Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Smethod
Uploaded by
Babar KhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Smethod
Uploaded by
Babar KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
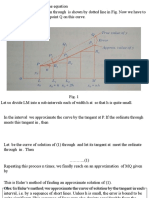
NUmerk:a/ methods Numet1ca1 Solution to OrdlnlllY Dlfferentlal Equations 11, 31
substituting all the requisites in Eqn (iv), we 'get , . , h h
,:. f{x1 + 2' >'t + 2 f(xI'Y I)} =f{0.15, l.1411216}
Y2 = 1.0959091 + 0~1[0.913422 + 0.8503373] I.
= 1.1840966 2(0.15) . , ,
= 1.1411216 - 1.1411216 = 0.8782223
(iii) Modified Euler's method: The formula is,
Now substituting the requisites in Eqn (vii), we get
h "h h Y2 = ~.0954762 + (0.1)(0.8782223) = 1.1832984
Y•••I =Y •• + !{x •• + 2'Y •• + 2 f(x ••,y",)} (v)
The value's obtained'ale shown below in a tabular form.
Putting m =:0 in the above Equation, we get ,
h h x Euler's method Improved ' 'Modified
yl=yo+h!{xo+ 2' Yo'+ 2f(~~YJ} (vi) "1! t
..
Euler's method Euler's method
. 2xo I
0, 1 1 1
.• ' ,,,
!(Xo,YJ = Yo - Yo = 1 0.1 '1'.1 " 'I, 1.0959091 1.0954762
0.2 1.19'18182 1.1840966 1.1832984
h 0.1· " h I" ••••
Yo + 2f(xo,YJ = 1 + T(1) = 1.05 ;xo + 2 = 0.05
h h ' '. " EXERCISE 11.2
:.! {xo + 2' Yo + 2 !(XC)' yJ} =! {0.05, l.05}
1. Use Euler's method and Improved Euler's method to approximate Y
2(0.05) whenx=O.l,giventhat ' ,
== 1.05 - 1.05 = 0.9547619 '''; t. '
dy y-x . ' ,
Hence, from Eqn (vi), we get ,. . :: dx'== Y+x ' y(0)=1 taktngh=0.2.
y) = 1 + (0.1) (0:09547619) = 1.095476i \
2. .' Solve y' = 3r +y in 0 ~ X ~ 1 by Euler's method taking h == 0.1 given
Putting m = 1 in Eqn (v), we get ,',
. tha(y(O)"; 4. .
h h ,: 3. Solve y' = x + y, y(0) choosing the step length 0.2 for y(1.2) by
Y2 = YI + hf {XI + 2' YI + '2 !(xl,y)} '(vii) Euler's
. , . method . ,/
,Using Euler'smethod solve y' == x + Y in 0 ~ X ~ 1 with h = 0.1, if I
XI +
h
'2= 0.1
0.1
+ T~0.15
- . ':- y(0) == 1. Find the exact value of Y at x = I, using analytical method.
, ,
Using Euler's method fmdy(0.6) ofy' = 1 - 2xy, given thaty(O) = 0
taking h ='0.2.
J( xl'Y) 2xI 2(01)
=Y - -, - = 1.0954762 _ .
Solve y' = - Y; y(0) = 1 by (i) Euler's method for y(0.04) and (ii)
I YI 1.0954762
Modified Euler's method for y(0.6).
== 0.9129071
Solve y' = x + Y + X)I, y(0) = 1 for y(0.1) taking h = 0.025, using
h 0.1 Euler's method. '
YI + '2 f (xl' Y I) == 1.0954762 +2 (0.9129071)
Given that y' = log(x + y) with y(0) = 1. Use (i) Improved Euler's
== 1.1411216 method to find y(O.2), y(O.5), (ii) Modified Euler's method to find
y(O.2).
Numerical methods Numerlcal Solution to Ordinary Dlff8l'8l1tial Equatlons 11. 33
Let h be the width of the equispaced values of x.
Use Euler's method and its' Modified form to obtain y(0.2), y(0.4)
and ),(0.6) correct to three decimal places given that y' = y - r, Then the first increment in~ is obtained by the following set offonnulae:
y(0) = 1. k =f(xo'yJ (11.41)
Use Euler's modified method to get y(0.25) given that y' = 2xy, == slope at the beginning of the interval (xo' yJ
y(0) = 1.
;; =f(xo + h, Yo + Jch)(say) (11.42)
Using Improved Euler's method, solve '
k" =f(xo+h, yo+;;h) (11.43)
y' = x + l..Jyl, y(0) = 1 in'the range 0 s'x S 0.6 taking h = 0.2. = slope at the beginning of the interval (xo' yo> -:
Given that j/ » 2 + ..J(xy) and'y(I) = 1. Findy(2) insteps ofO.:i'using Also, slope at the middle point of interval (xo' y J is
Improved Euler's method.
Givenyl)=r + y,y(O) = I, detenniney(O.I) andy(0.2) by Modified h h
Ie =f(x + -,
2
y + Ie-)
2
(11.44)
Euler's method. - 1 ,0 0
Solve yl) = Y + eX, y(0) ::I 0 for y(0.2), y(0.4) by Improved Euler's . Now the increment in the value ofy in the first interval is given by
method.
h
15. Solve yl) = Y + r, y(0) = 1 for y(0.02), y(0.04) and y(0.06) using Ay = '6 (Ie + 4le + ;;') l
(11.45)
Euler's Modified method.,
which can be easily obtained by the Simps~n's rule,
ANSWERS
. '
/ I .
1.0928, 1.0932
4.4, 4.843, 5.3393, 5.90023, 6.538253, 7.2670783, 8.1017861,
9.0589647,9.1039647,10.257361 '. , The increment in y in the second interval (XI' yJis obtained by the
y •
'J following formulae : '
3. 1.1831808
k = !(XI'YI)
4. 1.1; 1.22, 1.362, 1.5282, 1.7210, 1.9431, 2.1974,"-2.4871/2.8158, ;; = f(xi + h, YI + Jch)
3.1873; exact solution = 3.4366 '" " k" =!(xi + h. YI + ;;h)
S. 0.4748 6. 0.9603 ;.0.551368 ': h h
7. 1.1448 8. 1.0082, 1.0490; 1.0095
~ '\ ; ; .' ",",1:' I
k =f(x
I I
+ -,
2
y +k-)
I 2
9. 1.2, 1.432, 1.686; 1.218,,1.467, 1.737 ',." I " ". ,
~
.... _'.#... I, I . , ! h
10. 1.0625 11. 1.2309, 1.5253, 1.8851 and Ay = -(k+ 4k' + k")
6 .
12. 5.051 13. i.1105, 1.25026 .. .
, !
In the same way the increments in y can be obtained very easily in the
14. 0.24214,0.59116 '15. 1.0202, i.0408, 1.06.19 succeeding intervals.
\ ' .• ,r ,
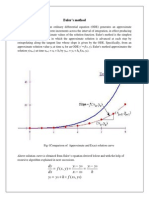
WOrk[n~,met!JOi! Given : =f(x, y), y(xJ =Yo
11.13 RUNGE'S METHOD
find out kl = hf(xo,yJ
let the differential equation be ." le2 = h!(xo + h, Yo + kl)
dy k, = h!(xo + h, Yo + A)
dx = !(x, y), y(xJ = Yo
You might also like
- Tutorials On MachinesDocument2 pagesTutorials On Machinesjenniferi_7No ratings yet
- Numerical methods-II PDFDocument9 pagesNumerical methods-II PDFRahul PinnamaneniNo ratings yet
- Maths Complete NotesDocument478 pagesMaths Complete NotesYashasvi VashishthaNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution of Ordinary DEDocument4 pagesNumerical Solution of Ordinary DEসৌভিক মাজিNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution of ODEDocument55 pagesNumerical Solution of ODETodd MaxeyNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods IIDocument9 pagesNumerical Methods IINik HenNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods Unit IVDocument41 pagesNumerical Methods Unit IVManoj SolankiNo ratings yet
- Math 432 HW 1.4 Solutions: Dy DXDocument7 pagesMath 432 HW 1.4 Solutions: Dy DXsamiNo ratings yet
- Euler's Method: Building The Function From The DerivativeDocument6 pagesEuler's Method: Building The Function From The DerivativeRamir Dann MalemitNo ratings yet
