Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bethametasone
Uploaded by
Westley Rubino0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesBetamethasone is a corticosteroid with glucocorticoid activity that suppresses inflammation and immune response. It is used to treat allergic disorders, inflammatory conditions, and certain cancers/autoimmune diseases. Common adverse effects include fluid retention, increased appetite, infections, and skin thinning with prolonged use. Nursing responsibilities involve monitoring for side effects, administering cautiously in certain patient populations, and tapering doses with long term or high dose therapy.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBetamethasone is a corticosteroid with glucocorticoid activity that suppresses inflammation and immune response. It is used to treat allergic disorders, inflammatory conditions, and certain cancers/autoimmune diseases. Common adverse effects include fluid retention, increased appetite, infections, and skin thinning with prolonged use. Nursing responsibilities involve monitoring for side effects, administering cautiously in certain patient populations, and tapering doses with long term or high dose therapy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views3 pagesBethametasone
Uploaded by
Westley RubinoBetamethasone is a corticosteroid with glucocorticoid activity that suppresses inflammation and immune response. It is used to treat allergic disorders, inflammatory conditions, and certain cancers/autoimmune diseases. Common adverse effects include fluid retention, increased appetite, infections, and skin thinning with prolonged use. Nursing responsibilities involve monitoring for side effects, administering cautiously in certain patient populations, and tapering doses with long term or high dose therapy.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
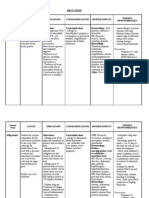
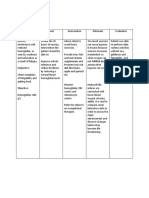
Drug Name Dosages Therapeutic Indications Adverse Contraindicati Nursing
Actions effects ons Responsibilities
Generic Drug: PO Betamethaso Systemic Sodium and Hypersensitivi Assessment
Betamethasone Allergic and ne is a administration fluid ty; systemic
inflammatory corticosteroi retention, fungal or History
Brand Name: disorders; d with mainly Hypercal potassium acute (Systemic
Celestone, congenital glucocorticoi cemia and calcium infections administration):
Celestone adrenal d activity. It associate depletion. Infections, fungal
Soluspan, hyperplasia prevents and d with Muscle infections,
Betaject, 0.5-5mg/day. by controlling cancer wasting, amebiasis, vaccinia
Betamethasone IM the rate of Short- weakness, and varicella, and
IM/PO Allergic and protein term osteoporosi antibiotic-resistant
inflammatory synthesis, manage s.GI infections; kidney
Classification: disorders as depressing ment of disturbance or liver disease;
Corticosteroids betamethasone the migration inflamm s and hypothyroidism;
Na phosphate of atory bleeding. ulcerative colitis
and polymorphon and Increased with impending
betamethasone uclear allergic appetite perforation;
acetate: leukocytes disorders and delayed diverticulitis; active
Initial:0.25-9 and , such as wound or latent peptic
mg/day in1-2 fibroblasts, rheumat healing; ulcer;
divided doses. and reversing oid hirsutism, inflammatory
Ophth Allergic capillary arthritis, bruising, bowel disease;
and permeability collagen striae, acne; CHF; hypertension;
inflammatory and diseases raised thromboembolic
conditions of lysosomal (eg, SLE), intracranial disorders;
the eye as 0.1% stabilization. dermatol pressure, osteoporosis;
soln: As Na ogic headache, seizure disorders;
phosphate: diseases depression, diabetes mellitus;
Instill 1-2 hrly (eg, psychosis, lactation
until symptoms pemphig menstrual
are controlled. us), irregularitie Physical:
As0.1% oint: status s. Baseline weight, T,
As Na asthmati Hyperglyce reflexes and grip
phosphate: cus, and mia, strength, affect
Apply2-4 autoimm DM. and orientation, P,
times/day or at une Suppression BP, peripheral
night w/ the disorders of pituitary- perfusion,
eyedrops. adrenocorti prominence of
Topical Skin Hematol cal axis. superficial veins,
disorders As ogic Growth Rand adventitious
dipropionate retardation
(0.05%) or disorders in children sounds, serum
valerate (0.025 : (prolonged electrolytes, blood
or 0.1%): Apply Thrombo therapy). glucose
as directed cytopeni Increased
a susceptibilit Interventions
purpura, y for
erythrobl infections. Systematic use
astopeni Topical use:
a Dermal Give daily
atrophy, dose 9am
Ulcerativ local to mimic
e colitis, irritation, normal
acute folliculitis, peak
exacerba hypertricho corticoste
tions of sis. roid blood
MS, and Inhalation: levels.
palliation Hoarseness, Increase
in some candidiasis dosage
leukemia of mouth when
s and and patient is
lympho throat. subject to
mas Topical stress
application Taper
Trichinos to the eye: doses
is with Corneal when
neurolog ulcers, discontinu
ic or raised IOP ing high
myocardi and reduced dose or
al visual long-term
involvem acuity. therapy
ent Intradermal
Do not
injection:
give live
Local
virus
hypopigmen
vaccines
tation of
with
deeply
immunos
pigmented
uppressiv
skin. Intra-
e doses of
articular
corticoste
injection:
roids.
Joint
damage,
Topical
fibrosis, esp.
dermatologic
in load
preparations
bearing
joints
Examine area for
infections and
skin integrity
before application
Administ
er
cautiousl
y to
pregnant
patients’
topical
corticost
eroids
have
caused
teratoge
nic
effects
and can
be
absorbed
from
systemic
site.
You might also like
- Pesci 12Document5 pagesPesci 12Rumana Ali100% (3)
- PeKa B40 Health Screening Form 3 - First Consultation - 201902Document4 pagesPeKa B40 Health Screening Form 3 - First Consultation - 201902Ezanii ShaharuddinNo ratings yet
- HydrocortisoneDocument2 pagesHydrocortisoneIvanne Hisoler100% (15)
- Beta Drug StudyDocument3 pagesBeta Drug StudyWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Nursing responsibilities for betamethasoneDocument5 pagesNursing responsibilities for betamethasoneWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- 13 3pm PrednisoneDocument1 page13 3pm PrednisoneReal TetisoraNo ratings yet
- Cardos - Bethamethasone Drug StudyformatDocument6 pagesCardos - Bethamethasone Drug StudyformatGabrielle CardosNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action, Indications, Contraindications, and Nursing Responsibilities for Magnesium SulfateDocument5 pagesMechanism of Action, Indications, Contraindications, and Nursing Responsibilities for Magnesium SulfateWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Brand and Generic Name Action Uses/ Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocument12 pagesBrand and Generic Name Action Uses/ Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationBiggs JuntillaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeDocument5 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyNikki RodrigoNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Drug MethoDocument4 pagesEctopic Drug MethoMary Reigns BuhatNo ratings yet
- DS Isph GS DRDocument7 pagesDS Isph GS DRTanya Victoria Lean ClaudioNo ratings yet
- Bibliography: Life Span - Philadelphia, PA 19103: F.A. Davis CompanyDocument5 pagesBibliography: Life Span - Philadelphia, PA 19103: F.A. Davis CompanyCarlos LleverNo ratings yet
- 1 Drug Study - DexamethasoneDocument6 pages1 Drug Study - DexamethasoneJohn100% (1)
- Nifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyDocument4 pagesNifedipine and Prednisone Drug StudyJomer GonzalesNo ratings yet
- StreptomycinDocument1 pageStreptomycinDemilyn Fat100% (2)
- MethotrexateDocument2 pagesMethotrexateIvanne Hisoler83% (6)
- Dexamethasone nursing assessment and managementDocument10 pagesDexamethasone nursing assessment and managementWinnie AriolaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument79 pagesDrug StudyShea Janson MercurioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyBella Cy LopezNo ratings yet
- Renal DiseasesDocument1 pageRenal DiseasesRebecca BernalNo ratings yet
- Arthritis, Blood/hormone/ Immune System Disorders, Skin and Eye Conditions, Breathing Problems, Cancer, and Severe AllergiesDocument4 pagesArthritis, Blood/hormone/ Immune System Disorders, Skin and Eye Conditions, Breathing Problems, Cancer, and Severe AllergiesSeanmarie CabralesNo ratings yet
- Arthritis, Blood/hormone/ Immune System Disorders, Skin and Eye Conditions, Breathing Problems, Cancer, and Severe AllergiesDocument4 pagesArthritis, Blood/hormone/ Immune System Disorders, Skin and Eye Conditions, Breathing Problems, Cancer, and Severe AllergiesSeanmarie CabralesNo ratings yet
- Generic Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMary Shine GonidaNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis and NCP Ob Ward PoldoDocument9 pagesDrug Analysis and NCP Ob Ward PoldosatruetalagaNo ratings yet
- Nursing responsibilities for mefenamic acidDocument4 pagesNursing responsibilities for mefenamic acidStephen VillegasNo ratings yet
- Drug LordsDocument25 pagesDrug LordsGlen DaleNo ratings yet
- Cabral Drug StudyDocument4 pagesCabral Drug StudyRein ArgosinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AmierDocument25 pagesDrug Study AmierKabang Moa100% (5)
- Project in Pharmacology: Prepared By: Reyes, Roselle Ann V. Level II - B Submitted To: Sir Rosauro BrionesDocument38 pagesProject in Pharmacology: Prepared By: Reyes, Roselle Ann V. Level II - B Submitted To: Sir Rosauro Brionesselle_06_20No ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications and Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationNicole CalpoturaNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY-FORMAT-Binangonan Lakeview 2ndDocument2 pagesDRUG-STUDY-FORMAT-Binangonan Lakeview 2ndDianne UlandayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: NCM 106 PharmacologyDocument4 pagesDrug Study: NCM 106 PharmacologyLore Anne Mhae SantosNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY Update (Table 3)Document5 pagesDRUGSTUDY Update (Table 3)SONY MANDAPNo ratings yet
- Tdi de AsisDocument1 pageTdi de AsisEnaWahahaNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGYDocument3 pagesPHARMACOLOGYjonel lorenzoNo ratings yet
- PTB DrugsDocument4 pagesPTB DrugsColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyLyka PerezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-Ibekwe Njideka VanessaDocument2 pagesDrug Study-Ibekwe Njideka VanessaFavor ColaNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument2 pagesDrugthe_greatpasawayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Far Eastern UniversityDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Far Eastern UniversityChoy DacanayNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesDrug Name Dopamine Indications Contraindications Mechanism of Action Common Side-Effects Nursing ConsiderationsPRINCESS LARA CASILAONo ratings yet
- Name Indication Action Adverse Effect Contraindication Nursing Consideration Patient TeachingDocument11 pagesName Indication Action Adverse Effect Contraindication Nursing Consideration Patient TeachingdianneingusanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyAlhadzra AlihNo ratings yet
- PREDNISONEDocument3 pagesPREDNISONEChelsea CuevasNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Mechanism, Uses, Side Effects & Nursing CareDocument2 pagesFurosemide Mechanism, Uses, Side Effects & Nursing CareFavor ColaNo ratings yet
- Must Read Medical Notes and Review QuestionsDocument8 pagesMust Read Medical Notes and Review QuestionsSarahSalvanNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Proteus Mirabilis, Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Enterobacter Species, Distress, NauseaDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Proteus Mirabilis, Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Enterobacter Species, Distress, Nauseacsy123No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug Studyjho_26100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY: FLUDROCORTISONEDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY: FLUDROCORTISONERein ArgosinoNo ratings yet
- Acute Exacerbations of Multiple Sclerosis, Cerebral Edema Associated With Primary or Metastatic Brain Tumor, Craniotomy, or Head Injury.Document3 pagesAcute Exacerbations of Multiple Sclerosis, Cerebral Edema Associated With Primary or Metastatic Brain Tumor, Craniotomy, or Head Injury.Micah Alexis CandelarioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AspirinDocument1 pageDrug Study AspirinMaria Charis Anne Indanan100% (1)
- Furosemide: Agranulocytosis, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopen Ia, Anemia, Aplastic AnemiaDocument9 pagesFurosemide: Agranulocytosis, Leukopenia, Thrombocytopen Ia, Anemia, Aplastic AnemiaRanee Diane AnanayoNo ratings yet
- TELMISARTANDocument8 pagesTELMISARTANCidny CalimagNo ratings yet
- Nursing implications for drug administrationDocument9 pagesNursing implications for drug administrationKathrina TumbagaNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY-formatDocument3 pagesDRUG-STUDY-formatJohn Edward CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandEndocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument5 pagesNursing DiagnosisWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Unfinish Drug StudyDocument3 pagesUnfinish Drug StudyWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeDocument5 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- DR StudyDocument7 pagesDR StudyWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeDocument5 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeDocument5 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Tin NCP AntepartumDocument2 pagesTin NCP AntepartumWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- NCP AntepartumDocument2 pagesNCP AntepartumWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Theo 1, Module 9, Assessment Task 2 (Journal Writing)Document1 pageTheo 1, Module 9, Assessment Task 2 (Journal Writing)Westley RubinoNo ratings yet
