Professional Documents
Culture Documents
FPC Manual: Arab Steel Fabrication
Uploaded by
Sherif YehiaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
FPC Manual: Arab Steel Fabrication
Uploaded by
Sherif YehiaCopyright:
Available Formats
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
FACTORY PRODUCTION CONTOL
SYSTEMS MANUAL
Date: 29/05/2019 Page1of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
CONTENTS:
1. OBJECTIVE
1.1. GENERAL REQUIREMENTS
1.2. SCOPE
1.3. COMPANY REPRESENTITIVE
1.4. CONFIDENTIALLY
1.5. MANUAL ADMINISTRATION
2. FACTORY PRDUCTION CONTROL SYSTEM
2.1. DOCUMENTATION
2.2. MANAGERIAL AUDITS
2.3. PERSONNEL
2.4. EQUIPMENT
2.5. PLANNING OF PRODUCTION AND PRODUCT REALISATION
2.6. COMPONENT SPECIFICATION
2.6.1. CUSTOMER COMMUNICATION
2.6.2. DETERMINATION OF REQUIREMENTS RELATED TO THE PRODUCT
2.7. PRODUCT EVALUATION
2.7.1. GENERAL
2.7.2. CE MARKING AND PREPARATION OF DoP
2.8. CONSTITUENT PRODUCTS USED IN MANUFACURE
2.8.1. DEFINITION OF CONSTITUENT PRODUCTS
2.8.2. PURCHASING OF CONSTITUENT PRODUCTS
2.9. PRESERVATION OF PRODUCT
2.10. PREPARTATION AND ASSEMBLY
2.10.1. IDENTIFICATION AND TRACEABILITY
2.10.2. CUTTING
2.10.3. HOLING
2.10.4. SHAPING
2.10.5. WELDING
2.10.6. INSPECTION AFTER WELDING
2.10.7. CORRECTION OF WELD
2.11. DURABILITY
2.12. CONTROL OF NON-CONFORMING PRODUCT
2.13. MEASUREMANT, ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT
2.13.1. GENERAL
2.13.2. CUSTOMER COMPLAINTS
2.14. IMPROVEMENT
2.14.1. CORRECTIVE ACTION
2.14.2. PREVENTIVE ACTION
2.15. ATTACHEMENT
Date: 29/05/2019 Page2of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
ORGANISATION
ORGANISATION DIAGRAM
Date: 29/05/2019 Page3of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
1.0 OBJECTIVE
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION specialises in the supply and installation of steel structure component, Plate Works, High
buildings and Bridge System.
01
To assist in achieving these objectives, it is the policy of the company to establish and maintain an effective and
efficient factory production control system which conforms to the requirements of EN 1090-1 in connection with the
requirement of EN ISO 9001:2015, and to ensure that the products placed on the market meet the required quality
standards and conform to the declaration of performance (DoP) delivered with the steel product.
The quality related Processes and procedures that support the implementation of factory production control system
are referenced in detail in section 2 and in the compliance matrix (Section 2.1.3) of this manual.
1.1 GENERAL REQUIREMENTS
The Company has established, documented, implemented & maintains a factory production control system in line
with the requirements of EN 1090-1 and BS EN 1090‑ 2:2018 EXC-4.
The key processes needed for the factory production control system and the interaction of these processes are
identified within the documented operational procedures and works instructions.
The company will determine criteria and methods needed to ensure that both the operation and control of these
processes is effective and maintained.
The company will ensure that adequate resources are provided to support the operation and monitoring of these
processes. Processes will be monitored, measured and analysed to ensure that planned results are achieved.
1.2 SCOPE
Our FPC system encompasses the manufacture of structural steel products only and it has been prepared so that it
conforms to the relevant requirements of standard EN1090-1 and EN1090-2. CE marking system is type 3a. The
design is supplied by the purchaser.
02
Production is done in-house and subcontracted. Tasks are divided according to the table shown below:
In-house Subcontracted Notes
Structural design No No Client
Cutting Yes No
Shaping Yes No
Holing Yes No
Mechanical fastening Yes No
Assembly Yes No
Welding Yes No
Surface treatment Yes No
Erection Yes No
1.3 COMPANY REPRESENTITIVE
The company has appointed The Quality Manager as the person who is responsible for ensuring that the processes
needed for the factory production control system are established, documented and maintained. In addition to this
he is responsible for ensuring that all employee who are involved with manufacturing of structural steel product
understand their individual responsibilities and duties that the subcontractor meet our quality standard.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page4of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
The Quality Manager is also responsible for reporting the performance and need for improvement of this FPC system
to company management and ensuring the promotion and awareness of FPC system throughout the organisation.
Internal communication in term of responsibilities, authorizations and changes related to the FPC system takes place
in meetings, via e-mail and via- personal communication
1.4 CONFIDENTIALLY
This Factory Production Control Manual is the intellectual property of ARAB STEEL FABRICATION and may not be
copied in whole or part or transmitted to any third party without the express written permission of the documented
information coordination. The Management Representative must approve the issue of any copy of this Factory
Production Control Manual to any external individual or organization. It must be emphasized that the operating
procedures relating to the core product realization processes are strictly confidential to the company. No copies will
be issued externally and the copies available on site are for internal use only. Where copies of supporting procedures
are issued externally, they are for information purposes only. The company reserves the right to withhold any
information without giving any reason.
1.5 MANUAL ADMINISTRATION
Controlled copies of the Factory Production Control Manual are distributed to the manual holders with defined
department reference as per the Factory Production Control Manual Distribution List. Change of manual holders’
positions is not a subject for amending the distribution of the manual, unless other major changes are needed.
Amendments of minor and/or editorial nature can be under taken and incorporated by the company’s Quality
assurance Manager while those affecting policy, management responsibilities and/or organization issues are only
carried-out by the authority of the management representative. Manual amendments/changes are listed in the
Manual Amendments List and each amendment is identified at the righthand margin by a triangular mark with the
change number inside. Amendments of minor and/or editorial nature are introduced by replacement of the
applicable page(s) without changing the manual issue number, while introducing major changes will affect the
manual issue number. In all cases, manual changes and/or issues are recorded in the Manual Amendments List. A
complete list of the Factory Production Control Manual holders with the amendment record retained by the Quality
assurance Manager.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page5of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
2.0 FACTORY PRDUCTION CONTROL SYSTEM
2.1 DOCUMENTATION
2.1.1 STRUCTURE OF DOCUMENTATION
The FPC manual, meaning this document, provides a general description of our FPC system and its scope.
Execution documentation contains written procedures and instructions related to and descriptions of, for example,
the control of raw materials, production machines and the manufacture of products. The execution documentation
also includes the most relevant standards used in manufacture.
