Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Francois Salazar
Uploaded by
Maria Ginalyn Janda Quiñones0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views20 pagesOriginal Title
francois salazar
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
24 views20 pagesFrancois Salazar
Uploaded by
Maria Ginalyn Janda QuiñonesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
Little-Known Facts About Volcanoes volcanoes are at the Ring of Fire. This Everest.
e. This Everest. Mauna Loa has also been very
includes the deadliest volcanoes in the active erupting 33 times since 1832.
So there you have it. These are the 10 most
fascinating facts about volcanoes.
United States, Japan, and the Philippines.
Indonesia is the most volcanically active 5. Volcanoes released water vapor for us to
Do you have an interest in learning more about country on the Ring of Fire. drink Volcanoes created much of the water
volcanoes? Here are some online courses we drink and the air we breathe. Degassing is
offered by universities around the world, which the process that water existed inside the
you can explore. rocks that made up the Earth itself. Because
When I was a kid, I used to play a game Earth’s interior contains minerals with
where everything was lava…Except for the hydrogen and oxygen, volcanoes continually
couch. And if you were stuck on the floor, degas releasing H2O as water vapor.
then you’d get burned by lava. But little did I
know: The lava I was referring to came from 6. Mount Olympus is the largest volcano in
a volcano, which is a real risk in life. So even the solar system On Mars, the largest
when you were a kid, you knew the stuff that volcano is Mount Olympus. But not only on
came out of volcanoes can be pretty deadly. planet Mars, but it’s also the largest in the
Today, we’re going to look at little-known whole solar system. Mount Olympus formed
facts about volcanoes. Enjoy billions of years ago. Mars didn’t have plate
3. Lava from volcanoes build new land tectonics. And it didn’t have surface geology
Volcanoes are areas inside the planet that like Earth. But it did have a period of active
1. Ash from volcanoes can spark lightning degassing where huge amounts of gases like
makes their way to the surface. They create
Lightning commonly occurs in sync with water and carbon dioxide ejected out from
new land like in Hawaii. Continents would be
volcanic eruptions. But how come? As the the interior of Mars.
smaller if it wasn’t for volcanoes. The majority
ash from a volcano rises, it builds static
of Earth’s surface is volcanic rock. All ocean
electricity the same way clouds do. It
seafloor is created by basalt coming out at
interacts with the weather system which
mid-ocean ridges.
allows lightning to strike.
Enter
4. Mauna Loa is taller than Mount Everest It’s
a little-known fact that the Mauna Loa
2. 75% of volcanoes are at the Ring of Fire. volcano in Hawaii is taller than Mount
The Pacific Ring of Fire is a string of Everest. This is because most of the Mauna
volcanoes is where the Pacific Ocean Loa is below the ocean surface. From sea
seafloor is subducting under the continents. It level base to its summit, it’s 9,170 meters in
brings water causing volcanic eruptions from height. That’s 300+ meters higher than Mount
stratovolcanoes. 75% of the world’s
7. The mysterious case of Paricutin A cinder among the most dangerous: Lava is molten
cone volcano “Paricutin” appeared out of hot rock. Temperatures reach up to 1200+°C.
nowhere in a cornfield in Mexico. It baffled Then, pyroclastics are deadly because
scientists and became a popular tourist they’re fast, hot, and poisonous. This type of
destination for volcanologists to study. During flow can travel at speeds up to 700 mph.
9 years of volcanic activity, it left a 420-meter Finally, VOG is a form of air pollution mixing
tall cone without erupting ever again. It’s now sulfur dioxide and other particles from
become one of the 7 natural wonders of the volcanic eruptions.
world.
8. Kilauea in Hawaii poses the highest threat
in the United States. The United States has a
large geographic footprint of volcanoes with
>10% of active volcanoes. According to the
USGS National Volcanic Threat Assessment,
Kilauea in Hawaii poses the highest threat in
the United States because developed areas
still exist on the flanks. Next on the list are
Mount St. Helens and Rainier as the
deadliest.
9. Mudflows (Lahars) are deadly hazards at
volcanoes Lahars are deadly mudflows
resulting from volcanoes. They are capable of
sweeping people to death and tearing down
infrastructure. According to USGS, lahars
caused the deaths of more than 44,000
worldwide between 1600-2010. Lahars are
among the most serious ground-based
hazards at volcanoes.
Enter
10. Temperatures can reach up to 1200+°C
at volcanoes When volcanoes erupt, lava,
pyroclastic and volcanic smog (VOG) are
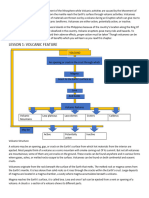
Stratovolcano Stratovolcanoes have relatively
steep sides and are more cone-shaped than
Why are there different types of volcano? shield volcanoes. They are formed from
viscous, sticky lava that does not flow easily.
Viscosity is important in volcanology. An
The lava therefore builds up around the vent
eruption of highly viscous (very sticky) magma
forming a volcano with steep sides.
tends to produce steep-sided volcanoes with Stratovolcanoes are more likely to produce
slopes that are about 30–35°. That’s because explosive eruptions due to gas building up in
the viscous volcanic material doesn’t flow that the viscous magma. Andesite (named after the
far from where it is erupted, so it builds up in Andes Mountains), is perhaps the most
layers forming a cone-shaped volcano known common rock type of stratovolcanoes, but
as a stratovolcano. Shield volcanoes, on the stratovolcanoes also erupt a wide range of
other hand, have gentle slopes that are less different rocks in different tectonic settings.
than 10° and erupt more fluid lavas called
basalt. When a shield volcano erupts, the
basalt can flow great distances away from the
vent to produce broad, gentle slopes.
Shield volcanoes Where a volcano produces
low viscosity, runny lava, it spreads far from the
source and forms a volcano with gentle slopes: Volcanoes spew hot, dangerous gases, ash,
a shield volcano. Most shield volcanoes are lava, and rock that are powerfully destructive.
formed from fluid, basaltic lava flows. Mauna People have died from volcanic blasts.
Kea and Mauna Loa are shield volcanoes. They Volcanic eruptions can result in additional
are the world’s largest active volcanoes, rising threats to health, such as floods, mudslides,
over 9 km above the sea floor around the island power outages, drinking water contamination,
of Hawai’ and wildfires. Health concerns after a
Lava dome The Soufrière Hills volcano, on the volcanic eruption include infectious disease,
Caribbean island of Montserrat, is well known
respiratory illness, burns, injuries from falls,
for its lava dome complex at the summit of the
and vehicle accidents related to the slippery,
volcano, which has gone through phases of
growth and collapse. As viscous lava is not very hazy conditions caused by ash. When
fluid, it cannot flow away from the vent easily warnings are heeded, the chances of adverse
when it is extruded. Instead it piles up on top of health effects from a volcanic eruption are
the vent forming a large, dome-shaped mass of very low.
material.
Volcanic ash Exposure to ash can be
harmful. Infants, elderly people, and people
with respiratory conditions such as asthma,
emphysema, and other chronic lung diseases
may have problems if they breathe in
volcanic ash. Ash is gritty, abrasive,
sometimes corrosive, and always unpleasant.
Small ash particles can abrade (scratch) the
front of the eye. Ash particles may contain
crystalline silica, a material that causes a
respiratory disease called silicosis.
Gases Most gases from a volcano quickly
blow away. However, heavy gases such as
carbon dioxide and hydrogen sulfide can
collect in low-lying areas. The most common
volcanic gas is water vapor, followed by
carbon dioxide and sulfur dioxide. Sulfur
dioxide can cause breathing problems in both
healthy people and people with asthma and
other respiratory problems. Other volcanic
gases include hydrogen chloride, carbon
monoxide, and hydrogen fluoride. Amounts of
these gases vary widely from one volcanic
eruption to the next. Although gases usually
blow away rapidly, it is possible that people
who are close to the volcano or who are in
the low-lying areas downwind may be
exposed to levels that may affect health. At
low levels, gases can irritate the eyes, nose,
and throat. At higher levels, gases can cause
rapid breathing, headache, dizziness,
swelling and spasm of the throat, and
suffocation.
