Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Polymer Da1
Polymer Da1
Uploaded by
Mugilan M0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesStyrene is the monomer used to produce polystyrene through polymerization. Styrene is produced from benzene and ethylene and is polymerized using organic peroxides as catalysts. Polystyrene has a melting point of 240 C, boiling point of 430 C, and density of 1.05 gm/cm^3. It is a hard but brittle, non-polar and amorphous plastic with good optical and electrical insulation properties.
Original Description:
Original Title
polymer-da1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentStyrene is the monomer used to produce polystyrene through polymerization. Styrene is produced from benzene and ethylene and is polymerized using organic peroxides as catalysts. Polystyrene has a melting point of 240 C, boiling point of 430 C, and density of 1.05 gm/cm^3. It is a hard but brittle, non-polar and amorphous plastic with good optical and electrical insulation properties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesPolymer Da1
Polymer Da1
Uploaded by
Mugilan MStyrene is the monomer used to produce polystyrene through polymerization. Styrene is produced from benzene and ethylene and is polymerized using organic peroxides as catalysts. Polystyrene has a melting point of 240 C, boiling point of 430 C, and density of 1.05 gm/cm^3. It is a hard but brittle, non-polar and amorphous plastic with good optical and electrical insulation properties.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
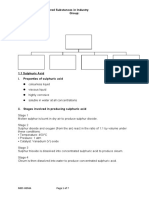
2.
Materials
2.1 Raw material
Styrene, also known as ethylbenzene, vinylbenzene, or phenylethane, is the
monomer for polystyrene, which is the precursor of polystyrene and other well-
known copolymers. Styrene is used to make a variety of strong, flexible, and
light products. Benzene and ethylene are used to make styrene, which is then
polymerized in the presence of catalysts, typically organic peroxides.
2.2 Molecular structure
Source:
https://read.nxtbook.com/wiley/plasticsengineering/september2016/consultantscorner_plastics.html
2.3 Physical and Chemical properties
Due of the hefty phenyl groups that are present, polystyrene is in an amorphous
condition and cannot be efficiently packed.
Polystyrene is non-polar in nature.
The Melting point of polystyrene is 240 C.
The Boiling point of polystyrene is 430 C.
The density of polystyrene is 1.05 gm/cm^3.
Since polystyrene is translucent and allows for strong transmission of all wavelengths,
it has good optical properties. Moreover, it has an especially high brightness due to its
high refractive index.
Thanks to the chain stiffening effect of the benzene ring, polystyrene is hard but
brittle. When it falls, it makes a typical metallic sound.
Being a non-polar amorphous polymer, it has a low softening temperature. It cannot
withstand the temperature of boiling water.
Polystyrene has a low ability to absorb moisture. In addition, it has good electrical
insulation properties. Therefore, it is used to make polystyrene insulation products.
Polystyrene is insoluble in water.
Polystyrene has good insulating properties. That is why it is used in the production of
polystyrene insulation products.
You might also like
- Catalog VALSIR Canalizare PDFDocument60 pagesCatalog VALSIR Canalizare PDFAlexandru Ilioiu100% (1)
- When Glass meets Pharma: Insights about glass as primary packaging materialFrom EverandWhen Glass meets Pharma: Insights about glass as primary packaging materialNo ratings yet
- Different Industrial PolymersDocument22 pagesDifferent Industrial PolymersSHYAMNo ratings yet
- Polymer Notes 2017Document10 pagesPolymer Notes 2017Bikram YadavNo ratings yet
- PolystyreneDocument2 pagesPolystyrenekaoutar naimiNo ratings yet
- 2nd Unit - PlasticDocument31 pages2nd Unit - PlasticAvantikaNo ratings yet
- Fiber Forming PolymerDocument11 pagesFiber Forming Polymerrony79909No ratings yet
- En SonDocument4 pagesEn SonMeryem KÜLAHLIOĞLUNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument8 pagesChapter IAnas NazarNo ratings yet
- 2 MeterialsDocument12 pages2 MeterialsthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesChemistry Investigatory Projectvidhisha makenNo ratings yet
- Material PropertyDocument19 pagesMaterial PropertyAHMED YOUSEFNo ratings yet
- Types of PlasticsDocument6 pagesTypes of PlasticsFarrukh ShahzadNo ratings yet
- FOAMING PresentationDocument15 pagesFOAMING PresentationWe'am almasri0% (1)
- Polyester, Cobalt Particulate and Rockwool FiberDocument66 pagesPolyester, Cobalt Particulate and Rockwool FiberShashank Singh100% (1)
- Unit 2 Polymer and CompositesDocument91 pagesUnit 2 Polymer and Compositesparth.choudhari.btech2023No ratings yet
- Denture Base Resin 2Document53 pagesDenture Base Resin 2Girish Yadav100% (1)
- E.G. E.G. E.G. E.G. I.E. Etc. Etc. E.GDocument13 pagesE.G. E.G. E.G. E.G. I.E. Etc. Etc. E.GjoshigautaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Class 12 PolymersDocument18 pagesChemistry Project Class 12 PolymersDeepamjyoti DivyaprakashNo ratings yet
- Aim of The Project: Synthesis and Property AnalysisDocument16 pagesAim of The Project: Synthesis and Property Analysissaurabh guptaNo ratings yet
- Polymers-Prep, Props, UsesDocument7 pagesPolymers-Prep, Props, UsesHarshal A ShahNo ratings yet
- PlasticsDocument40 pagesPlasticsNeerajaNo ratings yet
- Pastel Purple and Blue 3D Illustration STEM Science Education Presentation 2Document54 pagesPastel Purple and Blue 3D Illustration STEM Science Education Presentation 2Krize Anne CornejaNo ratings yet
- PolypropyleneDocument29 pagesPolypropyleneZeny Naranjo100% (1)
- Polycarbonates, Polyamides and PolyurethaneDocument8 pagesPolycarbonates, Polyamides and Polyurethanecopperfieldfrank3No ratings yet
- Mahmood Tariq Exp 2Document8 pagesMahmood Tariq Exp 2mahmood0901instaNo ratings yet
- Plastics Thermoplastics Thermosetting: Rivera, Patrick Joshua D. Perez, JaysonDocument13 pagesPlastics Thermoplastics Thermosetting: Rivera, Patrick Joshua D. Perez, Jaysonpatrick1101No ratings yet
- Blue Cream Simple Creative Writing Student PresentationDocument17 pagesBlue Cream Simple Creative Writing Student PresentationJoselle BiñanNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Material: Cast Iron 1200°CDocument6 pagesFerrous Material: Cast Iron 1200°CSquidward TentaclesNo ratings yet
- Plastic: Report in CMT PlasticDocument9 pagesPlastic: Report in CMT PlasticChris Michelle JapinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and PlacticsDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Synthetic Fibres and PlacticsDhyani PanchalNo ratings yet
- Lectures On PlasticDocument15 pagesLectures On PlasticKaushik RNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Fibres and PlasticsDocument6 pagesCH 1 Fibres and PlasticsRidham JainNo ratings yet
- Handout Packaging MaterialsDocument15 pagesHandout Packaging MaterialsShahnasNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FolioDocument30 pagesChemistry FolioMuhammad Syafiq AsyrafNo ratings yet
- Polyethylene TerephthalateDocument2 pagesPolyethylene TerephthalatesabbysamuraNo ratings yet
- Module 609 NotesDocument7 pagesModule 609 NotesHema LataNo ratings yet
- TPPP PBL 1 Kelompok 5Document13 pagesTPPP PBL 1 Kelompok 5Queena Fatima AzzahraNo ratings yet
- PolyethyleneDocument11 pagesPolyethyleneIvan German Ramos100% (1)
- 1.1 PolystyreneDocument8 pages1.1 PolystyreneajachurailNo ratings yet
- Polymers & Plastics NotesDocument4 pagesPolymers & Plastics NotessaheedvkNo ratings yet
- Sweet Gum Wood Is Valued For Its Attractive, Interlocked Grain. It Easily Takes On Staining, Painting and IsDocument2 pagesSweet Gum Wood Is Valued For Its Attractive, Interlocked Grain. It Easily Takes On Staining, Painting and IsClarisse Joyce GenerNo ratings yet
- Plastic Bottles and Bottle CapsDocument10 pagesPlastic Bottles and Bottle Capsikki kuroganeNo ratings yet
- Certificate and AknowledgementDocument22 pagesCertificate and AknowledgementAkhand PratapNo ratings yet
- For Muslim: Always Follow The Way of Islam Completely For Non Muslim: Always Set Goal Before Working Towards ItDocument36 pagesFor Muslim: Always Follow The Way of Islam Completely For Non Muslim: Always Set Goal Before Working Towards ItAman KashyapNo ratings yet
- Chem 111 PolymersDocument8 pagesChem 111 PolymersPaul Bronzon DurensNo ratings yet
- Transparent WoodDocument1 pageTransparent WoodSharanya N MNo ratings yet
- Polymers-Prep, Props, UsesDocument10 pagesPolymers-Prep, Props, Useslalithkumaran LNo ratings yet
- History of PlasticDocument3 pagesHistory of PlasticVikneshwaran BalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Consumer Goods - Low Cost and Easy Processability Make HDPE A Material of Choice inDocument5 pagesConsumer Goods - Low Cost and Easy Processability Make HDPE A Material of Choice inDwi YuliantoNo ratings yet
- PolymerDocument5 pagesPolymerOM SableNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature and StudiesDocument5 pagesReview of Related Literature and StudiesWayne Montemayor100% (2)
- Polystyrene and CopolymersDocument7 pagesPolystyrene and Copolymerskeerthi srijithNo ratings yet
- Polypropylene PP PlasticDocument8 pagesPolypropylene PP PlasticRyan VasquezNo ratings yet
- Polymer 3Document3 pagesPolymer 3Dhruv PatelNo ratings yet
- Preparation Properties PolyestersDocument1 pagePreparation Properties Polyestersdarshan baskarNo ratings yet
- Tacticity: Different Polymer Structures From A Monosubstituted Ethylene, (CH - CHR)Document7 pagesTacticity: Different Polymer Structures From A Monosubstituted Ethylene, (CH - CHR)A.Mohammad idhrisNo ratings yet
- Synthetic PolymersDocument45 pagesSynthetic PolymersIboniks Beponpiks DabondatskiNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument33 pagesPolymerssundara ramanNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument20 pagesPolymerslakshay ManglaNo ratings yet