Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DIFFERENT TYPES OF DEPOSIT PRODUCTS
Uploaded by
Kulgeet TanyaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DIFFERENT TYPES OF DEPOSIT PRODUCTS
Uploaded by
Kulgeet TanyaCopyright:
Available Formats
DIFFERENT TYPES OF DEPOSIT PRODUCTS
1. SAVINGS BANK ACCOUNT: As the name suggests this type of account
is suitable for people who have a definite income and are looking to
save money. Banks gives interest on these accounts with a view to
encourage saving habits. Savings accounts can be opened by
individuals, guardians ( on behalf of their minor children/wards),
Karta of Hindu Undivided Family (HUF), clubs, associations, trusts, etc.
For example, the people who get salaries or the people who work as
laborers. This type of account can be opened with a minimum initial
deposit that varies from bank to bank. Money can be deposited at any
time in this account.
The savings bank accounts are of two types:
a) Cheque book facility accounts – in which withdrawals are
permitted by cheques drawn in favour of self or other parties.
The payees of cheques can receive payment in cash at the
drawee bank branch or through their bank account via clearing
or collection. The account holder may also withdraw cash by
submitting a withdrawal form.
b) Non-cheque book facility accounts - where account holders are
permitted to withdraw only at the drawee bank branch by
submitting a withdrawal form or a letter accompanied with the
account pass book requesting permission for withdrawal. In such
accounts third parties cannot receive payments.
Withdrawals can be made either by signing a withdrawal form or by
issuing a cheque or by using an ATM card. Normally banks put some
restriction on the number of withdrawal from this account. Interest is
allowed on the balance of deposit in the account. The rate of interest
on savings bank account varies from bank to bank and also changes
from time to time. A minimum balance has to be maintained in the
account as prescribed by the bank.
DEPOSIT AT CALL ACCOUNTS: Call deposits or deposit at call accounts
are maintained by banks with other banks. These accounts may or
may not fetch interest, as per the rules framed by RBI or Indian Banks
Association (IBA) from time to time. Call Deposits cannot be made by
individuals/firms/companies etc.
2. CURRENT DEPOSIT ACCOUNT: Current account constitute a large
portion of demand deposits of a bank. Big businessmen, companies,
and institutions such as schools, colleges, and hospitals have to make
payment through their bank accounts. Since there are restrictions on
the number of withdrawals from a savings bank account, that type of
account is not suitable for them. They need to have an account from
which withdrawal can be made any number of times.
Banks open a current account for them. Like a savings bank account,
this account also requires a certain minimum amount of deposit
while opening the account. On this deposit, the bank does not pay
any interest on the balances. Rather the account holder pays a
certain amount each year as an operational charge.
Cheque book facility is provided to each current account holder and
bank undertakes to honour all cheques drawn correctly so long as
there is sufficient balance to the credit of the account. Withdrawals
are permitted by cheques in favour of self and also other parties.
The payees of cheques can endorse the cheques in favour of third
parties who can receive payment in cash at the drawee
bank/branch or through their bank account via clearing or
collection.
Overdraft facility is given for very short period or on a regular basis
up to specified limits - are permitted in current accounts. Regular
Overdraft facility is granted as prior agreement made by the
account holder with the bank. In such cases the bank would honour
cheques drawn in excess of the credit balance but not exceeding the
overdraft limit. Interest is levied by the bank on the overdraft
portion of drawings.
Cheques/bills collection and purchase facilities may also be granted
to the current account holders as per mutually agreed agreements
and charges.
Account holder periodically receives statements of accounts for
reconcillation and record letter from the bank. The statement shows
all the debit and credit transactions and balances, date-wise, as
recorded in the bank’s ledger account of the customer.
INVESTMENTS DEPOSITS
3. FIXED DEPOSIT ACCOUNT: Fixed deposits are repayable on the
maturity date along with interest at an agreed rate for the period. No
operations are allowed to be performed by the customer against the
deposit, as is permitted in demand deposits. This gives freedom and
opportunities to the bank to deploy such funds for loans/advances
and earn interest.
Some bank customers may like to put away money for a longer
time. Such deposits offer a higher interest rate. The reason for
banks paying higher interest on fixed deposits is that the
administrative cost in the maintenance of these accounts is lesser
as compared to savings bank accounts where several
transanctions can take place in cash, transfer or clearing thus
increasing the administrative cost. If money is deposited in a
savings bank account, banks allow a lower rate of interest.
Therefore, money is deposited in a fixed deposit account to earn
interest at a higher rate.
A deposit receipt is issued by the bank branch accepting the fixed
deposit mentioning – the depositor’s name, principal amount,
maturity period and interest rate, date of the deposit and its
maturity etc. The deposit receipt is not a negotiable instrument,
nor is it transferable like a cheque. However, a term deposit
receipt evidences contract for the deposit on the specified terms.
On maturity of a deposit, the principal and the interest can be
renewed for another term at an interest rate prevalent at that
time and a fresh deposit receipt is issued to the customer,
evidencing a fresh contract.
Note: This period of deposit may range from 15 days to three
years or more during which no withdrawal is allowed.
4. RECURRING DEPOSIT ACCOUNT: While opening the account a person
has to agree to deposit a fixed amount once in a month for a certain
period. The total deposit along with the interest therein is payable on
maturity. However, the depositor can also be allowed to close the
account before its maturity and get back the money along with the
interest till that period. These are intended to inculcate regular and
compulsory savings habit among the low/middle income group people
for meeting their specific future needs.
The customer deposits a fixed sum in the account at pre – fixed
frequency (generally monthly/quarterly) for a specific period ( 12
months to 120 months ).
The interest rate payable on recurring deposits is pre – fixed and
is generally lower than the fixed deposit rate for the same period.
The account can be opened by a person individually, or jointly with
another, or by the guardian in the name of a minor. The rate of
interest allowed on the deposits is higher than that on a savings bank
deposit but lower than the rate allowed on a fixed deposit for the
same period.
The Recurring Deposit Accounts may be of the following types:
Home Safe Account or Money Box Scheme
Cumulative-cum-Sickness deposit Account
Home Construction deposit Scheme/Saving Account
5. CASA DEPOSIT ACCOUNT: CASA is the acronym for Current and
Savings account, which is commonly used in the banking industry
across West Asia and South-East Asia. Banks usually receive the
majority of their funds from various kinds of deposit schemes like
current accounts, Savings Accounts and term deposits.
CASA deposit is the amount of money that gets deposited in the
Current and Savings Accounts of bank customers. The bank pays very
low or no interest for deposits in current accounts whereas the
deposits in Savings Accounts receives slightly higher interest rates. It is
the cheapest and major source of funds for banks. This fund source is
in turn used to distribute Home Loans, Personal Loans etc.
6. RE-INVESTMENT DEPOSIT ACCOUNT: This is special term deposits.
This plan helps you to earn interest on interest, thus giving you a two-
fold income. You deposit your money with us for any period
between six months to 10 years, and we pay you interest on your
deposited money plus on the interest you earn.
7. HYBRID DEPOSITS OR FLEXI DEPOSITS: These deposits are the
combination of demand and fixed deposits, invented for meeting
customer’s financial needs in a flexible manner. The new private
sector and foreign banks had introduced this new deposit product
some year ago to attract bulk deposits from individuals with high net
worth. Banks have given their own brand names to such deposits e.g.
Quantum Deposit Scheme of ICICI Bank, Multi Option Deposit Scheme
(MODS) of SBI.
Only one savings/current account is opened and the term
deposits issued under the scheme are recorded only on the
bank’s books as no term deposit receipts are issued to the
customer. However, the term deposits issuance and payment
particulars would be reflected in the statement of the
savings/current account for customer’s information/record.
Once the quantum of deposits in savings/current account
crossed a pre-agreed level, such surplus amount is
automatically transferred to the term deposit account of a pre-
determined maturity (usually one year) in the customer’s name
for increasing the interest earning.
In the event of a shortfall in the current/savings account, the
cheques drawn on the account are honoured by automatically
transferring back the required amount to the savings/current
account from the fixed deposit account (reverse sweep). In such
a case, the term deposit is broken and the amount of the
reverse sweep earns lower interest rate due to the pre-mature
payment of that portion of the term deposit. However, the
remainder amount of the term deposit continues to earn the
original interest rate.
Thus the main advantages of the flexi-deposits to a customer are:
Advantage of convenience: The customer opens only one
account (savings or current) under the scheme and need not
come to bank/branch each time for opening term deposit
accounts or for pre-paying/breaking term deposit for meeting
the shortfall in the savings/current account.
Advantage of higher interest earnings: The customer earns
higher interest on his surplus funds than is possible when he
opens two separate accounts – savings and term deposits.
You might also like
- DEMAND DEPOSITS: These Are The Deposit Accounts From WhichDocument3 pagesDEMAND DEPOSITS: These Are The Deposit Accounts From WhichShubhanjaliNo ratings yet
- Types of Bank Deposits ExplainedDocument4 pagesTypes of Bank Deposits ExplainedJhanvi KankaliyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9 Opening and Operating Bank AccountsDocument12 pagesChapter - 9 Opening and Operating Bank AccountsMd Mohsin AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Types of Bank Accounts-3-1Document36 pagesChapter 2 Types of Bank Accounts-3-1hncd6h2zyqNo ratings yet
- What Is A Bank AccountDocument6 pagesWhat Is A Bank AccountJan Sheer ShahNo ratings yet
- 2-Notes On Banking Products & Services-Part 1Document16 pages2-Notes On Banking Products & Services-Part 1Kirti GiyamalaniNo ratings yet
- Types of Bank DepositeDocument4 pagesTypes of Bank DepositeShailendrasingh DikitNo ratings yet
- Types of AccountDocument5 pagesTypes of AccountAkbari NamatullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 EditedDocument10 pagesChapter 5 EditedSeid KassawNo ratings yet
- A Bank Account Is A Financial Account Maintained by A Bank For A CustomerDocument2 pagesA Bank Account Is A Financial Account Maintained by A Bank For A CustomerArjab SinhaNo ratings yet
- US Bank Account Types and Features in 40 CharactersDocument7 pagesUS Bank Account Types and Features in 40 CharactersAbhilash RjNo ratings yet
- Types of Banks in PakistanDocument4 pagesTypes of Banks in PakistanMujahid IbrahimiNo ratings yet
- Banking Practice and Procedure Chapter TwoDocument27 pagesBanking Practice and Procedure Chapter TwoDEREJENo ratings yet
- Banking Law and PracticeDocument25 pagesBanking Law and PracticePRASHANT REVANKARNo ratings yet
- Presentation of B&i (1) - 1Document23 pagesPresentation of B&i (1) - 1Manish ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Bank Deposit Schemes: Types of Deposit AccountsDocument3 pagesProject Report On Bank Deposit Schemes: Types of Deposit AccountsAmit SinghNo ratings yet
- Banking ServicesDocument11 pagesBanking ServicesbeautykimberlyNo ratings yet
- Q.1 Define A Banker.: Fixed Deposit Account: Fixed Deposit Account Is Also Known As Time DepositDocument3 pagesQ.1 Define A Banker.: Fixed Deposit Account: Fixed Deposit Account Is Also Known As Time DepositYeezy YeezyNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument14 pagesDownloadashadabral.bjpNo ratings yet
- Banking Principle,,,Ch - 2Document11 pagesBanking Principle,,,Ch - 2Mubarik AhmedinNo ratings yet
- The Functions of BanksDocument6 pagesThe Functions of BanksMa Laney0% (1)
- 03 Sources of Funds PDFDocument12 pages03 Sources of Funds PDFSuraj SurajNo ratings yet
- Customer AccountsDocument32 pagesCustomer AccountsJitendra VirahyasNo ratings yet
- Fixed DepositDocument37 pagesFixed DepositMinal DalviNo ratings yet
- Customers and Account Holders: Types of Deposit Accounts: 1. Demand DepositDocument21 pagesCustomers and Account Holders: Types of Deposit Accounts: 1. Demand DepositMegha MurthyNo ratings yet
- IAPM AssignmentDocument8 pagesIAPM AssignmentgusheenaroraNo ratings yet
- Assignment Banking 3Document9 pagesAssignment Banking 3Al RafiNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction To BankingDocument8 pages1 Introduction To BankingGurnihalNo ratings yet
- BankingDocument14 pagesBankingFahmi AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Various Investment Avenues in IndiaDocument74 pagesVarious Investment Avenues in IndiaRakeshNo ratings yet
- Bank Deposit Types and Withdrawal RulesDocument7 pagesBank Deposit Types and Withdrawal RulesNandhini VirgoNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Deposit PolicyDocument13 pagesComprehensive Deposit PolicyShakirkapraNo ratings yet
- Types of DepOSIT 15-18-21-22Document94 pagesTypes of DepOSIT 15-18-21-22Saurab JainNo ratings yet
- Types of Bank Accounts in IndiaDocument4 pagesTypes of Bank Accounts in Indiagaurav069No ratings yet
- Policy On Bank Deposits: PreambleDocument6 pagesPolicy On Bank Deposits: PreambleLukumoni GogoiNo ratings yet
- Primary Functions Accepting Deposits - Accepting Deposits Is The Most Important Function of A Commercial BankDocument2 pagesPrimary Functions Accepting Deposits - Accepting Deposits Is The Most Important Function of A Commercial BankRegine VegaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - FIN 545Document7 pagesAssignment 2 - FIN 545tuna100% (3)
- Unit 4: Ethiopian Bank'S Loans and Advances ProceduresDocument37 pagesUnit 4: Ethiopian Bank'S Loans and Advances Proceduresመስቀል ኃይላችን ነውNo ratings yet
- Types of Bank Accounts Explained: Savings, Current, Fixed Deposit & MoreDocument1 pageTypes of Bank Accounts Explained: Savings, Current, Fixed Deposit & MoreDoorga SatpathyNo ratings yet
- Functions of BanksDocument3 pagesFunctions of BanksEbne FahadNo ratings yet
- Credit Management: MBA Banking & Finance 3rd TermDocument17 pagesCredit Management: MBA Banking & Finance 3rd Term✬ SHANZA MALIK ✬No ratings yet
- Bank DepositDocument8 pagesBank DepositHarmin ViraNo ratings yet
- Payment N Settlem, EntDocument17 pagesPayment N Settlem, EntNandini JaganNo ratings yet
- Credit Management: MBA Banking & Finance 3rd TermDocument17 pagesCredit Management: MBA Banking & Finance 3rd Term✬ SHANZA MALIK ✬No ratings yet
- Importance of Deposit, Shariah Principles - Mudaraba, Al-WadiahDocument12 pagesImportance of Deposit, Shariah Principles - Mudaraba, Al-WadiahKhan Kamranur Rahman ShovonNo ratings yet
- Important Functions of Bank: What Is A Bank?Document3 pagesImportant Functions of Bank: What Is A Bank?Samiksha PawarNo ratings yet
- 5 & 6types of AccountsDocument64 pages5 & 6types of AccountsNiharika SinghNo ratings yet
- Customers and Account HoldersDocument23 pagesCustomers and Account HoldersMAHESH VNo ratings yet
- Retail Banking: Vivek Saxena Asst. Prof. LSB, LPU Reference: Introduction To Banking by Vijayaragvan IyengarDocument16 pagesRetail Banking: Vivek Saxena Asst. Prof. LSB, LPU Reference: Introduction To Banking by Vijayaragvan IyengarninalakhotraNo ratings yet
- What Is BankDocument19 pagesWhat Is BankSunayana BasuNo ratings yet
- Bank Reserves and Bank DepositsDocument2 pagesBank Reserves and Bank DepositsH-Sam PatoliNo ratings yet
- Banking Products Assignment FINAL 2Document19 pagesBanking Products Assignment FINAL 2satyabhagatNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document57 pagesModule 2Tejaswini TejuNo ratings yet
- Opening of AccountsDocument6 pagesOpening of AccountswubeNo ratings yet
- Types of Bank Accounts in IndiaDocument3 pagesTypes of Bank Accounts in IndiaVasudev GovindanNo ratings yet
- CCBSDocument27 pagesCCBSNarender SinghNo ratings yet
- SIB's Policy On Bank Deposits: PreambleDocument8 pagesSIB's Policy On Bank Deposits: PreamblenithiananthiNo ratings yet
- Personal CheckDocument3 pagesPersonal CheckXjlan AhmedNo ratings yet
- KULGEETDocument5 pagesKULGEETKulgeet TanyaNo ratings yet
- Hi This Is KulgeetDocument1 pageHi This Is KulgeetKulgeet TanyaNo ratings yet
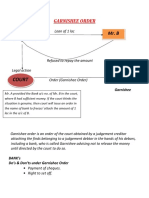
- Mr. A Mr. B: CourtDocument2 pagesMr. A Mr. B: CourtKulgeet TanyaNo ratings yet
- NullDocument9 pagesNullKulgeet TanyaNo ratings yet
- Fund Structure & Legal EnvironmentDocument32 pagesFund Structure & Legal EnvironmentKulgeet TanyaNo ratings yet
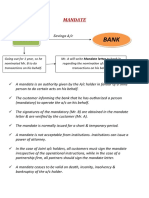
- MandateDocument2 pagesMandateKulgeet TanyaNo ratings yet
- Services Rendered by Banks.: Advancing of LoansDocument3 pagesServices Rendered by Banks.: Advancing of LoansKulgeet TanyaNo ratings yet
- Off-Balance Sheet BusinessDocument3 pagesOff-Balance Sheet BusinessKulgeet TanyaNo ratings yet
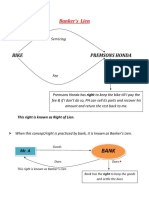
- Bike Premsons Honda: Banker's LienDocument2 pagesBike Premsons Honda: Banker's LienKulgeet TanyaNo ratings yet
- Accounting: NO Judul PengarangDocument14 pagesAccounting: NO Judul Pengarangkartini11No ratings yet
- FIN341 Excel Demo - Chapter 11Document23 pagesFIN341 Excel Demo - Chapter 11mai tharatharnNo ratings yet
- CALCUL STOCHASTIQUE ET FINANCEDocument293 pagesCALCUL STOCHASTIQUE ET FINANCEVictor VermèsNo ratings yet
- Ocbc XXDocument3 pagesOcbc XXLu Xiyun50% (2)
- Chapter 4 Measuring Financial PerformanceDocument4 pagesChapter 4 Measuring Financial Performanceabdiqani abdulaahi100% (1)
- Graham & Doddsville - Issue 20 - Winter 2014Document68 pagesGraham & Doddsville - Issue 20 - Winter 2014Tannor PilatzkeNo ratings yet
- Currency Derivatives Beginners ModuleDocument64 pagesCurrency Derivatives Beginners ModuleRam Kumar50% (2)
- Fxtradermagazine 1 EgDocument61 pagesFxtradermagazine 1 EgDoncov EngenyNo ratings yet
- Haskayne Resume Template 1Document1 pageHaskayne Resume Template 1Mako SmithNo ratings yet
- CalypsoTraining PDFDocument399 pagesCalypsoTraining PDFanubhav92% (13)
- International Financial Management 1Document7 pagesInternational Financial Management 1Kundan KarnNo ratings yet
- Rahul Singh 119Document13 pagesRahul Singh 119Jerry SinghNo ratings yet
- Impairment of financial assets under PFRS 9Document2 pagesImpairment of financial assets under PFRS 9Kendrew SujideNo ratings yet
- MID-TERM REVIEW TIPS AND PRACTICEDocument29 pagesMID-TERM REVIEW TIPS AND PRACTICEChou mỡNo ratings yet
- Study of Derivatives Market in IndiaDocument72 pagesStudy of Derivatives Market in IndiaDastha GiriNo ratings yet
- Hanzon ShadowcodesDocument82 pagesHanzon Shadowcodesback pain91% (141)
- BUSINESS FINANC Module 6Document3 pagesBUSINESS FINANC Module 6PepotVicenteNo ratings yet
- Business Research Method: DR Rajeshwari PatilDocument42 pagesBusiness Research Method: DR Rajeshwari Patilsakshi raiNo ratings yet
- HeikinAshi CandleStick Formulae For MetaStockDocument5 pagesHeikinAshi CandleStick Formulae For MetaStockKhaled Hammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Capital StructureDocument11 pagesCapital StructureSathya Bharathi100% (1)
- Momentum Picks New RecommendationsDocument25 pagesMomentum Picks New RecommendationstanmaygoonNo ratings yet
- Real Estate Portfolio Valuation Model v3.4Document11 pagesReal Estate Portfolio Valuation Model v3.4daniellehynes69No ratings yet
- Business Plan Template For AfterSchool ProgramsDocument6 pagesBusiness Plan Template For AfterSchool Programsshelana BarzeyNo ratings yet
- Trade Your Way 0329Document5 pagesTrade Your Way 0329randyNo ratings yet
- Valuation and Rates of Return: Foundations of Financial ManagementDocument42 pagesValuation and Rates of Return: Foundations of Financial ManagementBlack UnicornNo ratings yet
- Abeeb's ProjectDocument92 pagesAbeeb's ProjectOlu SamNo ratings yet
- 201510240338443i Group S Private Equity Investment in China S Little Sheep 1Document8 pages201510240338443i Group S Private Equity Investment in China S Little Sheep 1Shubham YadavNo ratings yet
- CF WACC, WC NewDocument5 pagesCF WACC, WC NewSanjana PottipallyNo ratings yet
- Financial Statements AnalysisDocument8 pagesFinancial Statements AnalysisyukiNo ratings yet
- Advance Financial ManagementDocument62 pagesAdvance Financial ManagementKaneNo ratings yet