Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Production of Speech Sound
Uploaded by
Eirlys NhiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Production of Speech Sound
Uploaded by
Eirlys NhiCopyright:
Available Formats
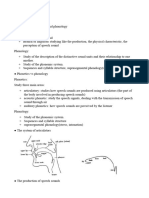
The production of speech sounds
1. Articulators above the larynx:
+ Nasal tract/ nasal cavity
+ oral tract/ oral cavity
+ pharynx (họng)
+ Larynx (thanh quản)
1. Nose - Nasal
2. Alveolar ridge (lợi) - alveolar
3. Palate ( vòm miệng) - palatal
4. Velum/ soft palate (Vòm mềm) - velar
5. Tongue - Lingual
6. Teeth - Dental
7. Lips - Labial
8. Lip to teeth - Labiodental
2. Vowel: voicing
- Manner of Articulation: Vowel are sounds in which there is no obstruction to the
air flow as it passes from the larynx to the lips
- Place of Articulation:
+ Tongue position:
* Tongue height: close - mid - open vowels
* Tongue shapes: front- central- back vowels
+ Lip shapes and positions: rounded- spread - neutral vowels
3. Consonant:
- Manner of Articulation: Consonants are sounds in which it is difficult or
impossible for the air to pas through the mouth
- Place of Articulation: Articualtors: eg: nasal, dental, bilabial, alveolar
consonants
PROBLEM: In some cases, it's difficult to classify vowel and consonant /h/; /w/;
/j/
4. English short vowels
/I, e,
5. Articulations
Tongue height:
+ a change by moving the tongue up and down, or moving the lower jaw up or down
(close-open)
+ Vertical distance between the upper surface of the tongue and the palate
Tongue shape: the part of the tongue which is raised highest (front and back)
6. Cardinal vowels ~ a standard reference system for English vowels and a range of
vowels human can make
Purposes:
+ To make vowels accurately
+ To recognize vowels correctly
2 types of cardinal vowels
+ Primary cardinal vowels: vowels are the most familiar to the speakers of most
European languages in square brackets.
+ Secondary cardinal vowels: sound less familiar
You might also like
- A Course in Phonetics by Peter Ladefoged PDFDocument15 pagesA Course in Phonetics by Peter Ladefoged PDFPralay SutradharNo ratings yet
- English Vowel Sounds (Description & Chart)Document14 pagesEnglish Vowel Sounds (Description & Chart)Jazmin SanabriaNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument2 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyHồ Như QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Meeting 2 PhonologyDocument17 pagesMeeting 2 Phonologydidik prihanantoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Production of Speech SoundsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 The Production of Speech Soundslinh nguyenNo ratings yet
- Vocal Elements: Voiced - The Vocal Folds Are Set in Voiceless - The Vocal Folds Do Not VibrateDocument3 pagesVocal Elements: Voiced - The Vocal Folds Are Set in Voiceless - The Vocal Folds Do Not VibrateIdate PatrickNo ratings yet
- Vowels AutosavedDocument16 pagesVowels AutosavedsangamitraachuNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument4 pagesPhoneticsnhutduynguyen31No ratings yet
- ÔN TẬP PHONETICSDocument53 pagesÔN TẬP PHONETICSChau Nhat ThanhNo ratings yet
- Symbol Systems: Nonverbal Symbols: Lesson 4Document24 pagesSymbol Systems: Nonverbal Symbols: Lesson 4Idate PatrickNo ratings yet
- Inglese Modulo TeoricoDocument48 pagesInglese Modulo TeoricoChiara D'AgostinoNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - VowelsDocument62 pagesUnit 2 - VowelsTrần Lê Ngọc VyNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument9 pagesPhoneticsNguyễn Đình ĐạtNo ratings yet
- Bài giảng Ngữ âm lý thuyết EHOU Bài 1Document6 pagesBài giảng Ngữ âm lý thuyết EHOU Bài 1tranthanhtambrNo ratings yet
- (Phonetics and Phonology) Session 1Document16 pages(Phonetics and Phonology) Session 1Đặng Lê Khánh LinhNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term Test (Dita Prameswari-B0320020) English Phonology ADocument4 pagesMid-Term Test (Dita Prameswari-B0320020) English Phonology AAbyan GalihNo ratings yet
- ArticulationDocument9 pagesArticulationMohan KalawateNo ratings yet
- Gral Ling.Document83 pagesGral Ling.kaclownNo ratings yet
- English Short Vowels and Long VowelsDocument16 pagesEnglish Short Vowels and Long VowelscloudexzNo ratings yet
- Fonética y Fonología I - Unidad 4 - 2019Document42 pagesFonética y Fonología I - Unidad 4 - 2019Yun LaraNo ratings yet
- 3 - Vowels & ClassificationDocument25 pages3 - Vowels & ClassificationDungNo ratings yet
- 10-Vowels Lecture NotesDocument17 pages10-Vowels Lecture NotesMystic MindNo ratings yet
- Vowel SoundsDocument6 pagesVowel Soundskieu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Phonetisc and Phonology Course BookDocument38 pagesPhonetisc and Phonology Course BookNgọc Ánh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument3 pagesEnglishSaba AnatiNo ratings yet
- NG Âm 3Document34 pagesNG Âm 3Chi ChiiNo ratings yet
- Speech Organs Produce The Many Sounds Needed For LanguageDocument7 pagesSpeech Organs Produce The Many Sounds Needed For LanguageSherwin Ryan AvilaNo ratings yet
- Vowel SoundsDocument12 pagesVowel SoundsoserobritonNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of MonophthongsDocument9 pagesMechanism of MonophthongsMaster VINAYNo ratings yet
- LECTURE - 2-Speech SoundsDocument28 pagesLECTURE - 2-Speech SoundsAsfasf OsigspodifghNo ratings yet
- 21/2/2022 An Introduction To Phonetics I. Phonetics and PhonologyDocument20 pages21/2/2022 An Introduction To Phonetics I. Phonetics and PhonologyK60 Vũ Khánh VyNo ratings yet
- Sound ClassificationDocument13 pagesSound Classificationjagodasielska99No ratings yet
- Vowels of English: Presented by Marwa Mahmoud Abd El FattahDocument5 pagesVowels of English: Presented by Marwa Mahmoud Abd El FattahSamar SaadNo ratings yet
- Speech and Theater ExamDocument22 pagesSpeech and Theater ExamCres Jules ArdoNo ratings yet
- FLA Phonological Development YeniDocument8 pagesFLA Phonological Development YeniBayu Christiana AdiNo ratings yet
- Tema 7Document8 pagesTema 7calendulahierbabuenaNo ratings yet
- 04b. VowelsDocument2 pages04b. VowelsJan HrbacekNo ratings yet
- Phonetics IDocument40 pagesPhonetics Iサイ-ドさんNo ratings yet
- NAAVDocument20 pagesNAAVd.duongnguyen1901No ratings yet
- Place of ArticulationDocument13 pagesPlace of ArticulationAarohi JagtapNo ratings yet
- Phonetics & Spoken EnglishDocument12 pagesPhonetics & Spoken EnglishCharanjit SinghNo ratings yet
- Speech OrgansDocument4 pagesSpeech OrgansJoshua Basa100% (1)
- Phonetic ADocument28 pagesPhonetic ANina BandalacNo ratings yet
- Ngân Hàng Câu Hỏi Môn Phonetics And Phonology (Khóa Nna-2019) A- Lý Thuyết 1. On the diagram provided, give the names for the articulatorsDocument20 pagesNgân Hàng Câu Hỏi Môn Phonetics And Phonology (Khóa Nna-2019) A- Lý Thuyết 1. On the diagram provided, give the names for the articulatorsTạ Hoàng AnhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6. Phonetics: The Sounds of LanguageDocument42 pagesLecture 6. Phonetics: The Sounds of Languageсымбат дуйсенNo ratings yet
- Phonetics and PhonologyDocument20 pagesPhonetics and PhonologyQuỳnh Nhi NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Fonetica TeoriaDocument40 pagesFonetica Teoriaal390486No ratings yet
- Principles of E Phonetics and PhonologyDocument74 pagesPrinciples of E Phonetics and PhonologyDuy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Phonetics Chapter 1 Module 2Document33 pagesPhonetics Chapter 1 Module 2Queenie CaraleNo ratings yet
- Mini Project 2Document6 pagesMini Project 2Vy Hoàng HạNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument37 pagesPhoneticsTejaswani RNo ratings yet
- Session 1Document20 pagesSession 1sergio lizzanoNo ratings yet
- PhoneticsDocument29 pagesPhoneticsM UsmanNo ratings yet
- Phonology1 1Document24 pagesPhonology1 1Mark Aldwin LopezNo ratings yet
- PhoneticDocument7 pagesPhoneticNuriNo ratings yet
- CH-5Document29 pagesCH-5Ecem EryılmazNo ratings yet
- Midterm Study GuideDocument2 pagesMidterm Study GuidePhilip LuoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Description & Classification ofDocument16 pagesChapter Four: Description & Classification ofarefe samadiNo ratings yet
- Speech OrgansDocument5 pagesSpeech OrgansprivateceeNo ratings yet
- The Pronunciation of English: A Reference and Practice BookFrom EverandThe Pronunciation of English: A Reference and Practice BookRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Group Task Week 6Document13 pagesGroup Task Week 6Eirlys NhiNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledEirlys NhiNo ratings yet
- The Oral and Situational Teaching ApproachDocument2 pagesThe Oral and Situational Teaching ApproachEirlys NhiNo ratings yet
- El022Iu Phonetics and Phonology: Chapter 8 The Syllable Chapter 9 Strong & Weak SyllablesDocument38 pagesEl022Iu Phonetics and Phonology: Chapter 8 The Syllable Chapter 9 Strong & Weak SyllablesEirlys NhiNo ratings yet
- Week 2's AssignmentsDocument38 pagesWeek 2's AssignmentsEirlys NhiNo ratings yet
- The Gift of The MagiDocument8 pagesThe Gift of The MagiEirlys NhiNo ratings yet