Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pcol Osteoarthritis
Pcol Osteoarthritis
Uploaded by
RAMOS, Khristine JoesellOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pcol Osteoarthritis
Pcol Osteoarthritis
Uploaded by
RAMOS, Khristine JoesellCopyright:
Available Formats
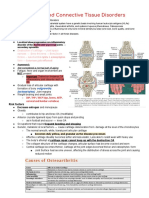
OSTEOARTHRITIS
● "OSTEO"- bones
● damage in the articular cartilage.
● If there's movement, damage in the bones, inflammatory cells will migrate.
● Too many Inflammatory cells, pain will ensue.
● Inflammation is always accompanied by pain.
○ARTICULAR CARTILAGE- white tissue that covers the end of bones, so that if there's friction
bones will not be damaged.
○INFLAMMATION PURPOSES- for protection
SYMPTOMS
○Grating sensation- movement friction
○Bouchard's nodes, and Herberden's nodes- hard Gelatinous cysts in the fingers.
○Bouchard's nodes- proximal joints
○Herberden's nodes- distal joints
PHARMACOLOGIC TX
1. ○Acetaminophen- analgesic
2. ○NSAID- First line because of inflammation
3. ○Corticosteroids
● unresponsive to NSAIDS
● route- INTRA-ARTICULAR route- injected into joints
4. ○Capsaicin
● chilli patch
● component of siling labuyo
● Before, counterirritant, when applied, the Thinking of the px will divert. Instead of
thinking about the pain, the attention will divert into the warm sensation.
● Based on studies, it has ANTI-INFLAMM activity, inhibiting SUBSTANCE P-
involved in pain and inflammation.
5. GLUCOSAMINE- present in the fluid around the joint, when deficient, must be
replenished.
6. CHONDROITIN- major component of cartilage that helps to retain water.
7. HYALURONATE (hyaluronic acid)- spreading agent, but for the joints, it is a lubricant
for joints.
8. NARCOTIC ANALGESIC- morphine- activate Mu receptors to cause analgesic property,
they mimic endorphins, they mimic endogenous opioids, such as endorphins and
enkephalins (natural pain relievers)
You might also like
- Chapter 20 - Group 5Document44 pagesChapter 20 - Group 5Thanh TrúcNo ratings yet
- TMJ DisordersDocument30 pagesTMJ DisordersDua'a Ma'an100% (3)
- Anaphy Reviewer PrefinalsDocument14 pagesAnaphy Reviewer PrefinalsIyah DyNo ratings yet
- RHEUMA Hour 9 - 8 - 21Document16 pagesRHEUMA Hour 9 - 8 - 21Nini Angelica SiringanNo ratings yet
- Finals 2Document36 pagesFinals 2mayangernszNo ratings yet
- Dibetic Neuropathic Pain FootDocument8 pagesDibetic Neuropathic Pain FootBill PapachristouNo ratings yet
- Accessory Navicular SyndromeDocument6 pagesAccessory Navicular SyndromeXin YiNo ratings yet
- Accessory Navicular SyndromeDocument6 pagesAccessory Navicular SyndromeXin YiNo ratings yet
- Hip Conditions 1Document18 pagesHip Conditions 1Carlos GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Post Operative Pain Management: Dr. Golam Mursalin Phase A Cvts Dr. Rushdah Mariam Phase A Paediatric SurgeryDocument48 pagesPost Operative Pain Management: Dr. Golam Mursalin Phase A Cvts Dr. Rushdah Mariam Phase A Paediatric SurgeryRun HajNo ratings yet
- Tara's CH. 64 Arthritis and Connective Tissue DisordersDocument34 pagesTara's CH. 64 Arthritis and Connective Tissue DisordersTara McNeillNo ratings yet
- Aaaaa AaaaaaaaaaaaaaaDocument48 pagesAaaaa AaaaaaaaaaaaaaaYaneth Angeles Benavente mamaniNo ratings yet
- Shade Selection: What Is Colour?Document39 pagesShade Selection: What Is Colour?RaiNo ratings yet
- Musculo-Skeletal SystemDocument10 pagesMusculo-Skeletal SystemAmir PermitivoNo ratings yet
- Penyakit Sendi Degeneratif & Patologi TulangDocument38 pagesPenyakit Sendi Degeneratif & Patologi Tulangnaufal ihsanNo ratings yet
- Non Surgical Management of Temporomandibular DisordersDocument63 pagesNon Surgical Management of Temporomandibular DisordersMugdha FrancisNo ratings yet
- Neuro 2009Document181 pagesNeuro 2009mcie22dwestNo ratings yet
- PainDocument124 pagesPainWinno Pradana UtomoNo ratings yet
- PalpationDocument4 pagesPalpationLucy EkwunifeNo ratings yet
- Pharma 2 PDFDocument6 pagesPharma 2 PDFMuhammad ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Analgesics: DR - Aziz PahadwalaDocument44 pagesAnalgesics: DR - Aziz PahadwalaazizNo ratings yet
- Glossopharyngeal NerveDocument8 pagesGlossopharyngeal NerveGEORGE MATHIASNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer PrefinalsDocument12 pagesAnaphy Reviewer PrefinalsNicole Faith L. NacarioNo ratings yet
