Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cash
Uploaded by
Kim0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesThis document defines and provides examples of cash and cash equivalents. Cash includes currency, checks, and other negotiable instruments that can be readily converted to cash. It must be available for immediate use. Cash equivalents are highly liquid, short-term investments that can be readily converted to a known amount of cash with little risk of changes in value, such as treasury bills acquired within 3 months of maturity. Both cash and cash equivalents are recorded at their face value on the balance sheet.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines and provides examples of cash and cash equivalents. Cash includes currency, checks, and other negotiable instruments that can be readily converted to cash. It must be available for immediate use. Cash equivalents are highly liquid, short-term investments that can be readily converted to a known amount of cash with little risk of changes in value, such as treasury bills acquired within 3 months of maturity. Both cash and cash equivalents are recorded at their face value on the balance sheet.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesCash
Uploaded by
KimThis document defines and provides examples of cash and cash equivalents. Cash includes currency, checks, and other negotiable instruments that can be readily converted to cash. It must be available for immediate use. Cash equivalents are highly liquid, short-term investments that can be readily converted to a known amount of cash with little risk of changes in value, such as treasury bills acquired within 3 months of maturity. Both cash and cash equivalents are recorded at their face value on the balance sheet.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
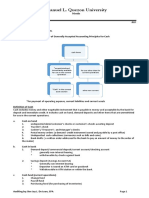
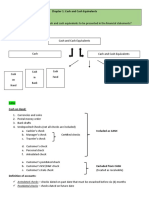
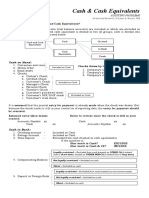
Cash – includes money and any other negotiable instrument that is payable in money and acceptable by
the bank for deposit and immediate credit.
Cash on Hand – undeposited collections and other current funds held as of the reporting date.
Cash in Bank – deposits in bank that are available for immediate withdrawal and unrestricted
use.
Examples of Cash: Not included as cash:
Cash Sinking Fund
Bank Drafts Preferred Redemption Fund
Money Orders Plant Expansion Fund
Petty Cash Fund Insurance Fund
Payroll Fund Post-dated checks
Travel Fund IOUs or advances to employees
Interest Fund (receivables)
Dividend Fund Depreciation Fund (form of asset
Tax Fund replacement fund)
Coins and Currencies Contingency Fund
Revolving Fund Preference share redemption Fund
Postage Stamps (prepaid supplies)
Valuation: In local currency = Face Value
In foreign currency = Current Exchange Rate
If Recoverable Value less than Face Value = Estimated Realizable Value
Financial Statement Classification
Classified as cash and cash equivalents Classified as a separate line item
1. Unrestricted/Current Use 1. Restricted/Non-current Use
2. Investment in time deposit, Money Market
and Treasury Bills
* If term ≤ 3 months
* There is an assumption of 3 month-term when the problem is silent.
3. General Rule: Bank Overdraft ( credit bal. bank account) – current liabilities
* Exception: it can be an offset against other bank acc. If
(a) immaterial
(b) 2 or more account maintain in 1 bank by an entity
4. Informal Compensating Balance 4. Formal Compensating Balance
→ not legally restricted → legally restricted
* If related loan is short term = cash held as
compensating bal.
* If related loan is long-term = non-current
investment
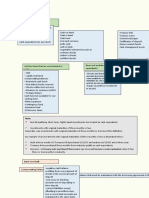
Cash includes money or its equivalent that is readily available for unrestricted use.
o Postdated check received from Exclude from cash
customer
o Undelivered check drawn Include in cash
o Postdated check drawn Include in cash
o Stale checks Include in cash
Cash Equivalents are short term highly liquid investment that are readily convertible to known amount
of cash and which are subject to an insignificant risk of changes in value.
Examples of CE:
a. Treasury Bills, Notes, or Bonds acquired 3
months before maturity date
Treasury bill – short term
- normally have 90 days to
less than a year
- 90 days to less than a year
Treasury notes and treasury bonds - log-
term
- have maturity date of 1
year to less than 10 years.
