Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PE - Viva Questions - N
PE - Viva Questions - N
Uploaded by
Hiren0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageThyristor is another name for SCR, which stands for Silicon Controlled Rectifier. SCRs are power semiconductor devices used for power control applications that can be turned on through several methods, including applying a gate signal. There are three modes of operation for an SCR: reverse blocking, forward blocking, and forward conduction. In reverse blocking mode, high power dissipation can occur if the reverse voltage exceeds the reverse breakover voltage.
Original Description:
viva questions of power electronics
Original Title
PE_Viva Questions_n
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThyristor is another name for SCR, which stands for Silicon Controlled Rectifier. SCRs are power semiconductor devices used for power control applications that can be turned on through several methods, including applying a gate signal. There are three modes of operation for an SCR: reverse blocking, forward blocking, and forward conduction. In reverse blocking mode, high power dissipation can occur if the reverse voltage exceeds the reverse breakover voltage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pagePE - Viva Questions - N
PE - Viva Questions - N
Uploaded by
HirenThyristor is another name for SCR, which stands for Silicon Controlled Rectifier. SCRs are power semiconductor devices used for power control applications that can be turned on through several methods, including applying a gate signal. There are three modes of operation for an SCR: reverse blocking, forward blocking, and forward conduction. In reverse blocking mode, high power dissipation can occur if the reverse voltage exceeds the reverse breakover voltage.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Viva Questions:
1. What is a Thyristor?
Thyristor is derived from the properties of a Thyratron tube and a Transistor. It is used as another
name for SCR’S. They are power Semiconductor devices used for power control applications.
2. What are SCR’s?
SCR’s is Silicon controlled Rectifiers. They are basically used as Rectifiers.
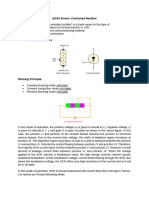
3. Draw the structure of an SCR?
4. What are the different methods of turning on an SCR?
1. Anode to cathode voltage is greater than break over voltage.
2. Gate triggering
3. When dv/dt exceeds permissible value.
4. Gate cathode junction is exposed to light.
5.What is Forward break over voltage?
The voltage Vak at which the SCR starts conducting is called as Forward Break over voltage V bo.
This happens when the junction J2 undergoes Avalanche breakdown due to high reverse bias on
junction J2.
6. What is Reverse break over voltage?
If the reverse voltage is increased more than a critical value, avalanche Breakdown will occur at
J1 and J3 increasing the current sharply. This is Reverse break over voltage VBO.
7. Why is Vbo greater than VBR?
In SCR the inner two p-n regions are lightly doped due to which the thickness of the depletion
region at junction J2 is higher during forward bias than that of J1 and J3 under reverse bias.
8. What are modes of working of an SCR?
Reverse blocking mode, Forward blocking mode and Forward conduction mode are the modes of
working of an SCR.
9. Draw the V-I characteristics of SCR.
10. Why does high power dissipation occur in reverse blocking mode?
High power dissipation occurs because as voltage increases beyond Vbr current increases
rapidly.
11. Why shouldn’t positive gate signal be applied during reverse blocking?
If we apply positive gate signal J3 becomes forward biased. Reverse leakage current increases
and Thyristor gets damaged due to large power dissipation.
12. Explain reverse current Ire?
You might also like
- SCR Triggering MethodsDocument17 pagesSCR Triggering MethodssriNo ratings yet
- Thyristor Triggering: Figure 1 Thyristor Circuit With Gate ResistorsDocument2 pagesThyristor Triggering: Figure 1 Thyristor Circuit With Gate ResistorsPrincess LandichoNo ratings yet
- Silicon Controlled RectifierDocument38 pagesSilicon Controlled RectifierPaoNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Manual1Document72 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual1Harish SvNo ratings yet
- Thyristors Sec B Power ElectronicsDocument38 pagesThyristors Sec B Power ElectronicsFederico AldoNo ratings yet
- Chat 3Document82 pagesChat 3Keneni AlemayehuNo ratings yet
- SCR CharacteristicsDocument4 pagesSCR CharacteristicsAnita Gloria100% (4)
- Pe Lab Viva QuestionsDocument15 pagesPe Lab Viva Questionssujithmrinal100% (5)
- Power Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument24 pagesPower Electronics & Drives: Unit: 1 Power Semiconductor DevicesTapobroto ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- EE6503 Power Electronics NotesDocument234 pagesEE6503 Power Electronics Notessyed ibrahimNo ratings yet
- Viva QuestionsDocument12 pagesViva QuestionsJayesh Tanwani50% (4)
- Power ElectronicsDocument27 pagesPower ElectronicsShreyas S RNo ratings yet