- Improved Euler (Heun'S) Method Calculator: Faktura, Timeføring, AltinnDocument7 pagesImproved Euler (Heun'S) Method Calculator: Faktura, Timeføring, AltinnazzamNo ratings yet
- DE Numerical PDFDocument43 pagesDE Numerical PDFVijayalakshmi MuraliNo ratings yet
- Solutions of Ordinary Differential Equations: Dr. Sukanta Deb and Dr. Subhash KumarDocument23 pagesSolutions of Ordinary Differential Equations: Dr. Sukanta Deb and Dr. Subhash KumarSheikh RiasatNo ratings yet
- ECC3012 TOPIC4 Numerical OdeDocument15 pagesECC3012 TOPIC4 Numerical Ode周天乐No ratings yet
- 4 Euler MethodDocument10 pages4 Euler MethodVivek GuptaNo ratings yet
- NM (Unit 4) NotesDocument16 pagesNM (Unit 4) NotesAxNo ratings yet
- Math4 Chapter 9Document34 pagesMath4 Chapter 9Muhd AzhiimNo ratings yet
- CHP 4.0 PDFDocument31 pagesCHP 4.0 PDFamiruddin sharifNo ratings yet
- Euler's MethodDocument10 pagesEuler's Methodbhupender ghosliyaNo ratings yet
- 6.7. Ordinary Differential Equation (Ode) and PDEDocument37 pages6.7. Ordinary Differential Equation (Ode) and PDEEyu KalebNo ratings yet
- Methods To Solve Part 3: Prepared by Khairi Ismail - 019 211 1389Document5 pagesMethods To Solve Part 3: Prepared by Khairi Ismail - 019 211 1389Khairi IsmailNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09Document33 pagesLecture 09uhjbjhNo ratings yet
- Sudhanshu 17026 Prac - 2Document7 pagesSudhanshu 17026 Prac - 2Yash SharmaNo ratings yet
- Transformation ProblemsDocument18 pagesTransformation Problemsrajya lakshmiNo ratings yet
- Finite Difference Method - Python Numerical MethodsDocument5 pagesFinite Difference Method - Python Numerical MethodsAmal ZakirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ODEDocument33 pagesChapter 5 ODEKhalid AlqahtaniNo ratings yet
- 10.3 Euler's MethodDocument12 pages10.3 Euler's MethodSatyanarayana NeeliNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 10 5Document12 pagesLecture Notes 10 5quarteyrichmond848No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 10 5Document12 pagesLecture Notes 10 5uncle wizNo ratings yet
- Euler's Method: Dy y y y y Fxy DX X X H y y H FxyDocument4 pagesEuler's Method: Dy y y y y Fxy DX X X H y y H FxySachin Kumar BhoiNo ratings yet
- Numerical Solution of Ordinary Differential EquationsDocument5 pagesNumerical Solution of Ordinary Differential EquationsAl Asad Nur RiyadNo ratings yet
- GEG 402 Slides of Numerical Analysis of Ordinary Differential Equations 3Document54 pagesGEG 402 Slides of Numerical Analysis of Ordinary Differential Equations 3Benedict HounsinouNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Numerical Methods For Initial Value ProblemsDocument60 pagesChapter 7 - Numerical Methods For Initial Value ProblemsAjayNo ratings yet
- OdeDocument17 pagesOdeMunir AslamNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Bessel Functions: Structure Page NoDocument30 pagesUnit 4 Bessel Functions: Structure Page NoJAGANNATH PRASADNo ratings yet
- Optimal ControlDocument26 pagesOptimal ControldannyabevoyagerNo ratings yet
- Ode 2Document29 pagesOde 2teperosombreroNo ratings yet
- MIT18 034s09 Proj02 EulerlDocument6 pagesMIT18 034s09 Proj02 EulerldecvsdsdfeNo ratings yet
- MIT18 034s09 Proj02 EulerlDocument6 pagesMIT18 034s09 Proj02 EulerlDeeksha MNo ratings yet
- Predictor-Corrector MethodDocument10 pagesPredictor-Corrector Method064 Jayapratha P RNo ratings yet
- Solve Numerical Differential Equation Using Euler Method CalculatorDocument3 pagesSolve Numerical Differential Equation Using Euler Method CalculatorSyed Rafay HashmiNo ratings yet
- Initial Value Problems For ODEsDocument38 pagesInitial Value Problems For ODEsAyananta GuhaNo ratings yet
- 2019 04 30 OctaveNBDocument6 pages2019 04 30 OctaveNBJose Luis GiriNo ratings yet
- Euler Modifiedeuler RunggkuttaDocument13 pagesEuler Modifiedeuler RunggkuttaKenjiDominicAdam SantosNo ratings yet
- Extra ProblemsDocument3 pagesExtra ProblemsahmedNo ratings yet
- ch2 PDFDocument6 pagesch2 PDFVienNgocQuangNo ratings yet
- Oscillations and Waves: Module 1: Oscillations Lecture 1: OscillationsDocument10 pagesOscillations and Waves: Module 1: Oscillations Lecture 1: OscillationsMahendra PanwarNo ratings yet
- Project 02: Simple Slope Static and Dynamic AnalysisDocument13 pagesProject 02: Simple Slope Static and Dynamic AnalysisJason YudhaNo ratings yet
- The Runge Kutta Memthod SilidesDocument3 pagesThe Runge Kutta Memthod SilidesMorneyNo ratings yet
- Euler's Method:Method of Solving Differential Equations of The First Order (The Easy Ones)Document12 pagesEuler's Method:Method of Solving Differential Equations of The First Order (The Easy Ones)Ahmed HassanNo ratings yet
- C8Document25 pagesC8Denis GarrixNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document3 pagesHomework 2amanidjeghloud04No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document25 pagesTutorial 3呀HongNo ratings yet
- T, y (T), y T y 0 y (T+H) y (T) H y (T+H) y (T) H T, y (T) U (T+H) U (T) H F T, U (T)Document11 pagesT, y (T), y T y 0 y (T+H) y (T) H y (T+H) y (T) H T, y (T) U (T+H) U (T) H F T, U (T)Trịnh Mạnh HùngNo ratings yet
- Lecture 07Document17 pagesLecture 07Atiq rifatNo ratings yet
- Intensity AdjustDocument14 pagesIntensity Adjustamorim.fatecNo ratings yet
- MEC 236 - Computer Applications 3Document224 pagesMEC 236 - Computer Applications 3Wafaa AimanNo ratings yet
- Taylor Series Method, Euler's Method and Modified Euler's MethodDocument8 pagesTaylor Series Method, Euler's Method and Modified Euler's MethodSourav PaulNo ratings yet
- Física Del Cosmos: Stars: Relativistic & NewtonianDocument28 pagesFísica Del Cosmos: Stars: Relativistic & NewtonianmariaNo ratings yet
- Transformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandTransformation of Axes (Geometry) Mathematics Question BankRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Tables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27From EverandTables of the Function w (z)- e-z2 ? ex2 dx: Mathematical Tables Series, Vol. 27No ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Silicon Controlled RectifiersDocument19 pagesSilicon Controlled RectifiersBabar KhanNo ratings yet
- Newton Raphson Method: Numerical AnalysisDocument8 pagesNewton Raphson Method: Numerical AnalysisBabar KhanNo ratings yet
- Budget 2018-2019 - Generators Diesel ConsumptionDocument1 pageBudget 2018-2019 - Generators Diesel ConsumptionBabar KhanNo ratings yet
- Estimated Budget 2018-2019 Department of Engineering and MaintenanceDocument6 pagesEstimated Budget 2018-2019 Department of Engineering and MaintenanceBabar KhanNo ratings yet
- Session#1Document35 pagesSession#1Babar KhanNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment and Risk Management PlanDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment and Risk Management PlanBabar KhanNo ratings yet