Treasury bonds – have a maturity of 10
yrs. or more.
b. Money Market instrument (commercial paper
acquired 3 months before maturity date
c. Three-month time deposit
Bank Overdraft – negative (credit) bal.
- may occur only in
You might also like
- Module 5 - Substantive Test of CashDocument6 pagesModule 5 - Substantive Test of CashJesievelle Villafuerte NapaoNo ratings yet
- Far.03 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument8 pagesFar.03 Cash and Cash EquivalentsRhea Royce CabuhatNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument32 pagesModule 3 Cash and Cash Equivalentschuchu tv100% (1)
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsCamille Joyce Corpuz Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- NU - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument14 pagesNU - Audit of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDawn QuimatNo ratings yet
- Cash Cash - Money and Other Negotiable Instrument That Is Payable in Money and Acceptable by TheDocument4 pagesCash Cash - Money and Other Negotiable Instrument That Is Payable in Money and Acceptable by TheannyeongNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EShaira BugayongNo ratings yet
- Audit - Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFDocument15 pagesAudit - Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFSiena Farne100% (1)
- Sta Clara - Summary Part 1Document49 pagesSta Clara - Summary Part 1Carms St ClaireNo ratings yet
- If Silent As To Date of Acquisition, Assume As Current: Cash and Cash Equivalents 1. CashDocument3 pagesIf Silent As To Date of Acquisition, Assume As Current: Cash and Cash Equivalents 1. CashKent Raysil PamaongNo ratings yet
- Cash Part1Document7 pagesCash Part1cuaresmamonicaNo ratings yet
- Far ReviewerDocument5 pagesFar ReviewerKairo ZeviusNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash EquivalentsDocument20 pagesCash & Cash Equivalentsalexis prada100% (2)
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument34 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsJennalyn S. GanalonNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsKent Raysil PamaongNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash Equivalents, LECTURE &EXERCISESDocument16 pagesCash & Cash Equivalents, LECTURE &EXERCISESNMCartNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesDocument16 pagesCash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesNMCartNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsJUST KINGNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesDocument16 pagesCash & Cash Equivalents, Lecture &exercisesDessa GarongNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Audit of Cash Transactions and BalancesDocument6 pagesTopic 1 - Audit of Cash Transactions and BalancesChelsea PagcaliwaganNo ratings yet
- 2021 Chapter 3 Audit of Cash Student GuideDocument29 pages2021 Chapter 3 Audit of Cash Student GuideJan Luis RamiroNo ratings yet
- Notes (Audit Prob)Document6 pagesNotes (Audit Prob)kodzuken.teyNo ratings yet
- Cce Part1 Cash and Cash Equivalents CompressDocument2 pagesCce Part1 Cash and Cash Equivalents CompressMARK JHEN SALANGNo ratings yet
- Handouts 51Document20 pagesHandouts 51Ziyeon SongNo ratings yet
- Module 2A - ACCCOB2 Lecture 2 - Cash and Cash Equivalents - FHV T1AY2021Document6 pagesModule 2A - ACCCOB2 Lecture 2 - Cash and Cash Equivalents - FHV T1AY2021Cale Robert RascoNo ratings yet
- Ia1 ReviewerDocument10 pagesIa1 ReviewerVeronica SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Audit Problems FinalDocument48 pagesAudit Problems FinalShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Intacc ReviewerDocument20 pagesIntacc ReviewerAvos NnNo ratings yet
