Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Neurotransmitter Chart-1
Uploaded by
Amanda Covert0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views1 pageThis document provides a chart summarizing key neurotransmitters:
1) It lists the main neurotransmitters (e.g. acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin), their functions (excitatory or inhibitory), and effects of deficits and surpluses.
2) Acetylcholine is involved in muscle contraction, attention, memory and learning. Deficits can cause Alzheimer's, while surpluses cause severe muscle spasms.
3) Dopamine regulates movement, attention and learning. Deficits result in Parkinson's and surpluses in schizophrenia and drug addiction.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a chart summarizing key neurotransmitters:
1) It lists the main neurotransmitters (e.g. acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin), their functions (excitatory or inhibitory), and effects of deficits and surpluses.
2) Acetylcholine is involved in muscle contraction, attention, memory and learning. Deficits can cause Alzheimer's, while surpluses cause severe muscle spasms.
3) Dopamine regulates movement, attention and learning. Deficits result in Parkinson's and surpluses in schizophrenia and drug addiction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
58 views1 pageNeurotransmitter Chart-1
Uploaded by
Amanda CovertThis document provides a chart summarizing key neurotransmitters:
1) It lists the main neurotransmitters (e.g. acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin), their functions (excitatory or inhibitory), and effects of deficits and surpluses.
2) Acetylcholine is involved in muscle contraction, attention, memory and learning. Deficits can cause Alzheimer's, while surpluses cause severe muscle spasms.
3) Dopamine regulates movement, attention and learning. Deficits result in Parkinson's and surpluses in schizophrenia and drug addiction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
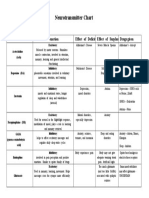
Neurotransmitter Chart
BI-HO?-091811
Neurotransmitter Function Effect of Deficit Effect of Surplus Additional Notes
Excitatory: Alzheimer’s Disease Severe Muscle Spasms
Released by motor neurons. Stimulates
Acetocholine
muscle contraction; involved in attention,
(Ach) memory, learning and general intellectual
functioning
Inhibitory: Parkinson’s Disease Schizophrenia
Dopamine (DA) pleasurable sensations involved in voluntary Drug Addiction
movement, attention, and learning
Inhibitory: Depression, Autism
moods and emotional states, hunger mood disorders
Serotonin regulation of sleep and wakefulness
(arousal)
Excitatory: Mental disorders, Anxiety
Used for arousal in the flight/fight response, especially depression
Norepinephrine (NE) modulation of mood, plays a role in learning
and memory retrieval
GABA Inhibitory: Anxiety, seizures, Sleep and eating
(gamma-aminobutyric helps to offset excitatory messages and tremors, and insomnia disorders
regulate daily sleep-wake cycles
acid)
Inhibitory: Body experiences pain Body may not give
Endorphins involved in pain perception and positive adequate warning about
emotions. Similar to opiate family of drugs. pain. Artificial highs
Excitatory: Too much glutamate
Used in memory, learning, movement. Helps (and too little GABA)
Glutamate messages cross the synapse more efficiently associated with epileptic
seizures
You might also like
- Neurotransmitter ChartDocument1 pageNeurotransmitter Chartmonster40lbs100% (2)
- ChartDocument1 pageChartAnggi Dwi PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Basic Human Needs, Pain, Comfort, Rest and SleepDocument2 pagesBasic Human Needs, Pain, Comfort, Rest and SleepFatima Asis100% (1)
- Dissertation - CD 2Document112 pagesDissertation - CD 2pavlov2No ratings yet
- 404 Veterinary Referral Hospital - BrochureDocument11 pages404 Veterinary Referral Hospital - BrochureJoanne FagnouNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument7 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorAsma Tariq JavedNo ratings yet
- Ch2neurotrans PDFDocument2 pagesCh2neurotrans PDFKentNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters Cuadro PDFDocument2 pagesNeurotransmitters Cuadro PDFCarina Castillo ValdiviezoNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter Cheat Sheet AP ReviewDocument2 pagesNeurotransmitter Cheat Sheet AP ReviewNathania DawitNo ratings yet
- PHARM250 Nervous System Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument15 pagesPHARM250 Nervous System Cheat Sheet: by ViaThư PhạmNo ratings yet
- PSYCHDocument2 pagesPSYCHJacquelyn HasiandaNo ratings yet
- Compre Ho PsychDocument114 pagesCompre Ho PsychRyan Mae Tutor GarciaNo ratings yet
- Psychia Notes Chapter 2 8Document43 pagesPsychia Notes Chapter 2 8Thaly ThalNo ratings yet
- Types of NeurotransmittersDocument4 pagesTypes of Neurotransmitterssophia0agulto-1No ratings yet
- PsychopharmacologyDocument171 pagesPsychopharmacologyVaib NigamNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 Mouse PartyDocument2 pagesActivity 4 Mouse PartyKolynNo ratings yet
- Neurobiologic Theories AND Psychopharmacology: BY Group 1Document15 pagesNeurobiologic Theories AND Psychopharmacology: BY Group 1PALEN, DONNA GRACE B.No ratings yet
- Chpt2INTROFall2023 Part TWO FeldmanDocument19 pagesChpt2INTROFall2023 Part TWO Feldmanzoe.johnston153No ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument5 pagesNeurotransmittersJoezerk Jhon Biel100% (1)
- 03 CNS AnsDocument153 pages03 CNS AnsMaria Arlyn Lacuña SagosoNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced Neurotransmitters and Abnormal BehaviorDocument3 pagesImbalanced Neurotransmitters and Abnormal BehaviorInah100% (1)
- Drugs Not Socially Accepted Drugs Socially Accepted Drugs Drug Abuse Drug Dependence Physiological Dependence Psychological DependenceDocument24 pagesDrugs Not Socially Accepted Drugs Socially Accepted Drugs Drug Abuse Drug Dependence Physiological Dependence Psychological Dependenceanette katrinNo ratings yet
- Continuation Lecture 2 CogpsyDocument3 pagesContinuation Lecture 2 CogpsyTracey GoldNo ratings yet
- Module IV: Central Nervous System MedicationsDocument4 pagesModule IV: Central Nervous System MedicationsVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology: Reviewer For Final Exam: Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesPharmacology: Reviewer For Final Exam: Nervous Systempatty janeNo ratings yet
- PsychopharmacologyDocument160 pagesPsychopharmacologyInah Sarita100% (1)
- NeurotransmitterDocument4 pagesNeurotransmitterGenblitz SoternoNo ratings yet
- Neurological Disorder: NeuronDocument8 pagesNeurological Disorder: NeuronMaica Lectana100% (2)
- Perez, Jayzyl B. (Module 2)Document6 pagesPerez, Jayzyl B. (Module 2)Jayzyl PerezNo ratings yet
- Neurotransmitter Function Examples of Malfunctions: Common Neurotransmitters - KEYDocument2 pagesNeurotransmitter Function Examples of Malfunctions: Common Neurotransmitters - KEYidjacobsNo ratings yet
- AnxiolyticsDocument5 pagesAnxiolyticsRawan AlshammaNo ratings yet
- JOEY - S PHARM LECTURES - Neuro pg1-8Document9 pagesJOEY - S PHARM LECTURES - Neuro pg1-8shivani patelNo ratings yet
- Unit 2-Biological Foundation of PsychologyDocument5 pagesUnit 2-Biological Foundation of PsychologyassmmNo ratings yet
- RHO Psych NtrsDocument1 pageRHO Psych NtrsKelli RuddNo ratings yet
- Psychotherapy Biomedical Techniques PresentationDocument92 pagesPsychotherapy Biomedical Techniques PresentationRhea Andrea UyNo ratings yet
- Nootropic: N/A N/ADocument18 pagesNootropic: N/A N/AKamille SchmittNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument12 pagesNeurotransmittersEya BaldostamonNo ratings yet
- Brandon Alexiz Ramos Baldovinos NeurotransmisoresDocument6 pagesBrandon Alexiz Ramos Baldovinos NeurotransmisoresBrandonNo ratings yet
- Cognium Syrup Pharmacological Properties SummaryDocument6 pagesCognium Syrup Pharmacological Properties SummaryMitzi MitchellNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases of Human Behavior (Neurotransmitters)Document3 pagesBiological Bases of Human Behavior (Neurotransmitters)Paula Maryvette Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Cognium Syrup Combination Rationale 2013Document10 pagesCognium Syrup Combination Rationale 2013Mitzi MitchellNo ratings yet
- Demerol DrugDocument2 pagesDemerol DrugMsOrange100% (1)
- NeurotransmittersDocument1 pageNeurotransmittersmegs13045No ratings yet
- Neurotransmitters Functions Effects Boost Its Production Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)Document4 pagesNeurotransmitters Functions Effects Boost Its Production Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA)Kent VillelaNo ratings yet
- Neurobiochemical Basis of Psychiatric DisorderDocument2 pagesNeurobiochemical Basis of Psychiatric DisorderMutya XDNo ratings yet
- Ateneo de Zamboanga University College of Nursing: Deliverables (Neurology)Document2 pagesAteneo de Zamboanga University College of Nursing: Deliverables (Neurology)Prince Mark BadilloNo ratings yet
- Yunida Farmakoterapi Obat-Obat SarafDocument18 pagesYunida Farmakoterapi Obat-Obat SarafrismNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Bio Asmuni CutDocument40 pagesWeek 3 Bio Asmuni CutNavanisha SekarNo ratings yet
- NeurotransmittersDocument8 pagesNeurotransmittersCamille CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonsDocument4 pagesAnti ParkinsonsMichaela BernadasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Brain and BehaviourDocument46 pagesChapter 3 Brain and Behaviour038 Suri HananNo ratings yet
- Information For Psychology ProjectDocument13 pagesInformation For Psychology ProjectElma CoradoNo ratings yet
- Psychoactive Drugs and Their EffectsDocument2 pagesPsychoactive Drugs and Their Effects85784703No ratings yet
- Brain Neurotransmitters.Document11 pagesBrain Neurotransmitters.salmankhan09215No ratings yet
- Some Drugs/ Medication Are Known To Act As Neurotransmitter. Try To Name at Least 5 of These Compounds and Identify What Responses Each Imitates in Some NeurotransmitterDocument2 pagesSome Drugs/ Medication Are Known To Act As Neurotransmitter. Try To Name at Least 5 of These Compounds and Identify What Responses Each Imitates in Some Neurotransmitterky apellidoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Muscle Relaxant, Antiseizure & Antiparkinson'sDocument12 pagesDrug Study - Muscle Relaxant, Antiseizure & Antiparkinson'sKristineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Psychotropic Drugs: Structure and Function of The BrainDocument9 pagesChapter 4: Psychotropic Drugs: Structure and Function of The BrainciaraNo ratings yet
- Aina Sabir:41635 Noshaba Ijaz:41062 Tabassum Ara:43220 Maryam Fatima:43480 Hafsa Khalid Awan:41191 Maria Tasaduq:41166Document21 pagesAina Sabir:41635 Noshaba Ijaz:41062 Tabassum Ara:43220 Maryam Fatima:43480 Hafsa Khalid Awan:41191 Maria Tasaduq:41166Hafsa AwanNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonsDocument4 pagesAnti ParkinsonsMichaela BernadasNo ratings yet
- Recept IDocument48 pagesRecept IEmilija Spasovska100% (1)
- 1102 Neurons and NeurotransmittersDocument28 pages1102 Neurons and NeurotransmittersDawud MuhammadNo ratings yet
- 3 Journal AssignmentDocument3 pages3 Journal AssignmentAmanda CovertNo ratings yet
- #2 Current EventDocument2 pages#2 Current EventAmanda CovertNo ratings yet
- 1-3 Epigenetics QuestionsDocument1 page1-3 Epigenetics QuestionsAmanda CovertNo ratings yet