- The Hypoglossal Nerve CN XII Course Motor TeachMeAnatomyDocument3 pagesThe Hypoglossal Nerve CN XII Course Motor TeachMeAnatomyMohammad HadiNo ratings yet
- Swedish Massage InfoDocument5 pagesSwedish Massage InfoJoy CelestialNo ratings yet
- or (See Spelling Differences From Greek ĮȞDocument4 pagesor (See Spelling Differences From Greek ĮȞOrene OnaicilefNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Web: .PH EmailDocument13 pagesRepublic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Web: .PH EmailCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- Analgesics Pain MedsDocument113 pagesAnalgesics Pain Medsalhader libraryNo ratings yet
- BOOK3 CamilleDocument8 pagesBOOK3 CamilleSteve tarucNo ratings yet
- Muscles of Mastication PDFDocument60 pagesMuscles of Mastication PDFteju patneediNo ratings yet
- Massage PowerpoingDocument11 pagesMassage Powerpoingapi-550556129No ratings yet
- Surgery Lec 1Document5 pagesSurgery Lec 1api-3775747No ratings yet
- Drugs and Their Physiological Effects:: 1. DexamethasoneDocument3 pagesDrugs and Their Physiological Effects:: 1. DexamethasoneSaima JabbarNo ratings yet
- FIDNDocument21 pagesFIDNBeta WattimenaNo ratings yet
- Midterm Part 3 PDFDocument12 pagesMidterm Part 3 PDFMae Arra Gilbao Lecobu-anNo ratings yet
- PharmokineticsDocument65 pagesPharmokineticsflash.43612No ratings yet
- FracturesDocument18 pagesFracturesNicole Anne ValerioNo ratings yet
- Pain 1ST Yr.Document45 pagesPain 1ST Yr.Anusikta PandaNo ratings yet
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Like Ibuprofen Act in Reversible Inhibition of The EnzymesDocument5 pagesNonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Like Ibuprofen Act in Reversible Inhibition of The EnzymesIekzkad RealvillaNo ratings yet
- MusculoskeletalDocument40 pagesMusculoskeletalseigelystic100% (14)
- Anesthesiology Practical CourseDocument27 pagesAnesthesiology Practical CourseAstha Tusharbhai PatelNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S025462720860028X Main PDFDocument4 pages1 s2.0 S025462720860028X Main PDFRilla Sonly IINo ratings yet
- Muscles of Mastication PHD Manoj JainDocument81 pagesMuscles of Mastication PHD Manoj JainArshdeep KaurNo ratings yet
- 1.gagging and Its Management in Prosthodontic PatientsDocument25 pages1.gagging and Its Management in Prosthodontic PatientsMithileshwari Patil100% (1)
- AcupressureDocument4 pagesAcupressureCharlene Grace ReginoNo ratings yet
- Dentistry: Orofacial Pain: A ReviewDocument6 pagesDentistry: Orofacial Pain: A ReviewAstriAl-hutamiNo ratings yet
- 1.basics of Anesthesiology. Anesthesia Machine and Equipments.Document41 pages1.basics of Anesthesiology. Anesthesia Machine and Equipments.karim hassanNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle AnatomyDocument21 pagesSkeletal Muscle AnatomyPeterNo ratings yet
- HIP Arthroplasty: by Tiong Me FahDocument18 pagesHIP Arthroplasty: by Tiong Me FahVivian TiongNo ratings yet
- Current Advances in Orthodontic Pain: ReviewDocument9 pagesCurrent Advances in Orthodontic Pain: ReviewCamila Alvarez GaravitoNo ratings yet
- LP 4 Semio ChirDocument31 pagesLP 4 Semio ChirMarius DanilaNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal DisordersDocument42 pagesMusculoskeletal DisordersSaddichhya TripathiNo ratings yet
- NCP PainDocument2 pagesNCP PainAnielle RceNo ratings yet
- Pcol - Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument2 pagesPcol - Rheumatoid ArthritisRAMOS, Khristine JoesellNo ratings yet
- Tongue and LymphaticsDocument73 pagesTongue and LymphaticsDyuti SikdarNo ratings yet
- Bms1052 Note l7-l9Document53 pagesBms1052 Note l7-l9leni110623No ratings yet
- PDF 20230624 122205 0000Document36 pagesPDF 20230624 122205 0000Maria EvergardenNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument19 pagesWe Are Intechopen, The World'S Leading Publisher of Open Access Books Built by Scientists, For ScientistsLuís CorreiaNo ratings yet
- CNS Drugs Analgesics V2023 1Document45 pagesCNS Drugs Analgesics V2023 1revelias.gracilla.cvtNo ratings yet
- Pcol OsteoporosisDocument2 pagesPcol OsteoporosisRAMOS, Khristine JoesellNo ratings yet
- Pcol - Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument2 pagesPcol - Rheumatoid ArthritisRAMOS, Khristine JoesellNo ratings yet
- Pcol GoutDocument2 pagesPcol GoutRAMOS, Khristine JoesellNo ratings yet
- Pcol AnginaDocument3 pagesPcol AnginaRAMOS, Khristine JoesellNo ratings yet