0% found this document useful (0 votes)
158 views15 pagesAnti-Lock Braking System Overview
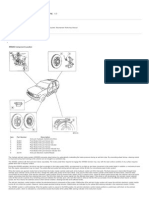
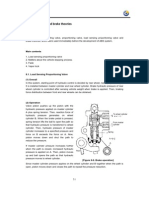
The document is a technical seminar presentation on anti-lock braking systems (ABS). It discusses the components of ABS including wheel speed sensors, electronic control unit, and hydraulic unit. It explains how ABS works by cycling between pressure retention, reduction, and increase phases to prevent wheel lockup during braking. ABS provides advantages like shorter stopping distances, improved stability and steerability during braking. While ABS improves safety, it also increases vehicle costs and is more expensive to repair.
Uploaded by
Kiran Gowda HMCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
158 views15 pagesAnti-Lock Braking System Overview
The document is a technical seminar presentation on anti-lock braking systems (ABS). It discusses the components of ABS including wheel speed sensors, electronic control unit, and hydraulic unit. It explains how ABS works by cycling between pressure retention, reduction, and increase phases to prevent wheel lockup during braking. ABS provides advantages like shorter stopping distances, improved stability and steerability during braking. While ABS improves safety, it also increases vehicle costs and is more expensive to repair.
Uploaded by
Kiran Gowda HMCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd