Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HW 11
Uploaded by
prashant kumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HW 11
Uploaded by
prashant kumarCopyright:
Available Formats
ESO 202A/204
ASSIGNMENT # 11
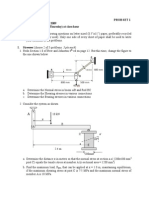
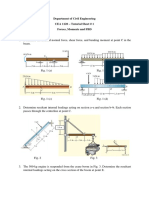
1. A 100×500 mm rectangular wooden beam supports a 40 kN load as shown in Fig.
1. At section a-a, the grain of the wood makes an angle of 20o with the axis of
the beam. Find the shearing stress along the grain of the wood at points A and B
caused by the applied concentrated force. [Ans. τA = 0.835 MPa, τB = 1.234 MPa]
2. A cast iron beam is loaded as shown in Fig. 2. Determine the principal stresses at
the three points, A, B, and C, caused by the applied force. The moment of inertia
of the cross-sectional area around the neutral axis is 124×106 mm4 . [Ans. At A,
σ2 = −18.87 MPa; At B, σ1,2 = 0.18 and −9.37 MPa; At C, σ1 = 16.61 MPa]
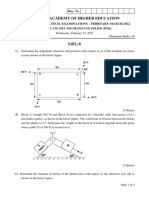
3. A shaft of 40 mm diameter is subjected to an axial tensile force of 50π kN. What
torque may be applied to this shaft in addition to this axial force without exceeding
the maximum shearing stress of 130 MPa? [Ans. 1.432 kN.m]
4. A 50-mm diameter rod is subjected at its free end to an inclined force, F = 225π
N, as shown in Fig. 3 (in plan view, F acts in the x-direction). Determine the
magnitudes and directions of the stresses due to F on the elements A and B at
section a-a. Show the results on elements clearly related to the points on the rod.
[Ans. At A, σyy = 17 MPa and τyx = −6.2 MPa; At B, σyy = −32.0 MPa and τyz
= 6.48 MPa]
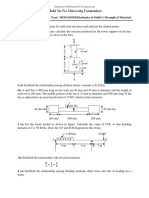
5. A steel pressure vessel, 500 mm in (mean) diameter and of 5 mm thickness, acts
also as an eccentrically loaded cantilever as shown in Fig. 4. If the internal pressure
is 2 MPa and the applied force, W = 125.7 kN, determine the principal stresses at
point A. [Ans. σ1,2 = 128.41 and 20.09 MPa]
6. Two pulleys of 100π mm radius are attached to a 50-mm diameter solid shaft which
is supported by the bearings as shown in Fig. 5. If the maximum shearing stress is
limited to 35 MPa, what is the largest magnitude which the forces F can assume?
The direct shearing stress caused by the internal shear force may be neglected.
[Ans. F = 2187.5 N]
You might also like
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practise Problems Set05Document8 pagesPractise Problems Set05rohit kumarNo ratings yet
- 11.a.ii - ME03031 QA 1Document22 pages11.a.ii - ME03031 QA 1Bakkiya Raj100% (1)
- TUT 1 Bending StressDocument8 pagesTUT 1 Bending StressVictoriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Simple StressesDocument39 pagesChapter 1 - Simple StressesJovy Notorio100% (2)
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 4-IiDocument4 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 4-IiMilton CobaNo ratings yet
- Tutorials 2016Document54 pagesTutorials 2016Mankush Jain100% (1)
- Problems DME PDFDocument22 pagesProblems DME PDFAbhay Sahu100% (1)
- Ce2201 QB2Document15 pagesCe2201 QB2Balaji KumarNo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument11 pagesStrength of Materialsjerold_arandiaNo ratings yet
- Sheet No.2 (Simple Stress)Document3 pagesSheet No.2 (Simple Stress)elhalawanyh46No ratings yet
- SOM Question BankDocument5 pagesSOM Question BankbmdbmdbmdNo ratings yet
- Ex1 Unsymmetrical BendingDocument3 pagesEx1 Unsymmetrical Bendinganon_530669663No ratings yet
- 212-Chpt 8Document5 pages212-Chpt 8zainabcomNo ratings yet
- Prac Prob PSADDocument10 pagesPrac Prob PSADjeannechoiashNo ratings yet
- Homework No. 1: Department of Strength of Materials and Vibrations Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringDocument2 pagesHomework No. 1: Department of Strength of Materials and Vibrations Faculty of Mechanical EngineeringTolea AdrianNo ratings yet
- 9A01301 Mechanics of SolidsDocument4 pages9A01301 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Civil Problem Set 7Document3 pagesCivil Problem Set 7ShreyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1Document3 pagesTutorial Chapter 1ACC SHNo ratings yet
