0% found this document useful (0 votes)
466 views4 pagesCation Precipitation Analysis Guide
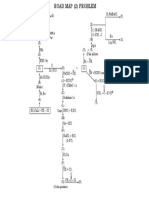
The document is a mind map that analyzes the reactions of various cations (Ag+, Pb2+, Hg22+, Cu2+, Hg2+, Cd2+, Bi3+, Al3+, Cr3+, Fe3+, Fe2+) with different reagents (NaOH, NH4OH, KCN, KI, K2CrO4, H2S/(NH4)2S). It lists the products and observations of each reaction through precipitation reactions and complex ion formations. The mind map acts as a guide for qualitative cation analysis through observation of color and solubility changes.
Uploaded by
HECopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
466 views4 pagesCation Precipitation Analysis Guide
The document is a mind map that analyzes the reactions of various cations (Ag+, Pb2+, Hg22+, Cu2+, Hg2+, Cd2+, Bi3+, Al3+, Cr3+, Fe3+, Fe2+) with different reagents (NaOH, NH4OH, KCN, KI, K2CrO4, H2S/(NH4)2S). It lists the products and observations of each reaction through precipitation reactions and complex ion formations. The mind map acts as a guide for qualitative cation analysis through observation of color and solubility changes.
Uploaded by
HECopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd