Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GIA 4Cs Download PDF
Uploaded by
raghuvansham boutiqueOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
GIA 4Cs Download PDF
Uploaded by
raghuvansham boutiqueCopyright:
Available Formats
GIA’S 4CS GUIDE TO
UNDERSTANDING DIAMOND QUALITY
Beautiful. Rare. Cherished. There is no gemstone quite like a diamond. Each one is unique.
And each has specific qualities that establish its value. As creator of the 4Cs and the International Diamond Grading System,™
GIA is the global authority and trusted source for unbiased diamond quality assessment.
This guide is devoted to helping you choose both well and wisely when shopping for a diamond.
The color evaluation of most gem-quality diamonds is
based on the absence of color. The GIA Color Grading
System measures the degree of colorlessness by
comparing a stone, under controlled lighting and precise
viewing conditions, to masterstones of established color
value. Many diamond color distinctions are so subtle
they are invisible to the untrained eye; however, these
distinction make a very big difference in diamond quality
and price.
Internal ‘inclusions’ and external ‘blemishes’ result from
the diamond’s natural formation process deep in the earth.
Evaluating diamond clarity involves determining the number,
size, relief, nature, and position of these characteristics, as
well as how they affect the overall appearance of the stone.
While no diamond is perfectly pure, the closer it comes, the
higher its value.
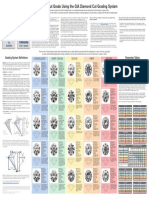
The quality of cut is crucial to the diamond’s final beauty
and value. Of all the 4Cs, it is the most complex and
technically difficult to assess. The GIA Cut Grading System
for the standard round brilliant diamond evaluates seven
components: brightness, fire, scintillation, weight ratio,
girdle thickness, symmetry, and polish.
C A R AT W E I G H T Carat weight is the measurement of how much a diamond
weighs. A metric “carat” is defined as 200 milligrams.
All else being equal, diamond price increases with carat
weight, because larger diamonds are more rare and more
C A R AT0.50Wct. E I G H T 1.0 ct. 2.0 ct. 3.0 ct. 5.0 ct.
desirable. However, two diamonds of equal carat weight can
have very different values (and prices) depending on three
other factors of the 4Cs: clarity, color, and cut.
CAllAdiamond
R AT0.50 Wct. E I G H T
images and diagrams are for reference only and may not reflect true diamond quality grades or weight. Images and diagrams are not for diamond grading.
1.0 ct. 2.0 ct. 3.0 ct. 5.0 ct.
C A R AT W E I G H T
0.50 ct. 1.0 ct. 2.0 ct. 3.0 ct. 5.0 ct.
www.4cs.gia.edu
0.50 ct. 1.0 ct. 2.0 ct. 3.0 ct. 5.0 ct.
You might also like
- Assignment 1 Assignment 2 Assignment 3 Assignment 4 Assignment 5 Assignment 6Document42 pagesAssignment 1 Assignment 2 Assignment 3 Assignment 4 Assignment 5 Assignment 6SamuelNo ratings yet
- Carbon Nanomaterials - Synthesis, Structure, Properties and Applications PDFDocument285 pagesCarbon Nanomaterials - Synthesis, Structure, Properties and Applications PDFGuillermo Idarraga83% (6)
- THE Diamond Buyers' GuideDocument4 pagesTHE Diamond Buyers' Guideqifar DammahumNo ratings yet
- Estimating A Cut Grade Using The GIA Diamond Cut Grading SystemDocument1 pageEstimating A Cut Grade Using The GIA Diamond Cut Grading SystempedroNo ratings yet
- ddg15 PrintableDocument45 pagesddg15 Printablerjvrglhchhqbxflmek100% (1)
- A Ruby Gradient System - GITDocument9 pagesA Ruby Gradient System - GITwwwyyyzzzNo ratings yet
- GIA, How To Purchase The Perfect Diamond Engagement RingDocument5 pagesGIA, How To Purchase The Perfect Diamond Engagement Ringkaveh25100% (1)
- An Introduction To Gem TreatmentsDocument27 pagesAn Introduction To Gem TreatmentsEvandro OliveiraNo ratings yet
- A Brief Review of Gemstone Optical Properties From A Lapidary's ...Document13 pagesA Brief Review of Gemstone Optical Properties From A Lapidary's ...Niloofar MousavipakNo ratings yet
- Most Popular Diamond Cuts (Explained For BeginnersDocument9 pagesMost Popular Diamond Cuts (Explained For Beginnersetikajewels100% (2)
- What Are Gemstone Absorption SpectraDocument4 pagesWhat Are Gemstone Absorption SpectratogoreanunuNo ratings yet
- Study of Gem and Jewellery: Types of Gem Stone Setting #DrneerujainDocument26 pagesStudy of Gem and Jewellery: Types of Gem Stone Setting #DrneerujainDr. Neeru jainNo ratings yet
- Girma Gemstone Introduction Instrumentation ApllicationDocument143 pagesGirma Gemstone Introduction Instrumentation ApllicationGirma TazebNo ratings yet
- Are Diamonds Unbreakable - Royal Coster Diamonds PDFDocument5 pagesAre Diamonds Unbreakable - Royal Coster Diamonds PDFVasile Diana AlexandraNo ratings yet
- The Allnatt Diamond ($3 Million) : JewelersDocument5 pagesThe Allnatt Diamond ($3 Million) : JewelersTomi TodinganNo ratings yet
- EmeraldDocument25 pagesEmeraldvikas agarwalNo ratings yet
- Types of Gem Stone Setting - Jewellery DesigningDocument30 pagesTypes of Gem Stone Setting - Jewellery DesigningDr. Neeru jainNo ratings yet
- Refraction Index of Various Substances For 3D ModelersDocument3 pagesRefraction Index of Various Substances For 3D ModelersescupopaNo ratings yet
- Gem-A CCFDocument4 pagesGem-A CCFAlfonso HarisNo ratings yet
- Je02 PrintableDocument30 pagesJe02 PrintableSamuelNo ratings yet
- VL User Manual Rev 1.05 March 2020Document30 pagesVL User Manual Rev 1.05 March 2020Kim Reis100% (1)
- Image Jewelers Diamond EssentialsDocument14 pagesImage Jewelers Diamond EssentialsJewellery Flyers100% (1)
- Wedunit - GemstonesDocument135 pagesWedunit - GemstonesSimona PascariuNo ratings yet
- A Simple Procedure To Separate Natural From Synthetic Amethyst On The Basis of Twinning PDFDocument10 pagesA Simple Procedure To Separate Natural From Synthetic Amethyst On The Basis of Twinning PDFrusdi mappedecengNo ratings yet
- Polymer Impregnated Turquoise PDFDocument3 pagesPolymer Impregnated Turquoise PDF8duke8No ratings yet
- Gemmological Laboratory BookDocument210 pagesGemmological Laboratory BookAntonioNo ratings yet
- Diamond Grading ScalesDocument1 pageDiamond Grading ScalesPrakriti PatelNo ratings yet
- 117-Gemstone IdentificationDocument17 pages117-Gemstone Identificationms_pmNo ratings yet
- Gemology Diamond Vs MossoniteDocument13 pagesGemology Diamond Vs MossonitezatiNo ratings yet
- Gemstone CuttingDocument2 pagesGemstone Cuttingxem lo hangNo ratings yet
- Precision Cutting Tools PDFDocument16 pagesPrecision Cutting Tools PDFHoang Truong DinhNo ratings yet
- Determining Gem Dispersion On RefractometerDocument19 pagesDetermining Gem Dispersion On RefractometerParallaxster100% (1)
- CJ GemDocument2 pagesCJ GemrivegaucheNo ratings yet
- Chalcedony Value, Price, and Jewelry Information - International Gem SocietyDocument8 pagesChalcedony Value, Price, and Jewelry Information - International Gem Societyasset68No ratings yet
- Gemology Sri LankaDocument10 pagesGemology Sri LankaDon Dilan BuddhikaNo ratings yet
- Dark Field LoupeDocument4 pagesDark Field Loupesaurabh_acmasNo ratings yet
- Course Colored Stone GradingDocument61 pagesCourse Colored Stone GradingAnonymous IcptMgwZlNo ratings yet
- Case Study - Branded JewelleryDocument4 pagesCase Study - Branded JewelleryHarsh MittalNo ratings yet
- Jewelry Design in 2020Document2 pagesJewelry Design in 2020ShipraDiamondNo ratings yet
- GG - Color Grading of Colored Diamonds in The GIA Gem Trade LaboratoryDocument24 pagesGG - Color Grading of Colored Diamonds in The GIA Gem Trade LaboratoryArmando Michel Gabriel Cury FilhoNo ratings yet
- Quartz and Chalsedony + Tourmaline Etc..Document186 pagesQuartz and Chalsedony + Tourmaline Etc..gabrielafeldmanNo ratings yet
- Winter 1997 Gems Gemology Synthetic Moissanite Diamond SubstituteDocument16 pagesWinter 1997 Gems Gemology Synthetic Moissanite Diamond SubstituteChressa RufonNo ratings yet
- D Lesson 14Document17 pagesD Lesson 14Mai Do AsensiNo ratings yet
- 2018 GIA London Education Catalog PDFDocument40 pages2018 GIA London Education Catalog PDFSilviu Andone100% (1)
- Gemstone: Gemology and Jewelry PortalDocument8 pagesGemstone: Gemology and Jewelry PortalNurzamzami IsmailNo ratings yet
- 10 Most Valuable Gemstones in The WorldDocument7 pages10 Most Valuable Gemstones in The WorldFire Star GemsNo ratings yet
- The Rough Diamond Guideline Price List From ADTEC (Pty) LTDDocument6 pagesThe Rough Diamond Guideline Price List From ADTEC (Pty) LTD1diamondgirlNo ratings yet
- Ruby Buying Guide: by International Gem SocietyDocument10 pagesRuby Buying Guide: by International Gem Societyasset68No ratings yet
- Ruby and Sapphire Production and DistributionDocument24 pagesRuby and Sapphire Production and DistributionAdvait DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Agate: For Other Uses, SeeDocument6 pagesAgate: For Other Uses, SeeGabi MarianaNo ratings yet
- An Update On Color in Gems - Part 2 - Gems & Gemology SP88A1Document13 pagesAn Update On Color in Gems - Part 2 - Gems & Gemology SP88A1MickShazan100% (1)
- Rolex DaydateDocument9 pagesRolex DaydateGnanasekaran RamachandranNo ratings yet
- (GIA) Colored Stones. Blue Sapphire.Document55 pages(GIA) Colored Stones. Blue Sapphire.hasanNo ratings yet
- Material Handling PresentationDocument71 pagesMaterial Handling Presentationegy pure100% (1)
- Jewellery Has Been Used For A Number of ReasonsDocument5 pagesJewellery Has Been Used For A Number of ReasonsSumesh Mirashi0% (1)
- Coloring Grading D To Z Diamonds at The GIA Laboratory PDFDocument27 pagesColoring Grading D To Z Diamonds at The GIA Laboratory PDFArmando Michel Gabriel Cury FilhoNo ratings yet
- How We Craft Jewellery ?: Vogue Crafts & DesignsDocument10 pagesHow We Craft Jewellery ?: Vogue Crafts & DesignsRaja Sekhar Reddy PaluruNo ratings yet
- Gems Stone BookDocument68 pagesGems Stone BookSaleem PervezNo ratings yet
- KristMin01 PengantarDocument66 pagesKristMin01 Pengantarmelvinda putriNo ratings yet
- Beryl Gemstones - A Collection of Historical Articles on the Varieties, Origins and Properties of BerylFrom EverandBeryl Gemstones - A Collection of Historical Articles on the Varieties, Origins and Properties of BerylNo ratings yet
- Retail-Goldsmith (Repairs)Document21 pagesRetail-Goldsmith (Repairs)raghuvansham boutiqueNo ratings yet
- Raghuvansham FranchiseDocument3 pagesRaghuvansham Franchiseraghuvansham boutiqueNo ratings yet
- 30 OctDocument1 page30 Octraghuvansham boutiqueNo ratings yet
- Distributer List RateDocument1 pageDistributer List Rateraghuvansham boutiqueNo ratings yet
- SU21 - Ho PDFDocument3 pagesSU21 - Ho PDFraghuvansham boutiqueNo ratings yet
- What Will You LearnDocument1 pageWhat Will You Learnraghuvansham boutiqueNo ratings yet
- Writing A Scientific Paper (Introduction)Document2 pagesWriting A Scientific Paper (Introduction)nivram alindayuNo ratings yet
- 2015 Stefan Catalogue DIGITALDocument28 pages2015 Stefan Catalogue DIGITALEarthMonkey GNo ratings yet
- Deskripsi Produk RaketDocument7 pagesDeskripsi Produk RaketNormaulanaAssalamNo ratings yet
- Pear Cut Diamond Size Chart (Carat Weight To MM Size)Document1 pagePear Cut Diamond Size Chart (Carat Weight To MM Size)Hitesh SinghviNo ratings yet
- Report Chem PBL 4Document24 pagesReport Chem PBL 4Dian Ratri CNo ratings yet
- Covalent - Bonding - Worksheet - Doc 2Document3 pagesCovalent - Bonding - Worksheet - Doc 2Zain AliNo ratings yet
- Proportions Grading Scales Gia Natural Diamond Grading ReportDocument1 pageProportions Grading Scales Gia Natural Diamond Grading ReportPamms IntlNo ratings yet
- IGI ReportDocument1 pageIGI ReportrodneyNo ratings yet
- Mechanical and Wear Behaviour of Al60601 PDFDocument9 pagesMechanical and Wear Behaviour of Al60601 PDFThiran Boy LingamNo ratings yet
- P Block Short NotesDocument22 pagesP Block Short Notesthapliyaldivyanshu274No ratings yet
- FullerenesDocument8 pagesFullerenesDeepak BaghelNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds Lesson PlanChinnala RameshNo ratings yet
- What Is Graphene?: Mohammad Wali KhuramiDocument6 pagesWhat Is Graphene?: Mohammad Wali Khuramimohammad wali khuramiNo ratings yet
- NanoChemistryDocument71 pagesNanoChemistrypooja doreamon89% (9)
- Test 2 PHY5205Document1 pageTest 2 PHY5205Ksp “Talented”No ratings yet
- 2022 GCSE Chemistry NotesDocument111 pages2022 GCSE Chemistry Notesmaulik mongaNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundDocument6 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundKartik meenaNo ratings yet
- An Important Exhibition of Seven Rare Gem DiamondsDocument8 pagesAn Important Exhibition of Seven Rare Gem DiamondsClaireNo ratings yet
- CarbonDocument21 pagesCarbonBandana SaruNo ratings yet
- Q1 M1 HistoryDocument17 pagesQ1 M1 HistoryGabrielle AlikNo ratings yet
- The Process of Crafting Lab Grown Diamonds!Document4 pagesThe Process of Crafting Lab Grown Diamonds!Diamonds DivaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Energy & Fuels: ReviewDocument17 pagesSustainable Energy & Fuels: ReviewcrystalquasiNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds - Chapter 3 - Chemistry: Q1) What Is Carbon? Ans)Document5 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds - Chapter 3 - Chemistry: Q1) What Is Carbon? Ans)Ronnith NandyNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its CompoundDocument41 pagesCarbon and Its CompoundSamKris Guerrero MalasagaNo ratings yet
- Why Is Carbon So Important in Spite of It Being Present in A Very Small QuantityDocument2 pagesWhy Is Carbon So Important in Spite of It Being Present in A Very Small QuantitySuman DasNo ratings yet
- GROUP 14 ELEMENTS (IVA Group Elements)Document8 pagesGROUP 14 ELEMENTS (IVA Group Elements)Premangshu GhoshalNo ratings yet
- Carbides, Fullerenes & Fluorocarbons (Inorg)Document21 pagesCarbides, Fullerenes & Fluorocarbons (Inorg)SamanNo ratings yet
- Soal STS B IngrDocument4 pagesSoal STS B Ingrlisa oktaviaNo ratings yet
- STD 9th Perfect Science and Technology Notes English Medium MH BoardDocument23 pagesSTD 9th Perfect Science and Technology Notes English Medium MH BoardShlok Bhokare100% (2)