0% found this document useful (0 votes)
127 views16 pagesHuman Rights
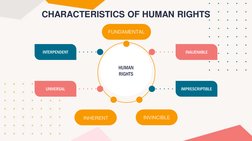
This document discusses upholding human rights and their importance for achieving sustainable peace. It defines key concepts like human dignity and human rights. Human rights are inherent to all humans regardless of attributes and include rights like life, liberty, freedom of expression. The document outlines characteristics of human rights like being fundamental, inalienable, universal. It discusses economic, social, cultural rights and civil/political rights. Finally, it explains how upholding human dignity and human rights through social justice is essential for sustainable peace and development by ensuring equal access and preventing discrimination.
Uploaded by
sarocamkentCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
127 views16 pagesHuman Rights
This document discusses upholding human rights and their importance for achieving sustainable peace. It defines key concepts like human dignity and human rights. Human rights are inherent to all humans regardless of attributes and include rights like life, liberty, freedom of expression. The document outlines characteristics of human rights like being fundamental, inalienable, universal. It discusses economic, social, cultural rights and civil/political rights. Finally, it explains how upholding human dignity and human rights through social justice is essential for sustainable peace and development by ensuring equal access and preventing discrimination.
Uploaded by
sarocamkentCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd