Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 3
Uploaded by
Phương Anh Nguyễn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views2 pagesOriginal Title
CHAPTER 3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views2 pagesChapter 3
Uploaded by
Phương Anh NguyễnCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Representative curr: has sth back its value.
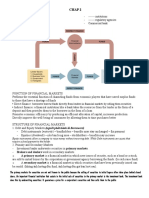
CHAPTER 3 WHAT IS MONEY?
Learning Objectives
3.1 Describe what money is
3.2 List and summarize the functions of money
3.3 Identify different types of payment systems
3.4 Compare and contrast the M1 and M2 money supplies.
MEANING OF MONEY:
- Money (or the “money supply”): anything that is generally accepted as
payment for goods or services or in the repayment of debts.
- A broad definition:
+ Currency, consisting of paper bills and coins, clearly fits this definition and is one
type of money.
+ The word money is frequently used synonymously with wealth. Wealth includes not
only money but also other assets such as bonds, common stock, art, land,
furniture, cars, and houses.
+ People also use the word money to describe what economists call income. ” Income
is a flow of earnings per unit of time. Money, by contrast, is a stock: It is a certain
amount at a given point in time.
FUNCTIONS OF MONEY:
• Medium of Exchange: (phương tiện trao đổi)
– Eliminates the trouble of finding a double coincidence of needs (reduces
transaction costs- The time spent trying to exchange goods or services.)
– Promotes specialization.
- Barter economy-> trade records-> coinage-> banknotes-> digital money
• A medium of exchange must:
– be easily standardized
– be widely accepted
– be divisible
– be easy to carry
– not deteriorate quickly. (kh bị giảm giá trị 1 cách nhanh chóng)
• Unit of Account: (đơn vị tính toán)
– Used to measure value in the economy
– Reduces transaction costs by reducing the number of prices that need to be
considered.
• Store of Value: (cất giữ giá trị)
– Used to save purchasing power over time.
– Other assets also serve this function.
– Money is the most liquid of all assets but loses value during inflation.
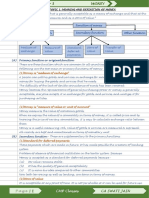
EVOLUTION OF THE PAYMENTS SYSTEM:
• Commodity Money: valuable, easily standardized, and divisible commodities
(e.g. precious metals, cigarettes)
- such a form of money is very heavy and is hard to transport from one place to
another.
• Fiat Money: paper money decreed by governments as legal tender but not
convertible into coins or precious metal. (there is some trust in the authorities)
• Checks: an instruction to your bank to transfer money from your account.
• Electronic Payment (e.g. online bill pay)
• E-Money (electronic money):
– Debit card
– Stored-value card (smart card)
– E-cash
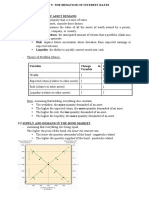
MEASURING MONEY:
• Construct monetary aggregates using the concept of liquidity:
- Narrow money= M0+M1.
– M1 (most liquid assets) = currency + traveler’s checks + demand deposits + other
checkable deposits (tiền trong lưu thông)
- Broad money= M2+M3+…
– M2 (adds to M1 other assets that are not so liquid) = M1 + small denomination
time deposits + savings deposits and money market deposit accounts + money
market mutual fund shares
- M1, M2 dịch chuyển có sự khác biệt lớn theo thời gian.
- Ngta thường sử dụng M2 nhiều hơn M1 vì theo thgian thì M1- tiền trong lưu thông có
thể mất giá nếu cứ cất giữ, trong khi M2 có những khoảng tiền lưu trữ sinh lời trong
ngắn hạn-> đo lường tiền theo M2> M1.
You might also like
- What is Money Functions and EvolutionDocument3 pagesWhat is Money Functions and EvolutionAmgad ElshamyNo ratings yet
- The Role of MoneyDocument39 pagesThe Role of Moneykangelaninizibone4477No ratings yet
- 2 - Econ 190.2 - What Is Money PDFDocument7 pages2 - Econ 190.2 - What Is Money PDFErielle SibayanNo ratings yet
- Teori Ekonomi Moneter: WWW - Debrina.lecture - Ub.ac - IdDocument17 pagesTeori Ekonomi Moneter: WWW - Debrina.lecture - Ub.ac - IdNicko Nur RakhmaddianNo ratings yet
- PDF Résumé ANGLAIS Current Monetary EconomicsDocument64 pagesPDF Résumé ANGLAIS Current Monetary EconomicsWiden EL KANDOUSSiNo ratings yet
- B A (Hon) Economics VI Semester Paper: Money and Financial MarketsDocument10 pagesB A (Hon) Economics VI Semester Paper: Money and Financial MarketsVikram SharmaNo ratings yet
- Monetary Eco BSC 2Document18 pagesMonetary Eco BSC 2tagashiiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Money and BankingDocument48 pagesUnit 1: Money and BankingAbhikaam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 5: MoneyDocument16 pagesChapter - 5: MoneyBeing NarratedNo ratings yet
- Concept of Money: Arpit KoshtiDocument15 pagesConcept of Money: Arpit KoshtiPallav SrivastavNo ratings yet
- Topic 3: Money AND The Payment SystemDocument30 pagesTopic 3: Money AND The Payment SystemDaireen ShahrinNo ratings yet
- Zoom Oec 330Document67 pagesZoom Oec 330abdul ahmad kilimaNo ratings yet
- Money ReviewerDocument5 pagesMoney ReviewerCalago, James Carlo V.No ratings yet
- Overview of The Study On Money, Banking and Financial MarketsDocument36 pagesOverview of The Study On Money, Banking and Financial MarketsFarapple24No ratings yet
- Money and Monetary Policy in Philippine SettingDocument48 pagesMoney and Monetary Policy in Philippine SettingIvan Jay AdobasNo ratings yet
- Forms: 3.1 Money and Its Importance DefinitionDocument26 pagesForms: 3.1 Money and Its Importance DefinitionBereket MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Characteristics and Functions of MoneyDocument2 pagesCharacteristics and Functions of Moneyanastasiasteele_greyNo ratings yet
- Monetary Economics Lectures Week 1Document14 pagesMonetary Economics Lectures Week 1Peggy van der meerNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document71 pagesCH 12DanielleNo ratings yet
- Prelims 2017: in DaysDocument34 pagesPrelims 2017: in Daysჯონ ფრაატეეკNo ratings yet
- Mishkin and Serletis 8ce Chapter 3Document24 pagesMishkin and Serletis 8ce Chapter 3Gillis Benson-ScollonNo ratings yet
- Summary Financial MarketsDocument12 pagesSummary Financial MarketsNgoc AnhNo ratings yet
- Money and Financial Markets Unit 1Document32 pagesMoney and Financial Markets Unit 1Teddy Jain100% (1)
- MoneyDocument18 pagesMoneyAkshit KansalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document39 pagesChapter 2Rashad MahmudzadaNo ratings yet
- Money and BankingDocument15 pagesMoney and BankingDj I amNo ratings yet
- Ch02 - Money and The Payment SystemDocument39 pagesCh02 - Money and The Payment SystemammendNo ratings yet
- Lu 2 - CH14Document50 pagesLu 2 - CH14bison3216No ratings yet
- Chap 2-3 - 4 - 5 LTTCDocument24 pagesChap 2-3 - 4 - 5 LTTCQuyên NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Lec 8.2 - What Is MoneyDocument18 pagesLec 8.2 - What Is MoneyAhmed MunawarNo ratings yet
- Nature and Functions of MoneyDocument99 pagesNature and Functions of MoneyAysha KamalNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Monetary Policy and Central BankingDocument7 pagesWeek 1 - Monetary Policy and Central BankingRestyM PurcaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 MBF MoneyDocument16 pagesChapter 1 MBF MoneyDuy Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- MONEYDocument12 pagesMONEYWALTER simsokweNo ratings yet
- Money PDFDocument26 pagesMoney PDFDevaang ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Monetary Economics - Lecture 2 - Functions of Money PDFDocument7 pagesMonetary Economics - Lecture 2 - Functions of Money PDFHariom LohiaNo ratings yet
- Monetary 2012E.CDocument434 pagesMonetary 2012E.CGirma Bekele0% (1)
- MONEYDocument5 pagesMONEYShazia SadhikaliNo ratings yet
- Functions of Money - Macro Extra Notes.Document2 pagesFunctions of Money - Macro Extra Notes.SONY GLANCY D SILVANo ratings yet
- Grade 12 The Evolution of MoneyDocument3 pagesGrade 12 The Evolution of MoneySalma AhmedNo ratings yet
- 4 Week GEHon Economics IInd Semeter Introductory MacroeconomicsDocument14 pages4 Week GEHon Economics IInd Semeter Introductory Macroeconomicskasturisahoo20No ratings yet
- Introduction Money PDGDocument46 pagesIntroduction Money PDGManav SonejaNo ratings yet
- Money and Banking 1: Dr. Rania Ramadan MoawadDocument11 pagesMoney and Banking 1: Dr. Rania Ramadan MoawadEhab HosnyNo ratings yet
- (133-137) Ae-111 (Assignment)Document18 pages(133-137) Ae-111 (Assignment)Asutosh PanigrahiNo ratings yet
- Nature and Functions of MoneyDocument23 pagesNature and Functions of MoneyMuhammad NazirNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document9 pagesUnit 1Morelate KupfurwaNo ratings yet
- Plastic Money Full Project Copy ARNABDocument41 pagesPlastic Money Full Project Copy ARNABarnab_b8767% (3)
- THE ECONOMICS OF MONEY AND FINANCIAL MARKETSDocument16 pagesTHE ECONOMICS OF MONEY AND FINANCIAL MARKETSThanh Thủy KhuấtNo ratings yet
- Money NotesDocument6 pagesMoney NotesNavya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Money Performs Four Specific FunctionsDocument8 pagesMoney Performs Four Specific FunctionsRabeeaManzoorNo ratings yet
- What Are The Important Functions of MoneyDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Important Functions of MoneyGanesh KaleNo ratings yet
- Evolution and Function of MoneyDocument16 pagesEvolution and Function of Moneys shaikhNo ratings yet
- Money and BankingDocument2 pagesMoney and BankingLý ĐinhNo ratings yet
- Cecchetti-5e-Ch02 - Money and The Payment SystemDocument46 pagesCecchetti-5e-Ch02 - Money and The Payment SystemammendNo ratings yet
- Banking, Money Supply and Monetary PolicyDocument13 pagesBanking, Money Supply and Monetary PolicySiti Nurul Alia RazaliNo ratings yet
- MA P.PointDocument40 pagesMA P.PointEndris ZeyinuNo ratings yet
- Economics - MoneyDocument15 pagesEconomics - MoneyChristopher John MwakipesileNo ratings yet
- Money & Banking: By: Professor Jermaine Whirl For Students of East Georgia CollegeDocument13 pagesMoney & Banking: By: Professor Jermaine Whirl For Students of East Georgia CollegeGuru CharanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document13 pagesChapter 18Phương Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 SummaryDocument6 pagesChapter 6 SummaryPhương Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document4 pagesChapter 2Phương Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- INTEREST RATES AND ASSET DEMANDDocument10 pagesINTEREST RATES AND ASSET DEMANDPhương Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Humana_Impact Report 2022Document125 pagesHumana_Impact Report 2022Raj KishoreNo ratings yet
- Origin:-The Term 'Politics, Is Derived From The Greek Word 'Polis, Which Means TheDocument7 pagesOrigin:-The Term 'Politics, Is Derived From The Greek Word 'Polis, Which Means TheJohn Carlo D MedallaNo ratings yet
- IFMP Mutual Fund Distributors Certification (Study and Reference Guide) PDFDocument165 pagesIFMP Mutual Fund Distributors Certification (Study and Reference Guide) PDFPunjabi Larka100% (1)
- The Cape Gelidonya Wreck: Preliminary ReportDocument19 pagesThe Cape Gelidonya Wreck: Preliminary ReportSerena MonacoNo ratings yet
- A Chart On The Covenant Between God and Adam KnownDocument1 pageA Chart On The Covenant Between God and Adam KnownMiguel DavillaNo ratings yet
- 121 - St. Jerome - Commentary On Galatians Translated by Andrew Cain The Fathers of The Church SerieDocument310 pages121 - St. Jerome - Commentary On Galatians Translated by Andrew Cain The Fathers of The Church SerieSciosis HemorrhageNo ratings yet
- Animal Farm WebquestDocument8 pagesAnimal Farm Webquestapi-388806678No ratings yet
- Phrases for Fluent English Speech and WritingDocument2 pagesPhrases for Fluent English Speech and WritingmolesagNo ratings yet
- Activity Design Gulayan Sa TahananDocument7 pagesActivity Design Gulayan Sa TahananArmelyn CasquejoNo ratings yet
- The World of Middle Kingdom Egypt (2000-1550 BC) : Contributions On Archaeology, Art, Religion, and Written SourcesDocument44 pagesThe World of Middle Kingdom Egypt (2000-1550 BC) : Contributions On Archaeology, Art, Religion, and Written Sourcesmai refaatNo ratings yet
- What Is Customer Relationship Management (CRM) ?Document4 pagesWhat Is Customer Relationship Management (CRM) ?MALAY KUMARNo ratings yet
- Tamil CinemaDocument7 pagesTamil CinemaPravin RamNo ratings yet
- HSBC Employees Union Vs NLRCDocument1 pageHSBC Employees Union Vs NLRCRobertNo ratings yet
- Court ObservationDocument2 pagesCourt Observationjobert cortez100% (1)
- Complete Golden Dawn System Index A CDocument15 pagesComplete Golden Dawn System Index A Charrisla11No ratings yet
- 2.tutorial - D V SDocument2 pages2.tutorial - D V SVivek MenonNo ratings yet
- Sir Thomas WyattDocument4 pagesSir Thomas WyattNoraNo ratings yet
- MARKET LEADER Pre U2 AVCN 1 PDFDocument11 pagesMARKET LEADER Pre U2 AVCN 1 PDFNgocdanNo ratings yet
- Donor Milk Banking and Breastfeeding in NorwayDocument6 pagesDonor Milk Banking and Breastfeeding in NorwayFrieta Diaz AstutiNo ratings yet
- Treaty of Detroit 1807Document3 pagesTreaty of Detroit 1807Hiram MillerNo ratings yet
- Plato Girls PDFDocument30 pagesPlato Girls PDFJohn Reigh CatipayNo ratings yet
- Case DigestDocument3 pagesCase DigestPaolo JamerNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Information Gathering For Through Listening For Everyday Life UsageDocument22 pagesEnglish: Quarter 1 - Module 1: Information Gathering For Through Listening For Everyday Life UsageGrayson RicardoNo ratings yet
- Datapage Top-Players2 NewJerseyDocument5 pagesDatapage Top-Players2 NewJerseydarkrain777No ratings yet
- Group 5 Regular-1Document33 pagesGroup 5 Regular-1SKY StationeryNo ratings yet
- Scribd 4Document1 pageScribd 4Churrita de OroNo ratings yet
- Peer Coaching Reflections and InsightsDocument8 pagesPeer Coaching Reflections and Insightsapi-269187486No ratings yet
- # 60 Abolafia Vs LiverpoolDocument5 pages# 60 Abolafia Vs LiverpoolMona LizaNo ratings yet
- Heavenly Nails Business Plan: Heaven SmithDocument13 pagesHeavenly Nails Business Plan: Heaven Smithapi-285956102No ratings yet
- Vandana SP - MacroeconomicsDocument3 pagesVandana SP - Macroeconomicssrikanth_balasubra_1No ratings yet