Professional Documents
Culture Documents
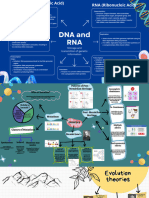
Comparison DNA and RNA
Uploaded by
Mani MentalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Comparison DNA and RNA
Uploaded by
Mani MentalCopyright:
Available Formats
Compariso DNA RNA
n
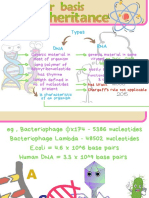
Name Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA). Ribonucleic Acid (RNA).
Function Long-term genetic data To form proteins, the
storage; transmission of genetic code is transferred
genetic information to createfrom the nucleus to the
mitochondria and organisms. ribosomes. In some
organisms, RNA is used to
transmit genetic
information, and it is
possible that it was the
molecule used to store
genetic blueprints in
primitive organisms.
Structural Double helix in B shape. DNA A-form helix RNA is typically
Features is a two-stranded molecule a single-strand helix made
made up of a long chain of up of shorter chains of
nucleotides. nucleotides.
Bases and backbone deoxyribose sugar- Backbone ribose sugar-
Sugars phosphate adenine, guanine, phosphate adenine,
composition cytosine, thymine bases. guanine, cytosine, uracil
bases.
Propagation DNA replicates itself. On an as-needed basis, RNA
is produced from DNA.
Base Pairing AT GC (adenine-thymine) AU (adenine-uracil) GC
(guanine-cytosine). (guanine-cysteine)
(guanine-cytosine)
Reactivity Because of the C-H bonds in When relative to DNA, the
DNA, it is rather stable, and O-H bond in RNA's ribose
the body eliminates enzymes makes the molecule more
that would damage DNA. The reactive. RNA is not stable
tiny grooves in the helix also under alkaline
protect by leaving little room environments, and its big
for enzymes to attach. grooves render it
vulnerable to enzyme
assault. RNA is continually
synthesized, utilized,
destroyed, and recycled.
You might also like
- Biological Significance of DNA and RNA SturucturesDocument2 pagesBiological Significance of DNA and RNA SturucturesDr.Charles BhaskarNo ratings yet
- DNA RNA: DefinitionDocument1 pageDNA RNA: Definitionkatrina668No ratings yet
- Difference Between Dna & Rna: Students NameDocument5 pagesDifference Between Dna & Rna: Students NameHisham MustafaNo ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNADocument2 pagesDNA Vs RNAMegat AmirulNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry BrochureDocument2 pagesBiochemistry BrochureCaryl Alvarado SilangNo ratings yet
- BacterialDocument2 pagesBacterialjulietaira quibilanNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For 3rd Test-BSC 2010LDocument7 pagesStudy Guide For 3rd Test-BSC 2010LPepitinNo ratings yet
- Comparison DNA RNA: Silicon WafersDocument2 pagesComparison DNA RNA: Silicon WafersAlia NajwaNo ratings yet
- Comparison Chart: DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, Is Like A Blueprint of BiologicalDocument5 pagesComparison Chart: DNA, or Deoxyribonucleic Acid, Is Like A Blueprint of BiologicalNova Divine De la PeñaNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesDNA Structure DNA ReplicationBianca RimandoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer FinalsDocument18 pagesBiochem Reviewer Finalscha cuteNo ratings yet
- Asam Nukleat Dan Protein With SoundDocument18 pagesAsam Nukleat Dan Protein With SoundFika Nurul HafidzohNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of DNA and RNADocument3 pagesStructure and Functions of DNA and RNAokonabasimfreke09No ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument1 pageDNA and RNADaly DaliaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Pre FinalsDocument31 pagesBiochemistry Pre FinalsArah Lyn ApiagNo ratings yet
- GenBIO REVIEWERDocument39 pagesGenBIO REVIEWERblismae genotivaNo ratings yet
- Chromosome, DNA, RNADocument5 pagesChromosome, DNA, RNAShahrat Farsim ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- (SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and PhotosynthesisDocument2 pages(SCI) LESSON 5 - DNA, RNA, and Photosynthesisitz.jdv1694No ratings yet
- How Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityDocument5 pagesHow Genes Work GENE - Biological Unit of HeredityAdonis Besa100% (1)
- PHA6112LAB - Experiment 4 Nucleic Acids ReviewerDocument8 pagesPHA6112LAB - Experiment 4 Nucleic Acids ReviewerMarie Eloise BugayongNo ratings yet
- L9-10: Genetic Engineering of Biosynthetic Pathways in Transgenic PlantsDocument72 pagesL9-10: Genetic Engineering of Biosynthetic Pathways in Transgenic PlantsTing Yan LeeNo ratings yet
- Virology TableDocument10 pagesVirology TableFrances Ijeoma ObiakorNo ratings yet
- Self Assessment Answers 6 Asal Biology CBDocument2 pagesSelf Assessment Answers 6 Asal Biology CBsaeed.khedrizaNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNA Compared Supplementary WorksheetsDocument4 pagesDNA and RNA Compared Supplementary WorksheetsVena Grace MendezNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance HalfDocument15 pagesMolecular Basis of Inheritance HalfNaY 7347No ratings yet
- Simone PostersDocument1 pageSimone PostersMasr RedaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument33 pagesLesson 5 - Central Dogma of Molecular BiologySherwin YenogacioNo ratings yet
- D - BW DNA & RNADocument2 pagesD - BW DNA & RNAWahaj MazherNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry SemiDocument5 pagesBiochemistry SemiTsukishima RinNo ratings yet
- Biochem ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiochem ReviewerKathleenNo ratings yet
- Week 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryDocument6 pagesWeek 10: November 15 - 19: MC 2: BiochemistryMary Rose CuentasNo ratings yet
- Differences Between DNA and RNADocument2 pagesDifferences Between DNA and RNAmonishaNo ratings yet
- 12 Biology Notes Ch06 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument14 pages12 Biology Notes Ch06 Molecular Basis of Inheritancehimanshu kumarNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and Replication Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 pageDNA Structure and Replication Cheat Sheet: by ViaThaboNo ratings yet
- Notes Chap 06Document21 pagesNotes Chap 06umamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument4 pagesCentral DogmaRodriguez MiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionGreatel Elijah TorregosaNo ratings yet
- BIOL1003 - Cell StructureDocument10 pagesBIOL1003 - Cell StructuresilentscreamsofloveNo ratings yet
- Assignment Topic: Difference Between DNA and RNA DNA RNADocument2 pagesAssignment Topic: Difference Between DNA and RNA DNA RNASamra ButtNo ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument3 pagesGeneticsbonoo.santuchoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document8 pagesAssignment 2Nesha VincentNo ratings yet
- General Biology - DNA ReplicationDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology - DNA ReplicationChristine Marylou PalomoNo ratings yet
- Biology (2nd Semester) - Grade 12 ReviewerDocument12 pagesBiology (2nd Semester) - Grade 12 ReviewerPatricia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNucleic AcidsAntonette SolaresNo ratings yet
- 6 Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pages6 Nucleic AcidsTala AlkhawajaNo ratings yet
- Sekolah Pelita Harapan Year 10 MYP ScienceDocument12 pagesSekolah Pelita Harapan Year 10 MYP Sciencejovanka kurniawanNo ratings yet
- RDNA and Genomics 2Document159 pagesRDNA and Genomics 2Ru ConduitNo ratings yet
- Nucleotides Nucleic Acids, and HeredityDocument15 pagesNucleotides Nucleic Acids, and Hereditycjolou100% (3)
- DNA Replication Translation and TrascriptionDocument32 pagesDNA Replication Translation and TrascriptionJero MarcelinoNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular Biology PDFDocument32 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular Biology PDFStephy LimboNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids 4Document4 pagesNucleic Acids 4Edgardo VILLASEÑORNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid: Genetic CodeDocument2 pagesNucleic Acid: Genetic CodeAngelica AycardoNo ratings yet
- DNA (Scie)Document3 pagesDNA (Scie)Michaela Shianne E. MatituNo ratings yet
- 1 Nucleic AcidDocument14 pages1 Nucleic AcidYlooner QuitsNo ratings yet
- CYTOGENDocument8 pagesCYTOGENRio CamoniasNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Fact SheetDocument1 pageNucleic Acids Fact Sheetasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- Molecular GeneticsDocument7 pagesMolecular GeneticsSiti Hajar RevillaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Central DogmaDocument3 pagesWorksheet Central DogmaRein Jhonnaley Dioso100% (1)
- 6 Molecular Genetics Part IIDocument51 pages6 Molecular Genetics Part II2021-204943No ratings yet
- Alternative Source of EnergyDocument2 pagesAlternative Source of EnergyMani MentalNo ratings yet
- Animal MimicryDocument1 pageAnimal MimicryMani MentalNo ratings yet
- Trucks TypeDocument2 pagesTrucks TypeMani MentalNo ratings yet
- The Ideology of PakistanDocument11 pagesThe Ideology of PakistanMani MentalNo ratings yet