Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Effect of Clove Oil Extract On Inhibition of Various Spoilage and Pathogenic Bacteria Isolated From Fermented Pickles by Agar Well Diffusion Method
Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Effect of Clove Oil Extract On Inhibition of Various Spoilage and Pathogenic Bacteria Isolated From Fermented Pickles by Agar Well Diffusion Method
Copyright:
Available Formats
Volume 8, Issue 3, March – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
Effect of Clove Oil Extract on Inhibition of Various
Spoilage and Pathogenic Bacteria Isolated from
Fermented Pickles by Agar Well Diffusion Method
*
P. Venkatesan1 and D. Kanchana2
1
Ph.D Scholar , 2Associate Professor
Department of Agricultural Microbiology, Faculty of Agriculture,
Annamalai University, Chidambaram 608 002
*
Corresponding Author
Abstract:- Ready-to-Eat types of food items are becoming and industrial practices regarding acidified pickled foods are
very common now-a-days. India has become a hub for possibly out of date because of the scarcity of information on
producing a variety of pickled food items. Pickling of food pathogen control in these foods (Lee S.Y and D.H. Kang,
items allows the formation of lactic acid bacteria which 2004). Spices are used as additives to flavour, colour or
are very important for the process of fermentation. Thus, preserve food from ancient time in India. These are pungent
physical conditions like temperature, humidity, acidity or aromatic substances obtained from by dried seeds, fruits,
and pH should be maintained to keep the pickles safe. The roots, bark or leaves. Spices are the potential source of natural
variation in environmental condition leads to microbial products and naturally derived compounds. These
growth. Different types of pathogenic bacteria grow at compounds show the antioxidant, antimicrobial properties.
different levels of pH and acidity. In recent investigation, Ashraf A. Mostafa et al. (2017) stated that ethanolic clove
some of the microorganisms responsible for the spoilage extract was potentially active against Staphylococcus aureus,
of pickles were studied. The present study was Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa while
undertaken to make further detailed studies on the it was inactive against E. coli and Salmonella enteritidis.
microorganisms responsible for spoilage of pickles and
their control. The samples were collected from different II. MATERIALS AND METHODS
places and isolated various bacteria that cause spoilage on
pickles and further bacterial strains identified based on A. Sample collection
morphological and physiological characters. The clove oil The three different pickle samples viz., mango pickle,
was collected from essential oil shops in local market and lemon pickle and cucumber pickle were collected from
tested for inhibitory activity against the spoilage bacteria. Ariyalur and Cuddalore District, Tamil Nadu, India. The
The clove oil were also tested for inhibition on pickle samples were collected at different storage period based on
bacteria by agar well diffusion method at different the methods of preparation. The samples of mango and lemon
concentration viz., 16.00, 32.00, 64.00, 128.00, 256.00 μl. pickle were taken from four to six months from the date of
Higher concentration shows higher inhibition zone. manufacturing and cucumber pickle sample was taken at 30-
45 days old. All the samples were further stored for
Keywords:- Pickles; Clove oil; Bacteria; Food. observation and growth of spoilage organisms. The clove oil
was collected from local essential oil shops.
I. INTRODUCTION
B. Isolation and Identification of spoilage bacteria from
In India pickling of food items is usually done using pickle sample
anaerobic fermentation process. Variety of agents like acetic The samples were isolated and identified the pathogenic
acid (vinegar), citric acid, brine solution (solution having high bacteria based on morphological and physiological
salt content) and vegetable oils are used for the process of characters.
fermentation. The application of quality and quantity of these
agents may vary depending upon the item that has to be C. Inhibitory Effect of clove oil on various pickle Bacterial
pickled. Different type of food products contains varying strains
amount of moisture content in them. If the food items contain The effect of different concentration of Spice oil on the
sufficient or high moisture content, than dry salt is added to growth of the bacterial was studied using clove oil. The
the pickling mixture. Sometimes sugar is also added as a sterilized Nutrient agar medium was prepared and seeded
preservative to increase the rate of fermentation and add with standard inoculums of the four bacterial strains viz., (PB-
sweet flavour to the pickled food. Lactobacillus bacilli a type 1), (PB-2), (PB-3), (PB-4) separately plated. Different
of Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) is used for the natural process concentration of clove oil viz., 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, µl ml-1
of fermentation. In pickled products, acid, salt, and heating were prepared. On the surface of the medium wells made by
are major factors that contribute to food preservation and using cork borer (6mm diameter) and discharged
these factors are applied in combination. Current regulations concentrations into well. The plates were incubated at
IJISRT23MAR543 www.ijisrt.com 919
Volume 8, Issue 3, March – 2023 International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology
ISSN No:-2456-2165
temperature of 30 oC and for 48 hrs and the diameter of IV. CONCLUSION
inhibition zone (in mm) around the well was measured. Three
replications were maintained in each treatment. Essential oils represent an alternative to synthetic
preservatives in the food industry against spoilage of bacteria.
III. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Most investigated bacteria showed some (higher or lower)
sensitivity to EOs or EO components. Therefore by using the
The characteristics of four pickle bacteria were studied clove oil, we can prevent the spoilage of various bacteria in
by using selective medium for respective bacteria and fermented pickles. The fermented pickles can be packed and
MacConkey agar. Based on the colony morphology, the stored long shelf life using some of the essential oils that are
bacteria were identified as Bacillus spp (PB-1), Clostridium not harmful to human health.
spp. (PB-2), Staphylococcus aureus (PB-3), and Proteus spp.
(PB-4). Microorganisms isolated from pickles samples in this REFERENCES
study have been earlier found in foods, environment and other
places, and their pattern in similar to previous reports [1]. Bassolé, I. H. N., and H. R. Juliani. (2012). Essential oils
(Clarence et al., 2009). in combination and their antimicrobial
properties. Molecules, 17(4), 3989-4006.
Identification of the different bacterial isolates was [2]. Benkeblia, N. 2004. Antibacterial activity of essential
carried out by the routine bacteriological methods i.e., By the oil extracts of various onions (Allium cepa) and garlic
colony morphology, Preliminary tests like Gram staining, (Allium sativum). Lebensmittel - Wissenschaft und -
Capsule staining, Endospore staining, Motility, plating on technologie, 37: 263 – 268.
selective media and by performing biochemical tests. [3]. Burt, S. (2004). Essential oils: their antibacterial
Identification of purified fungal cultures were characterized properties and potential applications in foods - a
by their morphology, hyphal characteristics, presence or review. International journal of food
absence of asexual spores, arrangement of conidia and microbiology, 94(3), 223-253.
reproductive structures (Beisher L, 1991) and by performing [4]. Cai, B.S., Y.Z. Mei Sun and H. Corke. 2005.
Lactophenol cotton blue mount. In addition, the necessary Antioxidant capacity of 26 spice extract and
concentration of essential oils and their components to characterization of their phenolic constituents. J. Agric.
achieve an antimicrobial effect in foods is much higher than Food Chem., 53(2): 7749-7759
under in vitro conditions. The presence of salt, proteins, fat, [5]. Chandara, H., S. Baluja and S.V. Chanda. 2005.
carbohydrates, and a low aw-value cause a decrease of the Comparison of antibacterial activities of selected
antimicrobial properties of essential oils (Klein et al., 2013). species of Zingiberaceae family and some synthetic
compounds. Turk. J. of Biol., 29: 83-97.
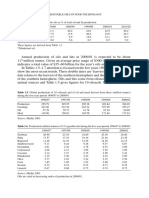
Table 1: Effect of clove oil on inhibition of pickle [6]. Dadgar, Hatha, A.A.M., C. Abirosh1, U. Harsha, and G.
bacteria and fungi by agar well diffusion method Vivekanandan. 2006, Antimicrobial activity of some of
Clove oil conc the south indian spices against serotypes of Escherichia
PB-1 PB-2 PB-3 PB-4 Mean coli, Salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes and
µl
Aeromonas hydrophila. Braz. J. Microbiol., 37:153-
0 NZ NZ NZ NZ -
158.
16.00 09.40 14.80 16.60 15.50 14.07 [7]. Lee, S. Y., & Kang, D. H. (2004). Microbial safety of
32.00 13.10 16.90 18.70 17.60 16.57 pickled fruits and vegetables and hurdle
64.00 15.20 18.30 20.80 19.70 18.5 technology. Internet Journal of food safety, 4, 21-32.
128.00 19.40 20.10 22.90 21.30 20.92 [8]. Mostafa, A. A., Al-Askar, A. A., Almaary, K. S.,
Dawoud, T. M., Sholkamy, E. N., & Bakri, M. M.
256.00 21.50 22.20 24.20 23.30 22.8 (2018). Antimicrobial activity of some plant extracts
Mean 15.72 18.46 20.64 19.48 - against bacterial strains causing food poisoning
NZ – No Zone of Inhibition diseases. Saudi journal of biological sciences, 25(2),
361-366.
In the present study the growth of four pickle bacteria [9]. Ukut, I. O., Okonko, I. O., Ikpoh, I. S., Nkang, A. O.,
strains viz., Bacillus spp (PB-1), Clostridium spp (PB-2), Udeze, A. O., Babalola, T. A., ... & Fajobi, E. A. (2010).
Staphylococcus spp (PB-3) and Proteus spp (PB-4) was Assessment of bacteriological quality of fresh meats
effectively inhibited at 256.00 μl concentration of clove oil. sold in Calabar metropolis, Nigeria. Electronic Journal
From the results, PB-3 shows higher inhibition zone followed of Environmental, Agricultural & Food
PB-4, PB-2 and PB-1. The increase in concentration leads to Chemistry, 9(1).
increased zone formation.
IJISRT23MAR543 www.ijisrt.com 920
You might also like
- Sahadeo 2011Document10 pagesSahadeo 2011Umbu SaefudinNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Activity of Basil Essential Oil (Ocimum Basilicum L.) : Evaluation in Vitro and On An Italian-Type Sausage SurfaceDocument8 pagesAntifungal Activity of Basil Essential Oil (Ocimum Basilicum L.) : Evaluation in Vitro and On An Italian-Type Sausage SurfaceMary Rose UmayamNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Activity StudiesDocument11 pagesAntimicrobial Activity Studiesfahrullah unhasNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Antimicrobial Activity of Some Currently Available Topical Antimicrobial ProductsDocument2 pagesInvestigation of Antimicrobial Activity of Some Currently Available Topical Antimicrobial ProductsZheefNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Antimicrobial Activities of Clove Oil & Its Extract On Some Food Borne MicrobesDocument7 pagesComparison of Antimicrobial Activities of Clove Oil & Its Extract On Some Food Borne MicrobesSeema YadavNo ratings yet
- Research Inventy: International Journal of Engineering and ScienceDocument10 pagesResearch Inventy: International Journal of Engineering and ScienceinventyNo ratings yet
- Preservatives in Food Products - ReviewDocument18 pagesPreservatives in Food Products - ReviewRenCraz03No ratings yet
- Broccoli FoodborneDocument4 pagesBroccoli FoodbornenuhajazminNo ratings yet
- Caracterización de Cultivos Iniciadores en Productos Cárnicos. PARTE 1. (Spanish)Document9 pagesCaracterización de Cultivos Iniciadores en Productos Cárnicos. PARTE 1. (Spanish)FATIMA ALVIZO ARRIAGANo ratings yet
- Screening, Isolation, and Antibacterial Activity of Antibiotic Producing Bacteria Obtained From Saprophytic Soil SamplesDocument5 pagesScreening, Isolation, and Antibacterial Activity of Antibiotic Producing Bacteria Obtained From Saprophytic Soil SamplesLenin Fernandez ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Beneficial Role of Micro-Organisms: StructureDocument20 pagesUnit 4 Beneficial Role of Micro-Organisms: StructureGuneet kaurNo ratings yet
- 603 1259 1 PBCVCXVDocument6 pages603 1259 1 PBCVCXVMaria AspriNo ratings yet
- TLC Bioautography-Guided Isolation of Essential OilDocument11 pagesTLC Bioautography-Guided Isolation of Essential OilSabina OproiuNo ratings yet
- Anti-Fungal Activities of Origanum Oil Against Candida AlbicansDocument9 pagesAnti-Fungal Activities of Origanum Oil Against Candida AlbicanscumbredinNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Optimization of Protease Production From Bacillus SP and Its ApplicationDocument13 pagesIsolation and Optimization of Protease Production From Bacillus SP and Its ApplicationRodrigo LaraNo ratings yet
- Physical and Antibacterial Properties of Alginate-Based Edible Film Incorporated With Garlic OilDocument6 pagesPhysical and Antibacterial Properties of Alginate-Based Edible Film Incorporated With Garlic OilMarcos OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Activity and Other Biological Properties of Oregano Essential Oil and Carvacrol (#842761) - 1455169Document17 pagesAntimicrobial Activity and Other Biological Properties of Oregano Essential Oil and Carvacrol (#842761) - 1455169Eljay DiezNo ratings yet
- 40EF7B663912Document5 pages40EF7B663912Fauzi SatriaNo ratings yet
- The Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oil of OreganoDocument3 pagesThe Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oil of OreganoMaría A. OdremanNo ratings yet
- BBRA Vol 7 No1p 361-365Document5 pagesBBRA Vol 7 No1p 361-365Leandro DouglasNo ratings yet
- 1 Pilihan Hari JugaDocument9 pages1 Pilihan Hari JuganadyasuwayviaNo ratings yet
- 56 139633598031 33 PDFDocument3 pages56 139633598031 33 PDFfitriNo ratings yet
- 2 PDFDocument9 pages2 PDFmimi boukNo ratings yet
- Viuda-Martos, M., Mohamady, M.A., Fernández-López, J., Abd El-Razik, K.A., Omer, E.A., Pérez-Alvarez, J.A. and Sendra, E. (2011) : in Vitro Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities O..Document9 pagesViuda-Martos, M., Mohamady, M.A., Fernández-López, J., Abd El-Razik, K.A., Omer, E.A., Pérez-Alvarez, J.A. and Sendra, E. (2011) : in Vitro Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities O..mimi boukNo ratings yet
- Application of Natural Antimicrobials For Food Preservation: Arrow@DitDocument16 pagesApplication of Natural Antimicrobials For Food Preservation: Arrow@DitpardeepNo ratings yet
- Phytochemical and Antimicrobial Activities of Acalypha WilkesianaDocument4 pagesPhytochemical and Antimicrobial Activities of Acalypha WilkesianaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Property of Over-the-Counter Essential Oils and Ayurvedic Powders Against Aeromonas Hydrophila Isolated From Labeo RohitoDocument4 pagesAntimicrobial Property of Over-the-Counter Essential Oils and Ayurvedic Powders Against Aeromonas Hydrophila Isolated From Labeo RohitoInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- 2 46 1637382809 7ijbrdec20217Document12 pages2 46 1637382809 7ijbrdec20217TJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Ciprofloxacin and Gentamicinmediated Inhibition of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms Is Enhanced When Combined The VolatilDocument8 pagesCiprofloxacin and Gentamicinmediated Inhibition of Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Biofilms Is Enhanced When Combined The VolatilLuis Carlos HernandezNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Properties and Phytochemical Analysis of Different Extracts of Murraya KoenigiiDocument6 pagesAntimicrobial Properties and Phytochemical Analysis of Different Extracts of Murraya Koenigiivanshika kelkarNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Activity of Phyto Essential Oils On Flaccherie Causing Bacteria in The Mulberry Silk Worm, B.Mori. LDocument5 pagesAntibacterial Activity of Phyto Essential Oils On Flaccherie Causing Bacteria in The Mulberry Silk Worm, B.Mori. LIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Inhibition Effect of Zataria Multiflora On Lactobacillus SPDocument3 pagesInhibition Effect of Zataria Multiflora On Lactobacillus SPsukriti bajpaiNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Estimation (Biochemical Analysis) of Lipolytic Bacteria From Unsalted ButterDocument5 pagesIsolation and Estimation (Biochemical Analysis) of Lipolytic Bacteria From Unsalted ButterLabiba TasnimNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity and Synergistic Effect Between Antibiotic and The Essential Oils of Some Medicinal PlantsDocument6 pagesEvaluation of Antibacterial Activity and Synergistic Effect Between Antibiotic and The Essential Oils of Some Medicinal PlantsxiuhtlaltzinNo ratings yet
- Roopan 2016Document16 pagesRoopan 2016Abdussataar KehindeNo ratings yet
- Fontanesii Boiss. Et Reut. and Origanum Glandulosum Desf. Essential OilsDocument8 pagesFontanesii Boiss. Et Reut. and Origanum Glandulosum Desf. Essential OilsBAZNAS Kabupaten MajalengkaNo ratings yet
- Ipdoaj MS Id 000115Document7 pagesIpdoaj MS Id 000115Monyet...No ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Activities of Spices and HerbsDocument7 pagesAntimicrobial Activities of Spices and HerbsLucía MercedesNo ratings yet
- Biological Activity of Cymbopogon Citratus (DC) Stapf and Its Potential Cosmetic ActivitiesDocument7 pagesBiological Activity of Cymbopogon Citratus (DC) Stapf and Its Potential Cosmetic ActivitiestdlamNo ratings yet
- Rosmary JurnalDocument4 pagesRosmary Jurnalakreditasi farmasiNo ratings yet
- F.MB (Experiment 02)Document3 pagesF.MB (Experiment 02)Joy ShahaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Basing 2Document9 pagesJurnal Basing 2ikrimahNo ratings yet
- Chemical Constituents and Antibacterial Activities of Crude Extract and Essential Oils of Alpinia Galanga and Zingiber OfficinaleDocument5 pagesChemical Constituents and Antibacterial Activities of Crude Extract and Essential Oils of Alpinia Galanga and Zingiber OfficinaleAbdulRasheedNo ratings yet
- Agronomy 12 00387 v2Document20 pagesAgronomy 12 00387 v2Rosa MutiaNo ratings yet
- Efficacyof Plant Essential Oils As Antimicrobial Agents Against Listeria Monocytogenes in HotdogsDocument8 pagesEfficacyof Plant Essential Oils As Antimicrobial Agents Against Listeria Monocytogenes in HotdogsBelen VignolaNo ratings yet
- Impedance Measurements To Study The Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils From Lamiaceae and CompositaeDocument9 pagesImpedance Measurements To Study The Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils From Lamiaceae and CompositaeHa MinhNo ratings yet
- Antifungal Effects of Basil Essential Oil Against Botrytis Cinerea Infection On Strawberries Storage in Modified PackagingDocument7 pagesAntifungal Effects of Basil Essential Oil Against Botrytis Cinerea Infection On Strawberries Storage in Modified PackagingLuis Pedro DominguesNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Bacillus Megaterium and Bacillus Mycoides Bacteria As Probiotic Bacteria in Fish and Shrimp FeedDocument9 pagesCharacterization of Bacillus Megaterium and Bacillus Mycoides Bacteria As Probiotic Bacteria in Fish and Shrimp FeedAusteridad LopezNo ratings yet
- Catalysts 09 00959Document16 pagesCatalysts 09 00959Lakatos SiminaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal EucalyptusDocument15 pagesJurnal EucalyptusTesaaulia BaharuddinNo ratings yet
- 2008 Book C5Document18 pages2008 Book C5an.s.lazaridouNo ratings yet
- Nerve Velocity Test by DoctorDocument40 pagesNerve Velocity Test by DoctorBadri NathNo ratings yet
- 2597 PDFDocument10 pages2597 PDFVũ Quyết ThắngNo ratings yet
- Identification and Bioactivities of Two Endophytic Fungi FusariumDocument11 pagesIdentification and Bioactivities of Two Endophytic Fungi Fusariummuhammad hamzaNo ratings yet
- 10 Benito Et Al PDFDocument8 pages10 Benito Et Al PDFRahmad RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Jurnal 3Document6 pagesJurnal 3Aldo HerisNo ratings yet
- Research Article: in Vitro Evaluation of Probiotic Properties of Lactic Acid BacteriaDocument12 pagesResearch Article: in Vitro Evaluation of Probiotic Properties of Lactic Acid BacteriaNatalija Atanasova-PancevskaNo ratings yet
- Essential Oil From Five Zingiberaceae For Anti Food-Borne BacteriaDocument10 pagesEssential Oil From Five Zingiberaceae For Anti Food-Borne Bacteriasukriti2812No ratings yet
- Fernandez and Tayab Print 1Document60 pagesFernandez and Tayab Print 1NEIZELNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Energy Consumption Analysis through Data Driven InsightsDocument16 pagesSustainable Energy Consumption Analysis through Data Driven InsightsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Vertical Farming System Based on IoTDocument6 pagesVertical Farming System Based on IoTInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Creative Thinking and Venture Performance: Reviewing the Influence of Psychomotor Education on the Profitability of Small and Medium Scale Firms in Port Harcourt MetropolisDocument10 pagesEntrepreneurial Creative Thinking and Venture Performance: Reviewing the Influence of Psychomotor Education on the Profitability of Small and Medium Scale Firms in Port Harcourt MetropolisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Influence of Principals’ Promotion of Professional Development of Teachers on Learners’ Academic Performance in Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education in Kisii County, KenyaDocument13 pagesInfluence of Principals’ Promotion of Professional Development of Teachers on Learners’ Academic Performance in Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education in Kisii County, KenyaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (1)
- Ambulance Booking SystemDocument7 pagesAmbulance Booking SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Utilization of Waste Heat Emitted by the KilnDocument2 pagesUtilization of Waste Heat Emitted by the KilnInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Digital Finance-Fintech and it’s Impact on Financial Inclusion in IndiaDocument10 pagesDigital Finance-Fintech and it’s Impact on Financial Inclusion in IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Detection and Counting of Fake Currency & Genuine Currency Using Image ProcessingDocument6 pagesDetection and Counting of Fake Currency & Genuine Currency Using Image ProcessingInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research Technology100% (9)
- An Overview of Lung CancerDocument6 pagesAn Overview of Lung CancerInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Osho Dynamic Meditation; Improved Stress Reduction in Farmer Determine by using Serum Cortisol and EEG (A Qualitative Study Review)Document8 pagesOsho Dynamic Meditation; Improved Stress Reduction in Farmer Determine by using Serum Cortisol and EEG (A Qualitative Study Review)International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Cloud-Powered Bidding MarketplaceDocument5 pagesAn Efficient Cloud-Powered Bidding MarketplaceInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Designing Cost-Effective SMS based Irrigation System using GSM ModuleDocument8 pagesDesigning Cost-Effective SMS based Irrigation System using GSM ModuleInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Impact of Stress and Emotional Reactions due to the Covid-19 Pandemic in IndiaDocument6 pagesImpact of Stress and Emotional Reactions due to the Covid-19 Pandemic in IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Effect of Solid Waste Management on Socio-Economic Development of Urban Area: A Case of Kicukiro DistrictDocument13 pagesEffect of Solid Waste Management on Socio-Economic Development of Urban Area: A Case of Kicukiro DistrictInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Computer Vision Gestures Recognition System Using Centralized Cloud ServerDocument9 pagesComputer Vision Gestures Recognition System Using Centralized Cloud ServerInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Auto Tix: Automated Bus Ticket SolutionDocument5 pagesAuto Tix: Automated Bus Ticket SolutionInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Examining the Benefits and Drawbacks of the Sand Dam Construction in Cadadley RiverbedDocument8 pagesExamining the Benefits and Drawbacks of the Sand Dam Construction in Cadadley RiverbedInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- An Industry That Capitalizes Off of Women's Insecurities?Document8 pagesAn Industry That Capitalizes Off of Women's Insecurities?International Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Forensic Advantages and Disadvantages of Raman Spectroscopy Methods in Various Banknotes Analysis and The Observed Discordant ResultsDocument12 pagesForensic Advantages and Disadvantages of Raman Spectroscopy Methods in Various Banknotes Analysis and The Observed Discordant ResultsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Predictive Analytics for Motorcycle Theft Detection and RecoveryDocument5 pagesPredictive Analytics for Motorcycle Theft Detection and RecoveryInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Comparative Evaluation of Action of RISA and Sodium Hypochlorite on the Surface Roughness of Heat Treated Single Files, Hyflex EDM and One Curve- An Atomic Force Microscopic StudyDocument5 pagesComparative Evaluation of Action of RISA and Sodium Hypochlorite on the Surface Roughness of Heat Treated Single Files, Hyflex EDM and One Curve- An Atomic Force Microscopic StudyInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Study Assessing Viability of Installing 20kw Solar Power For The Electrical & Electronic Engineering Department Rufus Giwa Polytechnic OwoDocument6 pagesStudy Assessing Viability of Installing 20kw Solar Power For The Electrical & Electronic Engineering Department Rufus Giwa Polytechnic OwoInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Unmasking Phishing Threats Through Cutting-Edge Machine LearningDocument8 pagesUnmasking Phishing Threats Through Cutting-Edge Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security Awareness and Educational Outcomes of Grade 4 LearnersDocument33 pagesCyber Security Awareness and Educational Outcomes of Grade 4 LearnersInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Blockchain Based Decentralized ApplicationDocument7 pagesBlockchain Based Decentralized ApplicationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Smart Health Care SystemDocument8 pagesSmart Health Care SystemInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Visual Water: An Integration of App and Web To Understand Chemical ElementsDocument5 pagesVisual Water: An Integration of App and Web To Understand Chemical ElementsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Parastomal Hernia: A Case Report, Repaired by Modified Laparascopic Sugarbaker TechniqueDocument2 pagesParastomal Hernia: A Case Report, Repaired by Modified Laparascopic Sugarbaker TechniqueInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing The Use of Improved Maize Seed and Participation in The Seed Demonstration Program by Smallholder Farmers in Kwali Area Council Abuja, NigeriaDocument6 pagesFactors Influencing The Use of Improved Maize Seed and Participation in The Seed Demonstration Program by Smallholder Farmers in Kwali Area Council Abuja, NigeriaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Impact of Silver Nanoparticles Infused in Blood in A Stenosed Artery Under The Effect of Magnetic Field Imp. of Silver Nano. Inf. in Blood in A Sten. Art. Under The Eff. of Mag. FieldDocument6 pagesImpact of Silver Nanoparticles Infused in Blood in A Stenosed Artery Under The Effect of Magnetic Field Imp. of Silver Nano. Inf. in Blood in A Sten. Art. Under The Eff. of Mag. FieldInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Emft2023 632 637Document6 pagesEmft2023 632 637aryapatel5508No ratings yet
