Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Costing: B.SC. (H&HA) & 6th Semester March 17, 2020 Page 1 of 7
Uploaded by
Saransh SachdevaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Costing: B.SC. (H&HA) & 6th Semester March 17, 2020 Page 1 of 7
Uploaded by
Saransh SachdevaCopyright:
Available Formats
FOOD AND BEVERAGE MANAGEMENT
UNIT -1 COST DYNAMICS
COSTING
COST: - Costs are expenses the company has to pay during the production of its product.
TYPES OF COST:- There are 3 main types of costs, these are:
1. Fixed cost:- Costs that don't change over a period of time and don't vary with output.
E.g.:- Salaries, Rent, Tax, Insurance, Heating and Lighting. Fixed costs can also be called
indirect costs as they are not directly associated with the final product. Fixed costs have to be
paid even if the company is not producing any goods.
2. Variable costs:- Costs that vary directly with output so when output increases,
variable costs also increase. E.g. raw materials, electricity. Variable costs can also be
called direct costs as they are directly associated with production.
3. Semi-variable costs:- These costs have fixed and variable elements. E.g. a person
working for the company may have a fixed salary but may also earn commission on
sales.
Total costs are calculated by adding together fixed, variable and semi-variable costs.
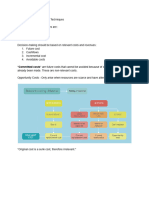
ELEMENTS OF COST: - We can divide total cost in following main elements of costs:
1. Direct Cost:-It is that element of cost in which we can include the cost of direct material
and direct labor. If we take its total, it will be prime cost.
a) Direct Material Cost :- Direct material is that material which we find in finished product
and easily measures its cost. For example, for making furniture, woods are direct material and
its cost will be the part of direct cost.
b) Direct Labour Cost:- Direct labour is used for producing the product. We pay wages for
making product to labourers and this cost will be the direct labour cost.
c) Direct Expenses Cost:- Except direct material and direct labour, all direct expenses will
be direct expenses cost.
2. Indirect Cost
1. Overheads :- When we cannot charge an expense directly on the product, we can say
it is indirect expense or overhead. In overhead, we can include indirect material cost,
indirect labour cost and other following indirect expenses.
i) Manufacturing overheads
ii) Administrative overheads
B.SC. (H&HA) & 6thd SEMESTER March 17, 2020
Page 1 of 7 BHM 305 , cost Dynamics
FOOD AND BEVERAGE MANAGEMENT
UNIT -1 COST DYNAMICS
iii) Selling overheads
iv) Research and development cost
Factory rent and rates, insurance of plants or telephone bill are the main examples of
overheads.
Factors Affecting the Percentage Of Food Costs
There are end numbers of factors that affects the percentage of efficiencies.
These are:-
a) Food Purchasing:- As a matter of fact the control starts from this first activity.
Skillful buying is quite an art and the proper discharge from this function may results
in considerable cost control. The following points in purchasing helps in reducing
costs. These are:-
Buy the right amount of stock
Determine the realistic stock level
Buy according to the standard purchase specification
b) Menu Planning: - It is most important step in controlling the food cost. This is
recognized by the progressive categories. A careless menu planning results in undue
wastage of resources hence is responsible for excessive. Most of caterers think that
offering a variety of food and adding more items of list will increase their reputation
market. But at the same time it increases the food cost which is not a healthier item. If
the number of items is more, the customers get confused. Sometimes the lack of
skilled labor. Lack of proper equipment’s.
c) Method Of Pricing:- a haphazard price of pricing will eventually results in a
financial disasters. The price should be realistic and must be based on facts. To keep
the desired rates each item of menu must be carefully considered in terms of its cost
and in relation to the selling cost. The market forces must determine the selling price.
Hence one of the responsibilities in any food service is an art full working. To keep
the desired weights each item of the menu.
d) Culinary Skills:- cooking skills affects the ultimate cost of food in any
establishments. Badly cooked food is a complete write off. Food preparation loses due
to unskilled labor; lack of proper equipment’s, heat is not properly carried out,
careless control of temperature. Normally high temperature causes the shrinkage of
food items and hence reduces in yield.
e) Service Skills
B.SC. (H&HA) & 6thd SEMESTER March 17, 2020
Page 2 of 7 BHM 305 , cost Dynamics
FOOD AND BEVERAGE MANAGEMENT
UNIT -1 COST DYNAMICS
f) Portion control
g) Careful order taker
h) Avoiding Wastage:- this particular activity starts with the receiving of food. All the
procedure for avoiding wastage is observed at each level i.e. in the store, during
transportation, from the store to kitchen, during preparation of food items and during
service.
Food Cost Control:- It can be define as guidance and regulation of cost of operation.
Undertaking to guide and regulate cost needs to ensure that they are in accordance of the
predetermined objectives of the business. Hence the guidance and regulation of costs are set
as per expressed in the policy statement and budget of undertakings.
Food costs controls mean that
a) You have to stick to your predetermined standards.
b) You exercise restrains or direction over the price you paid, buy, prepare and sell
goods.
c) You have your market as each food operation cater to a specific market. Standards
vary from different markets.
d) You set standards appropriate to your market before you buy, prepare and sell goods.
e) You prepare cost control procedures.
Objectives of Cost Control:-
a) To Analyze Income And Expenditure:- In financial accounts stress is usually
placed on the ascertainments of total costs and profits i.e. cost of sales, gross profit. In
food control on the other hand must stress is placed on various departments or a
section of a business.
Gross profit=sales –food cost
Net profit=sales- (food cost +labor cost+ overheads)
b) Pricing of food: - Another major objective of food cost control is to provide a sound
basis for menu pricing. It will also help in costing price for various types of banquets
and functions. It also helps in giving quotations.
B.SC. (H&HA) & 6thd SEMESTER March 17, 2020
Page 3 of 7 BHM 305 , cost Dynamics
FOOD AND BEVERAGE MANAGEMENT
UNIT -1 COST DYNAMICS
Sale=food cost + labour cost + overheads + Profits
(30%) (10%) (10%) (50%)
c) Prevention of inefficiencies: - We know that purpose of control is to ensure the
current results are in accordance with the predetermined objectives which were
expressed in terms of targets, costs, selling and profit margins. If such objectives are
to be reached all possible forms of wastage and inefficiencies should be prevented. In
order to be effective in preventing wastage inefficiencies, a system of food cost
control; must cover the whole field of catering operations right from the purchase of
food stuff to the sale of food material. The system of food cost control has an
important function to fulfill in providing of data for individual reports on food
operations.
Phase of Control Procedure
The control procedure consists of 3 broad phases.
1. Planning:- First of all the basic policies have to be defined. Policies are nothing but
predetermined guidelines lay down by the management of the organization. It outlines
such matters as the market that is being aimed at, how it is to be catered at the level of
profitability, which is to be achieved. The policy should be clearly defined before the
business is commenced. It can be charged but whenever a major change take place a
new policy should be written down. Three basic policies which need to be considered
are:-
Financial: - it will determine profitability and the contribution to the total profit.
Setting of the target that has to be achieved, the financial policy is prepared for each
single unit as well as for the whole organization. A budget is prepared at the
beginning of the year for the whole organization.
Marketing Policy: - it will identify the broad market that has to be served. It will also
identify the immediate and future consumer’s requirement in order to maintain the
broad market. A large city hotel could be broken down into a segment of various
types of users i.e. in a coffee shop, Chinese restaurant, Indian restaurants etc. each
unit having a specific customers. Marketing policy also defines customer, market
share, turnover, profitability, average spending power of customer, product and
customer satisfaction.
Catering Policy:- it is normally evolved from the marketing and financial policy. It
will also define the many objectives of operating F & B facilities and will also
B.SC. (H&HA) & 6thd SEMESTER March 17, 2020
Page 4 of 7 BHM 305 , cost Dynamics
FOOD AND BEVERAGE MANAGEMENT
UNIT -1 COST DYNAMICS
describe the method by which the objectives are to be achieved. It will usually include
the following;
The type of customer
The type of menu
Beverage provision necessary for operations
Food quality standard
Method of pricing
Type and quality of service
Degree of décor and comfort
Type and style of table & chairs.
2. Operational: - After defining the policies , it is important to outline that how they are
to be interpreted onto the day control activities of the catering operation. The
operational control consists of:-
Purchasing
Receiving
Storing
Issuing
Production control
3. Control of events: - It consists of 3 stages.
1. F & B Cost Reporting: - the cycle of production is often is perishable so it is
compulsory to update your F & B cost reporting weekly or monthly.
Assessment: - in case of a large unit it is necessary that someone from the f & b department
analyses the f & b reports and confirm them with the budget & with potential food cost.
Correction: - control system does not cure or prevent problems occurring when the analysis
of a performance of a department states that there is a problem. A corrective measure has to
be taken to set aside any problems.
2. Calculation of Food Cost: - there are several basic terms, which are used in the
calculation of the food cost.
Food cost- This refers to the cost of food incurred in preparing meals served.
Gross profit: - The excess of sales over the cost of the food expressed as a percentage.
Potential food cost: - The food cost under perfect conditions.
B.SC. (H&HA) & 6thd SEMESTER March 17, 2020
Page 5 of 7 BHM 305 , cost Dynamics
FOOD AND BEVERAGE MANAGEMENT
UNIT -1 COST DYNAMICS
3. Methods of food control:- Daily food cost report:- this system is used by big or
medium organization where managers control each activity as daily routine. It is a
reconciliation report of daily activities.
Monthly or weekly food cost report:- it is used by small organization where
everything is control by the owner of the or the manager of the hotel.
Food cost is calculated in two ways. These are:-
Recipe based costing:- This refers to the costing in which the recipe is pre- decided
and the manager is responsible for the controlling the cost or wastage .The total
numbers of items sales by the outlet is recorded and it is later subtract from the total
amount of purchase of received from the store. The price of each ingredient is pre
decided by the management and for the entire year it will remain same. It is calculate
in such manner. E.G.
Dal Makhni (1 portion)
Sr. no Ingredient name Quantity rate Amount (Rs.) Paisa
1 Bengal gram 50gms 50/kg 2 50
2 Ghee/oil 100gm 100/kg 10
3 Rajma 20gm 80/kg 1 60
4 Onion 50 gms 50/kg 2 50
5 Tomato 50 gms 40/kg 2 40
6 Salt 5 gm 10/kg 00 50
7 Peper 10gm 80/kg 00 80
8 Coriander 5 gm 10 bunch/100gm 00 50
Total cost 20 80
Indenting based costing:-this refers to the costing in which the total net sale is
divided by the total amount of purchase issued from the store in a day. However this
costing is not used in big hotels as each outlet or department can’t find the real
percentage of costing, but it is best for small hotels which has 1or 2 outlets.
Proof of inventory:-
Opening stock+ Purchase- Requisitions= closing stock
Advantage
It is simple and easy to follow.
It gives the day to day information about business.
B.SC. (H&HA) & 6thd SEMESTER March 17, 2020
Page 6 of 7 BHM 305 , cost Dynamics
FOOD AND BEVERAGE MANAGEMENT
UNIT -1 COST DYNAMICS
It records the daily stock level, daily purchase, daily requisition and food cost
percentage.
Problem occurs while controlling the food and beverage:-
The perishability life of products:-food whether raw or cooked, is a perishable commodity
and has a certain life. The caterer therefore has to ensure that he buys product in right
quantity and quality in relation to estimated
Costing:- It is simply the process of arithmetic, means of memorandum statements or the
methods of integral control. Costing is the technique and process of ascertaining costs. In
hotel industry different types of costing is calculated, these can be:-
1. Batch costing 2. Food costing
3. Beverage costing 4. Labor costing
5. Material costing 6. Operational costing
And so on.
Purpose of Cost Control:-
a) To know the cost of products and services.
b) To fix the selling price
c) Cost controlling
d) Preparation of profit and loss account
e) To Generate the Operating policies
Advantages of Costing:-
a) Cost control
b) Helps in making profit
c) Closing stocks
d) Financial statements
e) Effective costing system
f) In hotel industry two costs are very important. First is food cost (also refers to
material cost) & second is Labour cost. So it is necessary to understand how these
affect the entire system of hospitality industry and how it can control.
