Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 3 Gec Self
Topic 3 Gec Self
Uploaded by
Axyl Galacio0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views4 pagesTopic 3 Gec Self
Topic 3 Gec Self
Uploaded by
Axyl GalacioCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
“MIRROR, MIRROR ON THE WALL”
Make a short video presentation by asking your family members, friends,
Classmates, and even strangers to say something about their imp
can be positive or negative.
Bithe Self As a Product of Modern Society Among Other Constructions
Sociologists are concerned with questions about the person in the community. For
example, They ask questions, like: “How does society influence you?” “How do you affect
society?” More importantly, “Who are you as a person in the community?” Sociology
posits that socially formed norms, beliefs, and values come to exist within the person
toa degree where these become natural and normal (Elwell, 2003), thus, developing the
person's self-identity. .
Modernization has significantly changed society, and this has affected how an
individual builds and develops his or her self-identity. Pre-modern society was centered
on survival. People behaved according to social rules and traditions while the family
and the immediate environment provided supervision on how to get through life
‘Scanned with CamScanner
mongrier tte itnet kt dean een bots may ws ry
omnes 200
Modernization, however, has improved people's livin conditions. § person
on Aine et mde ete eee
family. have decreased in importance In modern societies, individualism ig 0
land developing one’s self entity is central (Giddens, 1991), ‘mina,
ees
ng ine GD, eH esr ngs
ait
ae Rode
1 Indastralnm, the social relations implied in the exten
powerand machinerginall processes of production," Sf Bera
2 Capitalism, a production system involvin
: i both competitive
and hecqnmodifcatin (puting «price tag of bor poner Product mar
‘3. Institutions of surveillance, the massive inc
institutions, especially in government; and
Dynamism, the most evident characteristic
chara
rease of power and reach bp
Social groups and social network
soca SOB George Simmel expressed that people reat soil networks by nin
Foups. A social groups described as having two or more people
ne another, sharing similar characteristic, and whose menben ently one,
oe ‘of the group.-An example of a social group is your family, your barkais, your
‘smates. Meanwhile, social network refers to the ties or connections that link you to.
Your social group (Khan Academy, WEB). The connection you have with your fii
‘Your blood relation; the connection you have with your barkads is your friendship; and
the connection you have with your classmate isthe common interest to lear,
A social group is either organic or rational. An organic group is naturally occuring
‘and tis highly influenced by your family. This is usually forme adiional societies
because there is little diversity in these commutes ee a a
Teen a tpt
a al network runs deep, thus, giving the
however is that organic groups imply
called it organic motivatios
rootedness. This means the foundation ofthe soc
person a sense of belongingness. The downside,
‘Scanned with CamScanner
Jess freedom:
to your commu
Hrettonal groups occur in moder toclties, Modeyn soietie ae ma
diffesene people coming from different places, The family in modern so eae
Steen rghen ining rational ol gongs, Rational pop re foe 4
nin ted el intreste moreover, people join there groupe ont of teow re
rate guna called this ratfonal motivation, Rational groups imply greater freed a
sine treadom of moveinent. Relationships based on self interest am as
and greater social conformity. Ye
; You are expected toact anv
rity standards (Allan, 2012). Ml bchavesccondig
especi
Wied as organic relationships. Interests change and when they do, group members
ship between rational social networks is tenuous, and the person
yn, 2012).
embed
change. The relation:
fee no meaningful connection with ehe others (All
[iMead and the Social Self
~
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5811)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Topic 6 Sexual Characteristics, Behaviors and Reproductive SystemDocument21 pagesTopic 6 Sexual Characteristics, Behaviors and Reproductive SystemAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Me and My CultureDocument11 pagesTopic 2 Me and My CultureAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- Axyl Kent Rubin Galacio - BSMT-1A - GEC STSDocument2 pagesAxyl Kent Rubin Galacio - BSMT-1A - GEC STSAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument3 pagesMicroscopeAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Philosopher's View On SelfDocument16 pagesTopic 1 Philosopher's View On SelfAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Assignment #1Document1 pageChemistry Assignment #1Axyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- Gec ComDocument2 pagesGec ComAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- Patterns and NumbersDocument1 pagePatterns and NumbersAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
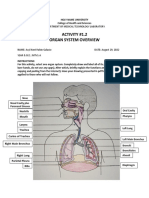
- Exercise No. 1.2 - Organ System OverviewDocument2 pagesExercise No. 1.2 - Organ System OverviewAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet