Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Increased Intracranial Pressure
Uploaded by
Nozomi Yuki0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThis document discusses increased intracranial pressure (ICP), which is a rise in pressure around the brain caused by factors like cerebral edema or a brain tumor. It outlines steps for assessing ICP such as obtaining vital signs, evaluating pupil response and level of consciousness, and using electronic monitoring. Signs of increased ICP include headache, vomiting, and changes to vital signs, pupil response, or level of consciousness. Treatment focuses on identifying and addressing the underlying cause while also taking steps to lower ICP such as keeping the head elevated and carefully monitoring breathing and body position. Medications like corticosteroids and osmotic diuretics may also be used.
Original Description:
Original Title
INCREASED INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses increased intracranial pressure (ICP), which is a rise in pressure around the brain caused by factors like cerebral edema or a brain tumor. It outlines steps for assessing ICP such as obtaining vital signs, evaluating pupil response and level of consciousness, and using electronic monitoring. Signs of increased ICP include headache, vomiting, and changes to vital signs, pupil response, or level of consciousness. Treatment focuses on identifying and addressing the underlying cause while also taking steps to lower ICP such as keeping the head elevated and carefully monitoring breathing and body position. Medications like corticosteroids and osmotic diuretics may also be used.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure
Uploaded by
Nozomi YukiThis document discusses increased intracranial pressure (ICP), which is a rise in pressure around the brain caused by factors like cerebral edema or a brain tumor. It outlines steps for assessing ICP such as obtaining vital signs, evaluating pupil response and level of consciousness, and using electronic monitoring. Signs of increased ICP include headache, vomiting, and changes to vital signs, pupil response, or level of consciousness. Treatment focuses on identifying and addressing the underlying cause while also taking steps to lower ICP such as keeping the head elevated and carefully monitoring breathing and body position. Medications like corticosteroids and osmotic diuretics may also be used.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
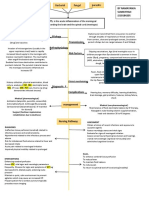
INCREASED Evaluating pupil response
DILATED PUPIL
INTRACRANIAL PRESSURE
(ICP)
a rise in pressure around the brain.
in the Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
volume, Blood entering the CSF,
Cerebral Edema, Head trauma or
Infection, space-occupying lesions Determining LOC
such as brain tumors, or the
development of Hydrocephalus or
Guillain-Barré Syndrome.
ASSESSMENT
Obtaining Vital Signs
Evaluating pupil response
Determining levels of consciousness
Motor and Sensory function
Electronic Monitoring (Subarachnoid
screw, Epidural Sensor, Intraventricular
catheter, Intraparenchymal
monitoring) SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
VITAL SIGNS Increased head circumference
Increase Temperature Fontanelle changes
Decrease Pulse Vomiting
Eye Changes
Decrease Respiratory
Vital Sign Changes
Increase Pulse Pressure
Pain (Headache)
Mentation (Irritability)
SIGNS OF INCREASED ICP IN INFANTS
Separated sutures of the skull
Fontanel bulge outward
THERAPEUTIC MANAGEMENT
The cause of ICP must be identified
and remedied as quickly as possible to
prevent brain injury or compression to
the brain-stem, which can lead to
both cardiac and respiratory failure.
Actions such as coughing, vomiting,
and sneezing and rapid administration
of intravenous (IV) fluid increase ICP.
When a parent is burping an infant
after a feeding, caution them to be
careful not to put pressure on the
jugular veins because this is another
action that increases ICP.
Placing a child in a semi-Fowler's
position (use an infant seat for babies).