- PE Unit-1 PDFDocument29 pagesPE Unit-1 PDFNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Thyristors Sec B Power ElectronicsDocument37 pagesThyristors Sec B Power ElectronicsTanveer MahmudNo ratings yet
- Scr-Diac-Triac-UjtDocument11 pagesScr-Diac-Triac-Ujtmmuz.backup4No ratings yet
- Lecture 7: Turn On Methods of SCR: Dr. Aadesh Kumar AryaDocument11 pagesLecture 7: Turn On Methods of SCR: Dr. Aadesh Kumar Aryaaadesh kumar aryaNo ratings yet
- Pe SCRDocument68 pagesPe SCRMuttoju VaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Pe FINALDocument131 pagesPe FINALAnonymous R4WpNxNo ratings yet
- POWER ELECTRONICsDocument120 pagesPOWER ELECTRONICsJeji HirboraNo ratings yet
- Agsie - Johnmark Exp1Document7 pagesAgsie - Johnmark Exp1CloudFarmInnovations IncorporatedNo ratings yet
- 10-17 SCR Into, CommutationDocument45 pages10-17 SCR Into, CommutationAdnan MagsiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Power SupplyDocument23 pagesChapter 3 Power SupplyBricksoe NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Trigering of SCRDocument7 pagesAssignment: Trigering of SCRAb CNo ratings yet
- Ex 5001 Electromagnetic Field Theory Nov 2018Document41 pagesEx 5001 Electromagnetic Field Theory Nov 2018Syed Khurshid AlamNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Control Circuit Digital Circuit Power Electronic Circuit LoadDocument13 pagesPower Electronics: Control Circuit Digital Circuit Power Electronic Circuit LoadNayon RoyNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf Merged PDFDocument19 pagesIlovepdf Merged PDFMohan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Thyristors: StructureDocument14 pagesModule 2 Thyristors: StructureChetangouda PatilNo ratings yet
- Silicon Controlled Rectifier DefinitionDocument10 pagesSilicon Controlled Rectifier DefinitionishmamNo ratings yet
- Batangas State University Alangilan - Main Campus Ii Electrical and Computer Engineering DepartmentDocument15 pagesBatangas State University Alangilan - Main Campus Ii Electrical and Computer Engineering DepartmentKarenMacalaladTanangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document38 pagesChapter 5Markos NiguseNo ratings yet
- Unidirectional ThyristorDocument5 pagesUnidirectional ThyristorArvin Dexter De CastroNo ratings yet
- ThyristorsDocument5 pagesThyristorsrakesh_pal_3No ratings yet
- Thyristor StudentsDocument81 pagesThyristor StudentsPritam PiyushNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 05Document5 pagesLab Report 05Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Turn-On Process of SCRDocument12 pagesTurn-On Process of SCRDeepika BairagiNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Interview Questions Set-2: What Are The Different Operation Regions of The SCR?Document9 pagesElectrical Engineering Interview Questions Set-2: What Are The Different Operation Regions of The SCR?Uzair AfridiNo ratings yet
- 20 Talking ElectronicsDocument23 pages20 Talking ElectronicsBalaki SrikanthNo ratings yet
- SCR Silicon Controlled RectifierDocument4 pagesSCR Silicon Controlled RectifierMichelle MamanoNo ratings yet
- 20 Talking ElectronicsDocument23 pages20 Talking ElectronicsJohn Mike SardengNo ratings yet
- 20 Talking ElectronicsDocument23 pages20 Talking ElectronicsAXLLE RHOESS DOMUGHO. ELLOREGNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power Electronics DevicesDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Power Electronics DevicesahmedsaeedobiedNo ratings yet
- 200 - EE8552, EE6503 Power Electronics - Notes 1 PDFDocument280 pages200 - EE8552, EE6503 Power Electronics - Notes 1 PDFShubhamNo ratings yet
- Ree601 PDFDocument9 pagesRee601 PDFJ JulietNo ratings yet
- On Thyristors and Their Firing CircuitsDocument13 pagesOn Thyristors and Their Firing CircuitsSimranjitNo ratings yet
- Special Semiconductor DevicesDocument40 pagesSpecial Semiconductor DevicesJairus OnkwaniNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document17 pagesModule 3Mohammed ShoaibNo ratings yet
- IECD Capsule NotesDocument59 pagesIECD Capsule NotesANANTHU PRADEEPNo ratings yet
- Silicon Controlled Rectifier SCRDocument11 pagesSilicon Controlled Rectifier SCRArmaan HossainNo ratings yet
- SCRDocument4 pagesSCRJoshua Amiel javines100% (1)
- I N T R o D U C T I o NDocument6 pagesI N T R o D U C T I o NManikandan P Engineering EEENo ratings yet
- Thyristor ValveDocument5 pagesThyristor ValveRisi SinghNo ratings yet
- Learning OutcomesDocument51 pagesLearning Outcomesdimpisingh004No ratings yet
- Module 1 NotesDocument30 pagesModule 1 NotesSoxamNo ratings yet
- 19MO504-IE 2 MarksDocument40 pages19MO504-IE 2 MarksSaranya. M SNSNo ratings yet
- SCR MechatronicsDocument50 pagesSCR MechatronicsBefu HailuNo ratings yet
- Expt - 1 - SCR IGBT and MOSFET CharacteristicsDocument16 pagesExpt - 1 - SCR IGBT and MOSFET CharacteristicsGaurav Verma100% (2)
- 200 - EE8552, EE6503 Power Electronics - Question Bank 3Document119 pages200 - EE8552, EE6503 Power Electronics - Question Bank 3NiteshNarukaNo ratings yet
- 2019-20 - 5EEU07 - Power Electronics LabDocument42 pages2019-20 - 5EEU07 - Power Electronics LabGautam AcharyaNo ratings yet
- BE 5 UnitDocument23 pagesBE 5 Unit08sunnyjaganNo ratings yet