Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer Fpe
Uploaded by
CHRISTINE JEAN ENOC0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesPeace can be defined in both negative and positive terms. Negatively, peace is the absence of direct harm and violence, while positively, peace involves just, non-exploitative relationships and resolving underlying issues. A culture of peace includes important ideas like inner stillness, harmony, and cooperation. Peace education teaches about threats of violence and strategies for peace. It aims to contribute to a culture of peace by ensuring education addresses conflicts non-violently and satisfies basic human needs. Conflict is natural and inevitable, but addressing its underlying sources like misinformation, incompatible values, competition over interests, and oppressive social structures can help resolve conflicts non-violently.
Original Description:
Original Title
Reviewer fpe
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPeace can be defined in both negative and positive terms. Negatively, peace is the absence of direct harm and violence, while positively, peace involves just, non-exploitative relationships and resolving underlying issues. A culture of peace includes important ideas like inner stillness, harmony, and cooperation. Peace education teaches about threats of violence and strategies for peace. It aims to contribute to a culture of peace by ensuring education addresses conflicts non-violently and satisfies basic human needs. Conflict is natural and inevitable, but addressing its underlying sources like misinformation, incompatible values, competition over interests, and oppressive social structures can help resolve conflicts non-violently.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesReviewer Fpe
Uploaded by
CHRISTINE JEAN ENOCPeace can be defined in both negative and positive terms. Negatively, peace is the absence of direct harm and violence, while positively, peace involves just, non-exploitative relationships and resolving underlying issues. A culture of peace includes important ideas like inner stillness, harmony, and cooperation. Peace education teaches about threats of violence and strategies for peace. It aims to contribute to a culture of peace by ensuring education addresses conflicts non-violently and satisfies basic human needs. Conflict is natural and inevitable, but addressing its underlying sources like misinformation, incompatible values, competition over interests, and oppressive social structures can help resolve conflicts non-violently.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
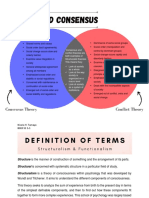
Reviewer WHAT IS PEACE?
MODULE 1 absence of harm and violence, not just personal or
direct harm and violence, but also structural or
-Peace education can be defined simply as “the
indirect harm and violence (Galtung,1996).
process of teaching people about the threats of
violence and strategies for peace.
-Hashim Salamat, the head of the largest Filipino -negative peace refers to the absence of war or
Muslim rebel group physical/ direct violence.
-Security, public order, safety, and peace are -positive peace refers to the presence of just and
accorded high priority by the government non-exploitative relationships,
-Executive Order No. 3, series of 2001, known as - Galtung, positive peace must resolve the
"Defining Policy and Administrative Structure for underlying issues
Government's Comprehensive Peace Action,"
CULTURE OF PEACE
where the Six Paths to Peace were unveiled
-comprehend important ideas and fundamental
-3 Programs for rebel returnee
values
Self reliance- developing and strengthening
- Culture can be defined as a social organization's
Islamization common symbols, norms, and values
Unity - Peace means inner stillness and calm, a sense of
well-being.
– harmony and cooperation.
President Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo issued
Executive Order (EO) No. 570 that mandates the -reality when societies are just and fair to all.
Department of Education (DepEd) and the
-Peace in societies exists when conflicts are
Commission on Higher Education (CHED) to
resolved non-violently and when there are practical
institutionalize Peace Education in Basic Education
efforts made to satisfy the basic needs of people in
and Teacher Education
a fair and reasonable manner.
PEACE EDUCATION IN MSU
- Peace is not simply the absence of conflict. Peace
- Mindanao State University was established encompasses more than the absence of conflict or
under Republic Act 1387, as amended, as a vehicle outward silence.
for peace and development in the MINSUPALA
PEACE IS JUSTICE DEVELOPMENT
- The Institute for Peace and Development in
-sufficient life goods{economic rights}
Mindanao
-dignity steem {cultural rights}
- BOR Resolution no. 225, S. 2007, known as
“Institutionalization of the Culture of Peace in -partcipation{political rights}
Education, Research and Action in Mindanao State
University System." aims integration and economic -solidarity{duty aswell as rights}
development of the Muslims and other cultural -ecological balance{integrational rights}
communities in Mindanao
- aims to ensure that education contributes to the
attainment of a culture of peace. - peace refers to the totality of existence
- conflicts of information, values, interests,
relationships, and structures{VILENDER 2021}
MODULE 2 PRT1
INFORMATION- have insufficient knowledge
CONFLICT AND VIOLENCE
CONFLICT VALUES- perceived or actual incompatibilities
with their belief systems
INTEREST- result of competition over perceived
- the Latin word “conflictus” which means collision or real incompatibilities in requirements
or clash. Conflict happens every day. RELATIONSHIPS- a result of misunderstandings,
intense negative emotions
-a fight or disagreement.
STRUCTURE- a result of other’s oppressive
activities.
- part of the human nature, it is a fact of human OTHER SOURCE OF CONFLICT
STERIOTYPE- negative opinion about a person or
- as antagonistic state of opposition, disagreement,
group
or incompatibility between two or more parties.
PREJUDICE- negative feeling or attitude towards
VIOLENCE
a person
• Racism -cultural or racial
- a response to a conflict, background is intrinsically superior
to that of others,
- any physical, emotional, verbal, institutional or • Sexism - beliefs, behaviors, and
structural action, behavior, attitude, policy, or institutional structures that
condition that aims to diminish, dominate or destroy marginalizes women (Mcginnis &
oneself and other Oehberg, 1991).
• Heterosexism -negative attitudes
toward lesbians and gay men.
- Violence is taken as a short cut method for
resolution of conflicts. • Classism - distancing from and
perceiving the poor as “the other”
(Lott, 1995).
PRINCIPLES OF CONFLICT • Linguicism - it refers to the negative
attitudes that members ofdominant
- ideas, principles, and beliefs are incompatible.
language groups have against members of
Diez et al. (2006),
non-dominant (Chen-Hayes, Chen &
-CONFLICT IN NATURAL Athat, n.d.).
- CONFLICT IS AN ON-GOING PROCESS • Ageism - it refers to negative views
toward the young and the elderly.
- CONFLICT IS A DYNAMIC PROCESS
• Lookism - bias against persons who do not
- CONFLICT IS POSITIVE conform to predetermined criteria of beauty
(Nario-Galace, 2003).
- CONFLICT IS EMBEDDED IN ALL
RELATIONSHIPS • Religious Intolerance - this pertains to the
prejudice against those who are
followers of religious other than one’s own.
SOURCES OF CONFLICT
DISCRIMINATION- negative actions toward
members of a specific social (Franzoi, 1986).
OPPRESSION- exercise of tyranny by a ruling
group.
You might also like
- Morality Vs EthicsDocument28 pagesMorality Vs EthicsBea Dacillo Bautista100% (1)
- Overcoming Systemic Prejudice and Discrimination: Achieving Success Through Ethical ResilienceFrom EverandOvercoming Systemic Prejudice and Discrimination: Achieving Success Through Ethical ResilienceNo ratings yet
- Mindfulness 101Document7 pagesMindfulness 101api-506328259No ratings yet
- Team Teach MethodsDocument25 pagesTeam Teach MethodsAitha michael100% (1)
- H2019ODC010 - Slumdog Millionaire - AnalysisDocument9 pagesH2019ODC010 - Slumdog Millionaire - AnalysisAfzal Mohammed100% (1)
- DRR11,12 Ic 9Document4 pagesDRR11,12 Ic 9ben lee100% (1)
- Amherst College Common Language GuideDocument40 pagesAmherst College Common Language GuideThe College Fix69% (16)
- NSTP CWTS Specific Module 3 Peace EducationDocument41 pagesNSTP CWTS Specific Module 3 Peace EducationShai MacapillarNo ratings yet
- Peace Education MidtermDocument23 pagesPeace Education Midtermjdj roberto100% (1)
- Apology Letter For BullyingDocument3 pagesApology Letter For BullyingAngela0% (1)
- UCSP Module 11Document14 pagesUCSP Module 11Eloisa Jane Bituin100% (3)
- Report Card Comments For ScholasticDocument5 pagesReport Card Comments For ScholasticEdison Uy100% (1)
- Critical Incide-WPS OfficeDocument18 pagesCritical Incide-WPS OfficeRimRose LamisNo ratings yet
- Ling-6 Sound Test - How ToDocument7 pagesLing-6 Sound Test - How ToJohnson JayarajNo ratings yet
- Peace EducationDocument42 pagesPeace EducationOnath OnadesNo ratings yet
- UCSP M11 Addressing-InequaltiesDocument14 pagesUCSP M11 Addressing-InequaltiesMayveil SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Peace and Global EducationDocument23 pagesPeace and Global EducationAnnaliza GalvezNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Creativity Prospects and ParadigmsDocument13 pagesThe Concept of Creativity Prospects and ParadigmsEstefaníaNo ratings yet
- Peace Ed Lesson 1 & 2 - OBALDocument14 pagesPeace Ed Lesson 1 & 2 - OBALRey Mark F Agac-acNo ratings yet
- Peace Education (Autosaved)Document34 pagesPeace Education (Autosaved)VI DALAGAN RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Cwts Module 3Document6 pagesCwts Module 3Belle MendozaNo ratings yet
- Peace Education (2) 1Document20 pagesPeace Education (2) 1marloulelanse5No ratings yet
- Peace EducationDocument27 pagesPeace Educationwemod20123No ratings yet
- Peaceful Conflict TransformationDocument26 pagesPeaceful Conflict TransformationJuNo ratings yet
- Peace Promoting To Peace BuildingDocument104 pagesPeace Promoting To Peace BuildingCPPO 2nd Cotabato PMFCNo ratings yet
- On Social ProcessDocument31 pagesOn Social ProcessAmlan jyoti thanapati0% (1)
- NSTP Module 8 - Peace Education: Example: War, Rape, Wife Battering, Child Abuse, and CrimesDocument4 pagesNSTP Module 8 - Peace Education: Example: War, Rape, Wife Battering, Child Abuse, and CrimesLove Jovellanos Ü100% (1)
- What Is PeaceDocument2 pagesWhat Is PeaceJhanice ArenzanaNo ratings yet
- Ge 11 Ethics ReviewerDocument6 pagesGe 11 Ethics ReviewerWalwal WalwalNo ratings yet
- FPE 101 Lec 1 and 2 NotesDocument4 pagesFPE 101 Lec 1 and 2 NotesReginaNo ratings yet
- Socsci 5-8 ReviewerDocument6 pagesSocsci 5-8 Reviewerjaymel gabrielle escasinasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - The Political SelfDocument4 pagesLesson 1 - The Political SelfJoana Mariel BalotroNo ratings yet
- Understanding Peace and ConflictDocument19 pagesUnderstanding Peace and ConflictAllen Carl Abcede PadayhagNo ratings yet
- What Is Peace EducationDocument10 pagesWhat Is Peace EducationMariam RehmanNo ratings yet
- Final Understanding Peace and ViolenceDocument10 pagesFinal Understanding Peace and Violencenica onicaNo ratings yet
- Finalnatalaga As inDocument25 pagesFinalnatalaga As inAnggeNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER II: Historical and Sociological/ Cultural Theories of PeaceDocument9 pagesCHAPTER II: Historical and Sociological/ Cultural Theories of PeaceKristine Mariz OchoNo ratings yet
- Gender Peacebuilding enDocument8 pagesGender Peacebuilding enK K GhoshNo ratings yet
- Davis - 1938 - Mental Hygiene and The Class StructureDocument11 pagesDavis - 1938 - Mental Hygiene and The Class StructureOscar MotaNo ratings yet
- Gender and Peace EducationDocument20 pagesGender and Peace EducationSay Say B. BullecerNo ratings yet
- Developing Social Justice Literacy: An Open Letter To Our Faculty ColleaguesDocument5 pagesDeveloping Social Justice Literacy: An Open Letter To Our Faculty ColleaguesYarisol Castillo PuertoNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Module 11Document2 pagesUcsp Module 11Alex Jethro TigoyNo ratings yet
- TNCT - 9Document15 pagesTNCT - 9Paulyne PascualNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 (FSS) - TAMAYODocument4 pagesActivity 1 (FSS) - TAMAYOMelvin TamayoNo ratings yet
- SOC SCI 2 MTE ReviewerDocument6 pagesSOC SCI 2 MTE ReviewerNini JimbuuNo ratings yet
- P.ed SIP - Readings For Midterms-1Document28 pagesP.ed SIP - Readings For Midterms-1Ca-ay, Clent Dave A.No ratings yet
- Unit 7 - Conformity and DevianceDocument30 pagesUnit 7 - Conformity and DevianceG9 P Sophia MarzoNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3: Knowledge, Skills and Attitudes/Values in PeaceDocument16 pagesLESSON 3: Knowledge, Skills and Attitudes/Values in PeaceMariz OchoNo ratings yet
- EDUM571Document25 pagesEDUM571Irreane Twenty-Third WPNo ratings yet
- Fiske, Virtuous Violence 24.09.2012 PDFDocument75 pagesFiske, Virtuous Violence 24.09.2012 PDFAlex E. MoralesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Lesson 3 (Text)Document9 pagesChapter 1 - Lesson 3 (Text)Mabang Reina Farhoney ShahanieNo ratings yet
- Dimensionalizing Cultures Hofstede ModelDocument13 pagesDimensionalizing Cultures Hofstede Modelt varshanNo ratings yet
- Hofstede's Cultural DimensionsDocument35 pagesHofstede's Cultural DimensionsAALIYA NASHATNo ratings yet
- Cultural DiffDocument17 pagesCultural DiffsushmanalavadeNo ratings yet
- GSPS SemiDocument35 pagesGSPS SemiFamela TacudNo ratings yet
- Peach Education SummaryDocument19 pagesPeach Education SummaryJohn Rommel Apostol SevillaNo ratings yet
- Uts ReviewerDocument15 pagesUts ReviewerVivien TaldoNo ratings yet
- MahiveDocument26 pagesMahivekhushi chopra 0050No ratings yet
- NSTP 1 ReviewerDocument7 pagesNSTP 1 ReviewerYassin BusarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Lesson 3Document8 pagesChapter 1 - Lesson 3Lorie Jane L. LabordoNo ratings yet
- Possessiveness-Control or Ownership of Nongenerosity - Unwillingness To Share Envy - Feelings of Hatred or Dislike atDocument5 pagesPossessiveness-Control or Ownership of Nongenerosity - Unwillingness To Share Envy - Feelings of Hatred or Dislike atPrecious ViterboNo ratings yet
- Totalitarianism Say-Mean-Matter (Students)Document4 pagesTotalitarianism Say-Mean-Matter (Students)nietoalianahNo ratings yet
- Binary SystemDocument9 pagesBinary Systemblessie balagtasNo ratings yet
- Ge 11 NotesDocument8 pagesGe 11 NotesCherie Mae TanNo ratings yet
