Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 7 Opti PDF
Class 7 Opti PDF
Uploaded by
Usama IdreesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Class 7 Opti PDF
Class 7 Opti PDF
Uploaded by
Usama IdreesCopyright:
Available Formats
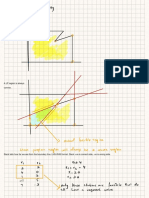
cornerpoint CP
oscpnf Cprft corner prints not in feasible region
e corner point feasible solutions m feasible region
I ne no of variables
m no of constraints
isoprilit live only a function
corner point will lie at the intersection of n lives
point will be called a corner point only if A would not lie
A corner
on a line segment joining any other two points in the same region
An isoprotit function will exit line segment when it is to
a parallel
any one constraint
Implication of this find Our search is confined to finite ports rather than
the
mfmite ponies in feasible region
Proof by contradiction
a L b T
use equality to proof by contradict
as b
If LP has
unique optimal so it will be a cpf True
let 2 such it is
unique optimal but not Cpf
Let 2 22 be the two other solutions
21 2 2222 2 not optimal X
i 22 C 2 L 21 A X
2 I 29 22 not unique X
operators here show or represent relative optimality
e g a21 2 29 L 22 means 2 is less opined than 29 which is
lets optimal than 22
a lb
9 a s b not true
A corner point is a point which would be solved dgebrically
Henie now we move from graphical method to algebraic methods
we now locate corner points and save them for optimality
constraints when put to
Every pair of two equations will give a corner point
The only drawback of algebraic method is extra effort graphical method works
brilliantly in case of large no of constraints by reducing the
a
effort
n 50
m 50
m t w 100
r 50
You might also like
- Gopi, E. S - Multi-Disciplinary Digital Signal Processing - A Functional Approach Using Matlab (2018, Springer)Document205 pagesGopi, E. S - Multi-Disciplinary Digital Signal Processing - A Functional Approach Using Matlab (2018, Springer)Muhammad AgungNo ratings yet
- (Measure Theory) D. H Fremlin-Measure Theory-Torres Fremlin (2001)Document563 pages(Measure Theory) D. H Fremlin-Measure Theory-Torres Fremlin (2001)mnemoniaNo ratings yet
- Microwave 03Document36 pagesMicrowave 03Cindrella MotlammeNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document28 pagesCH 02Rebecca AntoniosNo ratings yet
- 筆記 2023年1月10日Document7 pages筆記 2023年1月10日Vincy HuiNo ratings yet
- Class 9 PDFDocument3 pagesClass 9 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - Power Functions - ppt-2Document4 pages1.1 - Power Functions - ppt-2Pavni ChandaniNo ratings yet
- Class 7 PDFDocument3 pagesClass 7 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Beams Modeled As Single-Degree-Of-freedom SystemsDocument71 pagesBeams Modeled As Single-Degree-Of-freedom SystemsArizap MoltresNo ratings yet
- MATH1062, 2024, Week 6Document13 pagesMATH1062, 2024, Week 6sts20011022No ratings yet
- Basics of OptimisationDocument9 pagesBasics of OptimisationKunal BhargudeNo ratings yet
- Class 8 PDFDocument3 pagesClass 8 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Sec4 1Document9 pagesSec4 1haitham101297No ratings yet
- Lecture 01-After Lecture-L06Document10 pagesLecture 01-After Lecture-L06LincolnNo ratings yet
- Luminance Reflectances: F Luminance Contrast Standard JDocument15 pagesLuminance Reflectances: F Luminance Contrast Standard JIslam BmlNo ratings yet
- EECE 5639 Computer Vision I: Descriptors, Feature Matching, Hough TransformDocument68 pagesEECE 5639 Computer Vision I: Descriptors, Feature Matching, Hough TransformSourabh Sisodia SrßNo ratings yet
- Limits & DerivativesDocument52 pagesLimits & DerivativesKartik AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Graphical Method: Module - 1 Lecture Notes - 3 Linear Programming Problems-IDocument5 pagesGraphical Method: Module - 1 Lecture Notes - 3 Linear Programming Problems-Iraj ranjanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-Unit 1 Numerical Methods: MATH3510 B.Tech, V SemDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank-Unit 1 Numerical Methods: MATH3510 B.Tech, V Semsumit kumarNo ratings yet
- Question Bank-Unit 1 Numerical Methods: MATH3510 B.Tech, V SemDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank-Unit 1 Numerical Methods: MATH3510 B.Tech, V Semsumit kumarNo ratings yet
- Math Ch12Document6 pagesMath Ch12MbambaNo ratings yet
- ParabolaDocument48 pagesParabolateensdepressed774No ratings yet
- Question Bank-Unit 1 Numerical Methods: MATH 2300 B.Tech, III SemDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank-Unit 1 Numerical Methods: MATH 2300 B.Tech, III SemROHAN TRIVEDI 20SCSE1180013No ratings yet
- Garcia2019 PDFDocument13 pagesGarcia2019 PDFpouyan HosseiniNo ratings yet
- IROS '19 PosterDocument1 pageIROS '19 PosterSam LAINo ratings yet
- Geometry OfficeDocument28 pagesGeometry OfficeDG KumarNo ratings yet
- Cavity Resonator PDFDocument20 pagesCavity Resonator PDFkhanafzaal2576No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 FSMDocument6 pagesLecture 4 FSMMustafaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2.1 - Tangent and Derivative: AP CalculusDocument21 pagesLesson 2.1 - Tangent and Derivative: AP CalculusAatrox HavalorNo ratings yet
- Note Jan 16, 2019Document5 pagesNote Jan 16, 2019SeymurH-vNo ratings yet
- Brian Cvpr07Document1 pageBrian Cvpr07Que ImportaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Ideal Chains PDFDocument8 pagesLecture 1 - Ideal Chains PDFBrandon RawsonNo ratings yet
- DSP Lecture-7 F - 23Document23 pagesDSP Lecture-7 F - 23hassan ahmedNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07 Nov 2020 PDFDocument1 pageAdobe Scan 07 Nov 2020 PDFManila NandaNo ratings yet
- Network Synthesis ModifiedDocument109 pagesNetwork Synthesis ModifiedPranzal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Vibration PDFDocument13 pagesVibration PDFJohannis ReyNo ratings yet
- OT MCQ QuestionsDocument16 pagesOT MCQ QuestionsDarshana ThoratNo ratings yet
- ECE411 - 4d - The Z-TransformDocument6 pagesECE411 - 4d - The Z-TransformMartine JimenezNo ratings yet
- Prewitt Versus Sobel MasksDocument29 pagesPrewitt Versus Sobel MasksLal ChandNo ratings yet
- Hall ICTPDocument40 pagesHall ICTPapi-3819873100% (1)
- Linear Programming (Basic Concepts)Document4 pagesLinear Programming (Basic Concepts)vasuNo ratings yet
- Class 5 PDFDocument3 pagesClass 5 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- DIP Mod 4 Segement Part BDocument39 pagesDIP Mod 4 Segement Part BshivubhavvNo ratings yet
- Objectives To Find Compositions of Isometries, Including Glide ReflectionsDocument7 pagesObjectives To Find Compositions of Isometries, Including Glide ReflectionsAbood SafadiNo ratings yet
- EE 508 Lect 21 Fall 2020Document40 pagesEE 508 Lect 21 Fall 2020Sai KiranNo ratings yet
- The Inverse Z-Transform: Instructor: Dr. Ghazi Al Sukkar Dept. of Electrical Engineering The University of Jordan EmailDocument31 pagesThe Inverse Z-Transform: Instructor: Dr. Ghazi Al Sukkar Dept. of Electrical Engineering The University of Jordan EmailWasif IjazNo ratings yet
- BascalDocument9 pagesBascalVaughn MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document10 pagesLecture 5Daniel PaggiattoNo ratings yet
- Laser Diodes Light Emitting Diodes Photodetectors: EE4035 Optical Communications Semester A 2019-20Document46 pagesLaser Diodes Light Emitting Diodes Photodetectors: EE4035 Optical Communications Semester A 2019-20kant734No ratings yet
- Simplex Method 2022Document14 pagesSimplex Method 2022Ishika ParasrampuriaNo ratings yet
- 16351509-024 - Presentation - MATH-101 - Sec B - Spring 2021Document11 pages16351509-024 - Presentation - MATH-101 - Sec B - Spring 2021Ch M Sami JuttNo ratings yet
- OPIF13 Notes6 Lagrangian Mechanics IDocument30 pagesOPIF13 Notes6 Lagrangian Mechanics IABISAI RASCON ESTRADANo ratings yet
- 3D Short NotesDocument30 pages3D Short NotesRohan JenaNo ratings yet
- Particle Theory - Wave TheoryDocument30 pagesParticle Theory - Wave TheoryMd Jahirul IslamNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document11 pagesAssignment 2Luis David Cajavilca CutimancoNo ratings yet
- Projection Matrix TricksDocument43 pagesProjection Matrix TricksNick DufferNo ratings yet
- Me em 5150 Chapter 8Document53 pagesMe em 5150 Chapter 8ajeyaram369No ratings yet
- Cross Section:: Incident FluxDocument3 pagesCross Section:: Incident FluxsatyaavaniNo ratings yet
- Limits Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesLimits Cheat SheetAlexa Nicole PamaNo ratings yet
- Today's Lecture: Repetition and Refinement of Image BasicsDocument36 pagesToday's Lecture: Repetition and Refinement of Image BasicsAli KassabNo ratings yet
- Class 11 PDFDocument4 pagesClass 11 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 13 PDFDocument4 pagesClass 13 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Notes 1 PDFDocument39 pagesNotes 1 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Notes 3 PDFDocument3 pagesNotes 3 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 12 PDFDocument1 pageClass 12 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 10 PDFDocument2 pagesClass 10 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 5 PDFDocument3 pagesClass 5 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 8 PDFDocument3 pagesClass 8 PDFUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 2Document2 pagesClass 2Usama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 4Document3 pagesClass 4Usama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Human Resource ManagementDocument10 pagesHuman Resource ManagementUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 3Document2 pagesClass 3Usama IdreesNo ratings yet
- A1Document1 pageA1Usama IdreesNo ratings yet
- GP (G9) FinalDocument21 pagesGP (G9) FinalUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Class 1Document1 pageClass 1Usama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Managing The Diverse WorkforceDocument4 pagesManaging The Diverse WorkforceUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- UsamaIdreesDocument4 pagesUsamaIdreesUsama IdreesNo ratings yet
- Python Environment Setup PDFDocument11 pagesPython Environment Setup PDFAkhil ChavvaNo ratings yet
- Finding The Areas Under The Normal Curve RemindersDocument5 pagesFinding The Areas Under The Normal Curve RemindersLabLab ChattoNo ratings yet
- Part 4Document12 pagesPart 4md juel miaNo ratings yet
- CS 321-Analysis of Algorithms: Instructor: Asim RehanDocument23 pagesCS 321-Analysis of Algorithms: Instructor: Asim RehanSyed Jarar Ali BukhariNo ratings yet
- Slides ChannelCodingDocument98 pagesSlides ChannelCodingHuongNguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Basics of Set-Constrained and Unconstrained OptimizationDocument38 pagesChapter 6 Basics of Set-Constrained and Unconstrained OptimizationKantesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document13 pagesLecture 3JulianAndresGuessIronNo ratings yet
- Evans PDEDocument6 pagesEvans PDEJoey WachtveitlNo ratings yet
- Multivariate Time Series Clustering Based On Common Principal Component Analysis 2019Document9 pagesMultivariate Time Series Clustering Based On Common Principal Component Analysis 2019Houssem LoucheneNo ratings yet
- Open Platform Card-SpecificationDocument183 pagesOpen Platform Card-SpecificationRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- Jinkun Liu - Intelligent Control Design and MatLab Simulation (2018, Springer)Document294 pagesJinkun Liu - Intelligent Control Design and MatLab Simulation (2018, Springer)snri0da9100% (1)
- B. Sc. (IT) (Sem. II) Examination Data & File Structure: April / May - 2006Document2 pagesB. Sc. (IT) (Sem. II) Examination Data & File Structure: April / May - 2006Pankaj PareekNo ratings yet
- Sanjayram R ResumeDocument2 pagesSanjayram R Resumemridul.k2021aiNo ratings yet
- DAA NotesDocument200 pagesDAA Notessuren scribedNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 PDFDocument15 pagesLecture3 PDFblackhatson13No ratings yet
- AEAS 207 Lec 1Document44 pagesAEAS 207 Lec 1Samin Yaser AhmedNo ratings yet
- Dynamic - Characterstics of Instruments Aug 2023Document96 pagesDynamic - Characterstics of Instruments Aug 2023Sc RayaNo ratings yet
- Feedback Linearization and Back SettpingDocument14 pagesFeedback Linearization and Back Settpingsungraiz aliNo ratings yet
- Backwards Heat Equation InfoDocument1 pageBackwards Heat Equation InfoMelissa Marie HernandezNo ratings yet
- Lab-2-Course Matlab Manual For LCSDocument12 pagesLab-2-Course Matlab Manual For LCSAshno KhanNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics & Machine Learning: Regression AnalysisDocument58 pagesBusiness Analytics & Machine Learning: Regression AnalysisArda HüseyinoğluNo ratings yet
- Sarcasm Detection Using MCAB-BLSTM On News HeadlineDocument10 pagesSarcasm Detection Using MCAB-BLSTM On News Headlinesumathi yamiNo ratings yet
- CYK-Algorithm UpdatedDocument33 pagesCYK-Algorithm UpdatedSHILPA KELANo ratings yet
- Maximal Covering Location-Allocation Problem With MMK Queuing System and Side ConstraintsDocument18 pagesMaximal Covering Location-Allocation Problem With MMK Queuing System and Side ConstraintslfortesNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term Exam of Differential Equations and Transforms (MTH-423), Feb-2024Document2 pagesMid-Term Exam of Differential Equations and Transforms (MTH-423), Feb-2024Maryam SafdarNo ratings yet
- Algoritmul FEALDocument20 pagesAlgoritmul FEALnanacitesteNo ratings yet
- Data Mining Answer KeyDocument10 pagesData Mining Answer KeyRishabh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Sensors 20 02015Document12 pagesSensors 20 02015Alexander MarkhonkoNo ratings yet