- Tough Times: Amanda Covert Mrs. Seinko English 2nd Period 3rd May 2019Document1 pageTough Times: Amanda Covert Mrs. Seinko English 2nd Period 3rd May 2019Amanda CovertNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledAmanda CovertNo ratings yet
- Histology Practice Part 1Document22 pagesHistology Practice Part 1Amanda CovertNo ratings yet
- Score ReportDocument1 pageScore ReportAmanda CovertNo ratings yet
- Story of An HourDocument1 pageStory of An HourAmanda CovertNo ratings yet
- Full Ride EssayDocument5 pagesFull Ride EssayAmanda CovertNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Amanda Covert - Dream - Interpretation - Activity-1Document2 pagesKami Export - Amanda Covert - Dream - Interpretation - Activity-1Amanda CovertNo ratings yet
- Newton's LawsDocument4 pagesNewton's LawsAmanda CovertNo ratings yet
- General Bones IdentificationDocument1 pageGeneral Bones IdentificationAmanda CovertNo ratings yet
- Achalasia: History & ExamDocument28 pagesAchalasia: History & ExamMicija CucuNo ratings yet
- The Effects of A Shoulder Roll During LaryngosDocument11 pagesThe Effects of A Shoulder Roll During LaryngospaulaNo ratings yet
- Common Podiatry Diagnosis CodesDocument34 pagesCommon Podiatry Diagnosis CodesdarienDPM100% (2)
- Chapter 15 Lung Pathology ErnieDocument20 pagesChapter 15 Lung Pathology ErnieZandra Lyn AlundayNo ratings yet
- Elective Cases2aDocument156 pagesElective Cases2aMerlin MariandariNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Aortic RuptureDocument20 pagesTraumatic Aortic RuptureLisa MoyoNo ratings yet
- FP561 Suryakanta JayasinghDocument3 pagesFP561 Suryakanta Jayasinghsuryakanta jayasinghNo ratings yet
- Nplex Micro ChartDocument12 pagesNplex Micro Chartapi-26938624100% (2)
- Managing The Red Eye: Speaker NotesDocument46 pagesManaging The Red Eye: Speaker NotesAlina DănescuNo ratings yet
- National Filariasis Elimination ProgramDocument20 pagesNational Filariasis Elimination ProgramNaomi Cyden YapNo ratings yet
- 4 - Guidelines For HIV Care and Treatment in Infants and ChildrenDocument136 pages4 - Guidelines For HIV Care and Treatment in Infants and Childreniman_kundu2007756100% (1)
- Cervical Spine InjuriesDocument18 pagesCervical Spine InjuriesAnnapurna DangetiNo ratings yet
- Pleural Effusion - ClinicalKeyDocument13 pagesPleural Effusion - ClinicalKeyWialda Dwi rodyahNo ratings yet
- Neurocognitive Disorders: Ares Mari R. PadrejuanDocument33 pagesNeurocognitive Disorders: Ares Mari R. PadrejuanAres Mari PadrejuanNo ratings yet
- Gi DisordersDocument53 pagesGi DisordersJulie EstebanNo ratings yet
- DRUG FluimucilDocument1 pageDRUG FluimucilrholiboiNo ratings yet
- Head and Neck Seminal Papers From Tata HospitalDocument29 pagesHead and Neck Seminal Papers From Tata HospitalSudhir NairNo ratings yet
- Essay - Child DevelopmentDocument2 pagesEssay - Child DevelopmentTina AroraNo ratings yet
- Ent SpottersDocument18 pagesEnt SpottersJithin Gopal100% (1)
- International Classification of Diseases 9Document6 pagesInternational Classification of Diseases 9Carlos Alberto ZepedaNo ratings yet
- Acute Viral Syndrome: Case Presentation OnDocument22 pagesAcute Viral Syndrome: Case Presentation OnSafoora RafeeqNo ratings yet
- CA Breast New ChangedDocument72 pagesCA Breast New Changedbenak shivalingappaNo ratings yet
- Spondylosis Information LeafletDocument3 pagesSpondylosis Information LeafletAnis Azizah MogilNo ratings yet
- WBC DisorderDocument24 pagesWBC DisorderNirav SharmaNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Report of Hiv and Toxoplasma Gondii Occurrence in Pregnant Women From MozambiqueDocument5 pagesPreliminary Report of Hiv and Toxoplasma Gondii Occurrence in Pregnant Women From MozambiqueBla BlaNo ratings yet
- Psycho Pharmacology: by Dr. Alit Aryani SPKJDocument28 pagesPsycho Pharmacology: by Dr. Alit Aryani SPKJMienaNo ratings yet
- TergecefDocument2 pagesTergecefianecunar100% (3)
- Widiger 1991Document7 pagesWidiger 1991Ekatterina DavilaNo ratings yet