B.SC. (H&HA) & 6thd SEMESTER March 17, 2020
Page 7 of 7 BHM 305 , cost Dynamics
You might also like
- Food Cost ControlDocument4 pagesFood Cost Controldaringchennai100% (12)
- 2.food and Beverage MGT 2020 JuneDocument127 pages2.food and Beverage MGT 2020 JuneanshNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting, Job Costing & Batch CostingDocument10 pagesCost Accounting, Job Costing & Batch Costing✬ SHANZA MALIK ✬No ratings yet
- Digital Analytics For Marketing by Marshall Full TextbookDocument416 pagesDigital Analytics For Marketing by Marshall Full TextbookCathy Lorimer100% (4)
- Basic Concepts - Cost AccountingDocument28 pagesBasic Concepts - Cost AccountingSunil Vadhva100% (1)
- How To Work With OTAsDocument35 pagesHow To Work With OTAsSushil GhimireNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Cost AccountingDocument55 pagesUnit - I Cost AccountingRigved PrasadNo ratings yet
- Competitive Strategy Creating Competitive AdvantageDocument45 pagesCompetitive Strategy Creating Competitive AdvantageRaghuveer Reddy AnnamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29 Food Cost ControlDocument11 pagesChapter 29 Food Cost Controloutmane4No ratings yet
- Intro To Cost Control in FNBDocument47 pagesIntro To Cost Control in FNBBilly Joe VillenaNo ratings yet
- Branding Color PDFDocument35 pagesBranding Color PDFFlorinNo ratings yet
- Theory Problems Of: Cost AccountingDocument83 pagesTheory Problems Of: Cost AccountingDipak Mahalik100% (2)
- Tools and Techniques of Cost ReductionDocument27 pagesTools and Techniques of Cost Reductionপ্রিয়াঙ্কুর ধর100% (2)
- Cost AccountingDocument25 pagesCost Accountingmahendrabpatel100% (1)
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageFrom EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Costing in BriefDocument47 pagesCosting in BriefRezaul Karim TutulNo ratings yet
- Food& Beverage ManagementDocument14 pagesFood& Beverage ManagementMudassir Ahsan Ansari100% (1)
- Skills Framework HULDocument29 pagesSkills Framework HULMinardizaks100% (1)
- 272 Food Cost ControlDocument8 pages272 Food Cost ControlProbaron BaruahNo ratings yet
- 987 Food Cost ControlDocument8 pages987 Food Cost Controlalapanbanerjee132No ratings yet
- Introduction To Food Cost ControlDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Food Cost ControldarshNo ratings yet
- F&B Management ComoletDocument31 pagesF&B Management ComoletMudassir Ahsan AnsariNo ratings yet
- P 2Document444 pagesP 2Denis FernandesNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Topic 1 Overview of Cost - Part1Document10 pagesUnit 1 Topic 1 Overview of Cost - Part1Crystel Joyce UltuNo ratings yet
- ACC 321 Final Exam ReviewDocument6 pagesACC 321 Final Exam ReviewLauren KlaassenNo ratings yet
- Economic Analysis Policy - IDocument30 pagesEconomic Analysis Policy - IThaddeus De MenezesNo ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument26 pagesCost AccountingdivinamariageorgeNo ratings yet
- Text 2Document4 pagesText 2Leesan Ul NabiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Food CostingDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Food CostingSunil YogiNo ratings yet
- Unit Number/ Heading Learning OutcomesDocument21 pagesUnit Number/ Heading Learning OutcomesAna Marie AllamNo ratings yet
- BHMCT Sem Vii Spl. F B Mgt. II Ceb 702 Chapter 4Document19 pagesBHMCT Sem Vii Spl. F B Mgt. II Ceb 702 Chapter 4አልዓዛር መላኩNo ratings yet
- Aae601 CT2Document20 pagesAae601 CT2Shreya KumariNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Cost ControlDocument52 pagesObjectives of Cost Controlhailu tadeleNo ratings yet
- The Factors Influencing The Product Pricing DecisionsDocument2 pagesThe Factors Influencing The Product Pricing DecisionsthaluNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To Cost AccountingDocument4 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Cost AccountingRizeth Ahne Marie GarayNo ratings yet
- FBM Lesson 07Document8 pagesFBM Lesson 07lakshay kapurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document47 pagesChapter 2dawsonNo ratings yet
- Objectives of Cost AccountingDocument2 pagesObjectives of Cost AccountingPatrice ScottNo ratings yet
- Cost & Management Accounting Dec 2020Document10 pagesCost & Management Accounting Dec 2020Shivam mishraNo ratings yet
- Acc 3200 MidtermDocument5 pagesAcc 3200 MidtermCici ZhouNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document45 pagesCH 5reader100% (1)
- UGB253 Management Accounting Business FinalDocument15 pagesUGB253 Management Accounting Business FinalMohamed AzmalNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Chapter 1: Introduction To Cost AccountingDocument4 pagesCost Accounting Chapter 1: Introduction To Cost AccountingSinclair Faith GalarioNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 BUSI 3008Document21 pagesAssignment 1 BUSI 3008Irena MatuteNo ratings yet