- Business Plan Proposal: Willreen Bakery and CakeryDocument49 pagesBusiness Plan Proposal: Willreen Bakery and CakeryMonicah MuthokaNo ratings yet
- C60ib009en K Instrman Pba-Sd-Sid M v2.93 WebDocument68 pagesC60ib009en K Instrman Pba-Sd-Sid M v2.93 WebXavier ArévaloNo ratings yet
- TLE6 Q1 Mod3 Conduct Survey On The Types of Orchard Farm Version3Document55 pagesTLE6 Q1 Mod3 Conduct Survey On The Types of Orchard Farm Version3Agnes VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Katalog Metatron enDocument50 pagesKatalog Metatron enDamien DupuyNo ratings yet
- Hash House A Go Go Plano Menu PDFDocument2 pagesHash House A Go Go Plano Menu PDFSteven LindseyNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument10 pagesLesson PlanMa. ChrizelNo ratings yet
- Apple Cider Vinegar Health Benefits and Unwanted EffectsDocument4 pagesApple Cider Vinegar Health Benefits and Unwanted EffectsBlackpicassoNo ratings yet
- Meal Plan ISUDocument7 pagesMeal Plan ISUPretha VijayakumaranNo ratings yet
- Restaurant Report Card - Nov. 11, 2021Document5 pagesRestaurant Report Card - Nov. 11, 2021KBTXNo ratings yet
- MANUSCRIPT CARASI FINALnaDocument23 pagesMANUSCRIPT CARASI FINALnaNcip Ilocos NorteNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Good NutritionDocument23 pagesThe Importance of Good Nutritionrafaelarmildez02No ratings yet
- Listening b1Document4 pagesListening b1Trung DũngNo ratings yet
- CHN FinalsDocument43 pagesCHN FinalsNHICOLE YAO PORCESONo ratings yet
- Active and Passive VoiceDocument6 pagesActive and Passive VoiceÁngel Sánchez IbáñezNo ratings yet
- Science Module 1 Lesson 1 and 2 Module 2 Lesson 1Document31 pagesScience Module 1 Lesson 1 and 2 Module 2 Lesson 1Chester Allan EduriaNo ratings yet
- Genetically Modified OrganismsDocument38 pagesGenetically Modified OrganismsMARIA SOCORRO GENERNo ratings yet
- Edsci ReviewerDocument16 pagesEdsci ReviewerElla GuintoNo ratings yet
- Navigate A2: Level 1 (A1 / A2) Word List Cutting Edge ElementaryDocument12 pagesNavigate A2: Level 1 (A1 / A2) Word List Cutting Edge Elementaryქრისტინა საქუაშვილიNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Difference Between Object Oriented Design and Object Oriented Analysis With The Help of Suitable Diagram?Document7 pagesDiscuss The Difference Between Object Oriented Design and Object Oriented Analysis With The Help of Suitable Diagram?vineet kholaNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis KFCDocument43 pagesStructural Analysis KFCSamia Cornelius72% (32)
- Wucale 1-15 5 2016Document113 pagesWucale 1-15 5 2016etanalegesseayNo ratings yet
- Takeaway Indian Food CardonDocument2 pagesTakeaway Indian Food CardonFlavor of IndiaNo ratings yet
- 06 Food Guideline For WildFit Week 9Document5 pages06 Food Guideline For WildFit Week 9Han YiNo ratings yet
- Stabilitas Hasil Padi Hibrida Varietas Hipa 7 Dan Hipa 8 Dan Ketahanannya Terhadap Hawar Daun Bakteri Dan TungroDocument7 pagesStabilitas Hasil Padi Hibrida Varietas Hipa 7 Dan Hipa 8 Dan Ketahanannya Terhadap Hawar Daun Bakteri Dan TungrogagaNo ratings yet
- Adivinanzas en InglesDocument5 pagesAdivinanzas en InglesSponsa VerbiNo ratings yet
- Song Sheet: Need You Now by Lady AntebellumDocument2 pagesSong Sheet: Need You Now by Lady AntebellumJuanARNo ratings yet
- Health PromotionDocument82 pagesHealth Promotionsunielgowda100% (1)
- Source: Mielke 2001Document3 pagesSource: Mielke 2001Alfonso RuizNo ratings yet
- 408 Agriculture SQPDocument6 pages408 Agriculture SQPranapratapmondal155No ratings yet