- Fractions Improper1 PDFDocument2 pagesFractions Improper1 PDFthenmoly100% (1)
- Column Design For Unbraced Columns Via Ec2Document5 pagesColumn Design For Unbraced Columns Via Ec2Muhammad Wazim AkramNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis 1Document20 pagesQuantitative Analysis 1FirdoseNo ratings yet
- Datalogic P51 Operator's ManualDocument2 pagesDatalogic P51 Operator's ManualGodzilNo ratings yet
- Shreya Sharma ReportDocument62 pagesShreya Sharma ReportshreyakesharwaniaryabhataNo ratings yet
- Moody's Report 2005Document52 pagesMoody's Report 2005as111320034667No ratings yet
- AsasDocument180 pagesAsasAres SagaNo ratings yet
- What Is Dynamometer ?Document28 pagesWhat Is Dynamometer ?Harpreet RandhawaNo ratings yet
- BoT-IoT - GenerationDocument40 pagesBoT-IoT - GenerationHassina KouachiNo ratings yet
- 01 RationalNumbersDocument11 pages01 RationalNumbersSusana SalasNo ratings yet
- CEC2017 After Revision Final VersionDocument9 pagesCEC2017 After Revision Final VersionAli GhavamiNo ratings yet
- Priorclave Autoclave Benchtop 40 60 Smart Data SheetDocument2 pagesPriorclave Autoclave Benchtop 40 60 Smart Data Sheetbrayo4No ratings yet
- Be Summer 2012Document2 pagesBe Summer 2012babaf79912No ratings yet
- Science 6 Quarter 3 Module 1Document32 pagesScience 6 Quarter 3 Module 1Mitzi Faye Cabbab100% (2)
- Basic Electronics Troubleshooting and Repair: Topics CoveredDocument3 pagesBasic Electronics Troubleshooting and Repair: Topics CoveredMahadevNo ratings yet
- Create Resume Word 2007Document3 pagesCreate Resume Word 2007Bozz BostonNo ratings yet
- Worksheet On Carboxylic AcidsDocument3 pagesWorksheet On Carboxylic AcidsmalisnotokNo ratings yet
- Figure 7-11 Inter-VLAN Routing Example1Document10 pagesFigure 7-11 Inter-VLAN Routing Example1GoodsonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Chapter 5 - BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN - UpdatedDocument48 pagesLecture 5 - Chapter 5 - BASIC COMPUTER ORGANIZATION AND DESIGN - UpdatedsaifsunnyNo ratings yet
- Cispr18-2 (Ed2 0) enDocument76 pagesCispr18-2 (Ed2 0) enSajjad PirzadaNo ratings yet
- Choosing A Well Format Contents and Storage: Quick Reference Pub. No. MAN0009818 Rev. C.0Document4 pagesChoosing A Well Format Contents and Storage: Quick Reference Pub. No. MAN0009818 Rev. C.0silmaril trehNo ratings yet
- Fault Location PLN MD 032012BDocument54 pagesFault Location PLN MD 032012BSatria RizkyNo ratings yet
- Optimization of Material Handling Trolley Using Finite Element AnalysisDocument13 pagesOptimization of Material Handling Trolley Using Finite Element AnalysisRumah WayangNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport LabDocument7 pagesCell Transport Labapi-267594083No ratings yet
- Coolerado SI 2250m Letter 8 5x11 Chart PDFDocument1 pageCoolerado SI 2250m Letter 8 5x11 Chart PDFFelipe Correa MahechaNo ratings yet
- Tricks Tips Mandolin WorshipDocument1 pageTricks Tips Mandolin Worshipd-rail100% (1)
- Artificial Intelligence - Midterm ExamDocument7 pagesArtificial Intelligence - Midterm ExamMemo AlmalikyNo ratings yet
- Gas Detection and Mapping Using An Autonomous Mobile Robot: September 2015Document7 pagesGas Detection and Mapping Using An Autonomous Mobile Robot: September 2015Jake StorageNo ratings yet
- Physics II Honors E&M Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPhysics II Honors E&M Cheat SheetCeline ShawNo ratings yet