- New Management Accounting-1Document264 pagesNew Management Accounting-1leaky100% (1)
- MCODocument11 pagesMCOsubhaa DasNo ratings yet
- Marginal Costing PDFDocument26 pagesMarginal Costing PDFMasumiNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting: Information For Decision Making: Learning ObjectivesDocument11 pagesCost Accounting: Information For Decision Making: Learning ObjectivesJohn OpeñaNo ratings yet
- Costs in Management AccountingDocument21 pagesCosts in Management AccountingRODOLFO AUSTRIA JR.No ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Food Cost ControlDocument9 pagesChapter-1 Food Cost ControlJaved Mokashi100% (1)
- Cost AccountingDocument9 pagesCost Accountingyaqoob008No ratings yet
- Ca - Ii CH-5Document5 pagesCa - Ii CH-5Moti BekeleNo ratings yet
- Section B, C AND E NotesDocument29 pagesSection B, C AND E NotesCorrinaNo ratings yet
- Absorption Costing MethodDocument29 pagesAbsorption Costing MethodnaimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cost AccountingDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Cost Accountingiraleigh17No ratings yet
- Cost AccountingDocument12 pagesCost AccountingMeenakshi SeerviNo ratings yet
- Variance AnalysisDocument5 pagesVariance AnalysisTonie NascentNo ratings yet
- Stragetic Cost ManagementDocument6 pagesStragetic Cost ManagementLavina AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity 1-1 - INTRODUCTION TO COST ACCOUNTING, SCOPE, AND OBJECTIVES OF COST ACCOUNTINGDocument6 pagesLearning Activity 1-1 - INTRODUCTION TO COST ACCOUNTING, SCOPE, AND OBJECTIVES OF COST ACCOUNTINGRegina PhalangeNo ratings yet
- Cost NotesDocument16 pagesCost NotesKomal GowdaNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Business II PM Xii Chapter1Document27 pagesAccounting For Business II PM Xii Chapter1Anusga RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Business II PM Xii Chapter1Document27 pagesAccounting For Business II PM Xii Chapter1Senthil S. VelNo ratings yet
- Management Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesFrom EverandManagement Accounting Strategy Study Resource for CIMA Students: CIMA Study ResourcesNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Ismail IndustriesDocument29 pagesMarketing Management Ismail Industriesmehwishali72100% (6)
- The Demand Curve Facing A Competitive Firm The ...Document3 pagesThe Demand Curve Facing A Competitive Firm The ...BLESSEDNo ratings yet
- Weekly Sales Report and INdividual Progress Report FINAL GRADINGDocument2 pagesWeekly Sales Report and INdividual Progress Report FINAL GRADINGJupiter WhitesideNo ratings yet
- Quantitative ResearchDocument56 pagesQuantitative ResearchMaksen LimNo ratings yet
- A Report On "Summer Internship" at M&B Footwear (P) Ltd. A Project Report OnDocument79 pagesA Report On "Summer Internship" at M&B Footwear (P) Ltd. A Project Report OnNeha NigamNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - ASDocument46 pagesCH 4 - ASWilly JudovitchNo ratings yet
- 1510327-Fatema Binte Hussain Afsha-Final-case StudyDocument3 pages1510327-Fatema Binte Hussain Afsha-Final-case StudyAfsha HussainNo ratings yet
- JM holistik,+RIVAI+JournalDocument18 pagesJM holistik,+RIVAI+Journalsawit borneoNo ratings yet
- CV Pawel KontekDocument2 pagesCV Pawel KontekEmily RamirezNo ratings yet
- Marketin Buyer BehaviorDocument19 pagesMarketin Buyer BehaviorJake Austria50% (2)
- MARK1012 Marketing Fundamentals S12017 PDFDocument19 pagesMARK1012 Marketing Fundamentals S12017 PDFJayNo ratings yet
- Developing A Business Plan PWCDocument15 pagesDeveloping A Business Plan PWCgeracom10% (1)
- Strategy Recommendation For PepsicoDocument8 pagesStrategy Recommendation For Pepsicorajma2006No ratings yet
- Parag DairyDocument11 pagesParag DairyApurvaSingh100% (1)
- CRM LoyaltyDocument34 pagesCRM LoyaltyRohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Adidas Case StudyDocument14 pagesAdidas Case StudyMehatab NabiNo ratings yet
- Part IDocument51 pagesPart IDanielNo ratings yet
- General Manager Sales Operations in Seattle WA Resume Denis NealDocument2 pagesGeneral Manager Sales Operations in Seattle WA Resume Denis NealDenisNealNo ratings yet
- MRP Project Report of MbaDocument86 pagesMRP Project Report of Mbadhruv MehtaNo ratings yet
- Customer Journey PDFDocument15 pagesCustomer Journey PDFMohammad Darwis IbrahimNo ratings yet
- 1 QuizDocument23 pages1 QuizThu Hiền KhươngNo ratings yet
- Rose Hansen ResumeDocument2 pagesRose Hansen ResumepennebakerNo ratings yet
- TechnologyDocument19 pagesTechnologyAKSHAY NATHNo ratings yet
- F 204 (AutoRecovered)Document27 pagesF 204 (AutoRecovered)safiqulislam100% (1)
- Project Report On Brand Resonance Model of GoldstarDocument11 pagesProject Report On Brand Resonance Model of GoldstarSandesh ShahNo ratings yet