You might also like
- Top 10 Facts About VolcanoesDocument3 pagesTop 10 Facts About VolcanoesMohd ShamshuriNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument21 pagesTypes of VolcanoesAgaManlapazMacasaquitNo ratings yet
- 3 Types of Volcanic ConesDocument2 pages3 Types of Volcanic ConesKirsten Colin BermejoNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes The Ultimate Book: Experience the Heat, Power, and Beauty of VolcanoesFrom EverandVolcanoes The Ultimate Book: Experience the Heat, Power, and Beauty of VolcanoesNo ratings yet
- Abdullah VolcanoesDocument9 pagesAbdullah VolcanoesMariam MagdyNo ratings yet
- What Is It?: Earthquakes and VolcanismDocument13 pagesWhat Is It?: Earthquakes and VolcanismXylef Christiana Love YonsonNo ratings yet
- Science VolcanoDocument6 pagesScience Volcanosci PantallanoNo ratings yet
- Mary Drury - VOLCANOES TemplateDocument11 pagesMary Drury - VOLCANOES TemplateMary DruryNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Volcanoes and TypeDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Volcanoes and TypeMonaoray BalowaNo ratings yet
- VolcanoDocument3 pagesVolcanoRhienzane L. MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Earth Science HandoutDocument2 pagesEarth Science HandoutHanz Alecz Q. DasmariñasNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument15 pagesVolcanoesAliah GombioNo ratings yet
- What Happens Before and After Volcanoes Erupt? Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandWhat Happens Before and After Volcanoes Erupt? Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Kaboom! What Happens When Volcanoes Erupt? Geology for Beginners | Children's Geology BooksFrom EverandKaboom! What Happens When Volcanoes Erupt? Geology for Beginners | Children's Geology BooksNo ratings yet
- VOLCANESDocument10 pagesVOLCANESJahnisel A. CordovaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 VolcanoesDocument36 pagesLesson 1 VolcanoesErica NatividadNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes in Outer Space Cue CardsDocument4 pagesVolcanoes in Outer Space Cue CardsAmisha MoodleyNo ratings yet
- Science-6 Q4 W2 The Effects of Volcanic EruptionDocument8 pagesScience-6 Q4 W2 The Effects of Volcanic Eruptionkiandizon12No ratings yet
- Science 9 - Modules - Q3 - Sir AljonDocument11 pagesScience 9 - Modules - Q3 - Sir AljonNojla SenoirbNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Volcanism: After Having Learnt This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToDocument4 pagesChapter 4: Volcanism: After Having Learnt This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToVaansh DhirwaniNo ratings yet
- VolvanoDocument6 pagesVolvanoZarinaNo ratings yet
- DRRR ReviewerDocument8 pagesDRRR ReviewerVinz AlilingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 VolcanoesDocument16 pagesChapter 9 VolcanoesAlipio Christopher100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Volcanic EruptionsDocument7 pagesChapter 9 Volcanic Eruptionsrichelledultra72No ratings yet
- Chapter 9 VolcanoesDocument19 pagesChapter 9 VolcanoesaaahhhNo ratings yet
- I and S Volcano ReportDocument7 pagesI and S Volcano ReportJASMSJS SkskdjNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes and Types of Volcanic EruptionDocument87 pagesVolcanoes and Types of Volcanic EruptionjulaiannNo ratings yet
- Report No. 1Document9 pagesReport No. 1alberto.deuna001No ratings yet
- Volcanic Eruption - BrochureDocument5 pagesVolcanic Eruption - BrochureAngelo Justine ZaraspeNo ratings yet
- Pre-Assessment: Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerDocument60 pagesPre-Assessment: Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerheartNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument24 pagesVolcanoesBarbara BananaNo ratings yet
- Volcano - WikipediaDocument99 pagesVolcano - WikipediaMattyNo ratings yet
- For Earth Science !! 33Document91 pagesFor Earth Science !! 33art2rugraceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Volcanic EruptionsDocument22 pagesChapter 5 Volcanic EruptionsreesespufffNo ratings yet
- VOLCANO NotesDocument17 pagesVOLCANO NotesAlexander LahipNo ratings yet
- Volcano TriviaDocument22 pagesVolcano TriviaEman VidalloNo ratings yet
- Types of Volcanoes ReadingDocument2 pagesTypes of Volcanoes ReadingquintonmkzNo ratings yet
- Science9 Q3 Week1 Romo AmabelleDocument18 pagesScience9 Q3 Week1 Romo AmabelleGrace OroNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Midterm Lesson 2-2022Document44 pagesEarth Science Midterm Lesson 2-2022April Rose MarasiganNo ratings yet
- Science Q3 Week 1 2printDocument8 pagesScience Q3 Week 1 2printChelsea BialaNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes EarthquakeDocument83 pagesVolcanoes EarthquakeMeshal M ManuelNo ratings yet
- It's Getting Hot in Here: A Teacher Briefing On VolcanoesDocument5 pagesIt's Getting Hot in Here: A Teacher Briefing On VolcanoesHelen HodgsonNo ratings yet
- Carib Studies PresentationDocument12 pagesCarib Studies PresentationAudel RumKrumz HowardNo ratings yet
- Class-IX GEOGRAPHY, Chapter:-7 A. Answer The Following QuestionsDocument5 pagesClass-IX GEOGRAPHY, Chapter:-7 A. Answer The Following QuestionsVindhya SriNo ratings yet
- The Beauty and Danger of A Volcano by ChiongDocument3 pagesThe Beauty and Danger of A Volcano by ChiongCHIONG, ABEGAIL, T.No ratings yet
- - - What is a volcano - نسخةDocument13 pages- - What is a volcano - نسخةSafa AlzamelNo ratings yet
- All About VolcanoDocument7 pagesAll About VolcanoRi RiNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes PDF Format 5912b8dcDocument4 pagesVolcanoes PDF Format 5912b8dcsukesh sNo ratings yet
- DRRR 5Document13 pagesDRRR 5Abby MacatangayNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Activity محاضره 4و5Document12 pagesVolcanic Activity محاضره 4و5Hanna AngelaNo ratings yet
- Types of VolcanoesDocument15 pagesTypes of VolcanoesSally PocamasNo ratings yet
- VOLCANODocument4 pagesVOLCANOTristan BucaoNo ratings yet
- Shield VolcanoesDocument5 pagesShield VolcanoessebastianocaltabianoNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes - The Fiery Wonders of The EarthDocument2 pagesVolcanoes - The Fiery Wonders of The EarthMarcos MartinezNo ratings yet
- On Earth, Volcanoes Are Generally Found Where Tectonic Plates Are orDocument5 pagesOn Earth, Volcanoes Are Generally Found Where Tectonic Plates Are orrituNo ratings yet
- Hình ảnh đáp ánDocument4 pagesHình ảnh đáp ánTUẤN VŨNo ratings yet
- Volcanoes - Module 1 FinalDocument69 pagesVolcanoes - Module 1 FinalAngel rose OrbeNo ratings yet
- VolcanoesDocument6 pagesVolcanoesRoger Corre RivaNo ratings yet
