis VesicularDocument26 pagesLitiasis VesicularEULER FARADAY ALTAMIRANO FARFANNo ratings yet
- EMERGENCY CASE REPORTSDocument15 pagesEMERGENCY CASE REPORTSashyNo ratings yet
- C HPB (blue keyword pyq)Document5 pagesC HPB (blue keyword pyq)Irsyad SiddeeqNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Carcinoma Anatomy, Symptoms, Risk FactorsDocument5 pagesEsophageal Carcinoma Anatomy, Symptoms, Risk FactorsChiu ChunNo ratings yet
- The Porcelain GallbladderDocument3 pagesThe Porcelain GallbladderAdriana Florina BahnaNo ratings yet
- LiverDocument177 pagesLiverChiiraq EugeneNo ratings yet
- 1 LiverDocument10 pages1 LiverAlbino Fulgencio Santos III100% (1)
- Obstructive Jaundice: Abdel Rahman A. Al Manasra, MDDocument56 pagesObstructive Jaundice: Abdel Rahman A. Al Manasra, MDAmyandNo ratings yet
- CHOLECYSTITISDocument6 pagesCHOLECYSTITISAnar ChuluunNo ratings yet
- DiverticulitisDocument5 pagesDiverticulitisrywalkNo ratings yet
- Sangrado Gastrointestinal OscuroDocument20 pagesSangrado Gastrointestinal OscuroCristian Sandoval RojasNo ratings yet
- Gallstone Disease and Acute Cholecystitis MADDocument21 pagesGallstone Disease and Acute Cholecystitis MADMuhammad AbdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology - Pancreatitis PDFDocument2 pagesGastroenterology - Pancreatitis PDFMonica J Ortiz PereiraNo ratings yet
- The Gallbladder Diseases Bile Duct StoneDocument69 pagesThe Gallbladder Diseases Bile Duct Stoneحميد حيدرNo ratings yet
- Doctors in the Making: Introduction to General SurgeryDocument2 pagesDoctors in the Making: Introduction to General SurgerysammyNo ratings yet
- PancreasDocument1 pagePancreasMattNo ratings yet
- Bile Duct DilatedDocument4 pagesBile Duct DilatedAmit GauravNo ratings yet
- Obstructive JaundiceDocument1 pageObstructive JaundiceMattNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts for Patients and Supporters: Cholangiocarcinoma: A cancer of the bile duct and liver Information + Taking Control = Best OutcomeFrom EverandFast Facts for Patients and Supporters: Cholangiocarcinoma: A cancer of the bile duct and liver Information + Taking Control = Best OutcomeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Post-Surgical Bleeding RiskDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan for Post-Surgical Bleeding RiskRyan MirandaNo ratings yet
- Ica 2023Document13 pagesIca 2023Khalafalla MustafaNo ratings yet
- ST 8 PDFDocument2 pagesST 8 PDFsorinNo ratings yet
- Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: ReviewDocument11 pagesAcute Decompensated Heart Failure: ReviewFercee PrimulaNo ratings yet
- 1 SMDocument11 pages1 SMyuniNo ratings yet
- Ma A LoxDocument2 pagesMa A LoxMicah_Ela_Lao_2724No ratings yet
- Sandaletal UpdateonITPDocument18 pagesSandaletal UpdateonITPMarcellia AngelinaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Review for Maternal and Child NursingDocument7 pagesMidterm Exam Review for Maternal and Child NursingCres Padua QuinzonNo ratings yet
- N-acetylcysteine generic and brand names, dosage, mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, side effects and nursing implicationsDocument2 pagesN-acetylcysteine generic and brand names, dosage, mechanism of action, indications, contraindications, side effects and nursing implicationsAmira Paguyo QuilapioNo ratings yet
- Vyr GBL 2100296 Seven Ventilators Challenged With Leaks During Neonatal Nasal Cpap - Final - 0Document2 pagesVyr GBL 2100296 Seven Ventilators Challenged With Leaks During Neonatal Nasal Cpap - Final - 0Michael LevitNo ratings yet
- Nama Produk Per Rak Ethical 1Document74 pagesNama Produk Per Rak Ethical 1Akhmad “Billy Rafi” HambaliNo ratings yet
- A Comparative Clinical Study To Evaluate The Efficacy of Koshataki Ksharasutra in The Management of Bhagandara With Special Reference To Fistula in AnoDocument7 pagesA Comparative Clinical Study To Evaluate The Efficacy of Koshataki Ksharasutra in The Management of Bhagandara With Special Reference To Fistula in AnoEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Neuro ImagingDocument41 pagesNeuro ImagingRuchiyyihNo ratings yet
- Raynaud's Disease - JERAIZADocument23 pagesRaynaud's Disease - JERAIZAmaU439No ratings yet
- NBHS1112 Biochemistry/ Biokimia May Semester 2022Document16 pagesNBHS1112 Biochemistry/ Biokimia May Semester 2022amu tha100% (1)
- James L. Hallenbeck Palliative Care Perspectives 2022 Oxford University Press Libgen - LiDocument400 pagesJames L. Hallenbeck Palliative Care Perspectives 2022 Oxford University Press Libgen - Liluficor100% (2)
- Pox, Parvo, Adeno and Papova VirusesDocument33 pagesPox, Parvo, Adeno and Papova VirusesmicroperadeniyaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry and Medical Genetics: VideosDocument10 pagesBiochemistry and Medical Genetics: VideosRicardo ColomaNo ratings yet
- Patient Engagement and Safety - PSNetDocument5 pagesPatient Engagement and Safety - PSNetanithaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of The Quantitative and Qualitative Method For Determination of D - DimerDocument4 pagesComparative Analysis of The Quantitative and Qualitative Method For Determination of D - DimerDimitar KosturkovNo ratings yet
- Impaired Verbal CommunicationDocument4 pagesImpaired Verbal CommunicationDharylle CariñoNo ratings yet
- Answers to Your Questions About Intersex ConditionsDocument4 pagesAnswers to Your Questions About Intersex ConditionsJoshuaBalabboNo ratings yet
- Keratitis: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument28 pagesKeratitis: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentjantyNo ratings yet
- The Lamp of Umm HāshimDocument18 pagesThe Lamp of Umm HāshimbascutaNo ratings yet
- Meniere's DiseaseDocument14 pagesMeniere's DiseasedantydanesNo ratings yet
- Dementia Vs DeliriumDocument40 pagesDementia Vs DeliriumDr. Mushfique Imtiaz ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Pediatricians' Letter To LCS Superintendent Rocky HannaDocument2 pagesPediatricians' Letter To LCS Superintendent Rocky HannaWCTV Digital TeamNo ratings yet
- Massive Transfusion and Massive Transfusion ProtocolDocument9 pagesMassive Transfusion and Massive Transfusion ProtocolRamachandran SundararamanNo ratings yet
- NP Facts: The Voice of The Nurse Practitioner®Document1 pageNP Facts: The Voice of The Nurse Practitioner®giuzolinNo ratings yet
- Emergency Care For Birds, A Guide For Veterinary Professionals (VetBooks - Ir)Document262 pagesEmergency Care For Birds, A Guide For Veterinary Professionals (VetBooks - Ir)propigateNo ratings yet