Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cellular Respiration - Labster Theory
Cellular Respiration - Labster Theory
Uploaded by
pond_1993Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cellular Respiration - Labster Theory
Cellular Respiration - Labster Theory
Uploaded by
pond_1993Copyright:
Available Formats
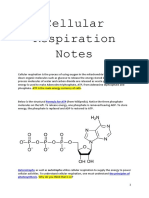
Cellular respiration - Labster Theory 14/4/2566 BE 01:29
Cellular respiration is the process by which animals convert food into a type of energy usable by their cells, known as ATP. The first
step of cellular respiration is called glycolysis and results in the formation of pyruvate.
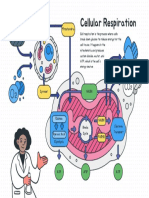
Aerobic cellular respiration occurs when oxygen is present, and pyruvate will enter the Krebs cycle allowing the electron transport
chain to proceed. Anaerobic cellular respiration does not require the presence of oxygen and pyruvate will undergo lactic acid
fermentation. Comparing the result of aerobic and anaerobic respiration highlights why oxygen is so important for cellular respiration.
Carbohydrates
Aerobic
Anaerobic
Glucose Respiration
Respiration
Glycolysis
Lactic
Acid Pyruvate
LacticAcid ElectronTransportChain
Nucleus AcetylCoA
Fermentation
Krebs
Cytosol
Cycle
Mitochondria
Figure 1: Cellular respiration steps.
Cellular respiration is the process that converts the energy from chemical bonds in food to a form of energy that the cell can use,
ATP.
This article was last modified: Nov. 8, 2022, 8:02 a.m.
Powered by django-wiki, an open source application under the GPLv3 license. Let knowledge be the cure.
Terms of Service Privacy Policy Testimonial FAQ Pricing Careers Contact Blog
https://theory.labster.com/cellular-respiration/ Page 1 of 1
You might also like
- Cellular Respiration: An Overview: Lesson SummaryDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration: An Overview: Lesson Summaryandrea plalu33% (6)
- CRH Cellular Respiration (Principles) - Measure Energy Consumption During Exercise Lab ManualDocument6 pagesCRH Cellular Respiration (Principles) - Measure Energy Consumption During Exercise Lab ManualVanesha AnesNo ratings yet
- Biology RespirationDocument20 pagesBiology Respirationhafizah_90100% (2)
- Cellular-Respiration-Group4-Genbio 20231205 011046 0000Document18 pagesCellular-Respiration-Group4-Genbio 20231205 011046 0000Clarisse De GuiaNo ratings yet
- Basis For Comparison: Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic RespirationDocument3 pagesBasis For Comparison: Aerobic Respiration Anaerobic RespirationLia JeonNo ratings yet
- Place Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideDocument52 pagesPlace Homework Into The Basket. 2. Pick Up Powerpoint GuideADR GARDIOLANo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration Notescsujithan100% (1)
- CellRespi 2Document21 pagesCellRespi 2Nudiya SappalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 12 Cellular RespirationDocument57 pagesLesson 12 Cellular RespirationNhelle IronVoltoxNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration - ReviewerDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration - ReviewerJoyce Cañal100% (1)
- Resporation WorksheetDocument6 pagesResporation WorksheetRosty Ann GrabilloNo ratings yet
- CS100 G1 Respiration in PlantsDocument80 pagesCS100 G1 Respiration in PlantsJanrick CabuñasNo ratings yet
- Process of Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesProcess of Cellular RespirationAlliah Vance O. CapuzNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument13 pagesCellular RespirationMohammedNo ratings yet
- BioDocument18 pagesBiomarcneil773No ratings yet
- 06 Lecture Presentation PDFDocument23 pages06 Lecture Presentation PDFJavier CorralNo ratings yet
- The Aerobic SystemDocument13 pagesThe Aerobic SystemTAIJOHNAE HENRYNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesCellular RespirationRavi Inder SinghNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument3 pagesBIOENERGETICSJaemsNo ratings yet
- CN in EARTH ANF LIFE - 12Document1 pageCN in EARTH ANF LIFE - 12Andro RomanoNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument16 pagesCellular Respiration백지연No ratings yet
- 6단원Document16 pages6단원백지연No ratings yet
- Lec 11,12 Energy of Life RMDocument9 pagesLec 11,12 Energy of Life RMEnmuskNo ratings yet
- Biology: Biochemistry, Genetics and Evolutionary TrendsDocument20 pagesBiology: Biochemistry, Genetics and Evolutionary TrendsRosalyn Marie SugayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document51 pagesChapter 6Naufal QaweimNo ratings yet
- 1.4 RespirationDocument11 pages1.4 RespirationPema GaleyNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument6 pagesCellular RespirationMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument33 pagesCellular RespirationAndres MarotoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 HomeworkDocument8 pagesChapter 5 HomeworkKvn4N6No ratings yet
- Biology Revision - NewDocument14 pagesBiology Revision - NewHamza TahaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio. 2ND Quarter RespirationDocument3 pagesGen Bio. 2ND Quarter RespirationChrislyn Eds Javier AcobNo ratings yet
- After Photosynthesis,: Glucose or Food Molecule Will Be Delivered To The Cells of The PlantsDocument10 pagesAfter Photosynthesis,: Glucose or Food Molecule Will Be Delivered To The Cells of The PlantsMelanie Tagudin TrinidadNo ratings yet
- 10.1 BiologyDocument3 pages10.1 Biologyminda.eslteacherNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 5Document14 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 5Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- Chap7F4 Cellular RespirationDocument45 pagesChap7F4 Cellular RespirationSyahir NajmiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Science Pink Lined StyleDocument1 pageCellular Respiration Science Pink Lined StyleMaria AlejandraNo ratings yet
- Q2 W1 W2 W3 General Biology 1Document8 pagesQ2 W1 W2 W3 General Biology 1Samantha ManibogNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Cellular Respiration 1Document6 pagesChapter 15 Cellular Respiration 1zeemboyzNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument10 pagesCellular RespirationXavier LecarosNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration DefinitionDocument9 pagesCellular Respiration Definitionmaria genioNo ratings yet
- Q2 L4 Science 9 Cellular RespirationDocument19 pagesQ2 L4 Science 9 Cellular RespirationRaph tsuNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration 1Document2 pagesCellular Respiration 1Naledi Noxolo BhenguNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Cellular RespirationDocument63 pagesWeek 5 Cellular RespirationtahaberrkayNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesCellular RespirationAirene JabagatNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respirationالتنفس الخلويDocument9 pagesCellular Respirationالتنفس الخلويIraqiNo ratings yet
- Mil4ch32 (How Animals Harvest)Document10 pagesMil4ch32 (How Animals Harvest)Muhammad AsadkhanNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: How We Obtain Chemical Energy From FoodDocument28 pagesCellular Respiration: How We Obtain Chemical Energy From FoodJanet LarideNo ratings yet
- Coupled Reaction ProcessesDocument6 pagesCoupled Reaction Processesmamariljasmine03No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument21 pagesCellular Respirationlovedovebirdqueenbee13No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cellular Respiration and FermentationDocument68 pagesChapter 5 Cellular Respiration and Fermentationbm-3272No ratings yet
- Cell Respiration Glycoloysis and Acetyl CoADocument30 pagesCell Respiration Glycoloysis and Acetyl CoAJ15No ratings yet
- General MicrobiologyDocument16 pagesGeneral MicrobiologyNecromancer Gtr75 GtNo ratings yet
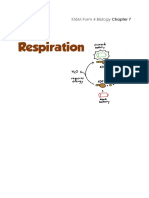
- # Form 4 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration (Student Copy)Document7 pages# Form 4 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration (Student Copy)VELLAMMAH A/P NARAYANASAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Pathways PDFDocument18 pagesBiochemical Pathways PDFJúlio Gabriel Queiroz dos SantosNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 - Power Point Presentation (Group 8)Document14 pagesGeneral Biology 1 - Power Point Presentation (Group 8)Archan Dom ReyesNo ratings yet
- Chapt06 Lecture 1Document45 pagesChapt06 Lecture 1vishwa kilariNo ratings yet
- Presentation 5Document15 pagesPresentation 5Rahanie Gadungan PajijiNo ratings yet
- 1991 - Badya, Pasha - A Pollen Calendar For Chittagong University Campus, Chittagong (Bangladesh)Document7 pages1991 - Badya, Pasha - A Pollen Calendar For Chittagong University Campus, Chittagong (Bangladesh)pond_1993No ratings yet
- 1986 - Plebani Et Al. - An Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay For Cow's Milk Protein-Specific IgE Using Biotinylated AntigenDocument6 pages1986 - Plebani Et Al. - An Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay For Cow's Milk Protein-Specific IgE Using Biotinylated Antigenpond_1993No ratings yet
- 1990 - Perez Et Al. - cDNA Cloning and Immunological Characterization of The Rye Grass Allergen Lol P IDocument7 pages1990 - Perez Et Al. - cDNA Cloning and Immunological Characterization of The Rye Grass Allergen Lol P Ipond_1993No ratings yet
- 1992 - McQueen-Mason, Durachko, Cosgrove - Two Endogenous Proteins That Induce Cell Wall Extension in PlantsDocument10 pages1992 - McQueen-Mason, Durachko, Cosgrove - Two Endogenous Proteins That Induce Cell Wall Extension in Plantspond_1993No ratings yet