- Toward More Inclusive Empathy: A Survey of Relational Worldviews and Alternative Modes of HelpingDocument17 pagesToward More Inclusive Empathy: A Survey of Relational Worldviews and Alternative Modes of HelpingOana BigNo ratings yet
- Purposive CommunicationDocument9 pagesPurposive CommunicationMARY ANGEL LOU GOMEZNo ratings yet
- CH - 21 Prejudice, Discrimination and InequalityDocument4 pagesCH - 21 Prejudice, Discrimination and Inequalitydpsr mathsNo ratings yet
- Civic and Peace Education 2019Document17 pagesCivic and Peace Education 2019Edwine Jeremiah ONo ratings yet
- Values CategorisationDocument16 pagesValues Categorisationmegh9100% (3)
- Information: Identifying Identifying Credible Credible Nutrition Nutrition Information Information Online OnlineDocument2 pagesInformation: Identifying Identifying Credible Credible Nutrition Nutrition Information Information Online OnlinePrince Joshua SumagitNo ratings yet
- Digital Harbor Foundation - Strategic Plan - 2019-2021Document20 pagesDigital Harbor Foundation - Strategic Plan - 2019-2021Andrew CoyNo ratings yet
- Career Preferences and Factors Influencing The Career ChoiceDocument2 pagesCareer Preferences and Factors Influencing The Career ChoiceEricka CabalunaNo ratings yet
- Quest To Learn: Developing The School For Digital KidsDocument165 pagesQuest To Learn: Developing The School For Digital KidsThe MIT Press100% (2)
- Chcpa301b v2 Deliver Care Services Using A Palliative ApproachDocument59 pagesChcpa301b v2 Deliver Care Services Using A Palliative Approachapi-87967494No ratings yet
- A Theoretical Model: Factors Influence Turnover Intention in Commercial Banks MalaysiaDocument9 pagesA Theoretical Model: Factors Influence Turnover Intention in Commercial Banks Malaysiasmart_kidzNo ratings yet
- WLP Life Skills Q1 W5 Module 3session 3 and 4 Leadership and TeamworkDocument4 pagesWLP Life Skills Q1 W5 Module 3session 3 and 4 Leadership and TeamworkPridas GidNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1: Submitted by Jeet Thakkar, DIV - C. PRNDocument2 pagesTutorial 1: Submitted by Jeet Thakkar, DIV - C. PRNJeetNo ratings yet
- Increasing Ecoliteracy and Student Creativity in Waste UtilizationDocument10 pagesIncreasing Ecoliteracy and Student Creativity in Waste UtilizationMujianiNo ratings yet
- Educational Phi-WPS OfficeDocument15 pagesEducational Phi-WPS OfficeMarkchester CerezoNo ratings yet
- 3 Coaching Styles: Command Style Submissive Style Cooperative StyleDocument5 pages3 Coaching Styles: Command Style Submissive Style Cooperative StylecikgujessNo ratings yet
- Group 2 FB Students Acad PerformanceDocument41 pagesGroup 2 FB Students Acad PerformanceHin YanNo ratings yet
- The Constructivist Turn in International Relations Theory: Jeffrey T. CheckelDocument19 pagesThe Constructivist Turn in International Relations Theory: Jeffrey T. Checkelain_94No ratings yet
- Being With OthersDocument18 pagesBeing With OthersBambi IbitNo ratings yet
- PPM AssignmentDocument8 pagesPPM AssignmenttwmailinatorNo ratings yet
- Rezumat in EnglezaDocument2 pagesRezumat in EnglezaBianca DorofteiNo ratings yet
- Ddis DSM 5Document20 pagesDdis DSM 5AlexisMolinaCampuzanoNo ratings yet
- Action Plan CriteriaDocument2 pagesAction Plan Criteriaapi-269517091No ratings yet
- Expert Systems TutorialDocument8 pagesExpert Systems TutorialKuganeswara Sarma AatithanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Accounting TheoryDocument20 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Accounting TheorydhfbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbhNo ratings yet
- RWS4THQUARTEREXAMDocument4 pagesRWS4THQUARTEREXAMDA FTNo ratings yet