Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Uploaded by
RENE MARANOCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled
Uploaded by
RENE MARANOCopyright:
Available Formats
Name: Rene D.
Maraño Course, Year & Section: BS CRIM2-G
Instructor: Engr. Ma. Denia A. Cortez Score:
UNIT 6
ASSESSMENTS
Chapter Assessment
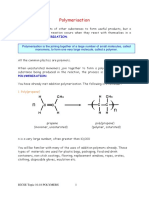
1. How does condensation polymerization differ from addition
polymerization?
Answer:
The main difference between addition and condensation polymerization is
that in addition polymerization the polymers are formed by the addition of
monomers with no by-products whereas in condensation polymerization,
the polymers are formed due to the condensation more than one different
monomer resulting in the formation of small molecules such as HCl, water,
ammonia, etc., as by-products.
2. A self-proclaimed “plastic expert” tells you that recycling HDPE is
difficult because this plastic must be broken down to monomers and
then polymerized again. Do you agree or disagree? Explain.
Answer:
I agree because High Density Poly Ethylene (HDPE) is a thermoplastic
polymer made from petroleum. And one of the most versatile plastic
materials around the world.
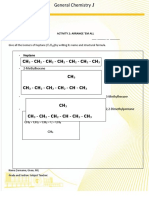
3. Natural rubber is the all-cis polymer of isoprene. Write the structure of
the polymers showing at least five isoprene units.
Answer:
Isoprene is the hemiterpene with the formula CH2 = C(CH3) CH=CH2. It
is the monomer unit of natural rubber. When 3-Isoprene units are joined
together, the structure will be,
Name: Rene D. Maraño Course, Year & Section: BS CRIM2-G
Instructor: Engr. Ma. Denia A. Cortez Score:
Unit 6
Assessment
Unit Assessment
1. What features allow organic molecules to form millions of compounds?
Discuss in terms of the nature of components.
Answer:
Organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain
carbon-hydrogen bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with
other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known.
2. With what groups of organic compounds are each of the biomolecules
related? Show the relationships with specific examples.
Answer:
The four major classes of biological macromolecules are carbohydrates,
lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
Carbohydrates are macromolecules with which most consumers are
somewhat familiar. To lose weight, some individuals adhere to “low-carb”
diets.
Lipids include a diverse group of compounds that are united by a
common feature. Lipids are hydrophobic (“water-fearing”), or insoluble in
water, because they are nonpolar molecules.
Proteins are one of the most abundant organic molecules in living
systems and have the most diverse range of functions of all
macromolecules.
Nucleic acids are key macromolecules in the continuity of life. They carry
the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning
of the cell.
You might also like
- SCH4U Chemistry 12 University Prep Solutions ManualDocument611 pagesSCH4U Chemistry 12 University Prep Solutions Manualkomal sheikh83% (12)
- CH09 EOC QuestionsDocument22 pagesCH09 EOC QuestionsSuresh ShahNo ratings yet
- A. Marakani - FEA and Design of A Plane TrussDocument7 pagesA. Marakani - FEA and Design of A Plane TrussLe Thanh PhanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledRENE MARANONo ratings yet
- Science: Whole Brain Learning SystemDocument20 pagesScience: Whole Brain Learning SystemKayrell AquinoNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Q2 - Week 5-M13-M16Document32 pagesScience 9 - Q2 - Week 5-M13-M16Rhyan Zero-four BaluyutNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY A CREDIT 2 AnswersDocument6 pagesBIOLOGY A CREDIT 2 AnswersAngelina GeorgievskiNo ratings yet
- Polymers NotesDocument10 pagesPolymers NotesThaarvena RetinaNo ratings yet
- Quarter-2 General-Chemistry-1 M12 V2Document20 pagesQuarter-2 General-Chemistry-1 M12 V2Lynette LicsiNo ratings yet
- Quarter-2 General-Chemistry-1 M12 V2Document17 pagesQuarter-2 General-Chemistry-1 M12 V2Raquel LicudineNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1 Quarter 2 Module 6 Colored PDFDocument15 pagesGen Chem 1 Quarter 2 Module 6 Colored PDFAndry Eloise JacaNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Q1 Module 4Document22 pagesPhysical Science Q1 Module 4Alfred RodellasNo ratings yet
- Consumer Chem. Q1 For Week 5 Riza Laxamana Version 3Document15 pagesConsumer Chem. Q1 For Week 5 Riza Laxamana Version 3Ces Michaela Cadivida100% (1)
- Science 10 - Module 35Document10 pagesScience 10 - Module 35Karlyn Kaye SalungaNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Imp Polymers MixDocument6 pages12 Chemistry Imp Polymers MixRahil ShamsiNo ratings yet
- Slideshow-1-How-do-we-make-plastics-Document20 pagesSlideshow-1-How-do-we-make-plastics-18811301255No ratings yet
- Exercise 3: A. Matching Type. Match The Different Types of Plastics Listed in Column A With TheirDocument3 pagesExercise 3: A. Matching Type. Match The Different Types of Plastics Listed in Column A With TheirJaymart ManganagNo ratings yet
- ADVANCED CHEMISTRY Q3 Module Jan 2021 PDFDocument48 pagesADVANCED CHEMISTRY Q3 Module Jan 2021 PDFLouis C. GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BLMs AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 2 BLMs AnswershelloblargNo ratings yet
- SMILE Science 9 Q2W4 5 EditedDocument8 pagesSMILE Science 9 Q2W4 5 EditedRaven Third-partyAccNo ratings yet
- CH 15 ExerciseDocument9 pagesCH 15 ExerciseTr Mazhar PunjabiNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules (Polymers, Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats)Document27 pagesMacromolecules (Polymers, Carbohydrates, Proteins, and Fats)Melva SibaraniNo ratings yet
- Grade-9-Science Q2 Wk4 GLAKDocument16 pagesGrade-9-Science Q2 Wk4 GLAKMorana TuNo ratings yet
- S9 Q2 HYBRID MODULE 4B Week 5 Final PDFDocument17 pagesS9 Q2 HYBRID MODULE 4B Week 5 Final PDFSally CustodioNo ratings yet
- CH CH CH CH CH CH CH: HeptaneDocument5 pagesCH CH CH CH CH CH CH: HeptaneKiana RamosaNo ratings yet
- PolymersDocument33 pagesPolymersNithishNo ratings yet
- Sch4uc Unit 2 Lesson 05Document28 pagesSch4uc Unit 2 Lesson 05Luis David Lazo CondoriNo ratings yet
- Correct AnswerDocument120 pagesCorrect Answerdebaprasad ghosh100% (1)
- How Is Plastic Made A Simple Step-By-Step ExplanationDocument12 pagesHow Is Plastic Made A Simple Step-By-Step Explanationsalemg82No ratings yet
- In ContextDocument4 pagesIn ContextRajlaxmi JainNo ratings yet
- MolBiol HL (2.1, 2.2,2.3.2.4,7.3) BookletDocument37 pagesMolBiol HL (2.1, 2.2,2.3.2.4,7.3) BookletSeo Young YOONNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 General Chemistry 1 m14 v2Document21 pagesQuarter 2 General Chemistry 1 m14 v2Lynette LicsiNo ratings yet
- PE Assignment 19-NTU-TE-0117-1Document16 pagesPE Assignment 19-NTU-TE-0117-1Ahmad ButtNo ratings yet
- Quarter2 Science9 Module5-EDITEDDocument29 pagesQuarter2 Science9 Module5-EDITEDKrystel Mae Pagela OredinaNo ratings yet
- PolimerDocument31 pagesPolimerAlief MoulanaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 PolymersDocument84 pagesModule 4 PolymersSai MedaNo ratings yet
- Review: Step Step From Organic Biochem Istry: Chemistry ToDocument57 pagesReview: Step Step From Organic Biochem Istry: Chemistry ToBarnali DuttaNo ratings yet
- Jose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolDocument8 pagesJose P. Laurel Sr. High SchoolEricha Solomon0% (1)
- Organic and Inorganic Compounds Identification and FunctionsDocument9 pagesOrganic and Inorganic Compounds Identification and FunctionsMark Brian FloresNo ratings yet
- Quarter2 Science9 Module5 EDITED FINALDocument29 pagesQuarter2 Science9 Module5 EDITED FINALAthena LaroyaNo ratings yet
- Quarter2 Science9 Module4-EDITEDDocument22 pagesQuarter2 Science9 Module4-EDITEDKrystel Mae Pagela OredinaNo ratings yet
- 9E Making Materials - Hydrocarbons Extra NotesDocument8 pages9E Making Materials - Hydrocarbons Extra NotessimplydharshiniNo ratings yet
- PBL_Polymer_2021 - Understanding Petroleum-Based and Bio-Based PolymersDocument2 pagesPBL_Polymer_2021 - Understanding Petroleum-Based and Bio-Based PolymersBima SetyaputraNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Q2 - Week 4 - M10-M12Document30 pagesScience 9 - Q2 - Week 4 - M10-M12Rhyan Zero-four Baluyut100% (1)
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 2: BiomoleculesDocument31 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 2: BiomoleculesMerrie Anne Pascual Bagsic75% (4)
- Unit 5-PolymerDocument27 pagesUnit 5-PolymerN x10No ratings yet
- Lecture-1 Summary (Brief Notes)Document5 pagesLecture-1 Summary (Brief Notes)yobroNo ratings yet
- G9 Ste Conchem Q1 WK1Document20 pagesG9 Ste Conchem Q1 WK1Breeza Marie VeralloNo ratings yet
- Consumer Chemistry-Q1 - Module6 - Functional-Groups-Landingin-v3Document15 pagesConsumer Chemistry-Q1 - Module6 - Functional-Groups-Landingin-v3Ces Michaela Cadivida100% (1)
- PolymersDocument22 pagesPolymersDr. Stan Wardel BA, MA, MChem, MBA, DPhil, DSc.No ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument6 pagesBIOMOLECULESzoyaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q2 Mod6 Organic Compounds For StudentsDocument27 pagesScience 9 q2 Mod6 Organic Compounds For Studentsnielle lasquetyNo ratings yet
- OC STR 1 WB - Intro & AlkanesDocument16 pagesOC STR 1 WB - Intro & Alkaneswayne.ilearnacadhkNo ratings yet
- Polymer ScienceDocument6 pagesPolymer ScienceAnonymous wt2BA7uNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Biology 14th Edition Enger Test BankDocument40 pagesConcepts in Biology 14th Edition Enger Test BankChristianBrownmisre100% (18)
- 12.4 Polymers of AlkenesDocument13 pages12.4 Polymers of Alkenesmulya1No ratings yet
- Unit 2Document88 pagesUnit 2pthangarasu sctengNo ratings yet
- A.P. Biology Summer WorksheetDocument10 pagesA.P. Biology Summer WorksheetedeceNo ratings yet
- Revision Lecture Notes Biological Molecules: Chapter No-2Document17 pagesRevision Lecture Notes Biological Molecules: Chapter No-2Ãrêêbã ÅsĦfåqNo ratings yet
- What is Organic Chemistry? Chemistry Book 4th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandWhat is Organic Chemistry? Chemistry Book 4th Grade | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- Miranda Rights & Rights of the AccusedDocument2 pagesMiranda Rights & Rights of the AccusedRENE MARANONo ratings yet
- Midterm Output IN Gee3: (Purposive Communication 2)Document3 pagesMidterm Output IN Gee3: (Purposive Communication 2)RENE MARANONo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper: Significance and Evolution of Personal IdentificationDocument31 pagesLesson Proper: Significance and Evolution of Personal IdentificationRENE MARANONo ratings yet
- Name: Rose Ann O. Sagurot Course, Year & Section: BS CPE 2-A Date: January, 2021 Instructor: Mrs. Mary Cris Yamuyam-Barion Activity No. ScoreDocument2 pagesName: Rose Ann O. Sagurot Course, Year & Section: BS CPE 2-A Date: January, 2021 Instructor: Mrs. Mary Cris Yamuyam-Barion Activity No. ScoreRENE MARANONo ratings yet
- Review Research Skills Chapter Provides OverviewDocument25 pagesReview Research Skills Chapter Provides OverviewRENE MARANONo ratings yet
- UNIT V: Chemical Bonding: at The End of This Unit, You Should Be Able To Answer The Following QuestionsDocument26 pagesUNIT V: Chemical Bonding: at The End of This Unit, You Should Be Able To Answer The Following QuestionsRENE MARANONo ratings yet
- Concept of Moral DilemmasDocument13 pagesConcept of Moral DilemmasRENE MARANONo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Lesson Proper: Introduction To Police Intelligence and Secret ServiceDocument30 pagesLesson 1 Lesson Proper: Introduction To Police Intelligence and Secret ServiceRENE MARANONo ratings yet
- Interview and InterrogationDocument47 pagesInterview and InterrogationRENE MARANONo ratings yet
- Interview and InterrogationDocument11 pagesInterview and InterrogationRENE MARANONo ratings yet
- Kip Thorne Journal Gravitational Collapse Death of StarDocument9 pagesKip Thorne Journal Gravitational Collapse Death of Starpatricius327No ratings yet
- Fourth Year Class: University of Baghdad College of Engineering Department of Civil EngineeringDocument19 pagesFourth Year Class: University of Baghdad College of Engineering Department of Civil Engineeringعبدالله ماجد عامر زغير-B-No ratings yet
- Activity Week 2 March 23 Grade 9Document3 pagesActivity Week 2 March 23 Grade 9LowelaNo ratings yet
- Calculating percentage of oxygen in air after evaporating liquid nitrogenDocument2 pagesCalculating percentage of oxygen in air after evaporating liquid nitrogenlutfi awnNo ratings yet
- The The: On Origin of Cosmic RadiationDocument6 pagesThe The: On Origin of Cosmic RadiationFelipeSilveiraNo ratings yet
- DGMS Circular No7 (1997) - IndiaDocument4 pagesDGMS Circular No7 (1997) - IndiaAntónio Nôro0% (1)
- Heat Transfer: Mechanical EngineeringDocument10 pagesHeat Transfer: Mechanical EngineeringVenkatasairamreddy KandulaNo ratings yet
- Seakeeping and Manoeuvring Prof. Dr. Debabratasen Department of Ocean Engineering and Naval Architecture. Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurDocument23 pagesSeakeeping and Manoeuvring Prof. Dr. Debabratasen Department of Ocean Engineering and Naval Architecture. Indian Institute of Technology, KharagpurkometmayorNo ratings yet
- Hibbeler Dynamics 12th Edition Solutions Chapter 12 Soup IoDocument3 pagesHibbeler Dynamics 12th Edition Solutions Chapter 12 Soup IoAli Doğru33% (3)
- Adverb PPT CO English 4 1 1Document27 pagesAdverb PPT CO English 4 1 1mizel dotillosNo ratings yet
- 9792 s1s3 QP 3Document40 pages9792 s1s3 QP 3Irtiza HussainNo ratings yet
- Bab 4 Hukum-Hukum Gerakan Soalan-Soalan Q5.4 Solution: A 2.00 I 5.00 J M/ SDocument8 pagesBab 4 Hukum-Hukum Gerakan Soalan-Soalan Q5.4 Solution: A 2.00 I 5.00 J M/ SJasdeepSinghNo ratings yet
- Applied Chemistry (UCB008) : - Instructor - Dr. Soumen Basu Associate Professor, School of Chemistry and BiochemistryDocument33 pagesApplied Chemistry (UCB008) : - Instructor - Dr. Soumen Basu Associate Professor, School of Chemistry and BiochemistrySukh SindhiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1Document8 pagesLab Report 1Iv ChenNo ratings yet
- Copper Cyanide ProblemsDocument3 pagesCopper Cyanide ProblemsDavidAlejandroGaonaNo ratings yet
- Guide To ODDocument2 pagesGuide To ODlb_BotsNo ratings yet
- Ads 0125 PDFDocument2 pagesAds 0125 PDFHossam A.MoneimNo ratings yet
- CEN412 Slide2 - Stair and Overhead Water Tank DesignDocument30 pagesCEN412 Slide2 - Stair and Overhead Water Tank DesignEmran Hossain EmonNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Guia InglishDocument10 pagesTrabajo Guia InglishAlejandroDuranNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Design of StructuresDocument36 pagesEarthquake Resistant Design of StructuresghchgNo ratings yet
- Yakan PeopleDocument671 pagesYakan PeopleNorleah MatabalaoNo ratings yet
- Temperature Measuring InstrumentsDocument11 pagesTemperature Measuring InstrumentsBen Aldrian Tariao Ibañez100% (1)
- Arch348 - Term Project-Central Heating SystemDocument17 pagesArch348 - Term Project-Central Heating Systemmert avlarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties of Soil: pH, CEC & PZCDocument17 pagesChemical Properties of Soil: pH, CEC & PZCHasnat QureshiNo ratings yet
- Epoxy-OAT Composites Improve Mechanical PropertiesDocument9 pagesEpoxy-OAT Composites Improve Mechanical PropertiesSanket AntreNo ratings yet
- Mce Full Course StructureDocument88 pagesMce Full Course StructurePantho PanhoNo ratings yet
- Importance of Hybrid Organic Carburizers On The Mechanical Properties of Mild Steel A ReviewDocument11 pagesImportance of Hybrid Organic Carburizers On The Mechanical Properties of Mild Steel A ReviewHema SalamNo ratings yet
- Atlas Copco-Nitrogen Generator IntroduceDocument42 pagesAtlas Copco-Nitrogen Generator IntroduceTân NguyễnNo ratings yet