Quality records contain the objective documentation and proof of product conformity. These documents include, for
example, component specifications, test results and complaints.
2.1.2 CONTROL OF DOCUMENTS
To ensure proper functioning of our FPC system, we continuously update our documentation and retain quality
records for ten (10) years after their creation.
2.1.3 CONFORMITY TO RELEVANT STANDARD
The conformity of the standard EN1090-1 and EN1090-2 to our FPC manual is presented in the below table:
EN 1090-1 FPC manual
Personnel 2.3
Equipment 2.4
Constituent products used in manufacture 2.8
Component specification 2.6
Product evaluation 2.7
Non-conforming products 2.12
Marking 2.10.1
Welding Coordinator 2.3
EN 1090-2 table A.3 FPC manual
Quality documentation 2.1
Traceability 2.10.1
Marking 2.10.1
Thermal cutting 2.10.2
Welding 2.10.5
Qualification of welding procedure 2.10.5.2
Welders and welding operatore 2.10.5.4
Welding Coordination 2.3
Tack welds 2.10.5.6
Acceptance criteria 2.10.6.3
Inspection after welding 2.10.6
correction of welds 2.10.7
Date: 29/05/2019 Page6of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
2.1.4 STANDARDS IN THE FPC SYSTEM
The following standard related to the manufacturing of steel structure products are part of the FPC system.
These standards are available to all employee to read and the company management is responsible for the
accessibility and validity of the standard.
Standard code Description/Contents
Execution of steel structures and aluminium structures
EN 1090-1 Part 1: Requirements for conformity assessment of structural components
Execution of steel structures and aluminium structures
EN 1090-2 Part 2: Technical requirements for steel structures
ISO 3834 Quality requirements for fusion welding of metallic materials
EN 14731 Welding coordination — Tasks and responsibilities
EN 1011-1&2&3 Welding —Recommendations for welding of metallic materials
Date: 29/05/2019 Page7of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
2.2 MANAGERIAL AUDITS
Once a year, our company quality assurance team perform an internal audit on the FPC system to ensure that the
system is suitable and functional.
The managerial audit includes the assessment of the following aspects where applicable:
• External audits reports.
• Quality statistics.
• Implementation and effects of corrective actions.
• Surveillance of suppliers.
• Sufficiency of the production process surveillance.
• Sufficiency of resources.
• Effectiveness and sufficiency of preventive actions.
• Overall assessment of the effectiveness and suitability of the FPC system for the requirements of quality
policy and quality objectives
Date: 29/05/2019 Page8of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
2.3 PERSONNEL
2.3.1 All personnel performing work-affecting the manufacture of product are competent on the basis of appropriate
education, training skills and experience.
To ensure competence of our personnel, job descriptions have been prepared identifying the qualifications required
for each position that performing works affecting conformity to product requirements. Qualifications include
requirements for education, skills and experience.
The job description of Welding Coordinator will identify the extent of required manufacturing experience, education
and technical knowledge as per requirement of EN ISO 14731.
Administration manager is responsible for providing those persons after they have successfully succeeded designed
examinations according to recruitment procedure (ASF-QP-6.2.1). Appropriate qualifications, along with required
training, provide the competence required for each position.
The company will determine the necessary competence for personnel performing work affecting product quality and
provide training according to procedure ASF-QP-7.2. The company maintains records of all training and education
affecting finished product.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page9of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
2.4 EQUIPMENT
2.4.1 To meet quality objectives and conformity to product requirements ARAB STEEL FABRICATION has determined
the needed infrastructure which includes buildings, workspace, utilities, process equipment and supporting services.
As new infrastructure requirements arise, they will be documented in quality plans. Existing infrastructure is
maintained to ensure product conformity. Maintenance requirements are documented in preventive maintenance
logs. Infrastructure is conducted according to infrastructure procedure (ASF-QP-7.1.3).
2.4.2 CONTROL OF MONITORING AND MEASURING DEVICES
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION has determined the monitoring and measurement to be undertaken and the monitoring
and measuring devices needed to provide evidence of conformity of product to determined requirements.
A documented calibration procedure (ASF-QC-CP-035 Rev. 0) outlines the process used to ensure that monitoring
and measurement are carried out in a manner that is consistent with the monitoring and measurement
requirements. Where necessary to ensure valid results, measuring equipment is:
Calibrated or verified at specified intervals, or prior to use, against measurement standards traceable to
international or national measurement standards.
Adjusted or re-adjusted as necessary.
Have identification to enable their calibration status to be determined.
Safeguarded from adjustments that would invalidate the measurement result.
Protected from damage and deterioration during handling, maintenance and storage.
Records of the results of calibration and verification is maintained. When used in the monitoring and measurement
of specified requirements, the ability of computer software to satisfy the intended application is confirmed.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page10of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
2.5 PLANNING OF PRODUCTION AND PRODUCT REALISATION
The company will plan and develop the processes needed for production product realisation according to procedure
ASF-QP-8.1A. The planning is consistent with the requirements of the other processes of this factory production
control system.
Planning for production and product realisation incorporates the determination of the;
i. Quality requirements of the product (component specification).
ii. The need to establish processes, documents, and provide resources specific to the product.
iii. Required verification, validation, monitoring, inspection and test activities specific to the product and criteria
for product acceptance.
iv. Records needed to provide evidence that the realisation processes and resulting product meet
requirements.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page11of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
2.6 COMPONENT SPECIFICATION
2.6.1 CUSTOMER COMMUNICATION
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION has implemented an effective procedure (ASF-QP-8.2) for communicating with customers
in relation to:
i. Component specification.
ii. Enquiries, contracts and order handling, including amendments.
iii. Customer Feedback, including customer complaints.
2.6.2 DETERMINATION OF REQUIREMENTS RELATED TO THE PRODUCT
The company will ensure that it determines;
iv. Component requirements specified by the customer, the execution class (EN1090-2 EXC1,2,3, or 4) to be
applied shall be given in the component specification.
v. Requirements not stated by the customer but necessary for specified intended use, where known.
vi. Statutory and regulatory requirements related to the product.
vii. Any additional requirements determined by the company.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page12of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
2.7 PRODUCT EVALUATION
2.7.1 In order to provide a component that complies with the PPCS (Purchaser provided component specification),
the company will implement a written execution or manufacturing procedure, inspection procedure and inspection
test plan in accordance with EN 1090-2 and EN 1090-1.
The company will review the requirements related to the product. The review will be performed prior to the
company’s commitment to supply a product to a customer and will ensure that;
i. Product requirements are defined.
ii. Contract or order requirements differing from those previously expressed are resolved.
iii. The company has the ability to meet the defined requirements.
Where a customer provides no documented statement of requirement, the company before acceptance will confirm
the customer requirements. If and when product requirements are changed the company will ensure that the
relevant documents are amended and that relevant personnel are made aware of the changed requirements.
2.7.2 CE MARKING AND PREPARATION OF DoP
For each component delivery, the company will declare that the final component is comply with the PPCS (Purchaser
provided component specification) in accordance with annex ZA of EN 1090-1.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page13of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
2.8 CONSTITUENT PRODUCTS USED IN MANUFACURE
2.8.1 DEFINITION OF CONSTITUENT PRODUCTS
Constituent product is referred to plates, sections, hollow sections, welding consumables, mechanical fasteners,
studs etc.
2.8.2 PURCHASING OF CONSTITUENT PRODUCTS
2.8.2.1 PURCHASING PROCESS
The company will ensure that purchased product required for production and product realisation conforms to
specified purchase requirements. The company will evaluate and select suppliers based upon their ability to supply
product in accordance with the company’s requirements. Details of supplier selection & evaluation are included
within procedure ASF-QC-PR-007 (Purchasing Procedure).
2.8.2.2 PURCHASING INFORMATION
Purchasing information describes the product to be purchased. These include the Material Specifications, type or
grade selected from the relevant European Standards listed in clause 5 EN 1090-2:2018. If constituent products that
are not covered by the standards listed are to be used, their properties shall be specified. The relevant properties to
be specified shall be as EN1090-2 clause 5.1.
The company will ensure the adequacy of specified purchase requirements prior to their communication to the
supplier as following:
1. The Material Requisition List (R2-1) and Technical Delivery Condition (R5-7) for Code Material, excluding Welding
Material, is prepared by the Design Engineer. Material Requisition List of Welding Materials (R5-1) and TDC for
Welding Materials (R5-9) are prepared by the Welding Engineer.
2. The Material Requisition Lists (R2-1) and Technical Delivery Condition (R5-7) shall also include marking
requirements and Material Test Report and/or Certificate of Compliance, if required, and any supplementary or
additional requirements of Code, such as special testing, charpy impact tests at minimum design metal temperature,
subsequent heat treatment, if any.
3. Completed Material Requisition Lists of Welding Materials (R5-1) and TDC for Welding Materials (R5-9) are signed
and dated by the Welding Engineer and forwarded to The Quality Control Manager to approve it, then forwarded to
the Material Controller to check material availability at store. The Material Controller shall verify the material
availability at store to deduct it from the quantity required to be purchased for each item and forwarded it to the
Technical Office Manager to review and approve and in case of Welding Materials he forwards it to the Quality
Control Manager to review and approve.
4. For the materials required to be purchased; Design Engineer prepares Purchase Requisition (R5-2) and obtains
approval from Technical Office Manager then forward to Purchase Engineer for Procurement.
5. The required Welding Material must be issued to the Purchasing Engineer in “Purchase Requisition” (R5-2) which
prepared by the Welding Engineer and approved by the Quality Control Manager.
6. The Projects Procurement Head attaches the approved Purchase Requisition to the Purchase Order (R5-3) and
forwards it to the Operations Manager to approve. The approved Purchase Order is sent to the selected Vendor
attached with all references.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page14of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
7. A copy of Purchase Order and Material Requisition List is sent to the Quality Control Receiving Inspector by Project
Procurement head for use during Material Receiving Inspection.
8. For material to be sent to a Field Site, a copy of the Purchase Order and Material Requisition List with the
Technical Delivery Conditions shall be sent to the Site Quality Control Inspector.
9. Changes to Purchase Order shall be prepared, reviewed and approved from revised Material Requisition List in the
same way as the originals.
10. For the ordering of welding material the Welding Engineer forwards the Material Requisition List of Welding
Material to the Projects Procurement Head for preparation of the Welding Consumables Purchasing Order (R5-13)
without change and forwards this to the appropriate vendor.
11. Substitution of Material is not permitted without the prior approval of the Technical Office Manager.
2.8.2.3 VERIFICATION OF PURCHASED PRODUCT
Documents supplied with constituent products in accordance will be checked to verify that the information on the
products supplied matches those in the component specification. These documents include inspection certificates,
test reports, declaration of compliance.
The company relies upon the supplier to take responsibility to ensure that product purchased conform to agreed
specified requirements. (EN10029, EN10163, ….etc)
The company will inspect incoming product as following:
1. All Code Materials received at the Shop or Site are placed in a hold area identified with a signboard “pending
Quality Control Examination.
2. The Quality Control Receiving Inspector, using his copy of Purchase Order or Material Requisition List, examines all
Code Materials except Welding Materials for marking, condition and quantities.
3. The Quality Control Receiving Inspector reviews the Material Certificate, Chemical Analysis and Physical Properties
and other test results, against those listed in the applicable Material Specifications. He shall also verify the marking
required by the material specification and the P.O/ Material Requisition List, the material marking should be verified
against the mill test certificate and record the original marking in the Material Receiving Inspection Report (R5-4).
4. When acceptable, the Quality Control Receiving Inspector signs and dates the Material Certificates, the Material
Receiving Inspection Report is forwarded to the Quality Control Manager for approval by signature and date then
return to the Material Controller and Quality Control Receiving Inspector to release the material to shop.
5. The Quality Control Receiving Inspector shall notify the Production Manager of all material released by sending
him a copy of the approved Materials Receiving Inspection Report.
6. The fabrication Engineer shall prepare the Material Request / Release Note (R5-10) to withdraw the accepted
material form the store for the fabrication process.
7. Material which does not meet all Purchase Order and Code requirements is tagged “HOLD” tag (R5-5), retained in
the “HOLD” area, and controlled as described in Section 2.12 of this Manual dealing with Correction of
Nonconformities.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page15of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
8. Before cutting Code Material into two or more pieces, the entire material marking is transferred by the
Fabrication Foreman and verified by the Quality Control Inspector, the QC Inspector will prepare the Material
Traceability Record (R5-11). For Code Material; a Coded marking traceable to the material certificate or material
specification, as required for the product form, may be used to identify each piece.
coded system and method of marking shall be acceptable to the quality manager. Coded marking for plates and
sections shall be a numbering code which referring to the material specification including grade, class, type, heat
number and plate number based on the material log sheet. The said marking shall be hard stamping unless hard
stamping would be harmful to material, in such case record of the material traceability shall be maintained by the
Summery of Material Certificate in lieu of hard stamping. The QC inspector shall prepare the material traceability
report (R5-11).
9. For receiving examination of Welding Materials, the Welding Engineer is responsible to apply the receiving
examination of welding materials procedure approved by the QC Manager and records his inspection details on the
welding consumables inspection report (R5-6).
10. The Fabrication Engineer shall prepare the Welding Material Request/Release Note (R5-13) to withdraw the
welding consumables for fabrication process
11. The production Engineer shall prepare the material request/release note (R5-10) to withdraw the material from
the store.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page16of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
2.9 PRESERVATION OF PRODUCT
As applicable, preservation includes identification, handling, packaging, storage and protection. Preservation also
applies to the constituent parts of a product. ARAB STEEL FABRICATION will ensure that it preserves the conformity
of product during internal processing and delivery to the intended destination by applying the procedures material
storage and preservation (ASF-QP-8.5.4A), handling procedure (ASF-QP-8.5.4B) and packing and shipment procedure
(ASF-QP-8.5.4C).
In addition to the requirements of the above-mentioned procedures, below instructions will be considered:
Lifting
1. Protection of components from damage at the lifting points
2. Avoidance of single point lifting of long components by use of spreader beams as appropriate
3. Bundling together lightweight components particularly prone to edge damage, twisting and distortion if handled
as individual items. Care taken to avoid localized damage where component touch each other, to unstiffened
edges at lifting points or other zones where a significant proportion of the weight of the bundle is imposed on a
single unreinforced edge
Storage
1. Stacking of manufactured components stored before transportation or erection clear of the ground to be kept
clean
2. Necessary supports to avoid permanent deformations
3. Storage of profiled sheeting, and other materials supplied with pre-finished decorative surfaces according to the
requirements of relevant standards
Protection against corrosion
1. Avoidance of accumulation of water
2. Precautions in order to avoid the penetration of moisture into bundles of sections with metallic pre coatings
NOTE In case of prolonged open storage on site, the bundles of sections should be opened, and the sections
separated to avoid the occurrence of 'black or white rust'.
Stainless steels
1. Handling and storage of stainless steel to prevent contamination by fixtures or manipulators etc.
2. Careful storage of stainless steel, so that the surfaces are protected from damage or contamination
3. If appropriate, use of protective film or other coating, to be left on as long as practicable
4. Avoidance of storage in salt-laden humid atmospheres
5. Protection of storage racks by suitable wooden, rubber or plastic battens or sheaths to avoid carbon steel,
copper-containing, lead etc. rubbing surfaces
6. Use of markers containing chloride or sulphide prohibited
NOTE An alternative is to use protective film and apply all marks only into this film.
7. Protection of stainless steel from direct contact with carbon steel lifting tackle or handling equipment such as
chains, hooks, strapping and rollers or the forks of fork lift trucks by use of isolating materials or light plywood or
suction cups. Use of appropriate erection tools to ensure that surface contamination does not occur
8. Avoidance of contact with chemicals, including dyes, glues, adhesive tape, undue amounts of oil and grease
NOTE If it is necessary to use them, their suitability is to be checked with their manufacturer.
Use of segregated manufacturing used for carbon steel and stainless steel to prevent carbon steel pick-up. Use of
separate tools dedicated for use with stainless steel only, particularly grinding wheels and wire brushes. Wire
brushes and wire wool of stainless steel, preferably an austenitic grade.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page17of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
2.10 PREPARTATION AND ASSEMBLY
The company will specify the requirements for cutting, shaping, holing and assembly of constituent products for
inclusion into components, and for assembly of components.
2.10.1 IDENTIFICATION AND TRACEABILITY
In order to trace the components during the manufacturing process, person who in charge of assembly will stamp
each component with a unique marking including the job number, drawing number and item number.
The identification must be made as indicated below:
The Serial Number must be stamped before the beginning of the component welding process,
Stamped with hard stamps (not permitted for stainless steel and areas where the marking method would
not affect the fatigue life; accordingly, only durable marking will be used)
The mark must have a depth of at least 1 mm.
Numbers and letters shall be applied in such a way they are easily readable after the surface treatments
(painting, shout blasting, …) has been completed.
Technical office is in charge of specifying the mark location.
2.10.2 CUTTING
Cutting will be carried out in accordance with procedure (ASF-QC-SP-040) in order to satisfy the requirements for
geometrical tolerances, maximum hardness and smoothness of free edges as specified in this European Standard are
met.
In order to comply with the requirement of EN 1090-2 the capability of automated thermal cutting processes will be
checked annually as set out below.
Four samples will be produced from the constituent product to be cut by the process:
a) a straight cut from the thickest constituent product;
b) a straight cut from the thinnest constituent product;
c) a sharp corner from a representative thickness;
d) a curved arc from a representative thickness.
Measurements will be taken on the straight samples over at least a 200 mm length on each and checked against the
required quality of the cut surface. The sharp corner and curved samples shall be visually inspected to establish that
they produce edges of equivalent standard to the straight cuts
In order to check the capability of automated thermal cutting processes, the following procedure in accordance with
EN1090-2 annex D will be issued. These procedures is based on preparing a preliminary cutting procedure
specification (pCPS) and verifying the quality of the cut surfaces produced using this pCPS in order to finalise a
cutting procedure qualification record (CPQR) . This CPQR is then used as the basis for control of cutting operations
in production using cutting procedure specifications (CPSs) .
.
The quality requirements for cut surfaces to be left as free edges (i.e. not to be subsequently incorporated into a
weld) will be verified according to Table 9 EN 1090-2 EXC 4 when assessed in accordance with EN ISO 9013, unless
otherwise specified.
Hardness of free edge surfaces will be verified accordance with the requirements given in Table 3 EN ISO 15614:2017
Date: 29/05/2019 Page18of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
Joint preparations will be suitable for welding process. Tolerances for joints preparations and fit-up will be given in
the WPSs
2.10.3 HOLING
2.10.3.1 DRILLING
The shop is equipped with several NC and standard drilling machines. Drilling of the flanges and webs of the plate
girders can be done on the strips plates before their welding or on the complete plate girder after welding. Small
strip plates (such as gussets, stiffeners and splice plates) are drilled using affix drilling station.
The sections are drilled in a special CNC drilling machine or in CNC sawing and drilling machine.
2.10.3.2 PUNCHING
Punching is will be used only if the nominal thickness of the component is not greater than 1,4 times the nominal
diameter of the hole, or for a non-circular hole.
The process capability of punching used for holing will be checked annually as follows:
a) a representative number of samples will be produced from procedure tests on constituent product encompassing
the range of hole diameters, constituent product thickness and grades processed;
b) hole sizes will be checked at both ends of each hole using go/no go gauges or other appropriate methods. Holes
will be verified to confirm that it complies with the appropriate tolerances specified in 6.6.2 EN1090-2.
Holes formed by punching or thermal cutting will be verified also to confirm that it complies with fig.1 EN1090-2
2.10.4 SHAPING
In order to satisfy the requirements and recommendations for hot, cold forming and flame straightening of steels,
procedure ASF-QC-SP-030 has been issued.
In order to comply with the requirements of EN 1090-2, the following requirements will be considered:
Unless otherwise specified, hot forming of stainless steels is not permitted.
For steels according to EN 10025-4 and in the delivery condition +M according to EN 10025-2 hot forming is
not permitted.
For quenched and tempered steels, hot forming is not permitted unless the requirements of EN 10025-6 are
fulfilled.
For steel grades up to and including S355, the hot forming process will take place in the red hot (600 °C to
650 °C) state and the temperature, timing and cooling rate will be appropriate to the particular type of steel.
Bending and forming in the blue heat range (250 °C to 380 °C) is not permitted
Flame straightening of stainless steels will be avoided as possible.
For circular tubes bending by cold forming will be verified to confirm that it complies with the following
three conditions, unless otherwise specified:
1) the ratio of the overall diameter of the tube to the wall thickness is not exceed 15;
2) the bend radius (at the centerline of the tube) is not be less than 1,5d or d+100 mm, whichever
is the larger, in which d is the overall diameter of the tube;
3) the longitudinal seam weld in the cross-section has been positioned close to the neutral axis, in order to reduce
the bending stresses at the weld.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page19of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
2.10.5 WELDING
2.10.5.1 All welding work is performed using qualified WPS (Exhibit 8-1) according to EN 15614 and EN 15609 and for
welders/welding operators, hereafter called welders, qualified and certified in accordance with the EN 9606, EN
14732 and the EN1090-2.
2.10.5.2 WELDING PROCEDURE SPECIFICATION
2.10.5.2.1 WPS’s are prepared by the Welding Engineer and will include all welding variables required for the
welding process by EN 15614 and EN 15609 and the intended range of production welding. The required test welds
are made under the supervision of the Welding Engineer or his designee in either workshop one or two considering
all essential and if required the supplementary essential variables and to record it in the PQR, preparation and
testing of the required test specimens are performed by an accredited testing laboratory according to ISO 17025
whose report of test results is reviewed by the Welding Engineer. If acceptable he prepares and certifies by signature
and date, the Procedure Qualification Record (PQR) (Exhibit 8-2). The PQR shall include at least all essential actual
variables used in making the qualification test welds.
2.10.5.2.2 WPSs are prepared by Welding Engineer and reviewed Welding Head and approved by the QC Manager.
The welding Engineer will prepare Qualified WPS List (Exhibit 8-8).
2.10.5.2.3 Copies of the qualified WPS’s together with the List are provided to the Project Manager, Quality Control
Manager the Production Manager and the after-client review and acceptance. The managers will distribute the WPS
to their subordinate as appropriate.
2.10.5.2.4 WPS’s may be revised whenever there is a change in a non-essential variable. Whenever there is a change
in an essential or supplementary essential variable, a new WPS shall be prepared, qualified and approved as the new
WPS.
2.10.5.2.5 WPS’s and PQR’s are submitted to the client for his review.
2.10.5.2.6 WPS’s, PQR’s, and demonstration whether issued in workshop one or two may be used at either
workshop provided that it is controlled in accordance with the Welding Book prepared by Welding Engineer.
2.10.5.3 WELDING MAP
To specify each individual welded joint; a Welding Map to be prepared using shop drawing(s) for Code items by the
Welding Engineer and reviewed by the Welding Head and approved by the Quality Manager.
2.10.5.4 QUALIFICATION OF WELDERS AND WELDING OPERATORS
2.10.5.4.1 All welders/operators to be assigned for welding at shop or site will be qualified to EN9606,
EN14732,EN1090-2 under the supervision of the Welding Engineer. Preparation and testing of the required
specimens of the test weld is performed by an accredited testing laboratory according to ISO 17025. Their report is
reviewed by Welding Engineer, and if acceptable, he prepares and certifies the Welder/Welding Operator
Performance Qualification Record (WPQ) (Exhibit 8-5 & 8-6). The WPQ documents the performance essential
variables actually used for the test welds and ranges qualified for production welding.
2.10.5.4.2 A WPQ is also issued for any welder who has welded a test coupon to qualify a WPS, based on the
performance essential variables used, and provided the test results meet the Code requirements.
Welders of a hollow section branch connection with angles less than 60° as defined in EN 1993-1-8 will be qualified
using separate qualification typical of those used in production.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page20of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
2.10.5.4.3 The original WPQ’s are retained on file maintained by the Welding Engineer.
2.10.5.4 The welding Engineer will prepare a Qualified Welder’s List (Exhibit 8-7) and will be reviewed and approved
by the Welding Head the distributed to the Production Manager and QC Manager
2.10.5.5 EXPIRATION AND RENEWAL OF QUALIFICATION
The expiration and renewal of welder and welding operator qualification will be according to EN ISO 9606-1 for
welder and EN ISO 14732 for operator.
2.10.5.5.1 CONFIRMATION OF VALIDITY
The qualifications of a welder for a process will be confirmed every 6 months by the welding coordinator
2.10.5.5.2 REVALIDATION OF WELDER AND WELDING OPERATOR
Revalidation will be carried out by welding coordinator. The welder and welding operator will be retested every 3
years and 6 years respectively.
2.10.5.5.3 REVOCATION OF QUALIFICATION
When there is a specific reason to question a welder's ability to make welds that meet the product standard
(EN1090-2 EXC4) quality requirements, the qualifications that support the welding he is doing will be revoked.
2.10.5.5.4 MAINTING OF WELDER QUALIFICATION
The Welding Engineer determines from the Qualified Welder’s List (exhibit-08-05) when the welder’s qualification
shall expire, so as to ensure he performs production welding, or is re-qualified.
The Welding Engineer has submitted WPQ forms and Qualified Welder’s List (Exhibit 8-7) to the quality manager for
his review and acceptance for such welders before they perform production welding.
2.10.5.6 TACK WELD
Deposition conditions for tack welds will be included in the WPS. Tack welds will be made using a welding procedure
specification based on a suitable qualified welding procedure. The minimum length of the tack will be the lesser of
four times the thickness of the thicker part or 50 mm. welds with impermissible defects, such as cracks, will be
removed.
Tack welds, whether incorporated into the final weld or not, are made by qualified welders. If left in place, the ends
of each tack weld are ground to ensure complete fusion into the final weld. After preparation, each tack weld is
visually examined by the QC inspector, and if cracked or otherwise defective, is completely removed.
2.10.5.7 WELDING MATERIAL
8.9.1 All welding material is purchased received, stored and distributed as described in procedure ASF-QC-WCH-001 -
welding consumable control-prepared by welding engineer and approved by QC Manager. In the shop the welding
foreman is responsible for requisitioning materials form the stores. This material is stored locally and issued to the
welder by the foreman on the basis of the WPS.
2.10.5.6 PRODUCTION WELDING
The Fabrication Engineer verifies that all production welders are qualified for the performance essential variables to
be used, and the welding foreman is responsible for instructing the welders in the correct use of the WPSs listed for
each weld.
Each qualified welder is issued a unique alpha/numerical identification symbol by the Welding Engineer, by which
each weld made by a welder is identified by marking adjacent to each weld, and the identification to be recorded on
the NDT reports. When a welder leaves the company, his symbol shall not be reissued.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page21of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
Flow diagram for development and use of a WPS
Development of a preliminary pWPS
↓
Qualification of the welding procedure by a method according to 7.4.1 EN1090-2(WPQR)
↓
Preparing the WPS for production based on the relevant welding procedure qualification record
(WPQR)
↓
Use of the WPS for the first 5 welds in production with NDT extent according to 12.4.2.2 EN1090-2
↓
Use of the WPS after the first 5 welds in production with NDT extent according to 12.4.2.3 EN1090-2 EXC-4
2.10.6 INSPECTION AFTER WELDING
2.10.6.1 GENERAL
Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods will be selected in accordance with EN ISO 17635 as the basis for the
inspection and test plan (ITP). NDT, with the exception of visual inspection, will be performed by personnel qualified
according to EN ISO 9712 level 2.
2.10.6.2 NDT PROCEDURES
1. All NDT is performed using Written Procedures that are prepared and approved personnel qualified according to
EN ISO 9712 level 2.
2. When procedures are detailed enough to provide the technique to meet the general principles given in EN ISO
17635 and with the requirements of the below standard particular to each method, they are approved by the quality
manager or his designee of the revision status with his signature and date.
a) penetrant testing (PT) according to EN ISO 3452-1;
b) magnetic particle inspection (MT) according to EN ISO 17638;
c) ultrasonic testing (UT) according to EN ISO 17640 and EN ISO 23279 or EN ISO 13588;
d) radiographic testing (RT) according to the EN ISO 17636 series
3. All NDT procedures are submitted to the client for his acceptance. After NDT procedures are accepted by the
client, the QA Manager shall distribute controlled copies to all NDT personnel qualified in those disciplines.
2.10.6.3 ACCEPTANCE CRITERIA
Acceptance criteria of Welded components will be mentioned at the ITP, NDT procedure and inspection reports and
it shall comply with the below requirements, unless otherwise specified:
a) EN ISO 5817 quality level B, for visual inspection.
b) ISO 23277 quality level 2X, for penetrant test.
c) ISO 23278 quality level 2X, for magnetic particle test.
d) ISO 10675-1 quality level 1, for radiographic test.
e) ISO 11666 quality level 2, for ultrasonic test.
f) For dimension test, EN1090-2 annex B for essential tolerance and functional tolerance (tabulated value
tolerance class 1 or alternative criterial EN13920 class CG)
2.10.7 CORRECTION OF WELD
Date: 29/05/2019 Page22of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
Repairs by welding will be carried out in accordance with the repair procedures ASF-QC-WRP-010 and it will be the
same WPS used for original weld. Corrected welds will be checked and will meet the requirements of the original
welds.
2.11 DURABILITY
All painting activities are performed using Written Procedure ASF-QC-PP-011 that are prepared and approved by
personnel qualified according to BGAS-CSWIP or equivalent. This procedure defines the minimum requirements
governing surface cleaning, the preparation and the application of corrosion protective paint systems on ferrous
steel alloys steel items to be applied for corrosion protection to withstand atmospheric corrosion in corrosion
categories C5-M, C5-H & C4 &C3 according to ISO 9223 and ISO12944-2.
Date: 29/05/2019 Page23of24 Issue:02
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION FPC MANUAL
2.12 CONTROL OF NON-CONFORMING PRODUCT
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION ensures that product which does not conform to product requirements is identified and
controlled to prevent its unintended use or delivery. The controls and related responsibilities and authorities for
dealing with nonconforming product are defined in the Control of Nonconforming Product procedure (G/G/255).
2.13 MEASUREMANT, ANALYSIS AND IMPROVEMENT
2.13.1 GENERAL
The company will plan and implement the monitoring, measurement; analysis and improvement processes needed
to demonstrate conformity of the product, to ensure conformity of the factory production control system and to
continually improve the effectiveness of the quality management system.
2.13.2 CUSTOMER COMPLAINTS
As one of the measurements of the performance of the quality management system,
ARAB STEEL FABRICATION monitors information relating to customer perception as to whether the organization has
fulfilled customer requirements. The method for obtaining and using this information is identified in the Customer
complaints and satisfaction (ASD-QP-9.1.2).
2.14 IMPROVEMENT
2.14.1 CORRECTIVE ACTION
The company will take action to eliminate the cause of nonconformities in order to prevent recurrence. Corrective
actions will be appropriate to the effects of the nonconformities encountered. (ASF-QP-10.2) procedure has been
established to define the requirements for;
i. Reviewing nonconformities (including customer complaints)
ii. Determining the causes of nonconformities.
iii. Evaluating the need for action to ensure that nonconformities do not recur.
iv. Determining and implementing action needed.
v. Records of the results of action taken.
vi. Reviewing corrective action taken.
2.14.2 PREVENTIVE ACTION
The company will determine action to eliminate the causes of potential nonconformities in order to prevent their
occurrence. (ASF-QP-10.2) procedure will ensure that the company can;
i. Determine potential nonconformities and their causes.
ii. Evaluate the need for action to prevent occurrence of nonconformities.
iii. Determining and implementing action needed.
iv. Establish and maintain records of results of action taken.
v. Review preventive action taken.