- Stress Practice ProblemsDocument6 pagesStress Practice ProblemsSayantan ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 3Document3 pagesTutorial Sheet 3Ayush KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture Eight PDFDocument9 pagesLecture Eight PDFdave limNo ratings yet
- Es 13 Thr1 Prob Set 1Document6 pagesEs 13 Thr1 Prob Set 1Tim AcostaNo ratings yet
- EMG 4103 SOLID AND STRUCTURAL MECHANICS III EXAM (Revised) - PrintreadyDocument4 pagesEMG 4103 SOLID AND STRUCTURAL MECHANICS III EXAM (Revised) - PrintreadyDuncoh DunNo ratings yet
- RC - Exam 2019Document2 pagesRC - Exam 2019aloy locsinNo ratings yet
- Design Preboard Exam NOV 2021Document17 pagesDesign Preboard Exam NOV 2021Glaiza Marie100% (1)
- MOS Endsem Paper 2022 Sem 1Document4 pagesMOS Endsem Paper 2022 Sem 1Xyz XyzNo ratings yet
- Worked Exp Mechanics 2 PDFDocument144 pagesWorked Exp Mechanics 2 PDFamit1234No ratings yet
- Tutorial 5Document4 pagesTutorial 5Kumar ShivamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document4 pagesTutorial 1NayefGhazaliNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering & ConstructionDocument13 pagesStructural Engineering & ConstructionREX AMPONGANNo ratings yet
- ME202Document2 pagesME202nitinsparksNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 StressDocument2 pagesSheet 1 Stressamr hassanNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 1 Properties of MaterialDocument9 pagesProblem Set 1 Properties of Materialale.123No ratings yet
- Theory of Elasticity Question PaperDocument2 pagesTheory of Elasticity Question PaperDESHMUKH ANKIT PRAKASHRAONo ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument7 pagesStrength of MaterialsBlessa IsidroNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials: Prepared By: Engr. Jeric P. SarteDocument30 pagesStrength of Materials: Prepared By: Engr. Jeric P. SarteGiacomo EllieNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1, Simple StressDocument71 pagesChapter-1, Simple Stresssherlockhisham100% (2)
- Assignment For IPEDocument4 pagesAssignment For IPEAbirHasanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6 BendingDocument4 pagesTutorial 6 BendingKishenNo ratings yet
- Strema 102Document4 pagesStrema 102Hazel VidallonNo ratings yet
- BAUTISTA, DARLENE JOY C. - 2CE-C - Activity 1-Prelim TermDocument24 pagesBAUTISTA, DARLENE JOY C. - 2CE-C - Activity 1-Prelim TermDARLENE JOY C. BAUTISTA67% (3)
- RC 2019Document3 pagesRC 2019aloy locsinNo ratings yet
- Enhancement Program TIMBER DESIGNDocument7 pagesEnhancement Program TIMBER DESIGNChristian VillenaNo ratings yet
- PS1 Mom IDocument4 pagesPS1 Mom IMuhammad QasimNo ratings yet
- Student Stresses in BeamsDocument3 pagesStudent Stresses in Beamsparamarthasom1974No ratings yet
- Strength of MaterialsDocument61 pagesStrength of MaterialsEkajara JoshNo ratings yet
- Som-Mos-I 205Document4 pagesSom-Mos-I 205Muzaffar AlamNo ratings yet
- ĐỀ THI CUOI HỌC KỲ ME3046Document2 pagesĐỀ THI CUOI HỌC KỲ ME3046Hữu NguyênNo ratings yet
- 2 - Shear StressDocument14 pages2 - Shear StressGerard CoNo ratings yet
- Draw The SFD BMDDocument12 pagesDraw The SFD BMDAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Normal Stress Stress: Simple StressesDocument24 pagesNormal Stress Stress: Simple StressesJake Tuwa MiguelNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsDocument7 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Review ProblemsadrianNo ratings yet
- Design 1qsy1718 QuestionsDocument9 pagesDesign 1qsy1718 QuestionsRachel Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheets SOMDocument20 pagesTutorial Sheets SOMPriyanshu Sharma100% (1)
- UTHMDocument8 pagesUTHMJoena LindaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 29 Strut Tie Modeling Example FW 18octDocument40 pagesLecture 29 Strut Tie Modeling Example FW 18octMitchell Mulvey100% (1)
- ME 212 Tutorial 4Document2 pagesME 212 Tutorial 4Mihir Kumar MechNo ratings yet