- Disaster Risk Reduction and Management of Tarlac CityDocument5 pagesDisaster Risk Reduction and Management of Tarlac CityMixsz LlhAdyNo ratings yet
- Bocoran Soal Utbk SNBT 2023 Hari Ke-4 Gelombang 1 Literasi Bahasa InggrisDocument2 pagesBocoran Soal Utbk SNBT 2023 Hari Ke-4 Gelombang 1 Literasi Bahasa InggrisManase PakpahanNo ratings yet
- Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction: Volcano HazardsDocument6 pagesDisaster Readiness and Risk Reduction: Volcano HazardsnonononowayNo ratings yet
- Pinatubo PDFDocument18 pagesPinatubo PDFGladys LuzungNo ratings yet
- Lahars and Their EffectsDocument15 pagesLahars and Their EffectsIrna Tiara Tri ArganiNo ratings yet
- FINAL DEMO Volcanic EruptionsDocument9 pagesFINAL DEMO Volcanic EruptionsjaneNo ratings yet
- Site DataDocument41 pagesSite DataCamille ArielNo ratings yet
- Volcanic Eruption HazardsDocument13 pagesVolcanic Eruption HazardsAdrian Carl BronolaNo ratings yet
- San Guillermo DraftDocument10 pagesSan Guillermo Draftaaronjg559No ratings yet
- Flood and Lahar ControlDocument38 pagesFlood and Lahar ControlAngelus Castiel78% (9)
- LaharreportDocument10 pagesLaharreportDave SallaoNo ratings yet
- Performance Task For Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction 1st SemDocument3 pagesPerformance Task For Disaster Readiness and Risk Reduction 1st SemAngelyn Lingatong100% (1)
- Maahas Phase 2Document6 pagesMaahas Phase 2DPWH R4A GEOTECHNo ratings yet
- Disaster Readiness and Risk ReductionDocument239 pagesDisaster Readiness and Risk ReductionGemma Rose LaquioNo ratings yet
- Exploring Geology 3rd Edition Reynolds Test Bank 1Document61 pagesExploring Geology 3rd Edition Reynolds Test Bank 1mary100% (40)
- DLL 16Document2 pagesDLL 16Marjorie BrondoNo ratings yet
- Aeta PDFDocument15 pagesAeta PDFDyanNo ratings yet
- Anguita Geologiacal Guidebook To Dantes PeakDocument6 pagesAnguita Geologiacal Guidebook To Dantes PeakDebra RuthNo ratings yet
- DRRR Final Exam 2020Document3 pagesDRRR Final Exam 2020Argie Joy Marie AmpolNo ratings yet
- DRRR Q3 LT2 Sy 1920 PDFDocument6 pagesDRRR Q3 LT2 Sy 1920 PDFFreyah DenisseNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes & Volcanoes: Disastrous WondersDocument1 pageEarthquakes & Volcanoes: Disastrous WondersAziana MontemayorNo ratings yet
- DLL 18Document2 pagesDLL 18Marjorie BrondoNo ratings yet
- Landslide 2Document16 pagesLandslide 2Prince JoeNo ratings yet
- POWERPOINT - Volcanic HazardsDocument18 pagesPOWERPOINT - Volcanic HazardsCherry GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Allah Se Mangiye اللہ سے مانگیےDocument48 pagesAllah Se Mangiye اللہ سے مانگیےArshad Ayoub KhanNo ratings yet
- Mt. Pinatubo Kabuhayan Sa Turismo Project: A Strategy For Sustainable DevelopmentDocument6 pagesMt. Pinatubo Kabuhayan Sa Turismo Project: A Strategy For Sustainable DevelopmentNet LogartaNo ratings yet
- Active Volcanoes of The World Merapi Volcano Geology, Eruptive ActivityDocument581 pagesActive Volcanoes of The World Merapi Volcano Geology, Eruptive ActivityJason E. OrtizNo ratings yet
- Week 7-Geologic Processes and HazardsDocument66 pagesWeek 7-Geologic Processes and Hazardsedgy bratNo ratings yet
- Wikipedia - Natural DisastersDocument1 pageWikipedia - Natural DisastersAkshay ThakurNo ratings yet
- Pryclastic Flows - Venus CompressedDocument27 pagesPryclastic Flows - Venus CompressedFhia Angelika IntongNo ratings yet