2.15 ATTACHEMENT
list of updated EN standards
Date: 29/05/2019 Page24of24 Issue:02
You might also like
- FPC ManualDocument15 pagesFPC ManualDavid SeeNo ratings yet
- FPC Manual PreviewDocument5 pagesFPC Manual PreviewIbrahim Levent AkkoyunluNo ratings yet
- Questionnaire Manufacturer Assessment PDFDocument27 pagesQuestionnaire Manufacturer Assessment PDFulasNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Qualification of Welders or Welding OperatorsDocument1 pageProcedure For Qualification of Welders or Welding OperatorsSatish KeskarNo ratings yet
- EN ISO 3834-2 (2021) (E) CodifiedDocument8 pagesEN ISO 3834-2 (2021) (E) CodifiedJózsef Hegedűs100% (1)
- DRAFT AS 3992:2019: Summary of Changes From As/Nzs 3992:2015Document18 pagesDRAFT AS 3992:2019: Summary of Changes From As/Nzs 3992:2015Osu AmpawanonNo ratings yet
- Iso 9712Document19 pagesIso 9712Daniel100% (1)
- BS 1724 (Bronze Welding by Gas)Document24 pagesBS 1724 (Bronze Welding by Gas)nandi_scrNo ratings yet
- Steel Construction: CE MarkingDocument20 pagesSteel Construction: CE MarkingMarshall BravestarNo ratings yet
- WPS ISO 15614-1 WeldNote MetricDocument1 pageWPS ISO 15614-1 WeldNote MetricVirgil SorcaruNo ratings yet
- Guide To ISO14731Document8 pagesGuide To ISO14731scandalthegoodNo ratings yet
- Iso 3834 1 2021Document10 pagesIso 3834 1 2021sosheyanNo ratings yet
- ISO 3834-2 Compliance Check List PDFDocument1 pageISO 3834-2 Compliance Check List PDFMichael TayactacNo ratings yet
- Filler Materials TestingDocument34 pagesFiller Materials TestingSunilNo ratings yet
- How To Carry Out Tack WeldingDocument2 pagesHow To Carry Out Tack WeldingwentropremNo ratings yet
- Model WopqDocument2 pagesModel WopqAnilkumarGopinathanNairNo ratings yet
- Iso 3834Document2 pagesIso 3834Jaay Vel0% (1)
- WeldingFabricatorCertificationScheme ISO3834Document11 pagesWeldingFabricatorCertificationScheme ISO3834Weld Bro Sandeep100% (1)
- Repair Dvs Supplement PDFDocument6 pagesRepair Dvs Supplement PDFGnana MoorthyNo ratings yet
- Steel Construction UKCA Marking v3Document20 pagesSteel Construction UKCA Marking v3ioancNo ratings yet
- WP-8.5.1-02 Role of RWCDocument3 pagesWP-8.5.1-02 Role of RWCNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Guidance To Prepare Wps PQR For WeldingDocument1 pageGuidance To Prepare Wps PQR For WeldingHamid MansouriNo ratings yet
- Iso 3834-5 2005Document14 pagesIso 3834-5 2005HARISH KUMAR B MEKINSNo ratings yet
- ISO - TR - 15608 - Welding Guide Line PDFDocument10 pagesISO - TR - 15608 - Welding Guide Line PDFDacher DanielNo ratings yet
- Visual Inspection - AWS & BS PDFDocument22 pagesVisual Inspection - AWS & BS PDFSelvakpm06No ratings yet
- CEN ISO TR 14745 (2015) (E) CodifiedDocument4 pagesCEN ISO TR 14745 (2015) (E) CodifiedacampanellajoaquimamNo ratings yet
- KGP-Flamme Cutting Proce For BEI PDFDocument4 pagesKGP-Flamme Cutting Proce For BEI PDFoomoomNo ratings yet
- WPS-6 Doc Rev00 On 17 Sept 2018 Final FormatDocument3 pagesWPS-6 Doc Rev00 On 17 Sept 2018 Final FormatSWARUP CHUGUGLENo ratings yet
- Conformity Assessment For The Execution of Steel & Aluminium StructuresDocument14 pagesConformity Assessment For The Execution of Steel & Aluminium StructuresJevgenijsKolupajevsNo ratings yet
- PBI-CCP-QA-0001 QA Welding Consumable Control ProcedureDocument15 pagesPBI-CCP-QA-0001 QA Welding Consumable Control ProcedureTadaya KasaharaNo ratings yet
- Welding Procedure Specification and Procedure Qualification RecordDocument2 pagesWelding Procedure Specification and Procedure Qualification RecordNatdanai NorawanNo ratings yet
- Production Planning RecordDocument1 pageProduction Planning RecordSatish Keskar100% (1)
- BS en Iso 8044-2020Document38 pagesBS en Iso 8044-2020ahmed sobhyNo ratings yet
- Tasks and Responsibilities of RWCDocument1 pageTasks and Responsibilities of RWCKDT100% (1)
- FactoryDocument72 pagesFactorywhitebrosNo ratings yet
- Iso 17640 2017 en PDFDocument11 pagesIso 17640 2017 en PDFTanveer Ahmed Quadri100% (1)
- QT2109958 - ITP For 1T-1201 Buffer Water Tank Itp PDFDocument3 pagesQT2109958 - ITP For 1T-1201 Buffer Water Tank Itp PDFGanesh EswaranNo ratings yet
- EN 15085 Part 5 - GaneshDocument36 pagesEN 15085 Part 5 - GaneshNiranjan Rajavel TigerNo ratings yet
- 6 Iso 03834-5-2021Document12 pages6 Iso 03834-5-2021bmqr100% (1)
- 4 Gerry McCarthy PDFDocument42 pages4 Gerry McCarthy PDFbharani dharanNo ratings yet
- Terms in Welding Standard en 15085Document6 pagesTerms in Welding Standard en 150850502raviNo ratings yet
- En15085 Guideline-Part2 2017-11Document22 pagesEn15085 Guideline-Part2 2017-11Quality MSIPLNo ratings yet
- ISO 9692-2-2024 Welding and Allied Processes. Types of Joint Preparation-Submerged Arc Welding of Steels (OCR)Document20 pagesISO 9692-2-2024 Welding and Allied Processes. Types of Joint Preparation-Submerged Arc Welding of Steels (OCR)ahugandkiss77071No ratings yet
- CE Marking ThesisDocument47 pagesCE Marking ThesisScott TrainorNo ratings yet
- 04.understanding of Iso 3834Document54 pages04.understanding of Iso 3834amit50% (2)
- En 13927 - 2003Document12 pagesEn 13927 - 2003gorkembaytenNo ratings yet
- SC Qual 145r4-10 Combined Document Finnish Proposal and Checklist DVS-Zert Germany ISO 3834 PDFDocument53 pagesSC Qual 145r4-10 Combined Document Finnish Proposal and Checklist DVS-Zert Germany ISO 3834 PDFAlienshowNo ratings yet
- Weldment Visual Inspection RequirementsDocument10 pagesWeldment Visual Inspection RequirementsKarthik P MuraliNo ratings yet
- Din en 15085 2Document24 pagesDin en 15085 2David Hoffman100% (1)
- CE Marking GuideDocument26 pagesCE Marking Guideshaggeruk100% (1)
- WPS & PQR - 2021Document82 pagesWPS & PQR - 2021Subramanian R100% (1)
- WPQR SBM 029Document3 pagesWPQR SBM 029HoJienHauNo ratings yet
- CE Marking of StructuralDocument31 pagesCE Marking of StructuralRavi ValiyaNo ratings yet
- Example Installer Factory Production Control System 04.04.13Document35 pagesExample Installer Factory Production Control System 04.04.13Scott TrainorNo ratings yet
- CBDD QAQC Manual (Rev G-2010Document18 pagesCBDD QAQC Manual (Rev G-2010lightsonsNo ratings yet
- Factory Production ControlDocument72 pagesFactory Production ControlDan Savin100% (1)
- Brilliant White Windows: FPC ManualDocument37 pagesBrilliant White Windows: FPC ManualGichuru RiriaNo ratings yet
- IPC-1720A July2014Document51 pagesIPC-1720A July2014RidwanNo ratings yet
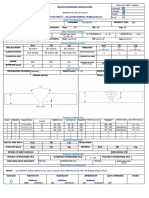
- Punching Validation-FACTORY 1Document3 pagesPunching Validation-FACTORY 1Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- (Iso/tr 17671-5) (Iso/tr 17671-6) (Iso/tr 17671-7) (Iso/tr 17671-8)Document1 page(Iso/tr 17671-5) (Iso/tr 17671-6) (Iso/tr 17671-7) (Iso/tr 17671-8)Ivan Briscoe100% (7)
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledSherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- 00 - 7563 SigmaTherm 450Document2 pages00 - 7563 SigmaTherm 450Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- NCR RegistryDocument5 pagesNCR RegistrySherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- Iso 4624 2002 en FR PDFDocument6 pagesIso 4624 2002 en FR PDFSherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- 04 - Material Receiving Inspection Procedure - Asf-Qc-Mri-001Document8 pages04 - Material Receiving Inspection Procedure - Asf-Qc-Mri-001Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- 01 - Asf-Qc-Itp-002Document4 pages01 - Asf-Qc-Itp-002Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- 04 - Product Traceability Procedure - Asf-Qc-Ptp-001Document5 pages04 - Product Traceability Procedure - Asf-Qc-Ptp-001Sherif Yehia0% (1)
- 02 - Calibration Procedure - Asf-Qc-Cal-001Document7 pages02 - Calibration Procedure - Asf-Qc-Cal-001Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- 04 - Material Receiving Inspection Procedure - Asf-Qc-Mri-001Document8 pages04 - Material Receiving Inspection Procedure - Asf-Qc-Mri-001Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- BS en ISO 5817 2014 Acceptance For NDTDocument38 pagesBS en ISO 5817 2014 Acceptance For NDTSherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- 02 - Calibration Procedure - Asf-Qc-Cal-001Document7 pages02 - Calibration Procedure - Asf-Qc-Cal-001Sherif YehiaNo ratings yet
- Easy Access Rules CS-P (Initial Issue)Document21 pagesEasy Access Rules CS-P (Initial Issue)bykr aknNo ratings yet
- Coto Coto: Standard Specifications For Road and Bridge Works For South African Road AuthoritiesDocument56 pagesCoto Coto: Standard Specifications For Road and Bridge Works For South African Road AuthoritiesTSHEPO DIKOTLANo ratings yet
- AMHQ1947 - Self Employed - Tailor - Version1 - 30 - 05 - 2019Document36 pagesAMHQ1947 - Self Employed - Tailor - Version1 - 30 - 05 - 2019Mayank Shekhar PareekNo ratings yet
- PBL 2.oDocument40 pagesPBL 2.oFE-B-247 DIPESH KUMAR YADAVNo ratings yet
- SAP Funds Management Configuration-FMDocument59 pagesSAP Funds Management Configuration-FMLiordi74% (27)
- PREN ISO 15614-2:2000: Testo Della NormaDocument35 pagesPREN ISO 15614-2:2000: Testo Della NormaAlessioNo ratings yet
- Astm B 606Document4 pagesAstm B 606Ryan LasacaNo ratings yet
- First Article Inspection 001ADocument21 pagesFirst Article Inspection 001AWalt PrystajNo ratings yet
- BS 5728 - 2 - 1984Document9 pagesBS 5728 - 2 - 1984surangaNo ratings yet
- Ansi MH16 1-2012Document71 pagesAnsi MH16 1-2012mloredoNo ratings yet
- مواصفات شركه الكهرباء السعوديهDocument24 pagesمواصفات شركه الكهرباء السعوديهahmedNo ratings yet
- Cut Sheet Rev.05Document196 pagesCut Sheet Rev.05Zeeshan YasinNo ratings yet
- Asme Section II A Sa-358 Sa-358mDocument10 pagesAsme Section II A Sa-358 Sa-358mAnonymous GhPzn1xNo ratings yet
- SAEP 357cDocument5 pagesSAEP 357cAnonymous 4IpmN7OnNo ratings yet
- 49 CFR Part 107Document63 pages49 CFR Part 107nvdinh511No ratings yet
- Deviation in Pharma: What Is A DeviationDocument2 pagesDeviation in Pharma: What Is A DeviationAshok KumarNo ratings yet
- QAP CI Flsnged PipesDocument11 pagesQAP CI Flsnged PipesNaveen NagisettiNo ratings yet
- LSTK D1003am1Document1 pageLSTK D1003am1VPNN 789No ratings yet
- Painting Procedure For CondenceDocument26 pagesPainting Procedure For CondenceNamta GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Is - 3038 - 2006Document10 pagesIs - 3038 - 2006sangitaghaisasNo ratings yet
- Graphic Detailing in CBE - AssignmentDocument8 pagesGraphic Detailing in CBE - AssignmentGenie LoNo ratings yet
- S-3000-3130-001 - 0-General Specification For Steel Structure and Miscellenous MaterialsDocument15 pagesS-3000-3130-001 - 0-General Specification For Steel Structure and Miscellenous MaterialsMessaoud Goutas100% (1)
- SRL Catalogue 2020-21Document288 pagesSRL Catalogue 2020-21akashh1981No ratings yet
- Typical Piping Project SequenceDocument13 pagesTypical Piping Project Sequencebusinessmannicholas100% (3)
- Chemical CleaningDocument32 pagesChemical Cleaningkae kae100% (2)
- Standard Auditing Nr4 EnglDocument16 pagesStandard Auditing Nr4 EnglPayal MittalNo ratings yet
- Procurement Methods (Student)Document43 pagesProcurement Methods (Student)Yeong Ern50% (2)
- Electrical Design GuidelineDocument101 pagesElectrical Design GuidelineTuấn Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 4005 Rev.3 - FS For FRP Cable TraysDocument5 pages4005 Rev.3 - FS For FRP Cable Trayssridar rNo ratings yet
- TDS - PP Yarn - Luban HP1102K - OQ PDFDocument2 pagesTDS - PP Yarn - Luban HP1102K - OQ PDFNazmul - Polymet SANo ratings yet