Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Blank Map
Blank Map
Uploaded by
Wedad AlfaqeehOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Blank Map
Blank Map
Uploaded by
Wedad AlfaqeehCopyright:
Available Formats
Voicing :
1- When the vocal folds are spread apart, the
air from the lungs passes between them
with no obstruction, producing voiceless
sounds.
For example,[P],[F],[T]
2- When the vocal folds are drawn together,
the air from the lungs repeatedly pushes
them apart as it passes through, with a
vibration effect, producing voiced sounds
Bilabials: The sounds formed using both
upper and lower lips.
For example: [P],[B],[M],[W] .
Labiodentals:
The sounds formed with upper teeth and the
lower lip.
For example: [F],[V]
Dentals:
the sound formed with the tongue tip and
the upper front teeth.
For example: [θ], [ð].
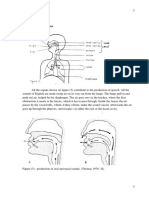
Place of articulation :
The location inside the mouth at which the Alveolar: The sounds formed with the front
constriction takes place, these symbols will part of the tongue on the alveolar ridge. For
be enclosed within square brackets [ ]. example: [t],[s],[d],[z]
The sounds of The general study of the characteristics
Phonetics of speech sounds, how speech sounds Palatals: the sounds formed with the tongue
language produced in the vocal track and and the very front of the palate. For
example: [ʃ], [ʧ] [ʒ], [ʤ], [j]
Velars: The sounds produced with the back
of the tongue, against the velum.
For example: [k], [g], [ŋ]
Glottals: The sounds produced without the
active use of the tongue and other parts of
the mouth.
For example: [h]
Stops: block air flow, let it go abruptly. For
example: [p], [t], [k] [b], [d], [g]
Fricatives: almost block airflow, let it escape
through a narrow gap
For example: [f], [θ], [s], [ʃ], [h], [v], [ð], [z], [ʒ]
Affricates:combine a brief stop with fricative.
For example [ʧ], [ʤ]
Manner of articulation: How the sounds
Nasals: lower the velum, let air flow out
articulated .
through nose
For example: [m], [n], [ŋ]
Liquids: raise and curl tongue, let airflow
escape round the sides
For example: [l], [r]
Glides: move tongue to or from a vowel
For example: [w], [j]
You might also like
- Savage Worlds - Horror Companion (BETA) (SWADE) (v1.0) (OEF) (2023-01-06)Document198 pagesSavage Worlds - Horror Companion (BETA) (SWADE) (v1.0) (OEF) (2023-01-06)coibraucrojeutra67% (3)
- Into The Unknown - The Dungeon Survival HandbookDocument162 pagesInto The Unknown - The Dungeon Survival HandbookAlejandro Nelson100% (2)
- Pangilinan v. CA. 279 SCRA 590 (1997)Document5 pagesPangilinan v. CA. 279 SCRA 590 (1997)ELIJAH GABRIEL GARCIANo ratings yet
- GHL #02Document8 pagesGHL #02esha khanNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument100 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyFheil Karl Failma100% (6)
- Eliade, Mircea - Portugal Journal (SUNY, 2010) PDFDocument298 pagesEliade, Mircea - Portugal Journal (SUNY, 2010) PDFCarlos De Lara100% (1)
- THE SOUNDS OF LANGUAGE PerubahanDocument15 pagesTHE SOUNDS OF LANGUAGE PerubahanArtika WulandariNo ratings yet
- 4 Phonetics 2 - Vowel Consonant - Place Manner of ArticulationDocument15 pages4 Phonetics 2 - Vowel Consonant - Place Manner of ArticulationFany WPNo ratings yet
- Distinctive Features 221220 040304Document77 pagesDistinctive Features 221220 040304imanezada01No ratings yet
- Fragmento de Clases Apuntes Generales 19-12-14Document7 pagesFragmento de Clases Apuntes Generales 19-12-14Jorge AriasNo ratings yet
- согласные звуки английского языкаDocument15 pagesсогласные звуки английского языкаГульжан АбдыкановаNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Phonetics ENG260Document58 pagesChapter 3 - Phonetics ENG260sdd642hcjpNo ratings yet
- Objectives: Introduction To Linguistics Session 2: Speech Sounds: Phonetics and PhonologyDocument13 pagesObjectives: Introduction To Linguistics Session 2: Speech Sounds: Phonetics and PhonologyExsin CotNo ratings yet
- Phonetics (II)Document29 pagesPhonetics (II)呂瀅綺No ratings yet
- Phonetics (I)Document30 pagesPhonetics (I)呂瀅綺No ratings yet
- Unit-IV: Phonetics 4.1 IPA SymbolsDocument27 pagesUnit-IV: Phonetics 4.1 IPA SymbolsAngel Mae RamosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document2 pagesChapter 3ellyna_elvindoNo ratings yet
- Prelim: Spa: Dentals/InterdentalsDocument2 pagesPrelim: Spa: Dentals/InterdentalsJoanna PerezNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument48 pagesPhoneticsBE 005No ratings yet
- Chapter Five: (The Sounds of Language) : Articulation: Voiced and VoicelessDocument2 pagesChapter Five: (The Sounds of Language) : Articulation: Voiced and VoicelessSara AHNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2-Phonetic and PhonologyDocument11 pagesUNIT 2-Phonetic and PhonologyIka UtamaNo ratings yet
- PHONETICS: The Sounds of LanguageDocument5 pagesPHONETICS: The Sounds of LanguageMayMay Serpajuan-SablanNo ratings yet
- 1 - Anterior StopsDocument1 page1 - Anterior StopsTessaNo ratings yet
- Consonants Place of ArticulationDocument3 pagesConsonants Place of ArticulationPenelope Selinee LopezNo ratings yet
- Linguistics: BasicsDocument13 pagesLinguistics: BasicsrobertNo ratings yet
- Sound Segments Identity of Speech SoundsDocument8 pagesSound Segments Identity of Speech SoundsGladys CedeñoNo ratings yet
- 1 Place of ArticulationDocument4 pages1 Place of ArticulationAmairani MellNo ratings yet
- Linguistics Xomplex Ok (Auto)Document12 pagesLinguistics Xomplex Ok (Auto)Sebas PNo ratings yet
- Consonants and Vowels Differences. According To The Specific Character of The WorkDocument3 pagesConsonants and Vowels Differences. According To The Specific Character of The WorkАнастасія СлободяникNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 NotesDocument8 pagesLesson 1 NoteslunajungkooktNo ratings yet
- Intro To Ling 3 - The Sounds of LanguageDocument11 pagesIntro To Ling 3 - The Sounds of LanguageChintyaNo ratings yet
- Features: Phonology (Lane 335)Document27 pagesFeatures: Phonology (Lane 335)ዘብሄረ መኧኸኧተኽ ኸብታሙNo ratings yet
- Features: Phonology (Lane 335)Document27 pagesFeatures: Phonology (Lane 335)ዘብሄረ መኧኸኧተኽ ኸብታሙNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Phonetics ENG260Document58 pagesChapter 3 - Phonetics ENG260sdd642hcjpNo ratings yet
- English Phonetics IDocument7 pagesEnglish Phonetics Ixalba14No ratings yet
- English Phonetics: Consonant SystemDocument7 pagesEnglish Phonetics: Consonant Systemxalba14No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document54 pagesChapter 3o0old3mNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument41 pagesPhoneticsDg Duy KimNo ratings yet
- Phonetics III The Sounds of LanguageDocument9 pagesPhonetics III The Sounds of Languagecarlosoba3No ratings yet
- Articulatory Phonetics: BilabialsDocument6 pagesArticulatory Phonetics: BilabialsRenier ArceNoNo ratings yet
- Intro To Language 2Document46 pagesIntro To Language 2Patrick LysonNo ratings yet
- Sounds of EnglishDocument35 pagesSounds of EnglishAlaizaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 The Sounds of LanguageDocument39 pagesUnit 3 The Sounds of LanguagebaderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Lin PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 3 Lin PDFMahmoud A harfoushNo ratings yet
- Articulatory PhoneticsDocument32 pagesArticulatory PhoneticsRahayu Ratu AzizahNo ratings yet
- Week #2 PDFDocument11 pagesWeek #2 PDFYocelyn EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - PhoneticsDocument41 pagesChapter 2 - Phoneticsthaitran1990proNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PhoneticsDocument52 pagesIntroduction To PhoneticsMarco AntonioNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2. ConsonantsDocument8 pagesLecture 2. ConsonantsEl Joumaili SimoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9 Sounds of EnglishDocument37 pagesLesson 9 Sounds of Englishzhumie10No ratings yet
- Phonetics Module ReferenceDocument17 pagesPhonetics Module ReferenceGabriel Angelo AlundayNo ratings yet
- Phonetic Transcriptions: Different Places of Articulation in The Vocal TractDocument2 pagesPhonetic Transcriptions: Different Places of Articulation in The Vocal TractFarrah Mie Felias-OfilandaNo ratings yet
- The Two Classes of SoundsDocument2 pagesThe Two Classes of SoundsbatutenataNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and Phonology: Speech Sounds and Their Systems: Adapted From: Wu HepingDocument37 pagesPhonetics and Phonology: Speech Sounds and Their Systems: Adapted From: Wu HepingNur FirdausNo ratings yet
- Week #1 PDFDocument25 pagesWeek #1 PDFYocelyn EspinozaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics 1-1Document69 pagesPhonetics 1-1Abdelghani BentalebNo ratings yet
- Phonetics: The Sounds of LanguageDocument86 pagesPhonetics: The Sounds of LanguageLillyNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument3 pagesPhoneticsعبد الرحيم فاطميNo ratings yet
- GROUP 4 - The Physiology Aspect of Language Phonetics and PhonologyDocument28 pagesGROUP 4 - The Physiology Aspect of Language Phonetics and PhonologyDavina AzhaarNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument9 pagesPhoneticsPrabal Chauhan- 'XII C'No ratings yet
- The Sounds of LanguageDocument19 pagesThe Sounds of LanguageAngelou Salamero100% (1)
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument22 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyYulia DeaNo ratings yet
- Phonology - CONSONANT FIXDocument4 pagesPhonology - CONSONANT FIXLaisah IdrNo ratings yet
- Present Tenses in EnglishDocument9 pagesPresent Tenses in EnglishWedad AlfaqeehNo ratings yet
- Alice in WonderlandDocument2 pagesAlice in WonderlandWedad AlfaqeehNo ratings yet
- 1st EssayDocument1 page1st EssayWedad AlfaqeehNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Paragraph PDFDocument1 pageDescriptive Paragraph PDFWedad AlfaqeehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document23 pagesChapter 3Redo AnwarNo ratings yet
- CPC Order 7 Rule 11 Rejection of PlaintDocument9 pagesCPC Order 7 Rule 11 Rejection of PlaintAdityaNo ratings yet
- TUGAS KELOMPOK BHS Inggris Simple Present Tense & Past Continous TenseDocument15 pagesTUGAS KELOMPOK BHS Inggris Simple Present Tense & Past Continous TenseDiki NugrahaNo ratings yet
- 4th Sem SeminarDocument6 pages4th Sem SeminarMousana BaruahNo ratings yet
- UNDP - Best Practices Report - PWC - Final PDFDocument80 pagesUNDP - Best Practices Report - PWC - Final PDFAleXandra Nikolova MarkovicNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Approaches To Community Development: Subject: Primary Health Care (PHC) 2Document14 pagesLesson 1: Approaches To Community Development: Subject: Primary Health Care (PHC) 2Michelle AmingNo ratings yet
- Sow English Year 1 2023Document13 pagesSow English Year 1 2023KONG SIAW YIENG KPM-GuruNo ratings yet
- Jim Crow 5thDocument16 pagesJim Crow 5thBreanna Navarre0% (1)
- Thermal Energy.Document7 pagesThermal Energy.romaehab201912No ratings yet
- Lit 2 QuizDocument2 pagesLit 2 QuizAvry DenairesNo ratings yet
- Patent Law Memorial On The Behalf of PetitionerDocument28 pagesPatent Law Memorial On The Behalf of Petitionerjahanvigupta792No ratings yet
- Lesson 21 PDFDocument4 pagesLesson 21 PDFShirmayne TangNo ratings yet
- SMM COMSOL Simulation MontiDocument6 pagesSMM COMSOL Simulation Montitamarco85No ratings yet
- Intelligent Building Research-A ReviewDocument17 pagesIntelligent Building Research-A ReviewSudiksha Amatya100% (1)
- A Study On The Product Life Cycle of Samsung Smartphone's in IndiaDocument9 pagesA Study On The Product Life Cycle of Samsung Smartphone's in IndiaadiNo ratings yet
- Activities - Mathematics - Class XIIDocument17 pagesActivities - Mathematics - Class XIIameerdeenNo ratings yet
- Marketing Mix DefinitionDocument14 pagesMarketing Mix DefinitionAnonymous ckTjn7RCq8100% (1)
- Group 2Document16 pagesGroup 2Zybelle DelosreyesNo ratings yet
- Athletics Athletics Is A Group ofDocument1 pageAthletics Athletics Is A Group ofGreen CrossNo ratings yet
- Ma de 402Document4 pagesMa de 402le0% (1)
- In The United States Bankruptcy Court For The Southern District of Texas Houston DivisionDocument11 pagesIn The United States Bankruptcy Court For The Southern District of Texas Houston DivisionsperlingreichNo ratings yet
- DSA-Class-Assignment 3Document2 pagesDSA-Class-Assignment 3dayij11605No ratings yet
- Elt 124 Castaneda UbbananDocument12 pagesElt 124 Castaneda UbbananDivine CastañedaNo ratings yet
- MARKSTRAT Racoons's StrategiesDocument25 pagesMARKSTRAT Racoons's StrategiesChloe Hsb SalmonNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Marketing Strategies Project On Pepsico India PRDocument36 pagesToaz - Info Marketing Strategies Project On Pepsico India PRPràçhí MálíkNo ratings yet
- Instructional Project 6 Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesInstructional Project 6 Lesson Planapi-322596215No ratings yet