MEDICAL INTERVENTION
Corticosteroid
o Dexamethasone (Decadron)
Effectiveness:
o Lowering ICP
o Reduce cerebral Edema
Osmotic Diuretics
o Mannitol
Effectiveness:
o Reduces pressure
You might also like
- Med Surg BundleDocument112 pagesMed Surg BundleCynthia Leyva100% (3)
- NBME CMS Forms NotesDocument4 pagesNBME CMS Forms NotesJack Guccione100% (7)
- CNS PDFDocument412 pagesCNS PDFSami Juggy G100% (1)
- ICP Head InjuryDocument57 pagesICP Head InjuryWengel RedkissNo ratings yet
- Med Surge 3 p2Document5 pagesMed Surge 3 p2Ivy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Notes - Moodle/Text: Paediatric Emergencies (Textbook Ch.5)Document6 pagesPaediatric Notes - Moodle/Text: Paediatric Emergencies (Textbook Ch.5)Jana AldourNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial Pressure (IICP)Document2 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure (IICP)Giselle Chloe Baluya icoNo ratings yet
- Birth AsphyxiaDocument32 pagesBirth AsphyxiaSANCHAYEETANo ratings yet
- NCM 116: Neurologic Dysfunctions: Joyce Bernadette P. Andot - Anna Delle Nicole P. Aranding, BSN-IIIDocument46 pagesNCM 116: Neurologic Dysfunctions: Joyce Bernadette P. Andot - Anna Delle Nicole P. Aranding, BSN-IIIMercy Anne EcatNo ratings yet
- MCQ in Implant Dentistry (2016) PDFDocument235 pagesMCQ in Implant Dentistry (2016) PDFAhmed Fikry100% (1)
- Intracranial Hypertension or Increased ICPDocument11 pagesIntracranial Hypertension or Increased ICPRomina Irish MatutinoNo ratings yet
- Thyroid ReportDocument105 pagesThyroid ReportAARVNo ratings yet
- Neuro Reviewer 2Document33 pagesNeuro Reviewer 2joanneNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial PressureDocument10 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressureapi-3822433100% (10)
- Cranial Base GrowthDocument100 pagesCranial Base Growtharvind junejaNo ratings yet
- Dragos Cirneci Ambiguitate Anxietate 2013Document9 pagesDragos Cirneci Ambiguitate Anxietate 2013dgavrileNo ratings yet
- Two Cortical Systems For Memory-Guided BehaviourDocument11 pagesTwo Cortical Systems For Memory-Guided Behaviourrigii nti100% (1)
- Increased Intracranial PressureDocument1 pageIncreased Intracranial PressureFredie O HadjimudinNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial Pressure and Seizure Feb 14Document2 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure and Seizure Feb 14anime listNo ratings yet
- Bacterial MeningitisDocument2 pagesBacterial Meningitisjennielunay00No ratings yet
- Neurological Disorders Key NotesDocument31 pagesNeurological Disorders Key NotesHannah aswiniNo ratings yet
- PHN Health TeachingDocument3 pagesPHN Health TeachingJeyser T. GamutiaNo ratings yet
- MeningococcemiaDocument4 pagesMeningococcemiaMenly Susada100% (1)
- Lesson 5 - Altered PerceptionDocument10 pagesLesson 5 - Altered PerceptionSTEFFANIE VALE BORJANo ratings yet
- Head Injury: Closed Head Injury EG: Falls, Motor Vehicle Crashes, Bicycle InjuriesDocument13 pagesHead Injury: Closed Head Injury EG: Falls, Motor Vehicle Crashes, Bicycle InjuriesJudy HandlyNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Pediatric Neurological Function: Lisa Musso, ARNP, MN, CPNP Seattle UniversityDocument66 pagesAlterations in Pediatric Neurological Function: Lisa Musso, ARNP, MN, CPNP Seattle Universityfadumo65No ratings yet
- Ii - Pedia-Rn DisordersDocument15 pagesIi - Pedia-Rn DisordersAnnie Rose Dorothy MamingNo ratings yet
- Nyeri Pada NeonatusDocument38 pagesNyeri Pada NeonatusRey AlwiwikhNo ratings yet
- 322 Convulsions and Status EpilepticusDocument7 pages322 Convulsions and Status EpilepticusMohammad Irfan khanNo ratings yet
- Pediatric NursingDocument14 pagesPediatric NursingJoanne PaulineNo ratings yet
- NCM 116 - Neurologic Disorders (MODULE 1)Document6 pagesNCM 116 - Neurologic Disorders (MODULE 1)Meryville JacildoNo ratings yet
- Head TraumaDocument54 pagesHead TraumaVidelia ArlitaNo ratings yet
- Headache in ChildhoodDocument28 pagesHeadache in ChildhoodAndreea FilaretaNo ratings yet
- Raised Intracranial Pressure: BY DR - Tallat Pervaiz AliDocument37 pagesRaised Intracranial Pressure: BY DR - Tallat Pervaiz AliCh Khurram HasnainNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial PressureDocument3 pagesIncreased Intracranial PressureDaryll Jeremy VirtudesNo ratings yet
- COURSE TASK 1 Increased ICP POLICIOS, SHARMAINE ANNE M. BSN 3Y2 - 3ADocument2 pagesCOURSE TASK 1 Increased ICP POLICIOS, SHARMAINE ANNE M. BSN 3Y2 - 3ASHARMAINE ANNE POLICIOS100% (1)
- Samson, BSN-4F (Nursing Responsibilities, Meningitis)Document3 pagesSamson, BSN-4F (Nursing Responsibilities, Meningitis)JONATHAN LYLE QUIBILAN. SAMSONNo ratings yet
- TBI PathophysioClinicalManifestationsDocument7 pagesTBI PathophysioClinicalManifestationsJan Philippe BelandoNo ratings yet
- Neonatal SeizuresDocument4 pagesNeonatal SeizuresSerag EdeenNo ratings yet
- Guillain - Barre SyndromeDocument63 pagesGuillain - Barre SyndrometheamaciasNo ratings yet
- Increased Intracranial Pressure Is A Rise in TheDocument3 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure Is A Rise in TheMark Anthony Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Cefalea Por Hipotensión.Document8 pagesCefalea Por Hipotensión.Farid Santiago Abedrabbo LombeydaNo ratings yet
- Case PBL ICM2 Week 3 Jumat-TSDocument33 pagesCase PBL ICM2 Week 3 Jumat-TSsylvia haryantoNo ratings yet
- Ijccm 23 s129Document7 pagesIjccm 23 s129Sonu AntonyNo ratings yet
- Ob2 Sas 34Document6 pagesOb2 Sas 34????No ratings yet
- COMA Dan Penurunan KesadaranDocument40 pagesCOMA Dan Penurunan KesadaranAhmad Shafwan NatsirNo ratings yet
- Neurologic AL Disorders: Aka: CephalgiaDocument19 pagesNeurologic AL Disorders: Aka: CephalgiaNicole AlcoberNo ratings yet
- Case 6Document41 pagesCase 6Christian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Massive Intracranial Fluid CollectionDocument29 pagesMassive Intracranial Fluid CollectionAiza QenNo ratings yet
- Iloilo Doctors' College College of Nursing West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo City Study Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesIloilo Doctors' College College of Nursing West Avenue, Molo, Iloilo City Study Guide Questionseloisa lyn pizNo ratings yet
- Meningitis and Fractures Concept MapDocument4 pagesMeningitis and Fractures Concept MapNamayanja SumayiyahNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesAlterations in Nervous SystemVIVIEN CONSIGNANo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument3 pagesHead InjuryItzel MahiyaNo ratings yet
- Life-Threatening Headaches in Children: Clinical Approach and Therapeutic OptionsDocument7 pagesLife-Threatening Headaches in Children: Clinical Approach and Therapeutic OptionsdelilamhrnNo ratings yet
- NeurologyDocument42 pagesNeurologyPierre BenardNo ratings yet
- Spontaneously, Without A Known CauseDocument6 pagesSpontaneously, Without A Known CauseAnalyn SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Nervous System AlterationsDocument45 pagesNervous System AlterationsMajesty ParkerNo ratings yet
- LP 02 - HeadacheDocument29 pagesLP 02 - HeadacheIoana CozmaNo ratings yet
- By Gilang Nispu SaputraDocument37 pagesBy Gilang Nispu SaputraMarogi Al AnsorianiNo ratings yet
- Increased ICPDocument24 pagesIncreased ICPNab MughalNo ratings yet
- Head Injury: Ibrahim Mahguob, M.DDocument44 pagesHead Injury: Ibrahim Mahguob, M.DAmir SharifNo ratings yet
- Coma and Related Disorders of ConsciousnessDocument80 pagesComa and Related Disorders of ConsciousnessIris BakerNo ratings yet
- TBI FinalDocument28 pagesTBI Finalawais mpNo ratings yet
- ICP and TIADocument4 pagesICP and TIANurse AmbassadorsNo ratings yet
- PATHOPISIOLOGYDocument2 pagesPATHOPISIOLOGYjennielunay00No ratings yet
- Funda AnaphyDocument36 pagesFunda AnaphyNozomi YukiNo ratings yet
- Advance Cardiac Life Support (ACLS)Document13 pagesAdvance Cardiac Life Support (ACLS)Nozomi YukiNo ratings yet
- When Are Focused Assessments ConductedDocument26 pagesWhen Are Focused Assessments ConductedNozomi YukiNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesDischarge PlanNozomi YukiNo ratings yet
- Basic Cardiac Life SupportDocument3 pagesBasic Cardiac Life SupportNozomi YukiNo ratings yet
- Comisuritis Posterior 2Document8 pagesComisuritis Posterior 2VORTIZNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Ch. 9 The Senses NotesDocument7 pagesAnatomy Ch. 9 The Senses Notesprincepalestine100% (1)
- Brain WorksheetsDocument6 pagesBrain WorksheetsInno RashNo ratings yet
- Learners Guide: Shb30416 Certificate Iii in Hairdressing Shb30516 Certificate Iii in BarberingDocument36 pagesLearners Guide: Shb30416 Certificate Iii in Hairdressing Shb30516 Certificate Iii in BarberingPetras LopasNo ratings yet
- Open-Throated Singing: A Roadmap For The Instructor: Part 1Document2 pagesOpen-Throated Singing: A Roadmap For The Instructor: Part 1psandyouNo ratings yet
- (NEU) 3.4 Examination of The Cranial Nerves - Dr. Nico Paulo M. Dimal MD FPNADocument11 pages(NEU) 3.4 Examination of The Cranial Nerves - Dr. Nico Paulo M. Dimal MD FPNAGeraldine TeopyNo ratings yet
- Cervical Sympathetic TrunksDocument25 pagesCervical Sympathetic TrunksShifa AhmedNo ratings yet
- No. Tgl. Tindakan Nama L/P UmurDocument152 pagesNo. Tgl. Tindakan Nama L/P UmurAndi ZulkarnaeNo ratings yet
- CT of The Paranasal Sinuses Normal Anatomyvariants and PathologyDocument10 pagesCT of The Paranasal Sinuses Normal Anatomyvariants and PathologyAndi FirdaNo ratings yet
- Le Fort II Osteotomy and Modified Technique Presentation: Riginal RticleDocument6 pagesLe Fort II Osteotomy and Modified Technique Presentation: Riginal RticleSamuel SuazaNo ratings yet
- TracheostomyDocument12 pagesTracheostomyHọ TrầnNo ratings yet
- A Fully Endoscopic Occipital Transtentorial Approach To The Pineal RegionDocument11 pagesA Fully Endoscopic Occipital Transtentorial Approach To The Pineal Regionjoao alfredoNo ratings yet
- Alekls 1202Document113 pagesAlekls 1202Joseph SikatumbaNo ratings yet
- Anatomical TerminologyDocument57 pagesAnatomical TerminologyAlicina DaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 29 The Nervous SystemDocument64 pagesChapter 29 The Nervous SystemAugustus Czar De LeonNo ratings yet
- Cortical Functions Ref v1 0 PDFDocument66 pagesCortical Functions Ref v1 0 PDFCarmen ChirivellaNo ratings yet
- 16 20 1 PBDocument3 pages16 20 1 PBKumaran Bagavathi RagavanNo ratings yet
- NO Judul Penulis EdisiDocument22 pagesNO Judul Penulis Edisimunzir100% (2)
- Neurology: by Dennis Jason Alcantara, RN, USRN, MAN CanDocument213 pagesNeurology: by Dennis Jason Alcantara, RN, USRN, MAN CanKristel-Mia Dimalanta RamosNo ratings yet
- Ears Lecture GuideDocument56 pagesEars Lecture GuidemajNo ratings yet
- Occipital LobeDocument5 pagesOccipital LobeShruthi P SNo ratings yet
- Sub Arachnoid HaemorrageDocument46 pagesSub Arachnoid HaemorrageShitaljit IromNo ratings yet
- Bhopal (M.P.) : Microteaching On TongueDocument7 pagesBhopal (M.P.) : Microteaching On TongueamitNo ratings yet
- A Neutral Zone Concept - An Overview: Dr. Anagha R. Dafade, Dr. Alhad I. GiradkarDocument5 pagesA Neutral Zone Concept - An Overview: Dr. Anagha R. Dafade, Dr. Alhad I. GiradkarSkAliHassanNo ratings yet