- 2020 Chapter 3 Audit of Cash Student GuideDocument29 pages2020 Chapter 3 Audit of Cash Student GuideBeert De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pagesCash and Cash Equivalentsyes it's kaiNo ratings yet
- Summary of Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument4 pagesSummary of Cash and Cash EquivalentsMhico Mateo100% (1)
- Secret-Notes BY Cayetano: Accountancy (University of Northern Philippines)Document99 pagesSecret-Notes BY Cayetano: Accountancy (University of Northern Philippines)Erika Faith HalladorNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument10 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsMs VampireNo ratings yet
- Intacc Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument2 pagesIntacc Cash and Cash EquivalentsKristalen ArmandoNo ratings yet
- C C E (N) : ASH AND ASH Quivalents OtesDocument13 pagesC C E (N) : ASH AND ASH Quivalents OtesJoan LaroyaNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents PDFDocument4 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents PDFJade Gomez100% (1)
- Module 1.2Document19 pagesModule 1.2Althea mary kate MorenoNo ratings yet
- Audit ProblemsDocument47 pagesAudit ProblemsShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Cash and Cash Equivalents Expected Question(s) :: Cash On Hand Cash Fund Cash in BankDocument8 pagesChapter 1: Cash and Cash Equivalents Expected Question(s) :: Cash On Hand Cash Fund Cash in BankJulie Mae Caling MalitNo ratings yet
- Cash & Cash EquivalentsDocument8 pagesCash & Cash Equivalentsbona jirahNo ratings yet
- Acccob 2 Lecture 2 Cash and Cash Equivalents T2ay2021Document7 pagesAcccob 2 Lecture 2 Cash and Cash Equivalents T2ay2021Rey HandumonNo ratings yet
- Nature of Cash AccountDocument10 pagesNature of Cash AccountLorena PernatoNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash Equivalents Lecture NotesDocument2 pagesCash and Cash Equivalents Lecture Notesyna kyleneNo ratings yet
- PPT2.1-1 Cash and Cash Equivalents (2020)Document42 pagesPPT2.1-1 Cash and Cash Equivalents (2020)Avery Paul MateoNo ratings yet
- Audit ProblemsDocument32 pagesAudit ProblemsShane TabunggaoNo ratings yet
- INTACC - Chapter 1Document4 pagesINTACC - Chapter 1MeriiiNo ratings yet
- Cash PDFDocument10 pagesCash PDFGabriel JonNo ratings yet
- Intermediate AccountingDocument4 pagesIntermediate AccountingjenNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Cash and Cash Equivalents - PDF Filename UTF-8''AccountingDocument2 pagesAccounting For Cash and Cash Equivalents - PDF Filename UTF-8''AccountingFrancis RaagasNo ratings yet
- Accounting NotesDocument20 pagesAccounting NotesAnonymous PersonNo ratings yet
- Aud 1&2 - CceDocument6 pagesAud 1&2 - Ccecherish melwinNo ratings yet
- Cfas - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument5 pagesCfas - Cash and Cash EquivalentsYna SarrondoNo ratings yet
- Notes - FAR - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument9 pagesNotes - FAR - Cash and Cash EquivalentsElaineJrV-IgotNo ratings yet
- CCE NotesDocument7 pagesCCE NotesHavanah Erika Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument6 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsPamela Mae PlatonNo ratings yet
- AE 111 Midterm Formative Assessment 1Document4 pagesAE 111 Midterm Formative Assessment 1Djunah ArellanoNo ratings yet
- ACCO 20053 Lecture Notes 1 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument3 pagesACCO 20053 Lecture Notes 1 - Cash and Cash EquivalentsVincent Luigil AlceraNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NOTES - Aud ProbDocument15 pagesLECTURE NOTES - Aud ProbJean Ysrael Marquez100% (1)