- NCP AntepartumDocument2 pagesNCP AntepartumWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- DR StudyDocument7 pagesDR StudyWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- NCP AntepartumDocument2 pagesNCP AntepartumWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- NCP AntepartumDocument2 pagesNCP AntepartumWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- 104 CompileDocument20 pages104 CompileWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Learning Levine's Theory TFNDocument1 pageLearning Levine's Theory TFNWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument8 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseYessamin Paith RoderosNo ratings yet
- 181B226 Internship ReportDocument48 pages181B226 Internship ReportSuyash SinghNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Practical Lecture StudentsDocument9 pagesRespiratory System Practical Lecture StudentsAmwaj MohammedNo ratings yet
- Thermodilution Cardiac Output: A Concept Over 250 Years in The MakingDocument7 pagesThermodilution Cardiac Output: A Concept Over 250 Years in The MakingWendi IochNo ratings yet
- Early Mobilization of Patients Receiving.6Document12 pagesEarly Mobilization of Patients Receiving.6guillermo guyetNo ratings yet
- Physiology Seminar: ElectrocardiographyDocument42 pagesPhysiology Seminar: ElectrocardiographyRajesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Can corona medicine cause heart rate over 100Document3 pagesCan corona medicine cause heart rate over 100Sky HussainNo ratings yet
- Section 3: Nomenclature of TumorDocument71 pagesSection 3: Nomenclature of TumorIsuri GanNo ratings yet
- Scaffolder Erector Medical ExaminationDocument6 pagesScaffolder Erector Medical ExaminationZulqarnain RamliNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetic Nerve Block ReviewDocument8 pagesLocal Anesthetic Nerve Block Reviewvelo100% (1)
- No-Reflow Phenomenon: DR - Surinder S HansraDocument17 pagesNo-Reflow Phenomenon: DR - Surinder S HansrasshansraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Medical Terminologies and AbbreviationsDocument6 pagesLesson 4: Medical Terminologies and AbbreviationsDapnie Ubalubao OcampoNo ratings yet
- Isosorbide Mononitrate: Adult: PO Regular Release (ISMO, Monoket) 20 MG B.I.D. 7 H ApartDocument2 pagesIsosorbide Mononitrate: Adult: PO Regular Release (ISMO, Monoket) 20 MG B.I.D. 7 H ApartAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- QN BNK Og PeadDocument39 pagesQN BNK Og PeadZemen addiss100% (2)
- PneumothoraxDocument26 pagesPneumothoraxToni-Ann AllenNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORYDocument3 pagesRESPIRATORYRizMarie67% (3)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Feb 2021Document56 pagesChronic Kidney Disease Feb 2021ToyoNo ratings yet
- NCM 114 Care For Older Adults MODULE 4Document5 pagesNCM 114 Care For Older Adults MODULE 4Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Acute Rheumatic FeverDocument9 pagesAcute Rheumatic FeverHarish Kumar KumawatNo ratings yet
- I1551 6776 12 3 138 PDFDocument9 pagesI1551 6776 12 3 138 PDFIvan VeriswanNo ratings yet
- CH 31 - Assessment and Management of Patients With Vascular Disorders and Problems of PeripheralDocument16 pagesCH 31 - Assessment and Management of Patients With Vascular Disorders and Problems of PeripheralPye Antwan DelvaNo ratings yet
- Embryology of The Heart and The Great VesselsDocument66 pagesEmbryology of The Heart and The Great VesselsNavya HegdeNo ratings yet
- CPC Case 1Document9 pagesCPC Case 1Astarte DimasalangNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 2 - Module 1B PDocument25 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Quarter 4: Week 2 - Module 1B PSyrine Myles Sullivan100% (2)
- Lazarus PhenomenonDocument6 pagesLazarus PhenomenonWanjaWx3No ratings yet
- Acute Exacerbation of AsthmaDocument48 pagesAcute Exacerbation of AsthmaWan Nur AdilahNo ratings yet
- Funda D1 by Prof Melody BautistaDocument6 pagesFunda D1 by Prof Melody BautistaJhonny pingolNo ratings yet
- ACLS Practice TestDocument5 pagesACLS Practice Testprettynpink0867% (3)