- 1989 - Cookson Et Al. - Linkage Between Immunoglobulin E Responses Underlying Asthma and Rhinitis and Chromosome 11qDocument4 pages1989 - Cookson Et Al. - Linkage Between Immunoglobulin E Responses Underlying Asthma and Rhinitis and Chromosome 11qpond_1993No ratings yet
- 1982 - Bayne, Mathews - Determination of Total IgE by ELISA in Tubes and Plates Compared With PRISTDocument3 pages1982 - Bayne, Mathews - Determination of Total IgE by ELISA in Tubes and Plates Compared With PRISTpond_1993No ratings yet
- 1990 - O'Kennedy Et Al. - Experimental Section A Review of Enzyme-Immunoassay and A Description of A Competitive Enzyme-Linked ImmunosorbentDocument5 pages1990 - O'Kennedy Et Al. - Experimental Section A Review of Enzyme-Immunoassay and A Description of A Competitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbentpond_1993No ratings yet
- 1991 - Chang Et Al. - Analysis of Allergenic Components of Bermuda Grass Pollen by Monoclonal AntibodiesDocument10 pages1991 - Chang Et Al. - Analysis of Allergenic Components of Bermuda Grass Pollen by Monoclonal Antibodiespond_1993No ratings yet
- 1989 - Gierasch - Signal SequencesDocument8 pages1989 - Gierasch - Signal Sequencespond_1993No ratings yet
- 1983 - Ruffin Et Al. - The Effects of Some Environmental Gaseous Pollutants On Pollen Wall Proteins of Certain Airborne Pollen Grains A PRDocument6 pages1983 - Ruffin Et Al. - The Effects of Some Environmental Gaseous Pollutants On Pollen Wall Proteins of Certain Airborne Pollen Grains A PRpond_1993No ratings yet
- 1976 - Johansson, Berglund, Kjellman - Comparison of IgE Values As Determined by Different Solid Phase Radioimmunoassay MethodsDocument9 pages1976 - Johansson, Berglund, Kjellman - Comparison of IgE Values As Determined by Different Solid Phase Radioimmunoassay Methodspond_1993No ratings yet
- 1982 - Platts-Mills Et Al. - Reduction of Bronchial Hyperreactivity During Prolonged Allergen AvoidanceDocument4 pages1982 - Platts-Mills Et Al. - Reduction of Bronchial Hyperreactivity During Prolonged Allergen Avoidancepond_1993No ratings yet
- 1981 - Norman, Lichtenstein, Marsh - Studies On Allergoids From Naturally Occurring Allergens IV. Efficacy and Safety of Long-Term AllergoidDocument11 pages1981 - Norman, Lichtenstein, Marsh - Studies On Allergoids From Naturally Occurring Allergens IV. Efficacy and Safety of Long-Term Allergoidpond_1993No ratings yet
- 1981 - Merrett - The Radioallergosorbent Test (RAST)Document6 pages1981 - Merrett - The Radioallergosorbent Test (RAST)pond_1993No ratings yet
- 1953 - Samter, Kofoed, Pieper - A Factor in Lungs of Anaphylactically Shocked Guinea Pigs Which Can Induce Eosinophilia in Normal AnimalsDocument13 pages1953 - Samter, Kofoed, Pieper - A Factor in Lungs of Anaphylactically Shocked Guinea Pigs Which Can Induce Eosinophilia in Normal Animalspond_1993No ratings yet
- 1968 - Bennich Et Al. - Immunoglobulin E A New Class of Human ImmunoglobulinDocument2 pages1968 - Bennich Et Al. - Immunoglobulin E A New Class of Human Immunoglobulinpond_1993No ratings yet
- 1976 - Ohman Et Al. - Allergens of Mammalian OriginDocument11 pages1976 - Ohman Et Al. - Allergens of Mammalian Originpond_1993No ratings yet
- 1972 - Parish - Eosinophilia. II. Cutaneous Eosinophilia in Guinea-Pigs Mediated by Passive Anaphylaxis With IgGl or Reagin, and Antigen-AntDocument16 pages1972 - Parish - Eosinophilia. II. Cutaneous Eosinophilia in Guinea-Pigs Mediated by Passive Anaphylaxis With IgGl or Reagin, and Antigen-Antpond_1993No ratings yet
- 9510 n จDocument4 pages9510 n จpond_1993No ratings yet
- 1961 - Voorhorst - The Eosinophil Cell and Its Role in Allergy and in InfectionDocument20 pages1961 - Voorhorst - The Eosinophil Cell and Its Role in Allergy and in Infectionpond_1993No ratings yet
- 1951 - Herxheimer - Induced Asthma in ManDocument5 pages1951 - Herxheimer - Induced Asthma in Manpond_1993No ratings yet
- 9510ưưDocument5 pages9510ưưpond_1993No ratings yet
- 79 1 2Document16 pages79 1 2pond_1993No ratings yet
- Swet 2Document4 pagesSwet 2pond_1993No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: What Is It, Its Purpose, and More (Osmosis)Document2 pagesCellular Respiration: What Is It, Its Purpose, and More (Osmosis)pond_1993No ratings yet
- 07Document6 pages07pond_1993No ratings yet
- L3-SCBM343-Pathology of RBC WBC 4p-NKDocument22 pagesL3-SCBM343-Pathology of RBC WBC 4p-NKpond_1993No ratings yet
- Scjrv014n003a005 PDFDocument9 pagesScjrv014n003a005 PDFpond_1993No ratings yet
- Discover The Difference Between Glycolysis and Krebs CycleDocument5 pagesDiscover The Difference Between Glycolysis and Krebs Cyclepond_1993No ratings yet
- L4 - SCBM 343-4 Lab CBC-WJDocument14 pagesL4 - SCBM 343-4 Lab CBC-WJpond_1993No ratings yet