Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gec Com
Gec Com
Uploaded by
Axyl GalacioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Gec Com
Gec Com
Uploaded by
Axyl GalacioCopyright:
Available Formats
Any number of physical distractions can interfere with the effectiveness of
communication, including a telephone call, drop-in visitors, distances between people,
walls, and static on the radio.
True
Not all languages have slangs, taboo words, and euphemism for them, such as john for
“toilet.”
False
The vocabulary of a language can be expanded to include new words for new
True
The words we choose, how we use them, and the meaning we attach to them can
cause many communication barriers.
True
Noise is one of the five steps in the communication process. False All living languages
change through time.
True
People's backgrounds, perceptions, values, biases, needs, and expectations cannot
affect the decoding of the message.
False
Communication requires at least three elements: sender, message, and receiver. Agree
There are no “primitive” languages—all languages are equally complex and equally
capable of expressing an idea.
Agree
Wherever human exists, language exists. Agree If noise is introduced, then the received
message contains certain distortions, certain errors, certain extraneous material, that
would certainly lead one to say that the received message exhibits, because of the
effects of the noise, an increased uncertainty.
Agree
Effective communication may result to either goodwill or chaos.
Disagree
Effective communication has an audience that depends on Occasion and purpose How
do you call the communication problem identified by Dr. Claude E. Shannon that is
concerned with the accuracy of transference from sender to the receiver of sets of
symbols (written speech), or of a continuously varying signal (telephonic or radio
transmission of voice or music), or of a continuously varying two-dimensional pattern
(television), etc?
Technical problem
Which among the intents of communication is related to teaching? To instruct In the
theory of Shannon and Weaver, they identified a problem that is concerned with the
identity, or a satisfactorily close approximation, in the interpretation of meaning by the
receiver, as compared with the intended meaning of the sender. This is a very deep and
involved situation, even when one deals only with the relatively simpler problems of
communicating through speech.
Semantic problem
During a meeting, the failure of the Student Body Organization to ask any questions
causes the University President to wonder if any real understanding has taken place.
Which among the process barriers exemplifies the above-given scenario. Feedback
barrier This is a type of barrier that often involves a psychological distance between
people that is similar to actual physical distance.
Psychosocial barrier
Which among the following intents of communication is related to argumentation and
sales talk? To persuade In the theory of Shannon and Weaver, they identified a problem
that is concerned with the success with which the meaning conveyed to the receiver
leads to the desired conduct on his part.
Effectiveness problem
This communication term is popularized by the work of Carl Rogers and Richard Farson
(n.d.) and advocated by counsellors and therapists (Brownell, 2009; Burstein, 2010).
Active listening
Which barrier is being referred to in the following: The same word may mean different
things to different people.
Semantic barrier
This refers to any number of physical distractions can interfere with the effectiveness of
communication, including a telephone call, drop-in visitors, distances between people,
walls, and static on the radio.
Physical barrier
You might also like
- Module 1 Purposive Communication - 21st Century CommunicationDocument48 pagesModule 1 Purposive Communication - 21st Century CommunicationRovin Jae Esguerra86% (7)
- Scavenger Hunt Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesScavenger Hunt Lesson Planapi-272778483No ratings yet
- 10 Minute Guide Phonics - PRIORITYDocument11 pages10 Minute Guide Phonics - PRIORITYfriendship434481No ratings yet
- 2.final LOURDES H. CASTRO Dissertation ProposalDocument38 pages2.final LOURDES H. CASTRO Dissertation ProposalJayson Dotimas Velasco100% (4)
- Four Principles of Interpersonal CommunicationDocument4 pagesFour Principles of Interpersonal CommunicationJolly SushmaNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Communication - Group 2Document88 pagesBarriers To Communication - Group 2shahhoneyNo ratings yet
- Research PosterDocument1 pageResearch PosterKhairul Anuar Abdul RahimNo ratings yet
- Rationale For Literacy and NumeracyDocument3 pagesRationale For Literacy and Numeracyapi-253471744100% (1)
- Name: Fayemi Seun Class: JSS3 School: Pythagoras College Date: 9-11-10 Teacher: MRS - Tina Adiele Subject: Integrated ScienceDocument10 pagesName: Fayemi Seun Class: JSS3 School: Pythagoras College Date: 9-11-10 Teacher: MRS - Tina Adiele Subject: Integrated ScienceSeun FayemiNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Effective CommunicationDocument2 pagesBarriers To Effective CommunicationVi JayNo ratings yet
- CommunicationDocument32 pagesCommunicationabdullah2020No ratings yet
- Assgment Oral Com Mu Cation Oum NewDocument10 pagesAssgment Oral Com Mu Cation Oum NewIqram Syawal IbrahimNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Oral CommunicationDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Oral CommunicationdoronelaczarinapanotesNo ratings yet
- Hand Outs in Ed 403 AutosavedDocument7 pagesHand Outs in Ed 403 Autosavedjenessa abrasaldoNo ratings yet
- Commucatin Skills NotesDocument29 pagesCommucatin Skills NotesPethias MusondaNo ratings yet
- Purcomm IhDocument5 pagesPurcomm IhChicken NoodlesNo ratings yet
- PC Midterms CoverageDocument31 pagesPC Midterms CoverageFant AsticNo ratings yet
- Advanced SpeechDocument51 pagesAdvanced SpeechMekonnen WubshetNo ratings yet
- Oral CommunicationDocument3 pagesOral CommunicationDoralynMarasiganFestijoNo ratings yet
- Occ Study Guide - Unit 1Document16 pagesOcc Study Guide - Unit 1Kurt Denver QuiranteNo ratings yet
- PALMA Comm - MediaM1A1Document4 pagesPALMA Comm - MediaM1A1Princes Janine A. PalmaNo ratings yet
- Notes For CPS: Chapter 1: Introduction To Human CommunicationDocument16 pagesNotes For CPS: Chapter 1: Introduction To Human CommunicationTalha ImranNo ratings yet
- Theories and Concepts of CommunicationDocument30 pagesTheories and Concepts of CommunicationPatrizzia Ann Rose Ocbina100% (1)
- Dr. Piyush Mathur 2017 11 19 14 54 37 220Document47 pagesDr. Piyush Mathur 2017 11 19 14 54 37 220SuNil SeeRviNo ratings yet
- Aditi Ma'am BC NotesDocument18 pagesAditi Ma'am BC NotesFisjdjjdjrjrNo ratings yet
- Effective CommunicationDocument7 pagesEffective CommunicationmanishsirNo ratings yet
- Communication BarriersDocument28 pagesCommunication BarriersArsh UniyalNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication: Communication Is The Activity of Conveying MeaningfulDocument10 pagesOral Communication: Communication Is The Activity of Conveying MeaningfulJeanlee Mercado BalubarNo ratings yet
- Language CommunicationDocument6 pagesLanguage CommunicationNazmul HasanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 OutlineDocument5 pagesLesson 1 OutlineXHYRICH ISLETANo ratings yet
- Role of Verbal and Non Verbal Communication in LanguageDocument14 pagesRole of Verbal and Non Verbal Communication in LanguageGTA V GameNo ratings yet
- Oral &verbal CommunicationDocument15 pagesOral &verbal CommunicationHamiz MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- What Is Communicatio1Document5 pagesWhat Is Communicatio1Thavindu RushanNo ratings yet
- Types of CommunicationDocument7 pagesTypes of CommunicationanushapillalamarriNo ratings yet
- Non-Verbal Communication: DiscussionDocument10 pagesNon-Verbal Communication: DiscussionChriscell Gipanao EustaquioNo ratings yet
- Non Verbal CommunicationDocument10 pagesNon Verbal CommunicationAtul NarayananNo ratings yet
- Untitled PDFDocument11 pagesUntitled PDFAnonymous c2Ho0XNo ratings yet
- Communication Disorders Final DraftDocument9 pagesCommunication Disorders Final Draftapi-537019967No ratings yet
- Semantika - Communication BreakdownDocument10 pagesSemantika - Communication BreakdownVioleta GolightlyNo ratings yet
- INSTFONTANA - LINGUISTCA 1eroDocument7 pagesINSTFONTANA - LINGUISTCA 1eroLucas AyalaNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Examination ReviewerDocument2 pagesPreliminary Examination ReviewerExodus GreyratNo ratings yet
- Documents - 521ffproficiency Test 2021-Study Material-Common Subject-Ug Programs-English Communication (Ug) - (All Domains)Document17 pagesDocuments - 521ffproficiency Test 2021-Study Material-Common Subject-Ug Programs-English Communication (Ug) - (All Domains)Rishabh JhaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Language and CommunicationDocument4 pagesModule 1 Language and CommunicationJay AnnNo ratings yet
- The Complexities of Human Communication PDFDocument4 pagesThe Complexities of Human Communication PDFNoman Ahmed ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Communication: Communication Is The Activity of ConveyingDocument14 pagesCommunication: Communication Is The Activity of ConveyingVijaya Krishna GudavalliNo ratings yet
- Creating and Sustaining Pseudo - RelationshipsDocument6 pagesCreating and Sustaining Pseudo - RelationshipsAy TacNo ratings yet
- Assg Oral ComunicationDocument16 pagesAssg Oral ComunicationHalimatus Saadiah MahadiNo ratings yet
- Barriers To CommunicationDocument29 pagesBarriers To CommunicationGuneet AulakhNo ratings yet
- L3 Barriers To CommunicationDocument36 pagesL3 Barriers To CommunicationVedansha SinghalNo ratings yet
- Purposive Communication ModuleDocument14 pagesPurposive Communication ModuleJhobeb VillasorNo ratings yet
- Question 1 (A)Document9 pagesQuestion 1 (A)ABDUR REHMAN HUSSAIN KHANNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Oral Cominication 11Document10 pagesReviewer in Oral Cominication 11Nicole BirjNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in ContextDocument3 pagesOral Communication in ContextHelmer PascualNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Barriers To Effective CommunDocument6 pagesAssignment - Barriers To Effective CommunWajiihah BaureekNo ratings yet
- Oral Com ReviewerDocument110 pagesOral Com ReviewerBella LunaNo ratings yet
- Barriers of CommunicationDocument20 pagesBarriers of CommunicationHassanNo ratings yet
- Communicative BehaviorsDocument4 pagesCommunicative BehaviorsAmeer KhanNo ratings yet
- Communication Process and Its ElementsDocument4 pagesCommunication Process and Its ElementsSoonyoung KwonNo ratings yet
- Communication 1Document11 pagesCommunication 1KaranPatilNo ratings yet
- Barriers To Effective CommunicationDocument33 pagesBarriers To Effective Communicationshumaila parveenNo ratings yet
- Principle of FeedbackDocument12 pagesPrinciple of FeedbackArthur TocloNo ratings yet
- Week 7Document28 pagesWeek 7Joshua JanerNo ratings yet
- Communication Application FinalDocument109 pagesCommunication Application Finalgardner_lauramarieNo ratings yet
- The Complete Communication & People Skills Training: Master Small Talk, Charisma, Public Speaking & Start Developing Deeper Relationships & Connections- Learn to Talk To AnyoneFrom EverandThe Complete Communication & People Skills Training: Master Small Talk, Charisma, Public Speaking & Start Developing Deeper Relationships & Connections- Learn to Talk To AnyoneNo ratings yet
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Comprehension and Meaning in LanguageFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Comprehension and Meaning in LanguageNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Sexual Characteristics, Behaviors and Reproductive SystemDocument21 pagesTopic 6 Sexual Characteristics, Behaviors and Reproductive SystemAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Me and My CultureDocument11 pagesTopic 2 Me and My CultureAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- Axyl Kent Rubin Galacio - BSMT-1A - GEC STSDocument2 pagesAxyl Kent Rubin Galacio - BSMT-1A - GEC STSAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Gec SelfDocument4 pagesTopic 3 Gec SelfAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Philosopher's View On SelfDocument16 pagesTopic 1 Philosopher's View On SelfAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Assignment #1Document1 pageChemistry Assignment #1Axyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument3 pagesMicroscopeAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- Patterns and NumbersDocument1 pagePatterns and NumbersAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
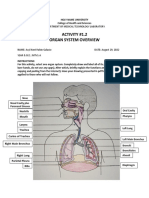
- Exercise No. 1.2 - Organ System OverviewDocument2 pagesExercise No. 1.2 - Organ System OverviewAxyl GalacioNo ratings yet
- Goal ProgramingDocument28 pagesGoal ProgramingAmritesh jhaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Artificial IntelligenceDocument4 pagesTerm Paper Artificial Intelligenceafdttjujo100% (1)
- Aplng 493 - Lesson PlanDocument12 pagesAplng 493 - Lesson Planapi-603889846No ratings yet
- Group TheoryDocument10 pagesGroup TheoryAmeyRuled AriffinNo ratings yet
- HMEF5063 Exam Sample SetDocument5 pagesHMEF5063 Exam Sample SetRinkie YeapNo ratings yet
- The+80 20+Guide+ExtractDocument2 pagesThe+80 20+Guide+ExtractRumki SarkarNo ratings yet
- 1123-Maldives w02 ErDocument11 pages1123-Maldives w02 ErkiasportageNo ratings yet
- Pembelajaran Tematik Berbasis Kontekstual Di SD Muhammadiyah 9 MalangDocument8 pagesPembelajaran Tematik Berbasis Kontekstual Di SD Muhammadiyah 9 Malangdewa_luv_uNo ratings yet
- Receive Reservation Request Record Details of Reservation Update Reservations 4. Advise Others On Reservation DetailsDocument6 pagesReceive Reservation Request Record Details of Reservation Update Reservations 4. Advise Others On Reservation DetailsmariettaNo ratings yet
- CreswellQI4e TB06Document6 pagesCreswellQI4e TB06Estef BrozoNo ratings yet
- Cvs Better Future OverviewDocument9 pagesCvs Better Future OverviewAnonymous YdFUaW6fBNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Cooperative LearningDocument16 pagesCharacteristics of Cooperative LearningHIZBULLAHNo ratings yet
- Course Outline PDFDocument2 pagesCourse Outline PDFNama DesalewNo ratings yet
- Collection, Analyses and Interpretation of DataDocument50 pagesCollection, Analyses and Interpretation of DataJun PontiverosNo ratings yet
- Study 1 Canli Et Al 2000Document1 pageStudy 1 Canli Et Al 2000emmaldavisNo ratings yet
- Rough Draft Research PaperDocument20 pagesRough Draft Research Paperapi-451581944No ratings yet
- 2010-2011 AP Psychology Midterm Exam ReviewDocument187 pages2010-2011 AP Psychology Midterm Exam Reviewjlvmrbd777No ratings yet
- Teacher Education Program: Core Gateway College, IncDocument17 pagesTeacher Education Program: Core Gateway College, IncAira Calderon100% (1)
- Multilingual Facilitation: March 2021Document16 pagesMultilingual Facilitation: March 2021Aastha AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- MAED - PRE - Course PackDocument3 pagesMAED - PRE - Course PackhanipaNo ratings yet
- Yi Liu Resume-EDocument1 pageYi Liu Resume-Eapi-711725785No ratings yet
- Creative Writing - LP Week1 2Document7 pagesCreative Writing - LP Week1 2Mara M. LabanderoNo ratings yet
- CPA-MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION OF FRACTION USING CPA APPROACH AMSDIGA (Autosaved)Document59 pagesCPA-MULTIPLICATION AND DIVISION OF FRACTION USING CPA APPROACH AMSDIGA (Autosaved)Armelou MagsipocNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1 - Introduction To SlopeDocument4 pagesLesson Plan 1 - Introduction To Slopedionnesartin67% (3)
- Critically Appraised Paper For SOS FeedingDocument6 pagesCritically Appraised Paper For SOS FeedingJohn DoeNo ratings yet