Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Landforms of Glaciation
Uploaded by
monte0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageGlacial landforms are shaped by the erosive and depositional forces of glaciers. Corries and cirques are rounded hollows where glacial ice accumulated and enlarged the mountainside. Tarns are circular lakes that often form in corries. U-shaped valleys have been deepened and widened by the abrasive action of large glaciers. Other landforms include truncated spurs formed where river spurs were eroded by glaciers, hanging valleys created by differential erosion, aretes between parallel U-shaped valleys, and pyramidal peaks where corries and aretes intersect. Ribbon lakes form in deeper troughs carved by glaciers in softer rock. Terminal moraines are deposited when a glacier mel
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGlacial landforms are shaped by the erosive and depositional forces of glaciers. Corries and cirques are rounded hollows where glacial ice accumulated and enlarged the mountainside. Tarns are circular lakes that often form in corries. U-shaped valleys have been deepened and widened by the abrasive action of large glaciers. Other landforms include truncated spurs formed where river spurs were eroded by glaciers, hanging valleys created by differential erosion, aretes between parallel U-shaped valleys, and pyramidal peaks where corries and aretes intersect. Ribbon lakes form in deeper troughs carved by glaciers in softer rock. Terminal moraines are deposited when a glacier mel
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageLandforms of Glaciation
Uploaded by
monteGlacial landforms are shaped by the erosive and depositional forces of glaciers. Corries and cirques are rounded hollows where glacial ice accumulated and enlarged the mountainside. Tarns are circular lakes that often form in corries. U-shaped valleys have been deepened and widened by the abrasive action of large glaciers. Other landforms include truncated spurs formed where river spurs were eroded by glaciers, hanging valleys created by differential erosion, aretes between parallel U-shaped valleys, and pyramidal peaks where corries and aretes intersect. Ribbon lakes form in deeper troughs carved by glaciers in softer rock. Terminal moraines are deposited when a glacier mel
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
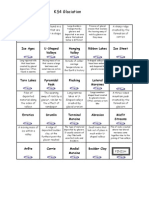
Landforms of Glaciation
Corrie/cirque (E) – Rounded hollow in mountainside where
glacial ice accumulated. Hollow has been enlarged by glacial
erosion and by frost weathering.
Tarn (C) – Circular lake usually found in the bottom of a
corrie.
U-Shaped Valley (D) - They are formed in river valleys have
been filled by a large glacier. These glaciers have deepened
and widened the valley by plucking and abrasion.
Truncated spurs (A) - Interlocking spurs created by a river are
eroded at the ends by the glacier to create truncated spurs.
Hanging valley, with waterfall (G) - Hanging valleys are
formed as a result of the erosion effects of glaciation.
Arete (F) - It is formed when two glaciers erode parallel U-
shaped valleys.
Pyramidal Peak (B) - A pyramidal peak is formed where three
or more corries and aretes meet.
Ribbon Lake (H) - A glacier flows over softer rock. Softer rock
isn’t very resistant, so a glacier will carve a deeper trough.
When the glacier withdraws the melted water will be
collected in the deeper area.
Scree (I) – These stones are a result of freeze-thaw
weathering.
Terminal Moraine (J) – It is formed when the ice melts and
deposits all the moraine it was transporting at the front of
the glacier
You might also like
- STD 7th Chp.4 Major LandformsDocument3 pagesSTD 7th Chp.4 Major LandformsVikas PandhareNo ratings yet
- Glacial LandformsDocument40 pagesGlacial LandformsJann Vic SalesNo ratings yet
- Glaciation2 1652534822Document10 pagesGlaciation2 1652534822spadesface240No ratings yet
- Glaciation NotesDocument3 pagesGlaciation NotesRobNo ratings yet
- Glacial Landforms-1Document11 pagesGlacial Landforms-1Satarupa BandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- Glaciers Note... CGC1DDocument4 pagesGlaciers Note... CGC1DLillianNo ratings yet
- Formation of Glaciers NotesDocument4 pagesFormation of Glaciers NotesBenson LeeNo ratings yet
- Ses 2103 Lectures - Unit Three-1Document8 pagesSes 2103 Lectures - Unit Three-1TREVOR MAVUNGANo ratings yet
- Glacier Vocabulary Words Completed 2Document2 pagesGlacier Vocabulary Words Completed 2api-239855791No ratings yet
- Glaciers: II. Subdivided Into 3 Major CategoriesDocument4 pagesGlaciers: II. Subdivided Into 3 Major CategoriesNayoon KimNo ratings yet
- GeomorphologyDocument27 pagesGeomorphologyPappu DiaNo ratings yet
- Glaciation in East Africa and RiversDocument21 pagesGlaciation in East Africa and Riverskalule elvisNo ratings yet
- Glaciation in East Africa: Formation of The Ice (Glaciers)Document7 pagesGlaciation in East Africa: Formation of The Ice (Glaciers)Benjamin MukalaziNo ratings yet
- Complete All The Tasks On The Following Sheets Name of LandformDocument5 pagesComplete All The Tasks On The Following Sheets Name of Landformdonotreply168436100% (1)
- Dynamic Planet Vocab ListDocument2 pagesDynamic Planet Vocab ListWHSStudent100% (1)
- 8 Glacial Deposition FeaturesDocument37 pages8 Glacial Deposition FeaturesKhalid YousafNo ratings yet
- GEO 110 NotesDocument9 pagesGEO 110 NotesaliNo ratings yet
- LandformsDocument7 pagesLandformsAtulJhaKumarNo ratings yet
- Geo-Chapter 12-FinalDocument32 pagesGeo-Chapter 12-FinalPaul Mangoma100% (1)
- Landforms Shaped by Erosion: Erosional Features and LandformsDocument4 pagesLandforms Shaped by Erosion: Erosional Features and LandformsYoumna BriguiNo ratings yet
- Geography Notes Unit 13Document4 pagesGeography Notes Unit 13nesuxcNo ratings yet
- ValleyDocument1 pageValleyKc CaymeNo ratings yet
- Geo Final Study GuideDocument3 pagesGeo Final Study GuideBrianna Lynn BauchNo ratings yet
- Glaciation StarterDocument1 pageGlaciation StarterSally AnneNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 - Friday 15-12-2012 GLACIAL LANDFORMSDocument42 pagesMODULE 2 - Friday 15-12-2012 GLACIAL LANDFORMSStephen ErickNo ratings yet
- Glaciation The Formation of Glaciers and The Process by WhichDocument20 pagesGlaciation The Formation of Glaciers and The Process by Whichbethturner12No ratings yet
- Geomorphology of River (Group-D)Document32 pagesGeomorphology of River (Group-D)Rajesh ranaNo ratings yet
- Glacier Outline CheatsheetDocument4 pagesGlacier Outline Cheatsheetbohongnih0% (1)
- Dynamic Planet NotesDocument4 pagesDynamic Planet NotesYoyo Kirby2100% (4)
- Glacierslandform 160625105649Document42 pagesGlacierslandform 160625105649Jann Vic SalesNo ratings yet
- Yr 8 Ice On The Land KODocument5 pagesYr 8 Ice On The Land KOHadad LwazeNo ratings yet
- 197glaciation in ScotlandDocument5 pages197glaciation in Scotlandapi-261914272No ratings yet
- Geomorphology GR 11Document85 pagesGeomorphology GR 11YONDELA MbandezeloNo ratings yet
- Sedimentasi Di Bentang Lahan GlasialDocument25 pagesSedimentasi Di Bentang Lahan GlasialIbrahim MovicNo ratings yet
- Glaciers and GlaciationDocument63 pagesGlaciers and Glaciationbaneblade1No ratings yet
- Glacier and Periglacial LandformsDocument4 pagesGlacier and Periglacial LandformsPeter PerezNo ratings yet
- Adeup CoDocument12 pagesAdeup CoPulkitNo ratings yet
- Glacier Jeopardy - Science BowlDocument62 pagesGlacier Jeopardy - Science BowlAnne ZhangNo ratings yet
- Glaciofluvial and Glaciolacustrine LandformsDocument17 pagesGlaciofluvial and Glaciolacustrine LandformsPritam GoswamiNo ratings yet
- 12 - Gaya EsDocument25 pages12 - Gaya EsR H SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Academic IELTS Reading Test 142Document11 pagesAcademic IELTS Reading Test 1428sakshipatelNo ratings yet
- Ice and GlaciersDocument31 pagesIce and GlaciersIvanne BrionesNo ratings yet
- There Are Two Basic Types of GlaciersDocument6 pagesThere Are Two Basic Types of GlaciersYhuli ZwitterzzajawchNo ratings yet
- Agents of Landform Change Chapter 2 Converted 1Document3 pagesAgents of Landform Change Chapter 2 Converted 1Rabab KashifNo ratings yet
- Glacial LandformsDocument42 pagesGlacial LandformsKingsuk BurmanNo ratings yet
- Glaciers, Desert and WindDocument63 pagesGlaciers, Desert and WindJoel JimenezNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Definitions - Glaciated Landscapes and Change - Edexcel Geography A-LevelDocument4 pagesGlossary of Definitions - Glaciated Landscapes and Change - Edexcel Geography A-LevelSashiNo ratings yet
- Glacial LandformsDocument25 pagesGlacial Landformsabila asokNo ratings yet
- Reading Passage 1: The Eisriesenwelt Ice CavesDocument14 pagesReading Passage 1: The Eisriesenwelt Ice CavesminakshiminsNo ratings yet
- Glacial Feature PhotosDocument18 pagesGlacial Feature PhotosjohnsoneianNo ratings yet
- GlaciersDocument4 pagesGlaciersgeethikasai117No ratings yet
- Glacial Deposition: Librea, MarianDocument12 pagesGlacial Deposition: Librea, MarianJackielyn AbasNo ratings yet
- Depositional EnvironmentDocument16 pagesDepositional EnvironmentIbrar UllahNo ratings yet
- 16 Mark Re Write PhysicalDocument1 page16 Mark Re Write PhysicalDaniel CowburnNo ratings yet
- Glaciers of the Rockies and SelkirksFrom EverandGlaciers of the Rockies and SelkirksNo ratings yet
- Glaciation Speed DatingDocument2 pagesGlaciation Speed DatingKenny73No ratings yet
- Journey of A RiverDocument4 pagesJourney of A RiverStudy is importantNo ratings yet
- Science Ch. 6 SummaryDocument15 pagesScience Ch. 6 SummaryYuan MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Geography All You Need To Know About GlaciersDocument9 pagesGeography All You Need To Know About GlaciersSham Al KarbiNo ratings yet
- Glaciation and Loch LomondDocument2 pagesGlaciation and Loch LomondJDMcDougall100% (1)
- Nervous System DamageDocument1 pageNervous System DamagemonteNo ratings yet
- Biology Homestasis DiagramDocument1 pageBiology Homestasis DiagrammonteNo ratings yet
- Biology GCSE RevisionDocument7 pagesBiology GCSE RevisionmonteNo ratings yet
- Physics RevisionDocument1 pagePhysics RevisionmonteNo ratings yet