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDocument12 pagesCash and Cash EquivalentsbelliissiimmaaNo ratings yet
- Measurement PrincipleDocument1 pageMeasurement PrincipleKimNo ratings yet
- Accounting CycleDocument1 pageAccounting CycleKimNo ratings yet
- Art in AsiaDocument1 pageArt in AsiaKimNo ratings yet
- PledgingDocument2 pagesPledgingKimNo ratings yet
- FARreviewerDocument5 pagesFARreviewerKimNo ratings yet
- Norman Gulley: A Christ-Centered Approach To Last-Day EventsDocument35 pagesNorman Gulley: A Christ-Centered Approach To Last-Day EventsJorge Luis Echeverry González100% (1)
- Akira 007Document70 pagesAkira 007Ocre OcreNo ratings yet
- Gynaecology Thesis TopicsDocument7 pagesGynaecology Thesis TopicsDawn Cook100% (2)
- Unit 8 Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry PDFDocument23 pagesUnit 8 Atomic Fluorescence Spectrometry PDFCh AswadNo ratings yet
- A Single-Stage Asymmetrical Half-Bridge Flyback CoDocument16 pagesA Single-Stage Asymmetrical Half-Bridge Flyback CoSantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Jahnteller Effect Unit 3 2017Document15 pagesJahnteller Effect Unit 3 2017Jaleel BrownNo ratings yet
- ISO StandardsDocument7 pagesISO StandardsHusnain BaigNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University Mba - Thesis 060517Document2 pagesFar Eastern University Mba - Thesis 060517Lex AcadsNo ratings yet
- LADA Niva 1600rebuild1Document39 pagesLADA Niva 1600rebuild1Douglas Antonio Paredes MarquinaNo ratings yet
- Metric Conversion WorksheetDocument3 pagesMetric Conversion WorksheetKaiden HughesNo ratings yet
- 160 78-m1Document70 pages160 78-m1George100% (7)
- Curriculum Vitae ofDocument4 pagesCurriculum Vitae ofAndrew OlsonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument45 pagesUntitledjemNo ratings yet
- Network Models For Seat Allocation On Flights: Moshe Dror,?Document12 pagesNetwork Models For Seat Allocation On Flights: Moshe Dror,?Isabel VillaNo ratings yet
- Tle10 Cookery DLL Q1-Week1 Sy2022-2023Document4 pagesTle10 Cookery DLL Q1-Week1 Sy2022-2023Edmar S AguilarNo ratings yet
- Blaine Ray HandoutDocument24 pagesBlaine Ray Handoutaquilesanchez100% (1)
- North-South Railway Project - South LineDocument49 pagesNorth-South Railway Project - South LinesuperNo ratings yet
- LoperAmid 1Document5 pagesLoperAmid 1Hemma KusumaningrumNo ratings yet
- McMurdo FastFind 220 PLB DatasheetDocument4 pagesMcMurdo FastFind 220 PLB DatasheetGiorgos PapadopoulosNo ratings yet
- Pengaruh Pemberian Dosis Pupuk Urea Terhadap Pertumbuhan Tanaman Bayam Cabut Putih (AmaranthusDocument10 pagesPengaruh Pemberian Dosis Pupuk Urea Terhadap Pertumbuhan Tanaman Bayam Cabut Putih (AmaranthusMartha YhunickeNo ratings yet
- Jerehy's ReportDocument65 pagesJerehy's Reportkupetroleum3No ratings yet
- Scan 03-Jan-2020 PDFDocument2 pagesScan 03-Jan-2020 PDFPavanSharmaNo ratings yet
- Brochure Delegation Training For LeadersDocument6 pagesBrochure Delegation Training For LeadersSupport ALProgramsNo ratings yet
- 1422-Article Text-3684-1-10-20211104Document57 pages1422-Article Text-3684-1-10-20211104f.kpobi1473No ratings yet
- Breaking News EnglishDocument13 pagesBreaking News English32. Nguyễn OanhNo ratings yet
- Another Look at Pistis ChristouDocument17 pagesAnother Look at Pistis Christouakimel100% (1)
- Kentucky Economic Development Guide 2010Document130 pagesKentucky Economic Development Guide 2010Journal CommunicationsNo ratings yet
- Graphs in ChemDocument10 pagesGraphs in Chemzhaney0625No ratings yet
- How Do I Predict Event Timing Saturn Nakshatra PDFDocument5 pagesHow Do I Predict Event Timing Saturn Nakshatra PDFpiyushNo ratings yet
- CV - en - Hamdaoui Mohamed AmineDocument2 pagesCV - en - Hamdaoui Mohamed AmineHAMDAOUI Mohamed Amine100% (1)